Are you wondering, How Much Does Gas Cost Per Month for your home or vehicle? The monthly expense for gas varies depending on several factors, but HOW.EDU.VN provides insights to help you understand and potentially lower these costs. By understanding the components that influence your monthly gas bill, you can take actions to reduce energy consumption and costs.
Table of Contents
1. Average Monthly Gas Bill
2. Average Natural Gas Bill by State
3. Factors Influencing High Gas Bills
4. Effective Strategies to Lower Your Gas Bill
5. Saving on Utility Costs
6. Understanding Natural Gas Prices
7. Seasonal Impacts on Gas Consumption
8. Energy-Efficient Home Improvement Projects
9. The Impact of Insulation on Gas Bills
10. Home Energy Audits
11. Maximizing Natural Heat
12. Weatherstripping and Its Impact
13. Maintaining Your HVAC System
14. Generator Usage and Gas Bills
15. Tax Credits for Energy Efficiency
16. Energy-Efficient Appliances
17. Comparing Gas Prices
18. Professional Energy Advice
19. Contacting HOW.EDU.VN Experts
20. FAQs
1. Average Monthly Gas Bill
What is the average monthly gas bill for a household? The typical gas bill in the U.S. ranges from $35 to $200 per month. This variation depends on several factors, including the season, geographic location, climate, home size, age, and the household’s natural gas consumption. Homes in colder climates that use gas for heating, water heating, cooking, and clothes drying will typically see higher monthly bills.
Seasonal Variations:
| Season | Average Monthly Gas Bill |
|---|---|
| Spring (April / May) | $40 – $75 |
| Summer (June through August) | $35 – $50 |
| Fall (September / October) | $40 – $75 |
| Winter (November through March) | $120 – $200 |
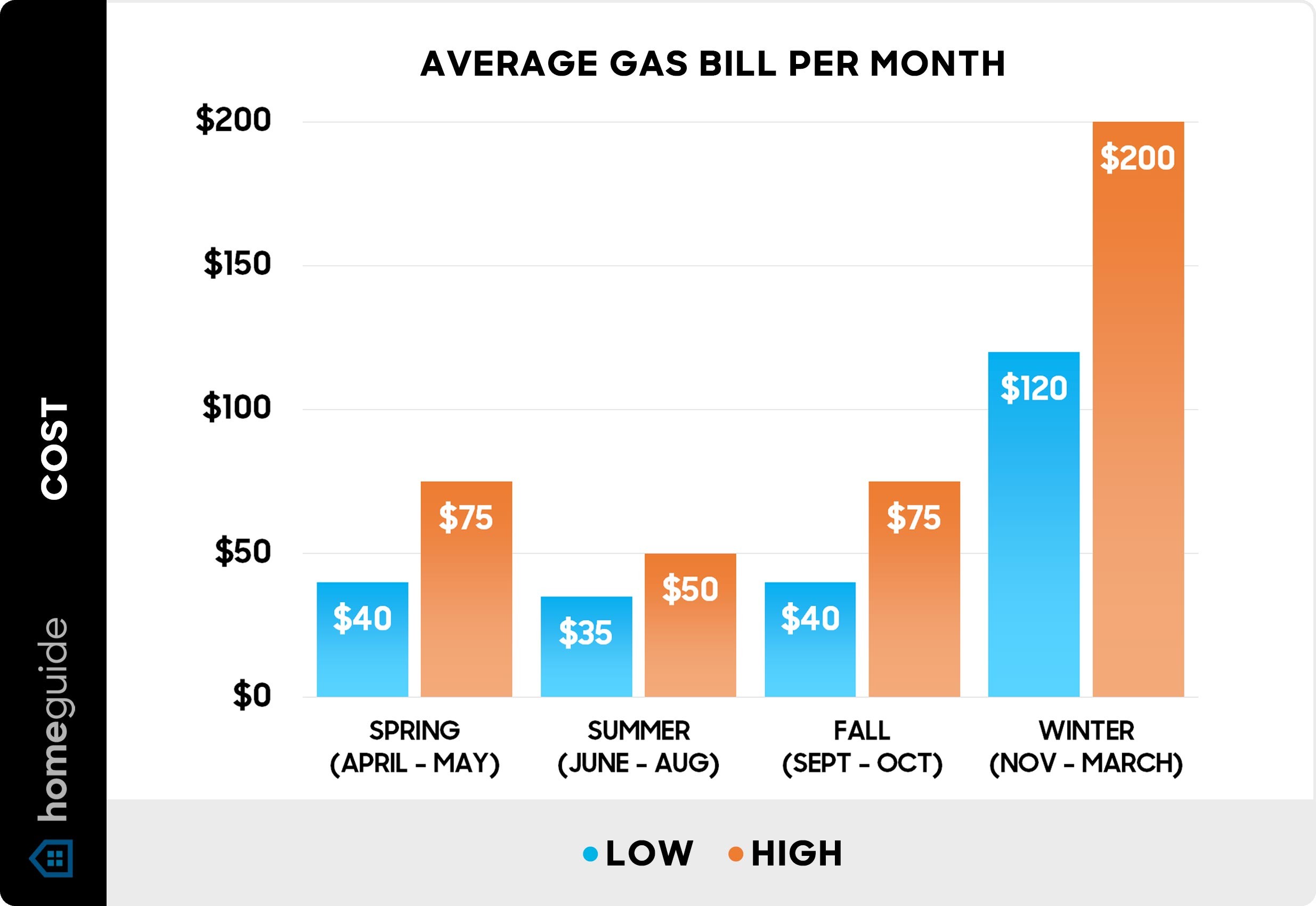

The average annual residential gas bill ranges from $420 to over $1,600, varying by state. Over 60% of U.S. households use natural gas for at least one purpose, highlighting its importance in daily living. The U.S. Energy Information Administration also notes the importance of understanding these variations to manage household budgets effectively.
2. Average Natural Gas Bill by State
How does the average natural gas bill vary by state? Monthly gas bills differ significantly by state due to variations in local gas prices and climate conditions. States with colder weather generally use more gas for heating, resulting in higher bills during the winter months.
