Answering your question about how much foreign aid the U.S. gives annually, HOW.EDU.VN clarifies that the U.S. government provides significant international assistance to support humanitarian, economic development, and various other global efforts. Understanding the scale, distribution, and impact of this aid is crucial for grasping its role in international relations and global welfare. This article delves into the specifics of U.S. foreign aid, its beneficiaries, and the attitudes surrounding it, further advising you on how you can learn from experts to solve similar problems.
1. What Is the Total Amount of US Foreign Aid?
The US government is projected to spend approximately $58.4 billion on international assistance programs in the 2025 fiscal year. However, this figure may change due to ongoing efforts to reshape and potentially reduce aid.
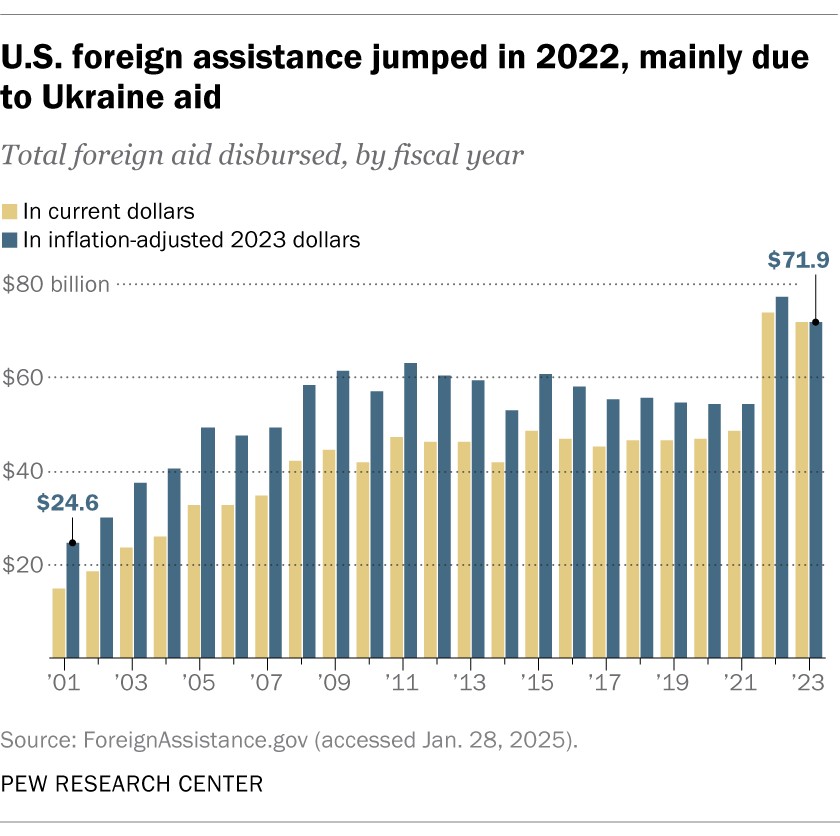
In fiscal year 2023, the U.S. government disbursed $71.9 billion in foreign aid, according to ForeignAssistance.gov. In comparison, nearly $74.0 billion was spent in fiscal 2022. These figures exclude most arms sales or transfers of military equipment to foreign countries.
U.S. foreign aid spending fluctuates yearly due to various factors such as wars, disasters, disease outbreaks, and evolving policy priorities. For instance, in fiscal year 2001, U.S. foreign aid spending was $24.6 billion (adjusted to 2023 dollars). Between fiscal years 2008 and 2023, annual aid spending ranged from $52.9 billion to $77.3 billion, adjusted for inflation. According to the United Nations, the U.S. government is the single-largest aid donor in the world, accounting for over 40% of all humanitarian aid tracked by the UN in 2024.
