How Much Does Medical School Cost? The financial commitment to pursue a career in medicine can be substantial, but understanding the costs involved is the first step toward planning your future with HOW.EDU.VN. Medical school expenses include tuition, fees, and living costs. These expenses can be daunting, but scholarships, loans, and financial planning can make this dream a reality. Let’s explore medical education expenses, tuition fees, and financial aid.
1. What Is the Average Cost of Medical School?
The average cost of medical school can vary significantly based on factors such as whether the institution is public or private and whether you are an in-state or out-of-state resident. The cost of a medical degree is a significant investment, but understanding the components can help in financial planning.
- Average Total Cost: The average total cost for a four-year medical school program is approximately $238,420.
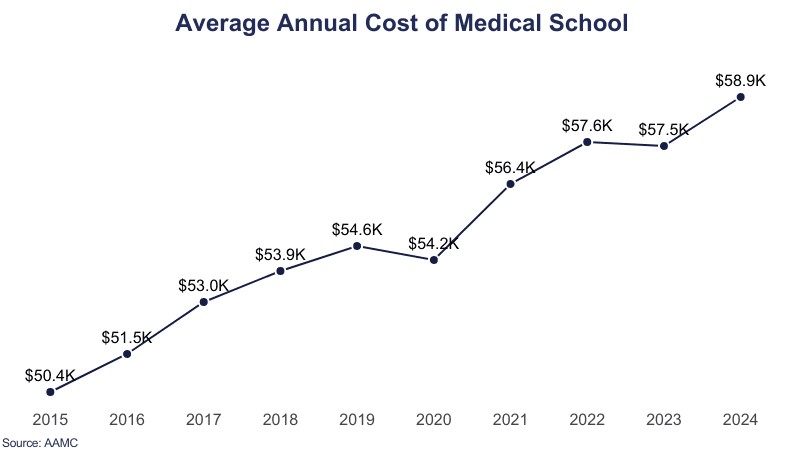
- Yearly Expenses: On average, students can expect to pay around $59,605 per year.
- Public vs. Private Schools: Public schools generally offer lower tuition rates, with total costs around $215,380, while private schools average about $271,800.
- In-State vs. Out-of-State: In-state residents typically pay less, averaging $208,428, compared to out-of-state residents, who may pay around $269,392.
These figures include tuition, fees, and health insurance. Depending on the medical school, additional expenses might include books, supplies, and living costs.
2. What Factors Influence the Cost of Medical School?
Several key factors can significantly impact the overall cost of medical school. Recognizing these elements is crucial for prospective students when budgeting and making informed decisions about their education.
- Type of Institution (Public vs. Private): Public medical schools often receive state funding, allowing them to offer lower tuition rates to residents. Private schools, which rely more on endowments and tuition, typically have higher costs.
- Residency Status (In-State vs. Out-of-State): Public schools offer preferential tuition rates to students who are residents of the state in which the school is located. Out-of-state students usually pay higher tuition fees.
- Location: The cost of living in the city or town where the medical school is located can greatly affect the overall expenses. Metropolitan areas typically have higher living costs than smaller towns.
- Program Length: While most medical programs are four years, some may offer accelerated programs or combined degree programs (e.g., MD/Ph.D.), which could affect the total cost.
- Financial Aid and Scholarships: The amount of financial aid, grants, and scholarships a student receives can significantly reduce the overall cost. Merit-based and need-based scholarships are available.
Understanding these factors can help prospective students target their applications and financial planning to manage costs effectively.
3. How Much Does Medical School Cost Per Year?
Breaking down the cost of medical school on a yearly basis can provide a clearer picture for budgeting and financial planning. The annual cost includes tuition, fees, and other direct educational expenses.
- Average Yearly Cost: The average annual cost for medical school is approximately $59,605.
- Public Schools: Public medical schools average around $53,845 per year.
- Private Schools: Private medical schools tend to be more expensive, averaging $67,950 per year.
- In-State Residents: In-state residents typically pay about $52,107 annually.
- Out-of-State Residents: Out-of-state students may pay around $67,348 per year.
