Accurate measurements are the cornerstone of consistent and delectable dishes, whether you’re a seasoned chef or a budding home cook. If you’re wondering, “How Much Is 3 Tbsp?”, HOW.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive guide to mastering kitchen conversions, ensuring precision in your culinary endeavors. Understanding these fundamental conversions optimizes recipes, minimizes ingredient waste, and elevates the overall quality of your cooking and baking. For expert advice tailored to your specific needs, connect with our seasoned Ph.D. experts for personalized guidance.
1. Understanding Tablespoons
A tablespoon (Tbsp, tbsp, Tb, or T) is a standard unit of volume commonly employed in cooking for measuring various ingredients. These include spices, sugars, oils, and liquid condiments.
- 1 Tbsp = 1/16 cup
- 1 Tbsp = 3 teaspoons (tsp)
- 1 Tbsp = 15 milliliters (ml)
- 1 Tbsp = 1/2 fluid ounce (fl oz)
2. Understanding Cups
A cup (C or c) is a unit of volume used to measure larger quantities of ingredients, such as flour, sugar, and liquids.
- 1 cup = 16 Tbsp
- 1 cup = 48 tsp
- 1 cup = 237 ml
- 1 cup = 8 fl oz
3. US Standard, US Legal, and Metric Cups
3.1. US Standard (Customary) Cup
The US customary cup, predominantly used in the United States for recipes, equals 8 US fluid ounces or roughly 236.59 milliliters.
3.2. US Legal Cup
The US legal cup, standardized at 240 milliliters, is primarily for nutrition labeling by entities like the FDA and USDA.
3.3. Metric Cup
The metric cup, common in countries using the metric system, is defined as 250 milliliters.
It’s vital to recognize the system you’re employing, as variations in cup volumes can significantly affect recipe outcomes, especially when scaling recipes.
