Rent increases are a common concern for both landlords and tenants. How Much Does Rent Increase Per Year? On average, rent in the U.S. increases by about 3% annually, but this can vary significantly based on local market conditions, inflation, and other economic factors. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights to help you navigate the complexities of rental pricing and tenant relations, ensuring fair and competitive rates while sustaining your investments. Understanding these dynamics can lead to better tenant retention and optimize your rental income, allowing for strategic property management and enhanced profitability.
1. Understanding Annual Rent Increase Trends
Rent prices in the U.S. are not static; they fluctuate each year due to a variety of factors. Understanding these trends is essential for both landlords and tenants.
1.1 Historical Rent Growth
Examining historical data provides a baseline for understanding rent increase patterns:
- 2021: Witnessed a significant surge, with rents increasing by 18% year-over-year as the market recovered from pandemic-related freezes. This sharp increase reflected pent-up demand and limited housing supply.
- 2022: Saw a moderation in the rate of increase, with the average rent increase slowing to 12.2%. While still high compared to historical averages, this indicated a cooling of the market.
- 2024: The market has continued to stabilize, with rent growth moderating to a modest 0.8% year-over-year as of August. This reflects a more balanced supply and demand dynamic.
1.2 Regional Variations
National averages can be misleading as local market conditions vary significantly. For example:
- New York City: Experienced rent increases of 3.6% in 2024, reflecting continued high demand in urban centers.
- Sun Belt Cities: Such as Austin and Atlanta, saw rent declines due to an oversupply of new apartments. This highlights the impact of new construction on rental prices.
- Midwest and Northeast: Areas like Erie, PA, and Duluth, MN, experienced rental price increases due to higher demand and limited supply.
1.3 The Importance of Local Market Knowledge
Staying informed about local trends is crucial for making informed decisions about rental pricing. Consulting with real estate experts through platforms like HOW.EDU.VN can provide valuable insights tailored to your specific market.
2. Key Factors Determining Rent Increases
Several factors influence how much a landlord can reasonably increase rent each year. Understanding these factors helps in making informed decisions that balance profitability with tenant satisfaction.
2.1 Inflation’s Impact
Inflation plays a significant role in rent increases. When the cost of goods and services rises, landlords often adjust rents to cover increased operating expenses.
- Correlation: While rental price growth and inflation don’t always rise at the same rate, they generally correlate. In 2021, inflation rose by 6.3%, and rent prices increased by over 10%.
- Expense Offset: Landlords often need to offset higher costs related to property maintenance, insurance, and utilities.
2.2 Home Sale Prices
The housing market directly affects rental demand. When home prices rise, fewer people can afford to buy, increasing the demand for rental properties.
- Increased Demand: Higher home prices lead to more competition among renters, pushing rental prices up.
- Affordability Issues: As homeownership becomes less accessible, more people remain in the rental market.
2.3 Supply and Demand Dynamics
The balance between supply and demand is a primary driver of rent prices. When demand exceeds supply, rents rise, and vice versa.
- Construction Lag: Since 2010, new construction hasn’t kept pace with demand, exacerbating the shortage of rental units.
- Future Needs: The U.S. needs to build 4.3 million additional apartments by 2035 to meet current and future demand.
- Regional Impacts: States like Texas, Florida, and California, which are expected to account for 40% of future rental demand, will likely see continued pressure on rental prices.
2.4 Vacancy Rates
High vacancy rates can discourage rent increases. Landlords are less likely to raise rents if they have many vacant units.
- Market Competitiveness: High vacancy rates mean landlords must compete to attract tenants, often by keeping rents stable or even lowering them.
- Income Stability: Maintaining occupancy is crucial for consistent rental income.
2.5 Economic Growth
A strong local economy typically leads to higher employment rates and increased demand for housing.
- Job Growth: Areas with growing job markets attract more residents, increasing the demand for rental properties.
- Wage Increases: Higher wages enable renters to afford higher rents.
3. Determining Fair Market Rent
Setting a competitive and reasonable rent is essential for attracting tenants and ensuring profitability. Fair market rent (FMR) represents the average rent for similar properties in the same area.
3.1 Methods for Determining FMR
- Research Local Listings: Check websites like Zillow, Rentometer, and local real estate platforms to see what similar properties are charging in your area.