2. What Percentage of the Federal Budget Is Foreign Aid?
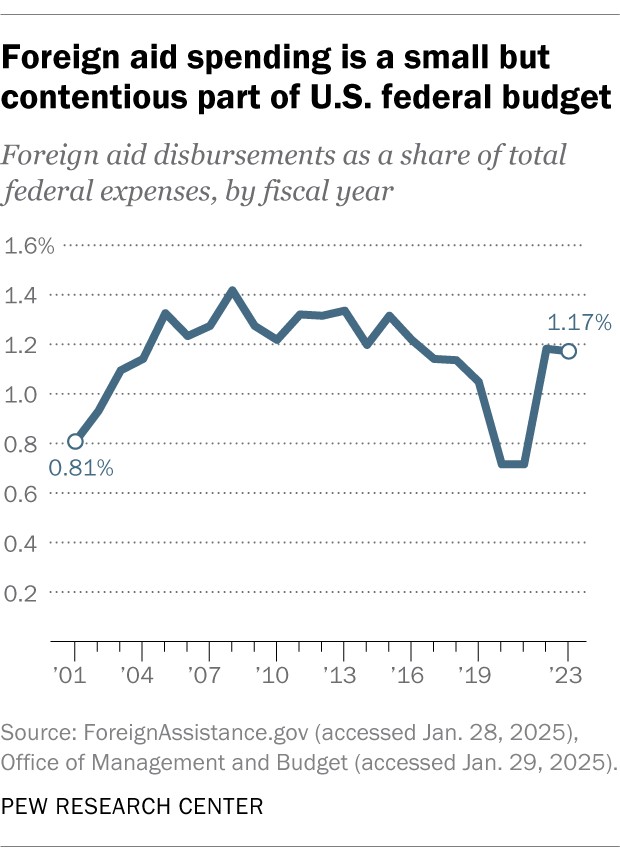
In fiscal year 2023, the $71.9 billion in foreign aid accounted for 1.2% of the total federal outlays, which exceeded $6.1 trillion.
Since fiscal year 2001, foreign aid has ranged between 0.7% and 1.4% of total federal outlays. The federal deficit in fiscal year 2023 was nearly $1.7 trillion.
During the Cold War, international assistance was a more significant portion of federal spending, amounting to about 4.7% of total federal outlays in fiscal year 1963. However, this share gradually decreased, reaching a low of 0.6% in fiscal year 1989.
3. What Are the Purposes of US Foreign Aid?
U.S. foreign assistance supports a broad spectrum of humanitarian, economic development, and democracy-promotion efforts.
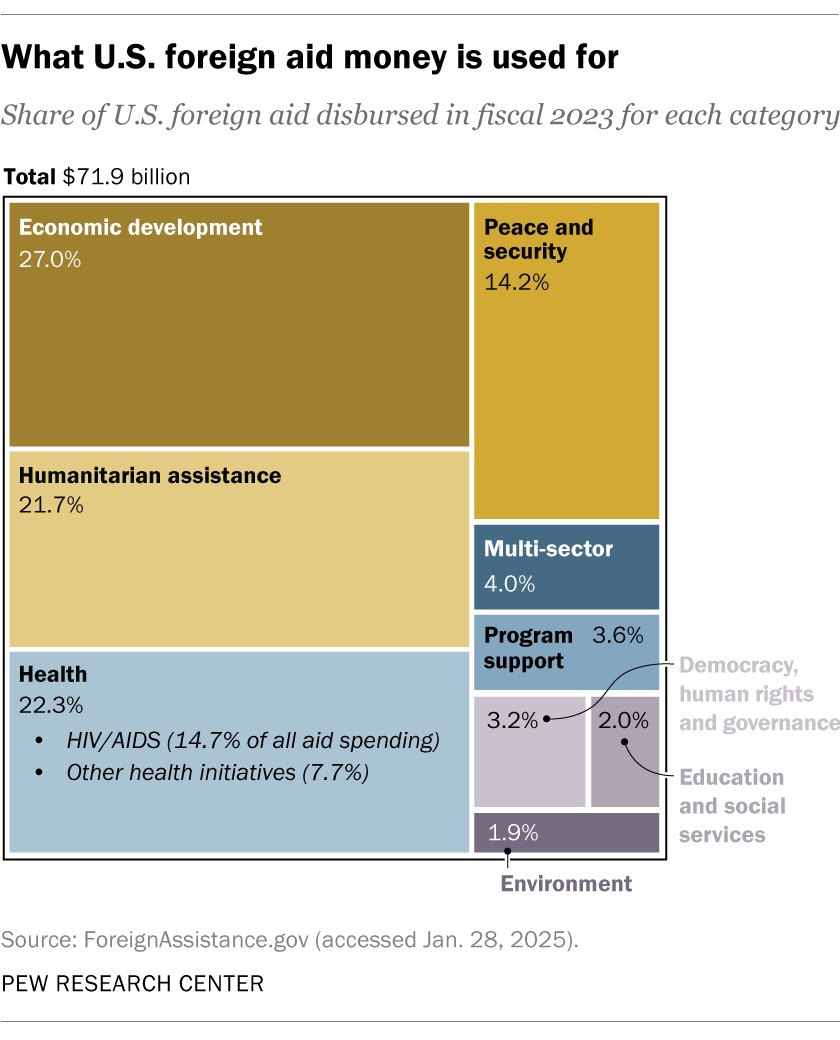
In fiscal year 2023, the largest activity area, accounting for $15.9 billion (22.1% of all disbursed aid), was “macroeconomic foundation for growth.” Of this, $14.4 billion was direct monetary support to the Ukrainian government in its conflict with Russia.
