Navigating the world of alcoholic beverages requires understanding the varying alcohol content in different drinks, and at HOW.EDU.VN, we’re here to provide clarity. Knowing “how much alcohol is in an ounce” is crucial for making informed decisions about your health and consumption habits. This guide breaks down alcohol content in various drinks and offers expert insights for responsible drinking. Understanding alcohol by volume, standard drink sizes, and the impact of different beverages can empower you to consume alcohol safely and responsibly.
1. Understanding Alcohol Content: What is Alcohol by Volume (ABV)?
Alcohol by Volume (ABV) is the standard measure of how much alcohol is contained in an alcoholic beverage. It’s expressed as a percentage of the total volume. For example, a beer with 5% ABV contains 5% pure alcohol. This figure is essential for understanding the potency of what you’re drinking. According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), knowing the ABV helps individuals track their alcohol consumption more accurately.
1.1. ABV in Different Beverages
The ABV varies significantly across different types of alcoholic beverages. Here’s a quick overview:
- Beer: Generally ranges from 4% to 10% ABV.
- Wine: Typically falls between 11% and 14% ABV.
- Spirits (Liquor): Commonly ranges from 40% to 50% ABV (80 to 100 proof).
Understanding these ranges allows you to estimate the alcohol content in your drink, but always check the label for precise information.
1.2. How ABV Affects Your Body
The higher the ABV, the more alcohol you are consuming per ounce. This directly impacts your blood alcohol concentration (BAC) and, consequently, your level of intoxication. Higher ABV drinks can lead to faster intoxication and increased risk of alcohol-related harm.
2. What is a Standard Drink? Defining “Ounce” in Alcohol Consumption
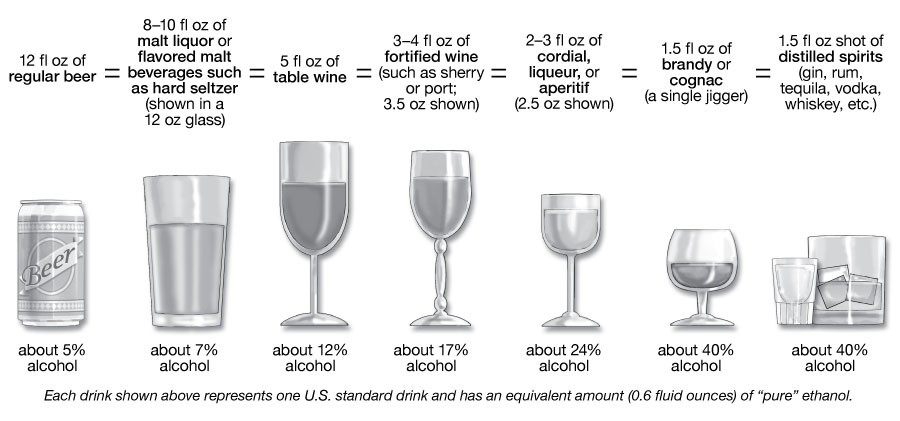
In the United States, a “standard drink” contains approximately 14 grams (0.6 fluid ounces) of pure alcohol. This measurement is used to help people understand and regulate their alcohol consumption. However, it’s essential to note that standard drink sizes don’t always align with typical serving sizes.
2.1. Standard Drink Equivalents
Here are some common examples of what constitutes one standard drink:
- Beer: 12 fluid ounces (355 ml) of regular beer with 5% ABV
- Wine: 5 fluid ounces (148 ml) of wine with 12% ABV
- Distilled Spirits (Liquor): 1.5 fluid ounces (44 ml) of spirits with 40% ABV
These equivalents help you gauge how much alcohol you’re consuming, regardless of the type of beverage.
2.2. Why Standard Drinks Matter
Understanding standard drinks is vital for several reasons:
- Health Guidelines: Health organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provide guidelines based on standard drink measurements.
- Responsible Drinking: Knowing standard drink sizes helps you stay within recommended limits.
- Legal Implications: Blood alcohol concentration (BAC) limits for driving are often based on standard drink equivalents.
Following standard drink guidelines can help you drink responsibly and minimize health risks.
3. Calculating Alcohol Content: Ounces and Fluid Ounces Explained
Understanding the difference between “ounces” and “fluid ounces” is essential when calculating alcohol content. A fluid ounce is a unit of volume, while an ounce is a unit of weight. In the context of liquids, we typically use fluid ounces (fl oz).