1 US Cup = 16 US tablespoons (tbsp)
1 US Cup = 15.77 metric tablespoons
4. Wet vs. Dry Measurement
The distinction between wet and dry measurements in tablespoons and cups is a point of accuracy rather than a change in the inherent unit. A tablespoon remains a tablespoon, and a cup, a cup, irrespective of whether you’re measuring liquids or dry ingredients.
5. How Much Is 3 Tbsp In Cups?
Three tablespoons is equal to 3/16 of a cup. This fundamental conversion plays a pivotal role in scaling recipes, ensuring accurate flavor profiles, and achieving culinary excellence. Understanding and applying this conversion streamlines the cooking process and reduces errors.
- 3 tablespoons (Tbsp) = 3/16 cup (c)
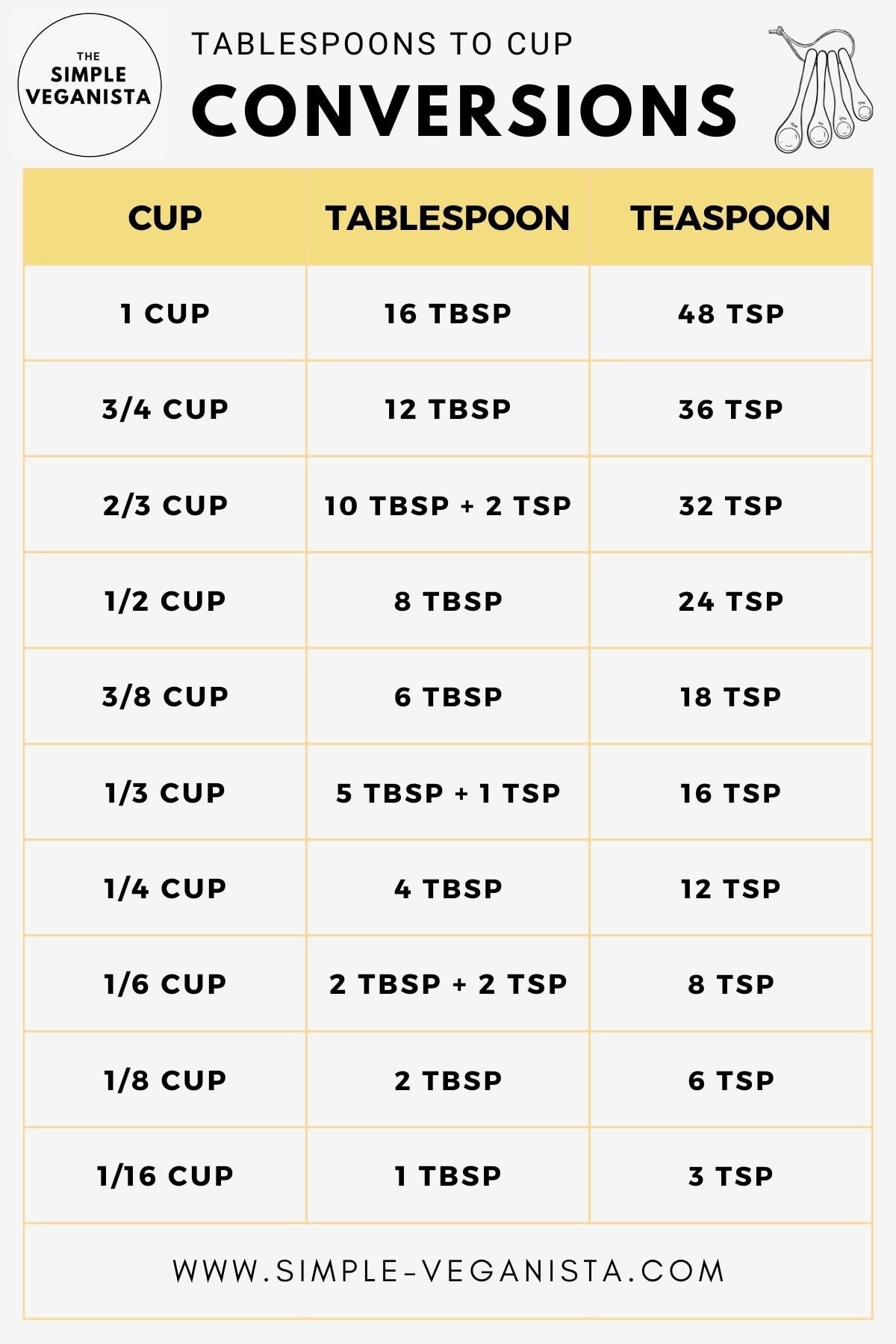
6. Tablespoon-to-Cup Conversions
- 1 tablespoon (Tbsp) = 1/16 cup (c)
- 2 tablespoons (Tbsp) = 1/8 cup (c)
- 4 tablespoons (Tbsp) = 1/4 cup (c)
- 5 tablespoons (Tbsp) + 1 teaspoon (tsp) = 1/3 cup (c)
- 6 tablespoons (Tbsp) = 3/8 cup (c)
- 8 tablespoons (Tbsp) = 1/2 cup (c)
- 10 tablespoons (Tbsp) + 2 teaspoons (tsp) = 2/3 cup (c)
- 12 tablespoons (Tbsp) = 3/4 cup (c)
- 16 tablespoons (Tbsp) = 1 cup (c)
7. Tablespoon to Cup Conversion Table
| Tablespoons | Cups |
|---|---|
| 1 tbsp | 1/16 c |
| 2 tbsp | 1/8 c |
| 3 tbsp | 3/16 c |
| 4 tbsp | 1/4 c |
| 5 tbsp | 5/16 c |
| 6 tbsp | 3/8 c |
| 7 tbsp | 7/16 c |
| 8 tbsp | 1/2 c |
| 9 tbsp | 9/16 c |
| 10 tbsp | 5/8 c |
| 11 tbsp | 11/16 c |
| 12 tbsp | 3/4 c |
| 13 tbsp | 13/16 c |
| 14 tbsp | 7/8 c |
| 15 tbsp | 15/16 c |
| 16 tbsp | 1 c |

8. Mathematical Formula
8.1. Converting Tablespoons to Cups
Divide the number of tablespoons by 16 to convert to cups.