- Consult Real Estate Agents: Local experts can provide insights into market trends and help refine rent pricing.
- Consider Property Features: Location, size, amenities, and the condition of the property all affect rent. Properties with modern amenities or prime locations may justify higher rent compared to others.
3.2 The Importance of Accurate Pricing
Setting a rent price aligned with fair market rent helps landlords attract tenants and maximize rental income.
- Tenant Attraction: Competitive pricing makes your property more attractive to potential renters.
- Income Maximization: Accurate pricing ensures you’re not undervaluing your property, helping you maximize rental income.
4. State-Specific Rent Increase Data
While national averages provide a general overview, state-specific data offers more precise insights into rent changes.
4.1 Rent Increase Breakdown by State (2024)
Here’s a breakdown of average rent changes by state, including median and maximum rents:
| State | Rent Change (%) | Average Rent ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 1.86 | 180 |
| Alaska | 3.3 | 1,240 |
| Arizona | -3.4 | 1,097 |
| Arkansas | 0.0 | 760 |
| California | 1.2 | 2,440 |
| Colorado | -3.8 | 1,780 |
| Connecticut | 4.4 | 2,150 |
| Delaware | 2.7 | 1,150 |
| District of Columbia | 1.6 | 2,380 |
| Florida | -2.3 | 1,218 |
| Georgia | -4.1 | 1,042 |
| Hawaii | 1.4 | 2,850 |
| Idaho | 2.1 | 887 |
| Illinois | 5.7 | 1,038 |
| Indiana | 2.8 | 1,095 |
| Iowa | 2.6 | 806 |
| Kansas | 1.3 | 863 |
| Kentucky | 2.4 | 783 |
| Louisiana | 3.7 | 876 |