Additional allocations in fiscal year 2023 included:
- Disaster relief and other humanitarian aid ($15.6 billion, or 21.7%)
- HIV/AIDS programs ($10.6 billion, or 14.7%)
- Combating pandemic influenza and other emerging public health threats ($1.5 billion, or 2.0%)
- Promoting democracy, good governance, and the rule of law ($2.3 billion, or 3.2%)
- Multi-sector programs ($2.9 billion, or 4.0%)
4. Which Countries Are the Main Recipients of US Foreign Aid?
In fiscal year 2023, U.S. aid supported programs and activities in 177 individual countries and 29 regions, as well as global endeavors. These projects were implemented by numerous foreign government agencies, nonprofit groups, international organizations, for-profit companies, and universities.
Ukraine was the largest recipient of U.S. aid in fiscal year 2023, receiving $16.6 billion. Israel received $3.3 billion in military aid. Other major recipients included Ethiopia, Jordan, Egypt, and Afghanistan.
| Recipient Country | US Foreign Aid (USD Billions) |
|---|---|
| Ukraine | 16.6 |
| Israel | 3.3 |
| Ethiopia | |
| Jordan | |
| Egypt | |
| Afghanistan |
5. What Agencies Distribute US Foreign Aid?
The primary U.S. aid agency since 1961 has been the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID). As of March 2024, USAID employed 4,675 people. In fiscal year 2023, USAID distributed nearly $43.8 billion in aid, which is approximately three out of every five foreign-assistance dollars.
In fiscal year 2023, the State Department disbursed $21.3 billion in aid, accounting for almost 30% of the total. Smaller amounts were disbursed by the Treasury and Health and Human Services departments, the Millennium Challenge Corporation, and 16 other agencies.
6. How Does Military Assistance Factor into US Foreign Aid?
In fiscal year 2023, $8.2 billion (11.4%) of the $71.9 billion in disbursements was designated as military aid, according to ForeignAssistance.gov. However, the U.S.’s overall military-assistance efforts are much more extensive.
Through the Foreign Military Sales program, approved foreign nations can purchase American weapons, ammunition, equipment, and services. In fiscal year 2024, such sales totaled $117.9 billion, up from $80.9 billion in fiscal year 2023.
Additionally, allies and partner nations can buy arms from their manufacturers independently. These “direct commercial sales” are regulated by law and totaled $200.8 billion in fiscal year 2024, up from $157.5 billion in fiscal year 2023.
7. What Is the Public Opinion on US Foreign Aid?
Americans have had mixed views regarding the effectiveness and desirability of foreign assistance.
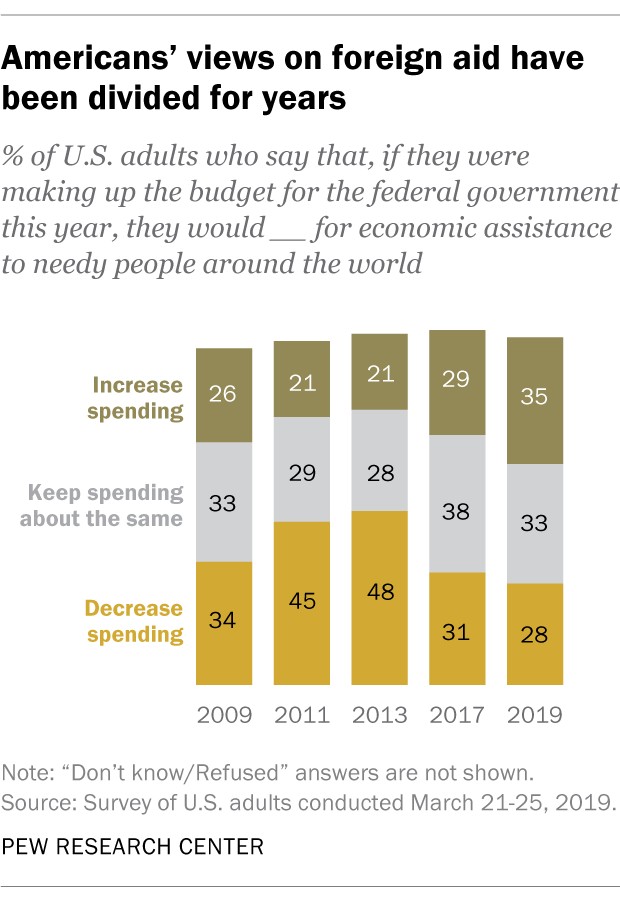
Recent Pew Research Center surveys indicate divided opinions on “economic assistance to needy people around the world.” A 2019 telephone survey found that 35% of U.S. adults wanted to increase spending on such aid, 33% wanted to keep it the same, and 28% wanted to decrease it.