Cups = Tablespoons ➗ 16
8.2. Converting Cups to Tablespoons
Multiply the number of cups by 16 to convert to tablespoons.
Tablespoons = Cups ✖️ 16
8.3. Converting Other Measurement Units
- Teaspoons to tablespoons: 1 tablespoon = 3 teaspoons
- Tablespoons to fluid ounces: 1 fluid ounce = 2 tablespoons
- Cups to pints: 2 cups = 1 pint
- Cups to quarts: 4 cups = 1 quart
- Cups to gallons: 16 cups = 1 gallon
- Fluid ounces to cups: 8 fluid ounces = 1 cup
- US customary to metric: 1 cup ≈ 240 ml
9. Understanding Basic Measurement Units
Familiarize yourself with common units of measurement for cooking success.
- Teaspoons (tsp): Smallest volume unit for spices, extracts, and leavening agents.
- Tablespoons (Tbsp): Three times larger than a teaspoon; ideal for butter, oil, and sugar.
- Cups (c): Larger volume measurements for ingredients like flour, milk, and vegetables.
- Fluid ounces (fl oz): Liquid volumes like water, juice, and syrup.
- Milliliters (ml) and liters (L): Metric units for volume outside the US.
- Volume measurements: The space an ingredient occupies.
- Weight measurements: Refer to an ingredient’s mass (e.g., grams or ounces).
10. Tips for Accurate Measuring
10.1. Selecting the Right Measuring Tools
- Measuring spoons: Use for small amounts like spices and extracts.
- Measuring cups: Ideal for dry ingredients like flour and sugar.
- Liquid measuring cups: Perfect for liquids with a spout and handle for easy pouring.
- Digital kitchen scale: Provides precise measurements by weight.
10.2. Measuring Dry Ingredients
Scoop the dry ingredient into the measuring spoon and level off with a straight-edged utensil for consistency.
10.3. Measuring Liquids
Use liquid measuring cups to measure liquids at eye level. Place the cup on a flat surface to ensure accuracy.
10.4. Adjusting Measurements for Altitude
High-altitude baking and cooking may require adjustments to ingredient measurements, as well as oven temperature and baking time. Consult high-altitude cooking resources for guidance.
11. Common Measurement Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Using the wrong tools: Invest in quality measuring spoons, cups, and a digital scale.
- Over-packing or under-packing dry ingredients: Spoon ingredients into measuring cups and level off the top.
- Not leveling off ingredients: Always use a straight-edged utensil.
- Measuring liquids inaccurately: Measure liquids at eye level on a flat surface.
12. Why Accurate Measurements Are Essential
12.1. Consistent Flavor Profiles
Accurate measurements ensure that the delicate balance of flavors in a recipe is maintained, leading to consistent and enjoyable culinary outcomes. Whether it’s the subtle sweetness of a dessert or the savory depth of a sauce, precision matters.
12.2. Optimal Texture
Measurements significantly impact the texture of baked goods and other dishes. Too much or too little of a particular ingredient can result in a dry, crumbly cake or a watery sauce.
12.3. Recipe Replication
When measurements are exact, replicating a successful dish becomes straightforward. This is particularly important for those who enjoy sharing their culinary creations with others.
12.4. Waste Reduction
By accurately measuring ingredients, you reduce the likelihood of errors that lead to wasted food and ingredients, making your kitchen more efficient and cost-effective.
12.5. Professional Results
Whether you’re a home cook or a professional chef, accuracy in measurement is a hallmark of culinary expertise. It reflects a commitment to quality and attention to detail.