| Maine | -8.1 | 873 |
| Maryland | 6.1 | 1,415 |
| Massachusetts | 2.1 | 2,900 |
| Michigan | 8.5 | 892 |
| Minnesota | 0.7 | 1,010 |
| Mississippi | 1.8 | 789 |
| Missouri | 3.9 | 843 |
| Montana | 4.5 | 836 |
| Nebraska | 2.3 | 857 |
| Nevada | -2.8 | 1,159 |
| New Hampshire | 2.1 | 1,145 |
| New Jersey | 4.8 | 1,550 |
| New Mexico | 2.7 | 857 |
| New York | 2.8 | 3,400 |
| North Carolina | -3.1 | 932 |
| North Dakota | 2.6 | 828 |
| Ohio | 1.5 | 825 |
| Oklahoma | 2.0 | 818 |
| Oregon | 1.1 | 1,173 |
| Pennsylvania | 2.6 | 958 |
| Rhode Island | 2.3 | 1,031 |
| South Carolina | 1.5 | 918 |
| South Dakota | 1.4 | 761 |
| Tennessee | 1.2 | 897 |
| Texas | 1.2 | 1,082 |
| Utah | 1.0 | 1,090 |
| Vermont | 3.7 | 999 |
| Virginia | 4.8 | 1,257 |
| Washington | 1.3 | 1,337 |
| West Virginia | 1.7 | 732 |
| Wisconsin | 7.8 | 872 |
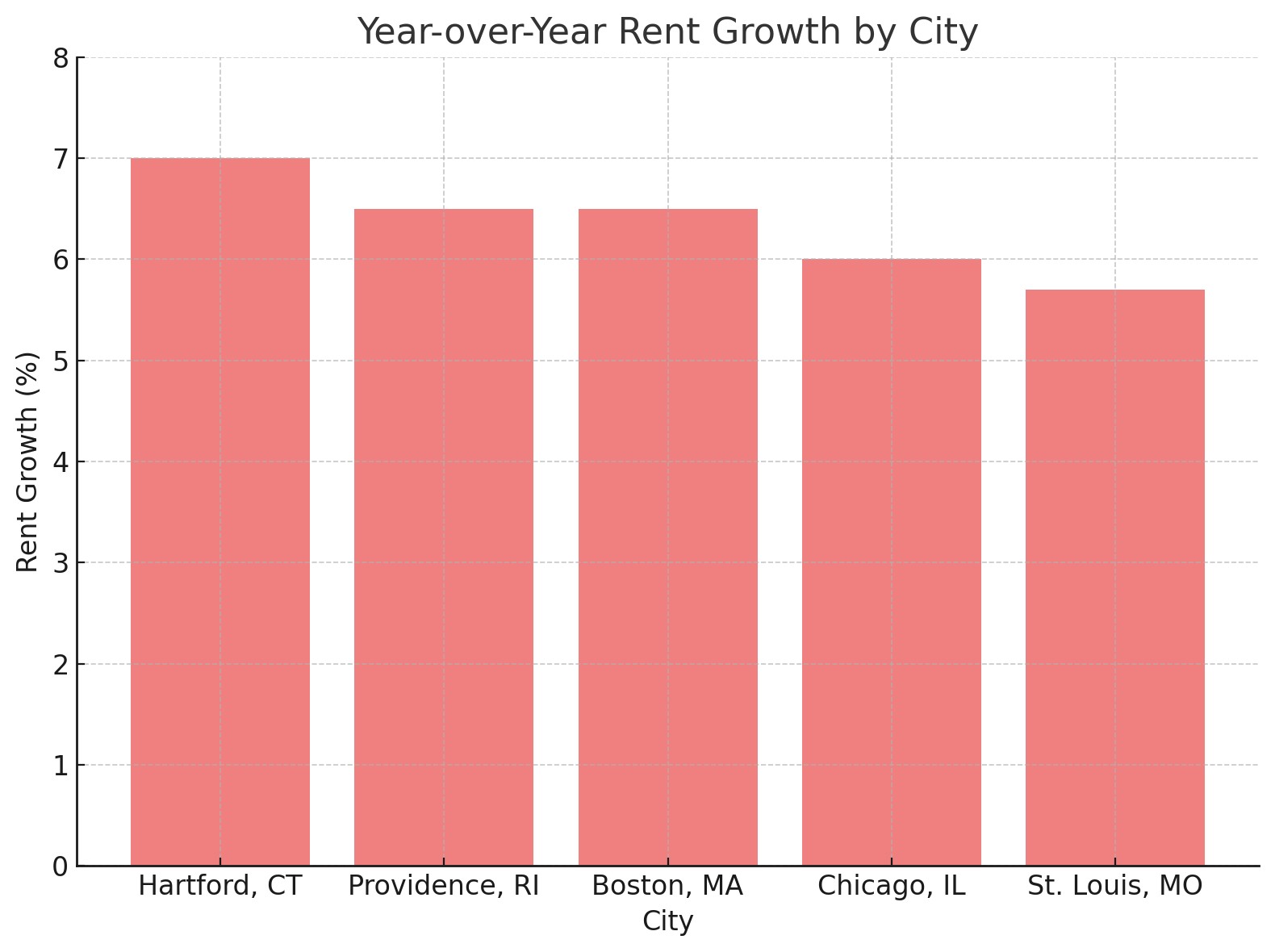
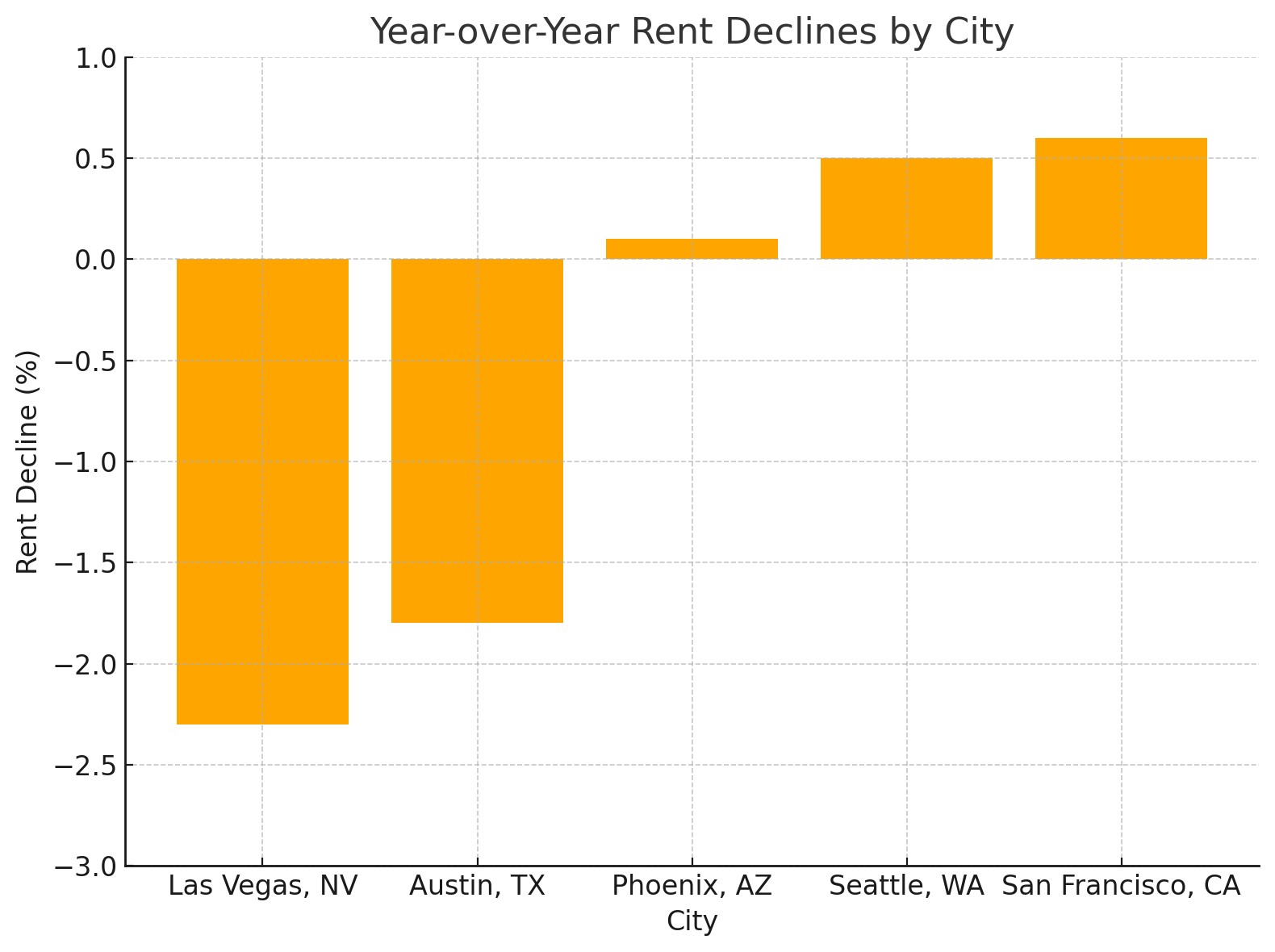
4.2 Interpreting State-Specific Data
This data highlights the significant variations in rent changes across the U.S. Landlords should focus on data relevant to their specific location to make informed decisions.
5. Future Rent Trends and Projections
Understanding future trends is crucial for long-term planning. While rent prices are still rising, the pace has slowed compared to the rapid increases of 2021 and 2022.
5.1 Market Stabilization
Recent reports indicate a more moderate growth rate in rent prices. As the market stabilizes, landlords should be prepared to justify any adjustments to rent prices based on these trends.