A March 2023 online survey revealed that only a third of Americans believed U.S. foreign aid primarily benefits developing countries, while slightly more (37%) thought it both benefits and harms these countries, and 8% felt it mostly harms them. A significant portion (17%) were unsure.
When considering broader foreign policy goals, Americans prioritize domestic security. In a 2024 online survey, 73% of U.S. adults emphasized protecting the country from terrorist attacks as a top priority, with 64% focusing on reducing illegal drug flow and preventing the spread of weapons of mass destruction. Only 26% prioritized promoting and defending human rights, and 18% prioritized promoting democracy in other nations.
Notably, U.S. foreign aid also supports many of these priorities. In fiscal year 2023, $417.8 million was allocated to counterterrorism efforts, $331.7 million to combating the spread of weapons of mass destruction, and $126.5 million to fighting the narcotics trade. A substantial portion of the $16 billion directed to health-related projects targets diseases such as HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, and influenza.
8. Decoding Foreign Aid: Insights from Experts
Understanding the intricacies of foreign aid requires expertise. Experts analyze the allocation, impact, and effectiveness of aid programs, providing insights into maximizing their benefits. They assess geopolitical factors, economic conditions, and social dynamics to ensure aid reaches those who need it most. For instance, economists can evaluate the impact of aid on economic growth, while political scientists can assess its influence on governance and stability.
Consulting with experts ensures that aid efforts are strategic, targeted, and effective. Experts help to navigate complex challenges, providing evidence-based recommendations for optimizing aid programs.
9. The Crucial Role of Transparency and Accountability in Foreign Aid
Transparency and accountability are fundamental to ensuring the effective use of foreign aid. Transparency involves providing clear and accessible information about aid flows, including the amount, purpose, and recipients of aid. Accountability mechanisms hold aid organizations and recipient governments responsible for using aid resources effectively and achieving intended outcomes.
Increased transparency and accountability can enhance public trust in aid programs, reduce corruption, and improve aid effectiveness. These principles ensure that aid is used responsibly and contributes to sustainable development.
10. Addressing Long-Term Challenges Through Foreign Aid
Foreign aid plays a pivotal role in addressing long-term challenges such as poverty, inequality, and climate change. By investing in education, health, and infrastructure, aid programs can help to break cycles of poverty and promote sustainable development. Aid can also support efforts to mitigate and adapt to climate change, promoting resilience and reducing vulnerability.
Effective aid strategies address the root causes of these challenges, fostering long-term solutions. International cooperation and partnerships are essential for maximizing the impact of aid and achieving lasting results.
11. How Can HOW.EDU.VN Help You Understand Complex Issues Like Foreign Aid?
Navigating complex topics like foreign aid requires expert guidance. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading PhDs and experts who can provide clarity, analysis, and strategic advice. Our experts offer personalized consultations to address your specific questions and concerns, ensuring you receive the most relevant and actionable insights.
11.1. Benefits of Consulting with Experts from HOW.EDU.VN
- Expert Guidance: Access to top-tier PhDs and professionals who specialize in international development, economics, and political science.
- Personalized Consultations: Tailored advice to address your unique questions and challenges.
- Data-Driven Insights: Evidence-based recommendations to inform your understanding and decision-making.
- Comprehensive Analysis: In-depth evaluations of aid programs, policies, and their impacts.
- Strategic Advice: Guidance on how to navigate complex issues and achieve your goals.