3.1. Converting Alcohol Content to Fluid Ounces
To calculate the amount of pure alcohol in a drink, you need to consider both the volume of the drink and its ABV. Here’s the formula:
Alcohol Content (fl oz) = Drink Volume (fl oz) x (ABV / 100)
For example, let’s calculate the alcohol content in a 12-fluid-ounce beer with 5% ABV:
Alcohol Content = 12 fl oz x (5 / 100) = 0.6 fl oz
This confirms that a 12-ounce beer with 5% ABV contains 0.6 fluid ounces of pure alcohol, which is one standard drink.
3.2. Examples of Alcohol Content in Various Drinks
Let’s explore a few more examples to illustrate how to calculate alcohol content:
-
8 fl oz Glass of Wine (12% ABV):
Alcohol Content = 8 fl oz x (12 / 100) = 0.96 fl oz
This is more than one standard drink. -
1.5 fl oz Shot of Whiskey (40% ABV):
Alcohol Content = 1.5 fl oz x (40 / 100) = 0.6 fl oz
This is one standard drink. -
20 fl oz Craft Beer (8% ABV):
Alcohol Content = 20 fl oz x (8 / 100) = 1.6 fl oz
This is more than two and a half standard drinks.
These calculations highlight how different drink sizes and ABVs can significantly impact your alcohol intake.
4. Variations in Alcohol Content: Craft Beers, Wines, and Spirits
Not all alcoholic beverages are created equal. Craft beers, wines, and spirits can have considerable variations in alcohol content, making it crucial to pay attention to the ABV listed on the label.
4.1. Craft Beers vs. Regular Beers
Craft beers often have a higher ABV than regular beers. While a typical beer might have around 5% ABV, craft beers can range from 6% to over 10%. This means that a single pint of craft beer could contain more than one standard drink.
4.2. Wine Varieties
Wine ABV can vary depending on the type and brand. Most wines fall within the 11% to 14% ABV range, but some fortified wines, like sherry or port, can have ABVs as high as 20%. Always check the label to understand the alcohol content of your wine.
4.3. Differences in Spirits
Spirits like vodka, gin, whiskey, and rum typically have an ABV of 40% (80 proof). However, some higher-proof spirits can reach 50% ABV or more. Knowing the proof and ABV of the spirits you consume is essential for accurate tracking.
5. The Impact of Different Beverages on Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC)
Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) is the percentage of alcohol in your bloodstream. It’s affected by several factors, including the amount of alcohol consumed, your body weight, gender, and metabolism.
5.1. How BAC Works
When you drink alcohol, it’s absorbed into your bloodstream through the stomach and small intestine. The liver metabolizes alcohol, but it can only process a certain amount per hour. The rest remains in your bloodstream, increasing your BAC.
5.2. Factors Affecting BAC
- Amount of Alcohol: The more alcohol you consume, the higher your BAC.
- Body Weight: People with lower body weights typically reach higher BAC levels faster.
- Gender: Women tend to have higher BAC levels than men due to differences in body composition and metabolism.
- Metabolism: Metabolic rate varies from person to person, affecting how quickly alcohol is processed.
- Food Intake: Eating before or while drinking can slow down alcohol absorption and lower BAC.
5.3. BAC Levels and Effects
Different BAC levels can lead to various effects:
- 0.02%: Mild relaxation and altered mood.
- 0.05%: Impaired judgment and coordination.
- 0.08%: Legal limit for driving in many countries; significant impairment of motor skills.
- 0.10%: Clear deterioration of reaction time and control.
- 0.20%: Confusion, disorientation, and potential loss of consciousness.
- 0.30%: Severe impairment, loss of consciousness, and risk of alcohol poisoning.
- 0.40%: Potentially fatal due to respiratory depression.
Understanding these levels can help you monitor your consumption and avoid dangerous situations.
6. Health Guidelines: Recommended Alcohol Consumption Limits
Health organizations provide guidelines for moderate alcohol consumption to minimize health risks. These guidelines are typically based on standard drink measurements.
6.1. CDC Recommendations
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends the following limits for adults of legal drinking age:
- Men: Up to 2 standard drinks per day.
- Women: Up to 1 standard drink per day.
These recommendations are intended for those who choose to drink and are not a suggestion to start drinking.
6.2. NIH Guidelines
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) echoes similar recommendations, emphasizing that moderation is key. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to numerous health problems, including liver disease, heart problems, and certain types of cancer.
6.3. Considerations for Different Individuals
Certain individuals should avoid alcohol altogether, including:
- Pregnant women
- Individuals with certain medical conditions
- People taking medications that interact with alcohol
- Those under the legal drinking age
If you have any concerns about your alcohol consumption, consult with a healthcare professional.