- Slowing Growth: From June to July 2024, asking rents increased by 0.5%, slightly down from previous months.
- No Return to Spikes: The dramatic spikes of the past few years are unlikely to return in the near future.
5.2 Regional Insights
Regional variations will continue to play a key role in rent trends. While Sun Belt cities are experiencing rent declines, the Midwest and Northeast are seeing upward pressure due to higher demand.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Tracking rent increases and decreases across regions is important for making informed real estate decisions.
5.3 Cities with Notable Rent Changes (2024)
- Highest Rent Increases: Cities experiencing the highest rent increases in 2024 include those with strong local economies and limited housing supply.
- Lowest Rent Increases: Cities with the lowest rent increases or even declines often have an oversupply of rental units.
6. Rental Industry Trends to Consider
Economic and social factors beyond supply and demand also influence rental price growth.
6.1 Impact of Junk Fees
Additional rental fees, such as pet fees and pest control fees, contribute to the growing burden on renters.
- Accessibility Issues: These “junk fees” make affordable housing less accessible.
- Financial Burden: 40% of U.S. renters already spend 30% or more of their income on housing.
- Policy Changes: The Biden Administration has committed to reducing or eliminating these fees and promoting transparency in the rental process.
6.2 Rising Homeownership Costs
Increasing homeownership costs keep more people in the rental market.