13. Real-World Applications of Measurement Accuracy
13.1. Baking
In baking, precise measurements are non-negotiable. The ratio of flour to liquid, sugar to fat, and leavening agents to other ingredients determines the final product’s rise, texture, and taste.
13.2. Sauces and Dressings
Creating the perfect sauce or salad dressing requires careful balancing of ingredients. Too much acid, salt, or sweetness can throw off the entire dish.
13.3. Cocktails
Bartenders rely on precise measurements to craft cocktails that are both delicious and consistent. A slight deviation can alter the flavor profile and overall experience.
13.4. Medicinal Preparations
In traditional and modern medicine, accurate measurements are vital for preparing herbal remedies and pharmaceutical compounds.
13.5. Industrial Processes
Industries such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals depend on precise measurements to ensure product quality and safety.
14. Advanced Measurement Techniques
14.1. Using a Kitchen Scale
A digital kitchen scale provides the most accurate measurements, especially for dry ingredients. It eliminates the variability associated with measuring cups and spoons.
14.2. Sifting Flour
Sifting flour before measuring removes lumps and aerates the flour, resulting in a more accurate measurement.
14.3. Packing Brown Sugar
When measuring brown sugar, pack it firmly into the measuring cup to ensure an accurate amount.
14.4. Measuring Sticky Ingredients
Coat measuring cups or spoons with a thin layer of oil or cooking spray before measuring sticky ingredients like honey or molasses to prevent them from sticking.
15. The Importance of Continual Learning and Improvement
15.1. Stay Updated
Culinary techniques and measurement standards evolve over time. Stay updated with the latest information through cookbooks, cooking blogs, and professional culinary resources.
15.2. Practice Regularly
The more you practice measuring ingredients accurately, the more natural it will become. Repetition builds confidence and skill.
15.3. Seek Expert Advice
Don’t hesitate to consult professional chefs or culinary experts for guidance on specific measurement challenges.
15.4. Embrace Technology
Utilize online measurement converters and culinary apps to streamline the measurement process and reduce errors.
16. FAQ’s
16.1. How many tablespoons are in a cup of butter?
A cup of butter contains 16 tablespoons. Butter is usually sold in 1/2 cup (8 tablespoons) or 1 cup (16 tablespoons) sticks.
16.2. How many tablespoons are in a cup of sugar?
There are 16 tablespoons in a cup of sugar, regardless of the type (cane sugar, powdered sugar, or coconut sugar).
16.3. How many tablespoons are in a cup of flour?
There are 16 tablespoons in a cup of flour. This is the same for any type of flour.
16.4. How many tablespoons in a cup of coffee?
A standard measuring cup holds 8 fluid ounces or 16 tablespoons, but a typical coffee cup or mug may hold between 6 to 12 fluid ounces (12 to 24 tablespoons).
16.5. How many tbsp in a cup?
There are 16 tbsp in a cup, a standard unit of measurement for volume.
16.6. How many tablespoons are in a cup and a half?
In a cup and a half (1.5 cups), there are 24 tablespoons.
16.7. How many tablespoons in a cup of brown sugar?
There are 16 tablespoons in a cup of brown sugar. Pack the brown sugar firmly into the measuring cup to ensure accurate measurement.
16.8. How many tablespoons are in a half cup?
In a half cup (1/2 cup), there are 8 tablespoons.
16.9. How many tablespoons are in a quarter cup?
There are 4 tablespoons in a quarter cup.
17. Food For Thought
Mastering the conversion between tablespoons and cups is essential for successful cooking and baking. Ensure your culinary creations turn out delicious and consistent every time.
18. Additional Tips and Tricks
18.1. Use Reliable Measurement Tools
Invest in high-quality measuring cups and spoons that are clearly marked and durable. Replace them if they become warped or damaged.
18.2. Double-Check Measurements
Before adding an ingredient, take a moment to double-check the measurement to avoid errors.