7. Tools and Resources: Measuring and Tracking Alcohol Intake
Several tools and resources can help you measure and track your alcohol intake, making it easier to stay within recommended limits.
7.1. Drink Calculators
Online drink calculators allow you to input the type and amount of alcohol you’ve consumed to estimate your BAC. These tools can provide a rough estimate, but remember that individual factors can affect actual BAC levels.
7.2. Mobile Apps
Several mobile apps are designed to help you track your alcohol consumption. These apps allow you to log your drinks, calculate your BAC, and set reminders to stay within your limits.
7.3. Standard Drink Measuring Tools
Using standard drink measuring tools, such as jiggers and marked glassware, can help you pour accurate servings. This is particularly useful when making cocktails or serving wine.
7.4. Printable Guides and Posters
Printable guides and posters that illustrate standard drink sizes can serve as a handy reference at home or in social settings. These resources are often available from health organizations and government agencies.
8. Responsible Drinking Tips: Staying Safe and Informed
Practicing responsible drinking is essential for protecting your health and well-being. Here are some tips to help you stay safe and informed:
8.1. Know Your Limits
Understand your personal tolerance and stick to recommended limits. Factors like body weight, gender, and metabolism can influence how alcohol affects you.
8.2. Pace Yourself
Avoid drinking too quickly. Savor your drinks and allow your body time to process the alcohol.
8.3. Eat While Drinking
Eating before or while drinking can slow down alcohol absorption and lower your BAC.
8.4. Stay Hydrated
Alternate alcoholic beverages with water to stay hydrated. Alcohol can dehydrate the body, leading to increased hangover symptoms.
8.5. Avoid Mixing Alcohol with Medications
Mixing alcohol with certain medications can have dangerous interactions. Consult with your doctor or pharmacist if you’re unsure about potential risks.
8.6. Never Drink and Drive
Driving under the influence of alcohol is illegal and incredibly dangerous. Always designate a sober driver, use public transportation, or call a taxi or rideshare service.
8.7. Be Aware of Peer Pressure
Don’t feel pressured to drink more than you’re comfortable with. It’s okay to say no or to switch to non-alcoholic beverages.
9. Debunking Common Myths About Alcohol Consumption
Many myths surround alcohol consumption. Understanding the truth can help you make informed decisions and avoid potential harm.
9.1. Myth: Drinking Coffee Will Sober You Up
Fact: Coffee can make you feel more alert, but it doesn’t reduce your BAC. The only thing that lowers BAC is time.
9.2. Myth: You Can “Sweat Out” Alcohol
Fact: While some alcohol may be eliminated through sweat, it’s a minimal amount. The liver primarily metabolizes alcohol, and this process takes time.
9.3. Myth: Tolerance Means You Can Drink More Safely
Fact: Developing a tolerance to alcohol means you need to consume more to achieve the same effects. It doesn’t mean your body is better equipped to handle alcohol’s harmful effects.
9.4. Myth: Mixing Drinks Makes You More Intoxicated
Fact: The order in which you consume different types of alcohol doesn’t affect your BAC. The total amount of alcohol you consume is what matters.
9.5. Myth: Eating a Large Meal Will Prevent Intoxication
Fact: Eating a large meal can slow down alcohol absorption, but it won’t prevent intoxication entirely. Alcohol will still enter your bloodstream, just at a slower rate.
10. Addressing Alcohol-Related Concerns: Seeking Professional Advice
If you have concerns about your alcohol consumption or the drinking habits of someone you know, seeking professional advice is essential.
10.1. Signs of Problem Drinking
Recognizing the signs of problem drinking is the first step toward getting help. Some common signs include:
- Drinking more than intended
- Experiencing withdrawal symptoms when not drinking
- Neglecting responsibilities due to alcohol
- Continuing to drink despite negative consequences
- Hiding alcohol consumption from others
10.2. Resources for Help
Several resources are available to provide support and treatment for alcohol-related issues:
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA): Offers information and resources on alcohol-related health issues.
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA): Provides a helpline and treatment locator.
- Alcoholics Anonymous (AA): Offers peer support and meetings for individuals with alcohol use disorders.
- Healthcare Professionals: Doctors, therapists, and counselors can provide personalized advice and treatment options.
10.3. Talking to a Healthcare Provider
If you’re concerned about your alcohol consumption, talking to a healthcare provider is a good idea. They can assess your drinking habits, provide guidance, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
11. The Role of Education: Promoting Responsible Alcohol Consumption
Education plays a crucial role in promoting responsible alcohol consumption and reducing alcohol-related harm.
11.1. School-Based Programs
School-based programs can educate young people about the risks of alcohol consumption and provide them with the skills to make informed decisions.