Natural gas prices are lowest in states like Montana and Idaho, while they are highest in Florida and Hawaii. Despite higher gas prices, Florida and Hawaii often have lower average monthly bills because their temperate climates reduce the need for gas heating.
Average Monthly Gas Bill by State
| State | Average Monthly Gas Bill* | Average Gas Price (per MCF) | Average Gas Price (per Therm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $55 – $70 | $23.33 | $2.25 |
| Alaska | $110 – $140 | $12.03 | $1.16 |
| Arizona | $45 – $60 | $22.96 | $2.21 |
| Arkansas | $75 – $85 | $18.55 | $1.79 |
| California | $50 – $65 | $18.41 | $1.77 |
| Colorado | $75 – $85 | $12.93 | $1.25 |
| Connecticut | $90 – $140 | $21.38 | $2.06 |
| Delaware | $75 – $100 | $22.74 | $2.19 |
| District of Columbia | $55 – $90 | $19.14 | $1.84 |
| Florida | $35 – $45 | $26.56 | $2.56 |
| Georgia | $65 – $100 | $25.19 | $2.43 |
| Hawaii | $55 – $120 | $53.46 | $5.15 |
| Idaho | $50 – $70 | $11.44 | $1.10 |
| Illinois | $95 – $120 | $15.28 | $1.47 |
| Indiana | $75 – $90 | $14.60 | $1.41 |
| Iowa | $75 – $90 | $13.99 | $1.35 |
| Kansas | $85 – $100 | $18.67 | $1.80 |
| Kentucky | $75 – $90 | $20.31 | $1.96 |
| Louisiana | $50 – $60 | $18.39 | $1.77 |
| Maine | $80 – $150 | $19.64 | $1.89 |
| Maryland | $85 – $95 | $19.32 | $1.86 |
| Massachusetts | $95 – $135 | $19.93 | $1.92 |
| Michigan | $90 – $100 | $13.04 | $1.26 |
| Minnesota | $90 – $100 | $14.40 | $1.39 |
| Mississippi | $60 – $75 | $19.69 | $1.90 |
| Missouri | $80 – $130 | $22.28 | $2.15 |
| Montana | $65 – $75 | $11.03 | $1.06 |
| Nebraska | $75 – $90 | $16.18 | $1.56 |
| Nevada | $50 – $80 | $19.95 | $1.92 |
| New Hampshire | $110 – $125 | $24.06 | $2.32 |
| New Jersey | $85 – $100 | $14.59 | $1.41 |
| New Mexico | $50 – $65 | $12.44 | $1.20 |
| New York | $81 – $120 | $18.52 | $1.78 |
| North Carolina | $75 – $85 | $21.06 | $2.03 |
| North Dakota | $80 – $95 | $14.58 | $1.40 |
| Ohio | $95 – $130 | $21.50 | $2.07 |
| Oklahoma | $75 – $100 | $21.54 | $2.08 |
| Oregon | $65 – $85 | $18.04 | $1.74 |
| Pennsylvania | $95 – $120 | $18.04 | $1.74 |
| Rhode Island | $100 – $150 | $22.72 | $2.19 |
| South Carolina | $50 – $65 | $20.43 | $1.97 |
| South Dakota | $60 – $70 | $12.10 | $1.17 |
| Tennessee | $55 – $65 | $12.81 | $1.23 |
| Texas | $55 – $75 | $21.99 | $2.12 |