These figures do not include living expenses, such as housing, food, transportation, and personal costs, which can add a significant amount to the total annual expenses.
 students in a medical lecture room
students in a medical lecture room
4. What Are the Additional Costs Associated with Medical School?
Beyond tuition and fees, medical students face several additional costs that can significantly impact their overall expenses. It is essential to account for these costs when planning a budget for medical school.
- Application Fees: Applying to medical school involves fees for the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) and application submissions. The MCAT costs around $335 per test. Initial application fees through the AAMC are $175, with each additional application costing $46.
- Travel and Interview Expenses: Traveling for interviews can be costly, including expenses for flights, accommodation, and professional attire. These costs can average around $1,000.
- Medical Equipment and Books: Medical students need to purchase textbooks, stethoscopes, and other medical instruments, which can total about $1,250.
- Licensing Exams: The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) costs between $600 and $1,200 per section, and repeated attempts can increase the price.
- Living Expenses: Housing, food, transportation, and personal expenses can vary widely depending on location. These costs should be factored into the overall budget.
- Health Insurance: Health insurance costs must be factored into your budget, and while many schools offer plans, you may be required to enroll or opt for an external plan.
- Professional Memberships: Joining medical societies may require membership fees.
- Technology: Laptops and software can be necessary for coursework.
5. How Does the Cost of Medical School Vary by State?
The cost of medical school can vary significantly from state to state, largely due to differences in public funding and tuition policies. This variation impacts the overall financial burden on students pursuing medical education.
- States with Lower Costs: States with robust public university systems often offer lower tuition rates, especially for in-state residents. Examples include Texas, where some medical schools have tuition below $30,000 per year for residents, thanks to state subsidies.
- States with Higher Costs: States with a higher proportion of private institutions or limited public funding may have higher tuition rates. Schools in the Northeast and some parts of California tend to be more expensive.
- Regional Differences: The Midwest and South generally offer more affordable options compared to the East and West Coasts.
- Cost of Living Impact: The cost of living in a particular state can also influence the overall cost. For example, while tuition in some states may be lower, higher living expenses can offset those savings.
6. What Are the Cheapest Medical Schools in the U.S.?
Identifying the most affordable medical schools can help prospective students minimize their debt and make informed choices about their education. Several institutions offer significantly lower tuition rates than the national average.
- New York University (NYU) Grossman School of Medicine: NYU Grossman School of Medicine offers free tuition for all students, regardless of merit or financial need. Students are responsible for living expenses.
- Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine: This school provides free tuition to its students, focusing on a more holistic approach to medical education.
- Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences: This federal school offers free tuition in exchange for a commitment to serve as a medical officer in the military.
- Texas A&M University College of Medicine: Offers very low tuition for Texas residents.
- University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (McGovern Medical School): Offers low tuition for Texas residents.
These schools make medical education more accessible by reducing or eliminating tuition costs.
7. What Are Some Strategies to Reduce the Cost of Medical School?
Several strategies can help reduce the financial burden of attending medical school. Planning and diligent financial management can make medical education more affordable.
- Apply for Scholarships and Grants: Numerous scholarships and grants are available from medical schools, professional organizations, and private foundations.
- Choose a Public In-State School: Attending a public medical school in your state of residence can significantly lower tuition costs.
- Live Frugally: Reducing living expenses by sharing accommodation, cooking at home, and minimizing discretionary spending can save a considerable amount of money.
- Use Used Textbooks: Buying used textbooks or renting them can save hundreds of dollars each year.
- Consider Loan Repayment Programs: Research and apply for loan repayment programs offered by the federal government, states, or employers.
- Work Part-Time: If feasible, working part-time during medical school can provide additional income to offset expenses.
8. What Types of Financial Aid Are Available for Medical School?
Understanding the types of financial aid available is crucial for students planning to finance their medical education. Various options can help cover tuition, fees, and living expenses.
- Federal Student Loans: The U.S. Department of Education offers several loan programs, including Direct Unsubsidized Loans and Direct Graduate PLUS Loans. These loans often have lower interest rates and flexible repayment options.