11.2. Community Initiatives
Community initiatives can raise awareness about responsible drinking and provide resources for individuals and families affected by alcohol-related problems.
11.3. Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns can disseminate information about alcohol consumption guidelines, the risks of excessive drinking, and strategies for responsible drinking.
11.4. Workplace Programs
Workplace programs can educate employees about the risks of alcohol consumption and provide support for those struggling with alcohol-related issues.
12. Understanding Alcohol and Its Impact: Expert Insights from HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing expert insights and resources to help you understand alcohol and its impact on your health and well-being.
12.1. Expert Consultations
Our team of expert consultants can provide personalized advice and guidance on alcohol-related issues. Whether you’re concerned about your own drinking habits or the drinking habits of someone you know, we’re here to help.
12.2. Educational Resources
We offer a wide range of educational resources, including articles, guides, and videos, to help you learn more about alcohol and its effects.
12.3. Support and Guidance
We provide support and guidance to individuals and families affected by alcohol-related problems. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge and resources you need to make informed decisions and live a healthy life.
13. Current Research and Studies on Alcohol Consumption
Ongoing research continues to shape our understanding of alcohol consumption and its effects. Staying informed about the latest findings can help you make the most informed decisions about your health.
13.1. Recent Findings
Recent studies have explored the long-term effects of moderate alcohol consumption on heart health, brain function, and cancer risk. These studies provide valuable insights into the complex relationship between alcohol and health.
13.2. University Research
Universities around the world are conducting research on alcohol consumption, including studies on the effectiveness of interventions for alcohol use disorders and the impact of alcohol on different populations. For example, a study by the University of California, San Francisco, in 2024, found that targeted interventions can significantly reduce alcohol-related hospitalizations among older adults.
13.3. Government Initiatives
Government agencies, such as the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), fund and conduct research on alcohol consumption to inform public health policies and guidelines.
14. Overcoming Challenges in Understanding Alcohol Content
Understanding alcohol content can be challenging due to variations in serving sizes, ABV levels, and individual factors. However, with the right knowledge and tools, you can overcome these challenges and make informed decisions about your alcohol consumption.
14.1. Decoding Labels
Learning to decode alcohol labels is essential for understanding the ABV and serving size of your drink. Pay attention to the fine print and be aware that serving sizes may not always match standard drink equivalents.
14.2. Estimating Accurately
Estimating alcohol content accurately requires practice and attention to detail. Use measuring tools, drink calculators, and standard drink guides to improve your accuracy.
14.3. Personalized Approaches
Recognize that everyone’s body processes alcohol differently. Pay attention to how alcohol affects you personally and adjust your consumption accordingly.
15. How to Get Expert Advice on Alcohol Consumption at HOW.EDU.VN
If you’re seeking personalized advice on alcohol consumption, HOW.EDU.VN offers a unique opportunity to connect with leading experts. Our team of over 100 Ph.D.s is ready to provide tailored guidance to address your specific concerns.
15.1. Connecting with Ph.D. Experts
HOW.EDU.VN provides a platform where you can directly connect with Ph.D. experts in various fields, including health, nutrition, and addiction. These experts can offer evidence-based advice and support to help you make informed decisions about your alcohol consumption.
15.2. Personalized Consultations
Through our platform, you can schedule personalized consultations with experts who can assess your drinking habits, provide tailored recommendations, and address any concerns you may have.
15.3. Comprehensive Support
Our experts offer comprehensive support to help you understand the impact of alcohol on your health, develop strategies for responsible drinking, and access resources for help if needed.
16. The Future of Alcohol Consumption: Trends and Predictions
As societal attitudes toward alcohol evolve, it’s important to stay informed about emerging trends and predictions in the world of alcohol consumption.
16.1. Changing Attitudes
Changing attitudes toward alcohol are driving the growth of non-alcoholic and low-alcohol beverages. Many people are seeking alternatives that allow them to socialize without the risks associated with alcohol consumption.
16.2. Technological Innovations
Technological innovations are transforming the alcohol industry, from new methods of production to innovative packaging and delivery systems. These innovations are making it easier than ever to access and enjoy alcoholic beverages.
16.3. Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes are shaping the landscape of alcohol consumption, from stricter laws on drunk driving to new regulations on the sale and marketing of alcoholic beverages.
17. Alcohol and Mental Health: Understanding the Connection
The relationship between alcohol and mental health is complex and multifaceted. Understanding this connection is essential for promoting overall well-being.