| Utah | $65 – $85 | $14.47 | $1.39 |
| Vermont | $95 – $110 | $20.41 | $1.97 |
| Virginia | $80 – $95 | $19.46 | $1.87 |
| Washington | $75 – $95 | $17.48 | $1.68 |
| West Virginia | $75 – $120 | $20.91 | $2.01 |
| Wisconsin | $65 – $85 | $12.13 | $1.17 |
| Wyoming | $85 – $110 | $16.85 | $1.62 |
*Prices are based on annual total household gas bills averaged across 12 months, according to data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration and the American Gas Association.
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) measures natural gas prices per thousand cubic feet (MCF). Residential gas bills typically measure household consumption in hundred cubic feet (CCF) or therms. Use the following formula to convert gas prices from one unit of measurement to another:
1 MCF = 10 CCF = 10.38 therms
Understanding these variations can help you budget and plan more effectively.
3. Factors Influencing High Gas Bills
Why is my gas bill so high, even with average gas prices? Several factors can increase your home’s energy use, leading to higher gas bills. These include:
- Home & Household Size: Larger homes and households generally use more natural gas for heating and water, increasing costs.
- Usage: In addition to heating and water heating, appliances like outdoor grills, clothes dryers, fireplaces, standby generators, and pool heaters can raise gas consumption.
- Season & Weather: Winter months typically result in higher gas bills due to increased heating needs, particularly in colder regions.
- Outdated or Inefficient Heating System: An old or poorly maintained furnace can consume more gas, significantly increasing your bill. According to the Department of Energy, heating accounts for 35% to 50% of a typical gas bill.
- Water Heating: Gas water heaters in older models are less efficient, using more gas than newer ones. Water heating accounts for 18% to 20% of total gas usage.
- Insulation: Many homes lack adequate insulation, forcing heating systems to work harder. According to the North American Insulation Manufacturers Association, up to 90% of U.S. homes are under-insulated.
- Generator: Standby generators that run on natural gas during power outages can lead to higher gas bills.
- Taxes & Fees: Gas bills include federal and local taxes and fees, such as utility taxes, pipeline usage fees, and excise taxes.