18.3. Keep a Conversion Chart Handy
Post a conversion chart in your kitchen for quick and easy reference.
18.4. Adjust Recipes Gradually
When scaling recipes, adjust the measurements gradually to ensure that the flavor and texture remain consistent.
18.5. Be Mindful of Ingredient Density
Different ingredients have different densities, so a cup of one ingredient may weigh more than a cup of another. Use weight measurements when possible for greater accuracy.
18.6. Practice Mindful Cooking
Pay attention to the details of the recipe and the measurements of the ingredients. This will help you develop a better understanding of how different ingredients interact and how to achieve the desired results.
18.7. Experiment with Confidence
Once you have a good understanding of measurement basics, feel free to experiment with recipes and create your own culinary masterpieces.
18.8. Learn from Mistakes
Everyone makes mistakes in the kitchen. When a recipe doesn’t turn out as expected, analyze what went wrong and learn from the experience.
18.9. Share Your Knowledge
Share your knowledge of measurement techniques and cooking tips with others. This will help to promote a culture of culinary excellence and inspire others to create delicious and consistent dishes.
18.10. Attend Cooking Classes
Consider taking cooking classes to learn more advanced techniques and refine your measurement skills.
19. The Role of Technology in Modern Measurement
19.1. Smart Kitchen Devices
Smart kitchen scales and measuring devices can automatically convert measurements and provide real-time feedback on accuracy.
19.2. Culinary Apps
Culinary apps offer a wealth of information, including measurement conversions, recipe scaling tools, and ingredient substitutions.
19.3. Online Resources
Online resources such as cooking blogs, forums, and video tutorials can provide valuable insights and tips on measurement techniques.
19.4. Virtual Cooking Classes
Virtual cooking classes allow you to learn from professional chefs and culinary experts from the comfort of your own home.
19.5. Social Media
Social media platforms can be a great source of inspiration and information for home cooks and professional chefs alike.
20. Future Trends in Culinary Measurement
20.1. Precision Cooking
Precision cooking techniques such as sous vide rely on precise temperature and measurement control to achieve consistent results.
20.2. Molecular Gastronomy
Molecular gastronomy explores the scientific principles behind cooking and utilizes precise measurements to create innovative and experimental dishes.
20.3. 3D Food Printing
3D food printing allows for the creation of customized dishes with precise nutritional content and ingredient ratios.
20.4. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is being used to develop culinary algorithms that can optimize recipes and provide personalized cooking recommendations.
20.5. Sustainable Cooking
Sustainable cooking practices emphasize the importance of reducing food waste and utilizing ingredients efficiently, which requires accurate measurement and portion control.
21. The Benefits of Consulting with Culinary Experts
21.1. Personalized Guidance
Culinary experts can provide personalized guidance and advice tailored to your specific needs and skill level.
21.2. Advanced Techniques
They can teach you advanced measurement techniques and cooking methods that are not commonly found in cookbooks or online resources.
21.3. Troubleshooting
They can help you troubleshoot cooking problems and identify the root causes of measurement errors.
21.4. Recipe Development
They can assist you in developing your own recipes and ensuring that the measurements are accurate and consistent.
21.5. Career Advancement
For aspiring chefs and culinary professionals, consulting with experts can provide valuable insights and networking opportunities that can help advance their careers.
22. Conclusion: Embrace Precision for Culinary Excellence
In conclusion, mastering the art of measurement is a lifelong journey that requires dedication, practice, and a willingness to learn from experts. Whether you’re a home cook or a professional chef, embracing precision in your culinary endeavors will lead to more consistent, delicious, and rewarding results.
Ready to elevate your culinary expertise? Contact the Ph.D. experts at HOW.EDU.VN today for personalized guidance and solutions to your culinary challenges. We offer unparalleled expertise and innovative solutions tailored to your unique needs.
Connect with us:
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Don’t let uncertainty hold you back. Trust how.edu.vn to guide you towards culinary excellence.