- Institutional Loans: Medical schools themselves may offer loans to students, sometimes with favorable terms.
- Scholarships and Grants: These are typically need-based or merit-based and do not require repayment. They can come from the medical school, private organizations, or government programs.
- Health Professions Student Loan (HPSL): This is a low-interest loan available to students pursuing degrees in certain health professions.
- National Health Service Corps (NHSC) Scholarship and Loan Repayment Programs: These programs offer financial assistance in exchange for a commitment to work in underserved communities.
It’s important to research and apply for all available financial aid options to minimize the need for high-interest loans.
9. How Can I Create a Budget for Medical School?
Creating a realistic budget is essential for managing finances during medical school. A well-thought-out budget helps students track expenses, avoid unnecessary debt, and maintain financial stability.
- Estimate Income: Determine all sources of income, including loans, scholarships, grants, savings, and any part-time employment.
- List Fixed Expenses: Include costs that remain consistent each month, such as tuition, fees, rent, loan payments, and insurance premiums.
- Calculate Variable Expenses: List costs that fluctuate, such as groceries, transportation, utilities, books, and personal expenses.
- Track Spending: Monitor your spending habits regularly using budgeting apps, spreadsheets, or notebooks.
- Identify Areas to Cut Back: Look for areas where you can reduce spending, such as eating out less often or finding cheaper housing options.
- Set Financial Goals: Establish short-term and long-term financial goals, such as reducing credit card debt or saving for future investments.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: Update your budget regularly to reflect changes in income or expenses.
10. How Does Medical School Debt Impact Future Earnings?
Medical school debt can significantly impact future earnings and financial planning. Understanding the long-term implications is essential for making informed decisions about borrowing.
- High Debt Burden: The average medical school graduate has a substantial amount of debt, which can affect their ability to save for retirement, purchase a home, or start a family.
- Delayed Financial Milestones: High debt levels may delay significant financial milestones, such as buying a home or investing in retirement accounts.
- Career Choices: The pressure to repay debt may influence career choices, with some graduates opting for higher-paying specialties or practicing in urban areas.
- Loan Repayment Options: Understanding and utilizing income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs can mitigate the impact of debt on future earnings.
- Financial Planning: Seeking advice from a financial advisor can help develop strategies to manage debt and plan for long-term financial goals.
11. What Are the Loan Forgiveness Programs for Medical School Graduates?
Loan forgiveness programs offer medical school graduates the opportunity to have a portion or all of their student loan debt forgiven in exchange for working in underserved areas or specific fields. These programs can provide significant financial relief.
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF): This federal program forgives the remaining balance on Direct Loans after 120 qualifying monthly payments made under a qualifying repayment plan while working full-time for a qualifying employer.
- National Health Service Corps (NHSC) Loan Repayment Program: This program repays a portion of student loans for medical professionals who commit to working in underserved communities for a set period.
- Indian Health Service (IHS) Loan Repayment Program: This program offers loan repayment assistance to health professionals who agree to serve at IHS facilities.
- State-Specific Loan Forgiveness Programs: Many states offer loan forgiveness programs for medical professionals working in underserved areas within the state.
- Military Loan Repayment Programs: The armed forces offer loan repayment programs to medical officers who commit to serving in the military.
12. How Can I Find Scholarships for Medical School?
Finding scholarships can significantly reduce the cost of medical school. Numerous scholarships are available through medical schools, professional organizations, and private foundations.
- Medical School Websites: Check the financial aid section of each medical school’s website for information on scholarships and grants.
- AAMC Website: The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) offers a database of scholarships and financial aid resources.
- Professional Organizations: Organizations such as the American Medical Association (AMA) and specialty-specific groups offer scholarships to medical students.
- Private Foundations: Many private foundations offer scholarships for students pursuing careers in healthcare.
- Online Scholarship Databases: Websites like Fastweb, Sallie Mae, and Scholarship America provide searchable databases of scholarships.
- Diversity Scholarships: Look for scholarships specifically for students from underrepresented backgrounds.