- Affordability Gap: Many first-time buyers are unable to afford a mortgage.
- Salary Requirements: First-time homebuyers in 2023 need an annual salary of $64,500 to afford a typical starter home, a 13% increase from the previous year.
- Extended Rental Periods: Tenants may rent for longer periods, providing property owners with greater tenant retention but also raising considerations for lease renewals and rent increases.
6.3 Effect of Rising Interest Rates
Rising mortgage rates have sharply increased the total number of renters.
- Mortgage Rate Impact: As of 2024, mortgage rates have surpassed 7%, making homeownership unattainable for many families.
- Sustained Demand: This combination of high mortgage rates and restricted housing supply is expected to sustain demand for rental units, driving prices higher in certain regions.
7. How to Raise Rent on Your Tenants Effectively
Incremental rent increases help maintain profitability over time. However, tenants may struggle to understand why their rent is going up without a clear explanation.
7.1 Providing Valid Reasons
Offering valid reasons, such as increased operating expenses, rising cost of living, or higher mortgage rates, can help tenants accept the changes.
- Expense Justification: Clearly explain the factors driving the need for a rent increase.
- Market Transparency: Share relevant market data to support your decision.
7.2 Giving Fair Notice
It’s important to give tenants fair notice – preferably at least three months before their lease expires – to allow them time to adjust.
- Time to Adjust: Adequate notice allows tenants to plan their budgets accordingly.
- Goodwill Building: This approach fosters goodwill and increases the chances of receiving rent on time.
7.3 Gradual Increases
Gradual rent increases, rather than steep hikes, can also preserve tenant satisfaction and reduce the risk of turnover.
- Market Conditions: Instead of raising rent by 10% at once, consider a 3-5% annual increase based on market conditions and expenses.
- Flexibility: Providing transparency and offering flexibility helps smooth the process for both parties.
8. Communicating Rent Increases to Tenants
Effectively communicating rent increases is essential to maintaining a positive landlord-tenant relationship.
8.1 Steps for Effective Communication
- Provide Written Notice: Clearly state the reasons for the increase and the new rent amount in a written notice. This transparency helps tenants understand the rationale behind the change.
- Offer Fair Notice: Although a month’s notice may be legally sufficient, consider providing at least three months’ notice to give tenants time to adjust their budgets and plan accordingly.
- Answer Questions: Be prepared to address tenant concerns by explaining the reasons for the increase and sharing information like market data or documentation of increased operating costs.
- Provide Supporting Evidence: Show local rent trends or improvements made to the property that justify the increase.
8.2 Benefits of Clear Communication
Clear communication, transparency, and a willingness to address tenant concerns can help ease the transition and reduce the risk of tenant turnover.
- Reduced Turnover: Open communication can prevent misunderstandings and tenant dissatisfaction.
- Improved Relations: Fosters a positive landlord-tenant relationship.
9. Negotiating Rent Increases
When negotiating rent increases with tenants, it’s important to approach the conversation with fairness and flexibility.
9.1 Strategies for Negotiation
- Listen to Concerns: Understand the tenant’s perspective and be open to compromise.
- Consider Compromises: Offer a smaller increase in exchange for a longer lease or spread the increase over time.
- Foster Trust: Building trust can lead to more amicable negotiations and avoid vacancies.
10. Timing Considerations for Rent Increases
Timing is key when raising rent. Landlords should consider the following factors:
10.1 Key Factors to Consider
- Local Rental Market: Implement rent increases during high-demand periods, such as peak rental seasons, when vacancies are less likely.
- Lease Renewal: Ensure that tenants receive ample notice of any rent increase before their lease expires, ideally at least three months in advance.
- Operating Expenses: Align rent increases with rising property costs like maintenance, taxes, or utilities to justify the timing of the increase.
- Tenant Retention: Consider how rent hikes will affect tenant satisfaction. A sharp increase may result in turnover, so balancing reasonable increases with market conditions can help maintain occupancy.
10.2 Market-Specific Strategies
In high-demand markets, tenants are more likely to accept rent increases, while in slower markets, smaller or staggered increases may be necessary to avoid vacancies.
11. Raising Rent Ethically and Responsibly
Understanding how rent increases work is important for both property owners and renters. Since the pandemic, rental markets have experienced significant economic and social changes, which have caused sharp spikes in rent prices across the country.