Comparing your gas bill to regional averages and past bills can help identify the cause of spikes. If you notice drastic increases, it may indicate issues with your heating system or water heater. For personalized advice on identifying and resolving these issues, consider consulting with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
4. Effective Strategies to Lower Your Gas Bill
How can I reduce my monthly gas bill effectively? Implementing simple changes in your household’s habits and investing in energy-efficient upgrades can significantly lower your gas bill. Energy-efficient home improvements, such as adding insulation and weatherstripping, can also lead to substantial annual savings.
- Turn Down Your Thermostat: Lowering your thermostat by just one degree can save you 3% per degree.
- Take Advantage of Natural Heat: Opening curtains on sunny sides of your home during the day and closing them at night can reduce heat loss.
- Turn Down the Water Temperature: Reducing the temperature on your water heater tank by 10 degrees can save 3% to 5% on water heating costs.
- Add Weatherstripping: Sealing gaps around windows and doors with weatherstripping prevents air leaks. Weatherstripping installation costs $130 to $470 for an average home.
- Add Insulation: Insulation can reduce energy costs by 10% to 40%. Insulation installation ranges from $1.00 to $4.50 per square foot, depending on the material and area of the house.
- Maintain Your HVAC System: Regularly clean or replace furnace filters and ensure vents are unobstructed. Dirty filters and blocked vents force the heating system to work harder, increasing energy use.
- Replace Old, Inefficient Windows: New double-pane and triple-pane windows are 30% to 50% more energy efficient than single-pane windows. Window replacement costs average $450 to $1,500 per window.
- Upgrade to Energy-Efficient Appliances: Replacing old gas water heaters, ovens, and clothes dryers with ENERGY STAR-rated models can save energy.
These steps can help lower gas consumption and reduce monthly costs, improving overall energy efficiency.
5. Saving on Utility Costs
What other steps can I take to save on utility costs beyond gas? Besides reducing gas consumption, there are numerous ways to save on other utility costs. According to the EPA, a comprehensive approach to energy efficiency can lead to significant savings. Here are some additional tips:
- Use Energy-Efficient Lighting: Replace incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs, which use up to 75% less energy and last much longer.
- Unplug Electronics: Many electronics consume energy even when turned off. Unplug devices like chargers, TVs, and computers when not in use.
- Wash Clothes in Cold Water: Using cold water for laundry can save on water heating costs.
- Install a Programmable Thermostat: A programmable thermostat can automatically adjust the temperature based on your schedule, saving energy when you’re away or asleep.
- Seal Air Leaks: In addition to weatherstripping, seal other air leaks around your home, such as those around pipes and electrical outlets.
- Regular Appliance Maintenance: Keep all appliances in good working order. Regularly clean refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioners to ensure they operate efficiently.
- Limit Air Conditioner Use: Use fans to circulate air and reduce the need for air conditioning. Consider using window units to cool only the rooms you’re using.
By implementing these measures, you can significantly reduce your overall utility costs and improve energy efficiency.
6. Understanding Natural Gas Prices
What factors influence natural gas prices and how can I stay informed? Natural gas prices are affected by various factors, including supply and demand, weather patterns, storage levels, and geopolitical events. Staying informed about these factors can help you anticipate changes in your gas bill.
- Supply and Demand: Increased demand during winter months typically drives up prices, while abundant supply can lower them.
- Weather Patterns: Severe weather events can disrupt production and transportation, affecting prices.
- Storage Levels: Low storage levels can lead to higher prices, especially during peak demand periods.
- Geopolitical Events: International events that affect gas production and distribution can impact domestic prices.
Resources for Staying Informed:
- U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA): Provides data and analysis on energy markets.
- American Gas Association (AGA): Offers insights into the natural gas industry.
- Utility Company Websites: Many utility companies provide information on gas prices and factors affecting them.
- Financial News Outlets: Stay updated on energy market trends through financial news sources.
Keeping informed about these factors can help you make informed decisions about your energy consumption and manage your gas bill effectively.