17.1. Alcohol as a Depressant
Alcohol is a central nervous system depressant, meaning it can slow down brain function and alter mood. While some people may experience temporary relaxation or euphoria when drinking alcohol, these effects are often followed by feelings of sadness, anxiety, or depression.
17.2. Alcohol and Anxiety
Alcohol can worsen anxiety symptoms, particularly during withdrawal. Many people who use alcohol to cope with anxiety find that their symptoms intensify when they stop drinking.
17.3. Alcohol and Depression
Alcohol can contribute to depression and make existing symptoms worse. Chronic alcohol consumption can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to changes in mood and behavior.
17.4. Seeking Help for Mental Health Concerns
If you’re struggling with mental health concerns, it’s important to seek help from a qualified healthcare professional. They can assess your symptoms, provide a diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
18. Navigating Social Situations: Drinking Responsibly in Company
Navigating social situations that involve alcohol can be challenging, but it’s important to prioritize your health and well-being.
18.1. Setting Boundaries
Setting boundaries is essential for drinking responsibly in company. Know your limits and don’t feel pressured to drink more than you’re comfortable with.
18.2. Offering Alternatives
Offering non-alcoholic alternatives can help create a more inclusive and supportive social environment. Consider bringing your own non-alcoholic beverages to parties or suggesting alcohol-free activities.
18.3. Supporting Others
Supporting others in their efforts to drink responsibly is a valuable way to promote a culture of health and well-being. Offer encouragement and support to those who are choosing to abstain or drink in moderation.
19. Debunking Myths: Alcohol and Weight Gain
Many myths surround alcohol and weight gain. Understanding the truth can help you make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle.
19.1. Alcohol as Empty Calories
Alcohol contains calories but provides little to no nutritional value. These “empty calories” can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess.
19.2. Alcohol and Metabolism
Alcohol can interfere with metabolism, making it harder for your body to burn fat. When you drink alcohol, your body prioritizes metabolizing the alcohol over other sources of energy, such as fat and carbohydrates.
19.3. Making Informed Choices
Making informed choices about alcohol consumption can help you maintain a healthy weight. Choose lower-calorie alcoholic beverages, drink in moderation, and avoid sugary mixers.
20. Conclusion: Empowering Informed Choices About Alcohol Consumption
Understanding “how much alcohol is in an ounce” is critical for making informed choices about your consumption. By grasping ABV, standard drink sizes, and the impact of different beverages, you can drink responsibly and protect your health. For personalized guidance and expert advice, reach out to HOW.EDU.VN, where our team of Ph.D. experts is ready to assist you. Remember, informed choices lead to a healthier, safer lifestyle.
Are you seeking expert guidance on responsible alcohol consumption? Do you have questions about how alcohol affects your health? Contact HOW.EDU.VN today for personalized advice from our team of Ph.D. experts. We’re here to provide the support and resources you need to make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
Contact us:
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
 Alcohol Content Comparison Chart
Alcohol Content Comparison Chart
FAQ: Common Questions About Alcohol Consumption
1. What is a standard drink?
A standard drink contains 0.6 fluid ounces or 14 grams of pure alcohol. This is equivalent to 12 ounces of beer (5% ABV), 5 ounces of wine (12% ABV), or 1.5 ounces of distilled spirits (40% ABV).
2. How does alcohol by volume (ABV) affect intoxication?
The higher the ABV, the more alcohol you are consuming per ounce, which directly impacts your blood alcohol concentration (BAC) and level of intoxication.
3. How can I calculate the alcohol content in a drink?
Use the formula: Alcohol Content (fl oz) = Drink Volume (fl oz) x (ABV / 100).
4. What are the recommended alcohol consumption limits?
The CDC recommends up to 2 standard drinks per day for men and up to 1 standard drink per day for women.
5. Can coffee sober me up?
No, coffee can make you feel more alert, but it doesn’t reduce your BAC. The only thing that lowers BAC is time.
6. Is it safe to mix alcohol with medications?
Mixing alcohol with certain medications can have dangerous interactions. Consult with your doctor or pharmacist if you’re unsure about potential risks.
7. How does food affect alcohol absorption?
Eating before or while drinking can slow down alcohol absorption and lower your BAC.
8. What are the signs of problem drinking?
Signs include drinking more than intended, experiencing withdrawal symptoms, neglecting responsibilities, and continuing to drink despite negative consequences.
9. Where can I find help for alcohol-related issues?
Resources include the NIAAA, SAMHSA, Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), and healthcare professionals.
10. How can HOW.EDU.VN help with alcohol consumption concerns?
how.edu.vn offers personalized consultations with Ph.D. experts who can provide tailored advice, assess your drinking habits, and offer comprehensive support.