13. What Is the Role of a Financial Advisor in Planning for Medical School Costs?
A financial advisor can play a crucial role in helping students plan for the costs of medical school. They can provide guidance on budgeting, financial aid, loan management, and long-term financial planning.
- Budgeting and Expense Management: Financial advisors can help create a realistic budget and identify strategies to reduce expenses.
- Financial Aid Advice: They can provide advice on applying for financial aid, understanding loan options, and maximizing scholarship opportunities.
- Loan Management Strategies: Financial advisors can help develop strategies for managing student loan debt, including choosing the right repayment plan and exploring loan forgiveness options.
- Long-Term Financial Planning: They can assist with long-term financial planning, such as saving for retirement and making investment decisions.
- Customized Financial Plans: Financial advisors can create customized financial plans tailored to individual circumstances and goals.
14. How Does the Cost of Medical School Compare to Other Professional Degrees?
The cost of medical school is generally higher than many other professional degrees, such as law or business, due to the length of the program and the specialized resources required. Understanding these differences can help students make informed career decisions.
- Law School: The average cost of law school is lower than medical school, with total expenses typically ranging from $120,000 to $200,000 for a three-year program.
- Business School (MBA): The cost of an MBA program can vary widely, but full-time programs at top schools can cost between $100,000 and $200,000 for a two-year program.
- Engineering: The cost of an engineering degree is generally lower than medical school, with total expenses ranging from $80,000 to $150,000 for a four-year program.
- Dental School: Dental school costs are comparable to medical school, with total expenses ranging from $200,000 to $300,000 for a four-year program.
- Pharmacy School: Pharmacy school costs are also similar to medical school, with total expenses ranging from $150,000 to $250,000 for a four-year program.
15. What Resources Are Available for International Students to Finance Medical School in the U.S.?
International students seeking to study medicine in the U.S. face unique financial challenges. However, several resources are available to help them finance their education.
- Scholarships and Grants: Many scholarships and grants are specifically for international students, offered by universities, private organizations, and government programs.
- International Student Loans: Some lenders specialize in providing loans to international students, often requiring a U.S. co-signer.
- University Financial Aid: Some universities offer financial aid to international students, although the availability may be limited.
- Embassy and Government Programs: Check with your home country’s embassy or government for scholarships and financial aid programs.
- Private Funding: Explore private funding options, such as crowdfunding or support from family and friends.
16. How Does Choosing a Specialty Impact Future Earning Potential and Debt Repayment?
The choice of medical specialty can significantly impact future earning potential and the ability to repay medical school debt. Some specialties offer higher salaries, making it easier to manage debt.
- High-Earning Specialties: Specialties such as surgery, cardiology, dermatology, and radiology typically offer higher salaries.
- Lower-Earning Specialties: Specialties such as primary care, pediatrics, and family medicine generally have lower salaries.
- Impact on Debt Repayment: Choosing a higher-earning specialty can accelerate debt repayment and provide more financial flexibility.
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF): Working in public service or non-profit healthcare settings may qualify graduates for PSLF, regardless of their specialty.
- National Health Service Corps (NHSC): Working in underserved areas through the NHSC can provide loan repayment assistance.
17. What Are the Long-Term Financial Benefits of Becoming a Doctor?
Despite the high cost of medical school and the burden of student loan debt, there are significant long-term financial benefits to becoming a doctor.
- High Earning Potential: Physicians generally have high earning potential, providing financial security and the ability to achieve financial goals.
- Job Security: The demand for healthcare professionals is consistently high, providing job security and career stability.
- Retirement Savings: Doctors can save for retirement and build wealth, ensuring a comfortable future.
- Investment Opportunities: High income allows for investment in real estate, stocks, and other assets.
- Financial Independence: Achieving financial independence and the ability to support a family are significant long-term benefits.
18. What Role Does Mentorship Play in Navigating the Costs of Medical School?
Mentorship can play a significant role in helping students navigate the costs of medical school. Mentors can provide guidance, advice, and support, helping students make informed financial decisions.
- Financial Advice: Mentors can share their experiences and provide advice on budgeting, financial aid, and debt management.
- Career Guidance: They can offer insights into specialty choices and career paths that align with financial goals.