7. Seasonal Impacts on Gas Consumption
How does seasonal weather affect my gas bill and what adjustments can I make? Gas consumption varies significantly with the seasons due to changes in heating and cooling needs. Understanding these patterns can help you adjust your energy usage and reduce costs.
- Winter: Heating is the primary driver of high gas bills in winter. Lowering your thermostat and ensuring proper insulation can help reduce consumption.
- Summer: While gas consumption is typically lower in summer, using gas appliances like water heaters and clothes dryers can still impact your bill.
- Spring and Fall: These shoulder seasons offer opportunities to reduce gas consumption by relying on natural ventilation and milder temperatures.
Adjustments to Reduce Seasonal Gas Consumption:
- Winter: Seal drafts, use space heaters efficiently, and schedule regular furnace maintenance.
- Summer: Minimize use of gas appliances, use cold water for laundry, and utilize fans for cooling.
- Spring and Fall: Open windows for natural ventilation, use outdoor grills instead of indoor ovens, and adjust thermostat settings to reduce heating or cooling needs.
Making these adjustments can help you manage your gas bill more effectively throughout the year.
8. Energy-Efficient Home Improvement Projects
What energy-efficient home improvements offer the best return on investment for reducing gas bills? Investing in energy-efficient home improvements can significantly reduce your gas bill and increase your home’s overall value. According to the Department of Energy, some of the most effective projects include:
- Adding Insulation: Proper insulation can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 40%.
- Replacing Windows: Energy-efficient windows can reduce heat loss and gain, improving comfort and lowering energy bills.
- Upgrading HVAC Systems: New, high-efficiency furnaces and air conditioners use less energy and provide better performance.
- Sealing Air Leaks: Caulking and weatherstripping can prevent drafts and reduce energy waste.
- Installing a Tankless Water Heater: Tankless water heaters heat water on demand, eliminating the standby heat loss associated with traditional water heaters.
Return on Investment:
| Home Improvement Project | Estimated Cost | Potential Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Adding Insulation | $1,000 – $4,000 | 10% – 40% reduction in energy bills |
| Replacing Windows | $450 – $1,500 per window | 15% reduction in heat loss |
| Upgrading HVAC Systems | $4,000 – $10,000 | 20% – 30% more efficient than older models |
| Sealing Air Leaks | $200 – $500 | 5% – 15% reduction in energy bills |
| Installing a Tankless Water Heater | $1,000 – $3,000 | 20% – 30% more efficient than traditional water heaters |
These improvements can lead to substantial savings and improve the comfort and energy efficiency of your home.
9. The Impact of Insulation on Gas Bills
How does insulation affect gas bills and what types of insulation are most effective? Insulation plays a crucial role in maintaining a consistent temperature in your home, reducing the need for excessive heating and cooling. According to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), homes with proper insulation consume significantly less energy.
Types of Insulation:
- Fiberglass: A common and affordable option.
- Cellulose: Made from recycled materials and provides good insulation.
- Spray Foam: Offers excellent insulation and can seal air leaks.
- Mineral Wool: Made from rock or slag and is fire-resistant.
Effectiveness of Insulation:
The effectiveness of insulation is measured by its R-value, which indicates its resistance to heat flow. Higher R-values provide better insulation. The recommended R-values vary depending on the climate and area of the home.
| Area of the Home | Recommended R-Value |
|---|---|
| Attic | R-30 to R-60 |
| Walls | R-13 to R-23 |
| Floors | R-13 to R-30 |
Proper insulation can significantly reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, lowering your gas bill and improving your home’s comfort.
10. Home Energy Audits
What is a home energy audit and how can it help lower my gas bill? A home energy audit assesses your home’s energy efficiency and identifies areas where you can save energy and reduce costs. According to the Department of Energy, a comprehensive energy audit can help you identify the most cost-effective improvements for your home.
What a Home Energy Audit Includes:
- Inspection of Insulation: Checking the levels and condition of insulation in attics, walls, and floors.