11.1 Current Market Conditions
Rental price growth has begun to stabilize and is expected to continue on a stable trajectory. However, rental demand remains strong, particularly for studio and one-bedroom apartments.
- Stable Growth: The peak rent prices of 2021 and 2022 are likely a thing of the past.
- Healthy Competition: Property owners can still expect healthy competition among renters.
11.2 Local Market Relevance
Rental market conditions vary widely from state to state and even within cities and neighborhoods. Determining when to raise rent, and by how much, will depend on factors relevant to your local rental market.
11.3 Balanced Approach
By taking a balanced and informed approach to rent adjustments, property owners can ensure the sustainability of their investments while providing fair and competitive rates for their tenants.
12. Expert Guidance from HOW.EDU.VN
Navigating the complexities of rent increases requires expert guidance. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading PhDs and experts who can provide personalized advice tailored to your specific needs and market conditions.
12.1 Benefits of Consulting with Experts
- Informed Decisions: Get access to the latest market data and insights.
- Strategic Planning: Develop effective strategies for rent adjustments and tenant relations.
- Risk Mitigation: Minimize the risk of vacancies and tenant turnover.
12.2 Connect with Our Team of Experts
Whether you’re a landlord looking to optimize your rental income or a tenant seeking fair rental rates, HOW.EDU.VN offers the expertise you need to succeed. Our team of over 100 PhDs and professionals are ready to provide the support and guidance you deserve.
13. Call to Action
Don’t navigate the complexities of rent increases alone. Connect with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN today for personalized advice and strategic solutions.
13.1 Contact Us
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let HOW.EDU.VN help you make informed decisions, optimize your rental income, and foster positive tenant relations.
14. FAQs About Rent Increases
14.1 How Often Can a Landlord Increase Rent?
Typically, a landlord can increase rent once per lease term. If it’s a month-to-month lease, they can increase it with proper notice, usually 30 days.
14.2 What Is Considered a Reasonable Rent Increase?
A reasonable rent increase is generally between 3% and 5% annually, depending on local market conditions, inflation, and property improvements.
14.3 How Much Notice Is Required Before a Rent Increase?
Most jurisdictions require at least 30 days’ notice before a rent increase. However, providing 60 to 90 days’ notice can help maintain good tenant relations.
14.4 Can a Landlord Increase Rent in the Middle of a Lease?
No, a landlord typically cannot increase rent in the middle of a fixed-term lease unless the lease agreement specifically allows for it.
14.5 What Factors Justify a Rent Increase?
Justifiable factors include increased operating expenses (such as property taxes, insurance, and maintenance), rising cost of living, and significant property improvements.
14.6 How Do I Negotiate a Rent Increase?
Tenants can negotiate by researching comparable rental rates in the area, pointing out any property defects, and proposing a compromise, such as a smaller increase in exchange for a longer lease term.
14.7 What Are My Rights as a Tenant Regarding Rent Increases?
Tenants have the right to proper notice before a rent increase, a written explanation of the increase, and the right to refuse the increase and move out at the end of their lease term.
14.8 Can a Landlord Discriminate When Increasing Rent?
No, a landlord cannot discriminate based on race, religion, gender, familial status, or disability when increasing rent. Such actions are illegal under the Fair Housing Act.
14.9 How Does Rent Control Affect Rent Increases?
Rent control laws limit the amount and frequency of rent increases in certain cities and states. Landlords in these areas must adhere to these regulations.
14.10 Where Can I Find Information About Local Rent Trends?
You can find information about local rent trends on websites like Zillow, Rentometer, and local real estate platforms. Consulting with local real estate agents can also provide valuable insights.
15. Enhance Your Property Management Strategies with HOW.EDU.VN
Partner with HOW.EDU.VN to elevate your property management strategies and tenant relations. Our expert advice ensures you stay competitive while maintaining ethical and responsible rental practices.
15.1 Customized Solutions
We offer tailored solutions to address your unique challenges and objectives, ensuring you make informed decisions that drive success.
15.2 Commitment to Excellence
Trust how.edu.vn to deliver exceptional guidance, helping you create a thriving rental environment for both property owners and tenants.
15.3 Take the Next Step
Contact us today to discover how our expertise can benefit you.