11.2. Featured Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
| Expert Name | Area of Expertise | Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Anya Sharma | International Development Economics | 20+ years of experience, PhD in Economics, former advisor to the World Bank. |
| Dr. Ben Carter | Political Science and Foreign Policy | 15+ years of experience, PhD in Political Science, published numerous articles on foreign aid and international relations. |
| Dr. Emily Rodriguez | Humanitarian Aid and Disaster Relief | 10+ years of field experience, PhD in Public Health, worked with leading NGOs and international organizations. |
| Dr. Kenji Tanaka | Sustainable Development and Climate Change | 25+ years of experience, PhD in Environmental Science, led multiple projects on sustainable development and climate resilience. |
| Dr. Ingrid Müller | Governance and Public Administration | 18+ years of experience, PhD in Public Administration, advised governments on improving governance and public service delivery. |
| Dr. Omar Hassan | International Law and Human Rights | 22+ years of experience, PhD in International Law, worked with international tribunals and human rights organizations. |
| Dr. Lena Petrova | Global Health and Infectious Diseases | 14+ years of experience, PhD in Epidemiology, worked with the World Health Organization and other global health agencies. |
| Dr. Samuel Dubois | Conflict Resolution and Peacebuilding | 28+ years of experience, PhD in Conflict Resolution, mediated numerous international conflicts and worked on peacebuilding initiatives. |
| Dr. Mei Zhang | Education Policy and International Education | 16+ years of experience, PhD in Education Policy, designed and evaluated education programs in developing countries. |
| Dr. Ravi Patel | Economic Growth and Poverty Reduction | 23+ years of experience, PhD in Development Economics, advised governments on economic growth strategies and poverty reduction policies. |
11.3. Consulting Services Offered by HOW.EDU.VN
- One-on-One Consultations: Discuss your specific questions and concerns with a leading expert.
- Comprehensive Reports: In-depth analysis of aid programs and their effectiveness.
- Strategic Planning: Guidance on developing effective strategies for international development.
- Webinars and Workshops: Educational sessions on key topics related to foreign aid and global development.
- Customized Research: Tailored research services to meet your unique needs.
FAQ: Your Questions About Foreign Aid Answered
- What is foreign aid?
- Foreign aid is the assistance provided by governments, organizations, or individuals to support the economic, social, and political development of other countries. It can include financial assistance, technical assistance, humanitarian aid, and military assistance.
- Why does the U.S. provide foreign aid?
- The U.S. provides foreign aid for various reasons, including promoting economic development, addressing humanitarian crises, supporting democratic governance, and advancing U.S. foreign policy interests.
- How is foreign aid different from military aid?
- Foreign aid encompasses a wide range of assistance programs, including economic, humanitarian, and development aid. Military aid specifically refers to assistance provided for military purposes, such as training, equipment, and security assistance.
- What are the main goals of U.S. foreign aid?
- The main goals of U.S. foreign aid include promoting sustainable economic growth, improving global health, strengthening democratic institutions, providing humanitarian assistance, and enhancing U.S. national security.
- How can I be sure that foreign aid is used effectively?
- To ensure foreign aid is used effectively, transparency and accountability mechanisms are crucial. Regular monitoring, evaluations, and audits can help track aid flows and assess their impact.
- What role do international organizations play in foreign aid?
- International organizations such as the United Nations, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund play a significant role in coordinating and delivering foreign aid. They provide technical expertise, financial resources, and a platform for international cooperation.
- How can recipient countries ensure they benefit from foreign aid?
- Recipient countries can maximize the benefits of foreign aid by aligning it with their national development priorities, promoting good governance, and ensuring effective coordination among government agencies and aid organizations.
- What are some examples of successful foreign aid projects?
- Successful foreign aid projects include initiatives that have significantly improved public health, increased access to education, stimulated economic growth, and strengthened democratic institutions. Examples include the eradication of smallpox, the fight against HIV/AIDS, and the expansion of access to clean water and sanitation.
- How does public opinion affect foreign aid policies?
- Public opinion can significantly influence foreign aid policies. Policymakers often consider public attitudes when determining the level and priorities of foreign aid programs.
- Where can I find more information on U.S. foreign aid?
- You can find more information on U.S. foreign aid from sources like ForeignAssistance.gov, USAID, the State Department, and reputable research organizations such as the Pew Research Center. Additionally, experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide deeper insights and analysis.
Do you feel overwhelmed by the complexities of foreign aid and its impact? At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges in navigating these intricate issues. Our team of over 100 world-renowned PhDs is dedicated to providing you with clear, actionable advice tailored to your specific needs. Whether you’re seeking to understand global economics, policy implications, or humanitarian efforts, our experts are here to guide you. Don’t navigate these complexities alone; reach out to us today for a consultation and gain the insights you need to make informed decisions. Contact us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp +1 (310) 555-1212, or visit our website at how.edu.vn for personalized support.