- Air Leak Detection: Identifying drafts and air leaks around windows, doors, and other openings.
- HVAC System Evaluation: Assessing the efficiency and performance of your heating and cooling systems.
- Appliance Review: Evaluating the energy consumption of your appliances.
- Report and Recommendations: Providing a detailed report with recommendations for improvements.
Benefits of a Home Energy Audit:
- Identify Energy Waste: Pinpoint areas where your home is wasting energy.
- Prioritize Improvements: Determine the most cost-effective energy-saving projects.
- Reduce Energy Bills: Lower your gas and electricity bills by implementing recommended improvements.
- Improve Comfort: Make your home more comfortable by reducing drafts and maintaining consistent temperatures.
The cost of a home energy audit ranges from $200 to $600, but this expense is eligible for the federal Energy Efficient Home Improvement tax credit.
11. Maximizing Natural Heat
How can I maximize natural heat in my home to reduce gas consumption? Utilizing natural heat sources can significantly reduce your reliance on your heating system, lowering your gas bill. Here are some strategies:
- Open Curtains and Blinds: During sunny days, open curtains and blinds on south-facing windows to allow sunlight to warm your home.
- Close Curtains at Night: At night, close curtains and blinds to insulate windows and reduce heat loss.
- Use Thermal Curtains: Thermal curtains are designed to block drafts and insulate windows, helping to keep your home warm in the winter and cool in the summer.
- Passive Solar Heating: Design your landscaping to allow sunlight to reach your home in the winter. Deciduous trees can provide shade in the summer and allow sunlight in the winter.
- Sunrooms: If you have a sunroom, use it as a heat source by opening doors and windows to allow warm air to circulate throughout your home.
These strategies can help you harness natural heat and reduce your gas consumption, especially during the colder months.
12. Weatherstripping and Its Impact
What is weatherstripping and how can it reduce my gas bill? Weatherstripping involves sealing gaps around windows and doors to prevent air leaks. This simple and cost-effective measure can significantly reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, lowering your gas bill.
Types of Weatherstripping:
- Foam Tape: Easy to install and suitable for small gaps.
- Felt: Inexpensive but less durable.
- Vinyl: Durable and weather-resistant.
- Metal: Long-lasting and effective for larger gaps.
Installation Tips:
- Clean Surfaces: Clean the surfaces where you will be applying weatherstripping to ensure good adhesion.
- Measure and Cut: Measure the length of the gaps and cut the weatherstripping to the appropriate size.
- Apply Weatherstripping: Carefully apply the weatherstripping, ensuring a tight seal.
- Check for Leaks: After installation, check for any remaining air leaks and reapply weatherstripping as needed.
Weatherstripping costs $130 to $470 for an average home and can reduce energy costs by up to 10%.
13. Maintaining Your HVAC System
Why is it important to maintain my HVAC system to reduce gas bills? Regular maintenance of your HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system ensures it operates efficiently, reducing energy consumption and lowering your gas bill.
Maintenance Tasks:
- Change Filters Regularly: Dirty filters restrict airflow, forcing your HVAC system to work harder. Change filters every 1-3 months.
- Clean Vents and Registers: Keep vents and registers clear of obstructions to ensure proper airflow.
- Schedule Professional Inspections: Have your HVAC system inspected and serviced by a qualified technician at least once a year.
- Check Ductwork: Inspect ductwork for leaks and seal any gaps to prevent energy loss.
- Clean Coils: Dirty coils reduce the efficiency of your HVAC system. Clean coils regularly to maintain optimal performance.
Benefits of Regular Maintenance:
- Improved Efficiency: Regular maintenance can improve the efficiency of your HVAC system, reducing energy consumption.
- Extended Lifespan: Proper maintenance can extend the lifespan of your HVAC system, saving you money on replacement costs.
- Reduced Repair Costs: Regular inspections can identify and address minor issues before they become major problems.