- Networking Opportunities: Mentors can connect students with valuable networking opportunities, leading to scholarships, research positions, and job opportunities.
- Emotional Support: Mentors can provide emotional support and encouragement, helping students cope with the stress of medical school and financial pressures.
- Real-World Perspectives: Mentors can offer real-world perspectives on the financial realities of being a physician, helping students prepare for their future careers.
19. How Can I Prepare Financially Before Applying to Medical School?
Preparing financially before applying to medical school is crucial for ensuring a smooth transition and minimizing financial stress.
- Save Money: Start saving as early as possible to accumulate funds for application fees, interview expenses, and initial living costs.
- Create a Budget: Develop a realistic budget that includes all anticipated expenses and income sources.
- Improve Credit Score: A good credit score can improve your chances of obtaining loans with favorable terms.
- Research Financial Aid Options: Explore scholarships, grants, and loan programs to understand the available resources.
- Consult a Financial Advisor: Seek advice from a financial advisor to develop a comprehensive financial plan.
- Reduce Debt: Pay off existing debt, such as credit card balances, to improve your financial position.
20. What Are the Ethical Considerations When Considering the Cost of Medical School?
The cost of medical school raises ethical considerations related to access to education, healthcare disparities, and the influence of debt on medical practice.
- Access to Education: The high cost of medical school can create barriers for students from low-income backgrounds, limiting diversity in the medical profession.
- Healthcare Disparities: Debt-burdened physicians may be more likely to practice in high-paying specialties or urban areas, exacerbating healthcare disparities in underserved communities.
- Influence on Medical Practice: Financial pressures may influence medical decision-making, potentially leading to over-testing or unnecessary procedures.
- Social Responsibility: Medical schools have a responsibility to address the cost of education and ensure that financial constraints do not compromise patient care or limit access to the profession.
- Advocacy: Medical professionals can advocate for policies that address the cost of medical education and promote equitable access to healthcare.
The financial burden of medical school is substantial, but with careful planning, diligent financial management, and access to resources, it is possible to pursue a career in medicine without being overwhelmed by debt.
Navigating the complexities of medical school costs and financial aid can be overwhelming. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with experienced Ph.D. experts who can provide personalized guidance. Our experts will help you navigate the financial aid process, create a realistic budget, and develop a long-term financial plan so you can focus on your education. Contact us today at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN for a consultation. Let how.edu.vn help you achieve your dreams of becoming a doctor.
FAQ Section
1. How much does the MCAT cost?
The Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) costs approximately $335 per test. This fee is necessary for all students planning to apply to medical school.
2. What is the initial application fee for medical school?
The initial application fee is $175 through the AAMC. Each additional application costs $46.
3. How can I reduce my living expenses during medical school?
You can reduce living expenses by sharing accommodation, cooking at home, minimizing discretionary spending, and using public transportation.
4. What is the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program?
The Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program forgives the remaining balance on Direct Loans after 120 qualifying monthly payments made under a qualifying repayment plan while working full-time for a qualifying employer.
5. Are there scholarships specifically for minority students in medical school?
Yes, there are scholarships specifically for minority students in medical school. Organizations like the National Medical Fellowships offer scholarships to underrepresented minority students.
6. Can I work part-time during medical school to offset costs?
Yes, if feasible, working part-time during medical school can provide additional income to offset expenses. However, it’s important to balance work with your studies and well-being.
7. What is the Health Professions Student Loan (HPSL)?
The Health Professions Student Loan (HPSL) is a low-interest loan available to students pursuing degrees in certain health professions.
8. How does the cost of attending a private medical school compare to a public one?
The cost of attending a private medical school is generally higher than a public one. Private schools average around $67,950 per year, while public schools average around $53,845 per year.
9. What are some strategies to minimize student loan debt in medical school?
Strategies to minimize student loan debt include applying for scholarships and grants, choosing a public in-state school, living frugally, and considering loan repayment programs.
10. How can a financial advisor help with medical school costs?
A financial advisor can provide guidance on budgeting, financial aid, loan management, and long-term financial planning to help students manage the costs of medical school.