- Improved Air Quality: Clean filters and ductwork improve indoor air quality, creating a healthier home environment.
14. Generator Usage and Gas Bills
How does using a generator affect my gas bill and how can I manage it? Many homes use natural gas-powered generators to provide backup power during outages. However, using a generator can significantly increase your gas bill. Understanding how to manage generator usage can help you control these costs.
Factors Affecting Gas Consumption:
- Generator Size: Larger generators consume more gas.
- Load: Running more appliances and devices increases gas consumption.
- Duration of Use: Longer outages result in higher gas consumption.
Tips for Managing Generator Usage:
- Use Efficient Appliances: Use energy-efficient appliances and devices to reduce the load on your generator.
- Prioritize Essential Loads: Focus on powering essential appliances like refrigerators, freezers, and medical equipment.
- Limit Usage: Use the generator only when necessary and turn it off when power is restored.
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure your generator is properly maintained for optimal efficiency.
- Consider Alternative Fuel Sources: Explore alternative fuel sources like propane or solar power.
Managing your generator usage can help you minimize its impact on your gas bill and ensure you have backup power when you need it.
15. Tax Credits for Energy Efficiency
What tax credits are available for energy-efficient home improvements? The federal government offers tax credits for energy-efficient home improvements, helping you save money while reducing your energy consumption.
Key Tax Credits:
- Energy Efficient Home Improvement Credit: This credit covers 30% of the cost of qualified energy-efficient improvements, such as insulation, windows, doors, and HVAC systems, up to a certain limit.
- Residential Clean Energy Credit: This credit covers 30% of the cost of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, solar water heaters, and wind turbines.
Eligible Improvements:
- Insulation: Must meet specific energy efficiency standards.
- Windows and Doors: Must be ENERGY STAR certified.
- HVAC Systems: Must meet or exceed minimum efficiency requirements.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Must meet performance and quality standards.
How to Claim Tax Credits:
- Keep Records: Maintain detailed records of all eligible expenses.
- Use IRS Form 5695: Complete IRS Form 5695, Residential Energy Credits, to claim the credits when filing your taxes.
- Consult a Tax Professional: Seek advice from a tax professional to ensure you are taking full advantage of available credits.
These tax credits can significantly reduce the cost of energy-efficient home improvements, making it easier to save money and reduce your gas bill.
16. Energy-Efficient Appliances
How do energy-efficient appliances help reduce gas bills and what should I look for? Upgrading to energy-efficient appliances can significantly reduce your gas bill and lower your overall energy consumption.
Key Appliances:
- Water Heaters: ENERGY STAR certified water heaters use less energy and can save you money on your gas bill.
- Furnaces: High-efficiency furnaces use less gas and provide better performance.
- Clothes Dryers: ENERGY STAR certified clothes dryers use less gas and have features that save energy.
- Ovens: Gas ovens with improved insulation and controls can reduce energy consumption.
What to Look For:
- ENERGY STAR Certification: Look for the ENERGY STAR label, which indicates that the appliance meets strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the EPA.
- Energy Factor (EF): For water heaters, look for a high Energy Factor (EF), which indicates how efficiently the water heater uses energy.
- Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE): For furnaces, look for a high AFUE rating, which indicates how efficiently the furnace converts fuel into heat.
- Advanced Features: Look for appliances with advanced features like smart controls, energy-saving modes, and improved insulation.
Upgrading to energy-efficient appliances can significantly reduce your gas bill and improve the overall energy efficiency of your home.
17. Comparing Gas Prices
How can I compare gas prices to ensure I’m getting the best deal? Comparing gas prices from different suppliers can help you ensure you are getting the best deal and reducing your gas bill.
Ways to Compare Prices:
- Shop Around: Contact multiple gas suppliers in your area and compare their prices.
- Use Online Comparison Tools: Use online tools to compare gas prices from different suppliers.
- Check Utility Company Websites: Many utility companies provide information on gas prices and supplier options.
- Consider Fixed vs. Variable Rates: Decide whether you prefer a fixed rate, which stays the same over a set period, or a variable rate, which fluctuates with market conditions.
- Read the Fine Print: Carefully read the terms and conditions of any gas supply agreement before signing up.
Factors to Consider:
- Price per Therm: Compare prices per therm to get an accurate comparison.
- Contract Length: Consider the length of the contract and whether there are any early termination fees.
- Customer Service: Check the supplier’s customer service record and reputation.
- Additional Fees: Be aware of any additional fees, such as monthly service fees or delivery charges.
Comparing gas prices can help you find the best deal and reduce your gas bill.
18. Professional Energy Advice
When should I seek professional energy advice and how can it help? Seeking professional energy advice can provide you with tailored solutions to reduce your gas bill and improve your home’s energy efficiency.
When to Seek Advice:
- High Gas Bills: If you are experiencing high gas bills and are unsure of the cause.
- Energy Efficiency Improvements: If you are considering energy efficiency improvements and want to know which ones are most cost-effective.
- HVAC System Issues: If you are having issues with your HVAC system and want to improve its performance.
- Home Energy Audit: If you want to schedule a home energy audit to assess your home’s energy efficiency.
Benefits of Professional Advice:
- Tailored Solutions: Professionals can provide you with tailored solutions based on your specific needs and circumstances.
- Expert Knowledge: Professionals have the knowledge and experience to identify energy-saving opportunities you may have overlooked.
- Cost-Effective Recommendations: Professionals can recommend the most cost-effective improvements for your home.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: By implementing professional recommendations, you can significantly improve your home’s energy efficiency and reduce your gas bill.
19. Contacting HOW.EDU.VN Experts
How can HOW.EDU.VN experts help me reduce my gas bill? At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading PhDs and experts who can provide personalized advice and solutions to reduce your gas bill and improve your home’s energy efficiency.
How We Can Help:
- Personalized Consultations: Connect with experts for personalized consultations tailored to your specific needs.
- Expert Analysis: Receive expert analysis of your energy consumption patterns and recommendations for improvements.
- Cost-Effective Strategies: Learn about cost-effective strategies to reduce your gas bill and improve energy efficiency.
- Comprehensive Support: Get comprehensive support and guidance throughout the process.
Contact Us Today:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Don’t let high gas bills drain your budget. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today and let our experts help you save money and improve your home’s energy efficiency.
20. FAQs
1. What is the average monthly gas bill in the US?
The average monthly gas bill in the US ranges from $35 to $200, depending on factors like location, season, and usage.
2. Why is my gas bill so high?
High gas bills can be due to factors such as outdated appliances, poor insulation, high usage, and seasonal weather changes.
3. How can I lower my gas bill?
You can lower your gas bill by turning down the thermostat, improving insulation, sealing air leaks, and using energy-efficient appliances.
4. What is weatherstripping and how does it help?
Weatherstripping is the process of sealing gaps around windows and doors to prevent air leaks, reducing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer.
5. What is a home energy audit?
A home energy audit is an assessment of your home’s energy efficiency, identifying areas where you can save energy and reduce costs.
6. How can I maximize natural heat in my home?
You can maximize natural heat by opening curtains during the day to let sunlight in and closing them at night to retain heat.
7. What tax credits are available for energy-efficient home improvements?
The federal government offers tax credits for energy-efficient home improvements, such as insulation, windows, and HVAC systems.
8. How do energy-efficient appliances help reduce gas bills?
Energy-efficient appliances use less gas and electricity, reducing your overall energy consumption and lowering your bills.
9. How can HOW.EDU.VN experts help me reduce my gas bill?
how.edu.vn connects you with leading PhDs and experts who can provide personalized advice and solutions to reduce your gas bill and improve your home’s energy efficiency.
10. What is the best way to compare gas prices?
Compare gas prices by shopping around, using online comparison tools, and checking utility company websites for the best deals.