Are you curious about the value of a 1944 steel penny? The value of a 1944 steel penny can range from hundreds to over a million dollars, contingent on its condition and mint mark. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights into the rare coin market, helping you understand the true worth of your collectible coins. Let’s dive into the details of these unique coins, exploring their history, characteristics, and current market value, ensuring you have all the information you need to assess your coin’s worth. Discover more about rare coin values, coin collecting, and numismatic valuation.
1. A Brief Overview of Wheat Pennies
Wheat pennies, designed by Victor David Brenner, were minted from 1909 to 1958. These coins are notable for being the first U.S. currency to feature a real historical figure, Abraham Lincoln, on the obverse side, with two stalks of wheat on the reverse. The initial idea to feature a historical figure was criticized by George Washington as too monarchical.
Initially, the new penny coin was designed to be minted starting in 1908 and was meant to be designed by sculptor Augustus Saint-Gaudens, but he passed away in 1907 before submitting a finalized design for the penny.
Some wheat pennies are called VDB pennies because they include Victor David Brenner’s initials. Wheat pennies were minted in Philadelphia, Denver, and San Francisco.
According to the 2020 version of A Guide Book of United States Coins, also known as the “Red Book,” more than 24 billion wheat pennies were minted in total. The variant with the highest mintage was the 1944 wheat penny minted by the Philadelphia Mint, of which 1.435 billion coins were minted.
2. What Determines the Value of a 1944 Penny?
The value of a 1944 penny varies significantly based on several factors, including its composition, mint location, and condition. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurately assessing the worth of your coin.
2.1. Metal Composition
Most 1944 pennies are made of gilding metal, which is 95% copper and 5% zinc and tin. However, the rare and highly valuable 1944 steel pennies are made of zinc-coated steel. This difference in metal is a primary factor in determining the coin’s value.
2.2. Mint Mark and Location
The mint mark indicates where the coin was produced. 1944 wheat pennies were minted in Philadelphia (no mint mark), Denver (D), and San Francisco (S). The scarcity of pennies from certain mints can increase their value.
2.3. Condition
The condition of a coin is a critical factor in determining its worth. Coins are graded on a scale, with “uncirculated” coins in pristine condition being the most valuable. Wear and tear, scratches, and other damage can significantly reduce a coin’s value. Coin collectors are willing to pay a decent chunk of change even for relatively unremarkable coins, provided they are in very good condition. Of course, uncirculated coins, which have next to no wear if stored properly, are usually worth the most.
2.4. Errors
Minting errors can also increase the value of a 1944 penny. Errors such as double die errors, missing mint marks, or off-center strikes can make a coin more desirable to collectors.
3. How Much Is A 1944 Penny Worth?
Here’s a breakdown of the approximate values for different 1944 pennies, reflecting their composition, mint location, and condition. This table provides a quick reference for understanding the potential value of your 1944 penny.
| Version | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Philadelphia Mint (no mint mark) | $0.06 – $6.05 |
| Denver Mint (D mint mark) | $0.06 – $4.80 |
| San Francisco Mint (S mint mark) | $0.12 – $4.80 |
| Steel Penny | $423,000 – $1,178,000 |
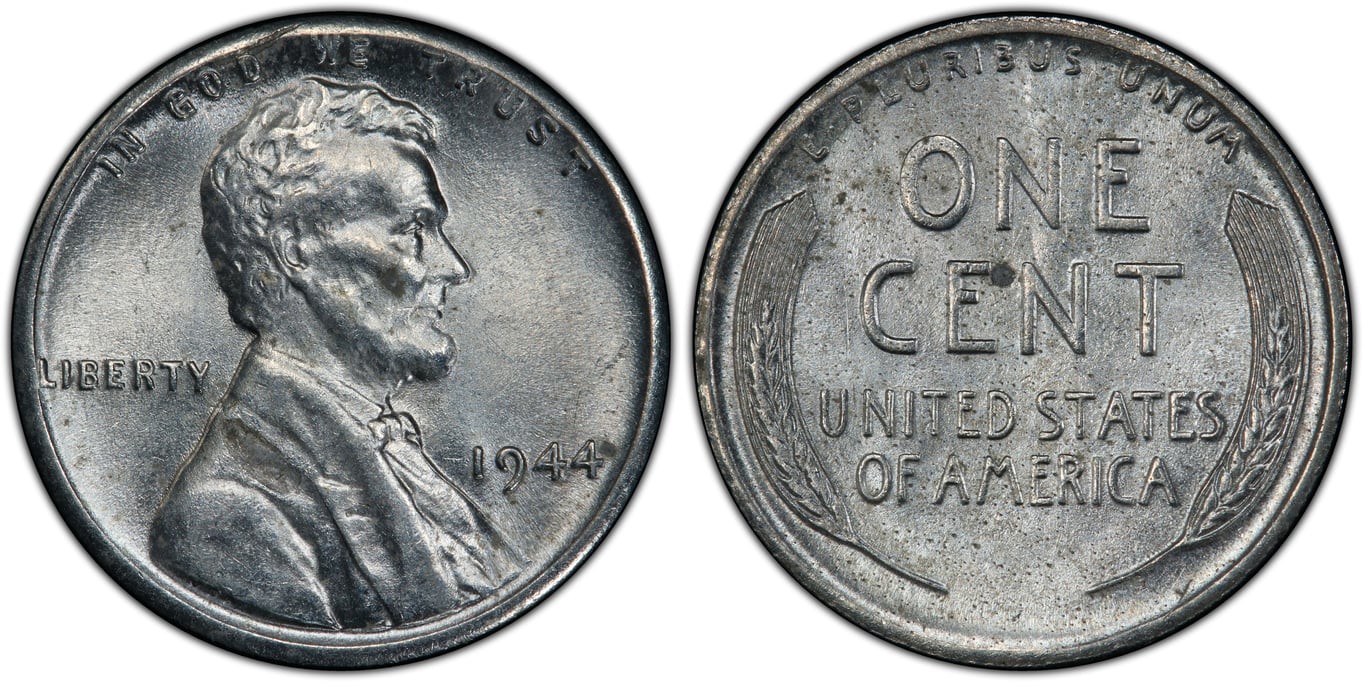
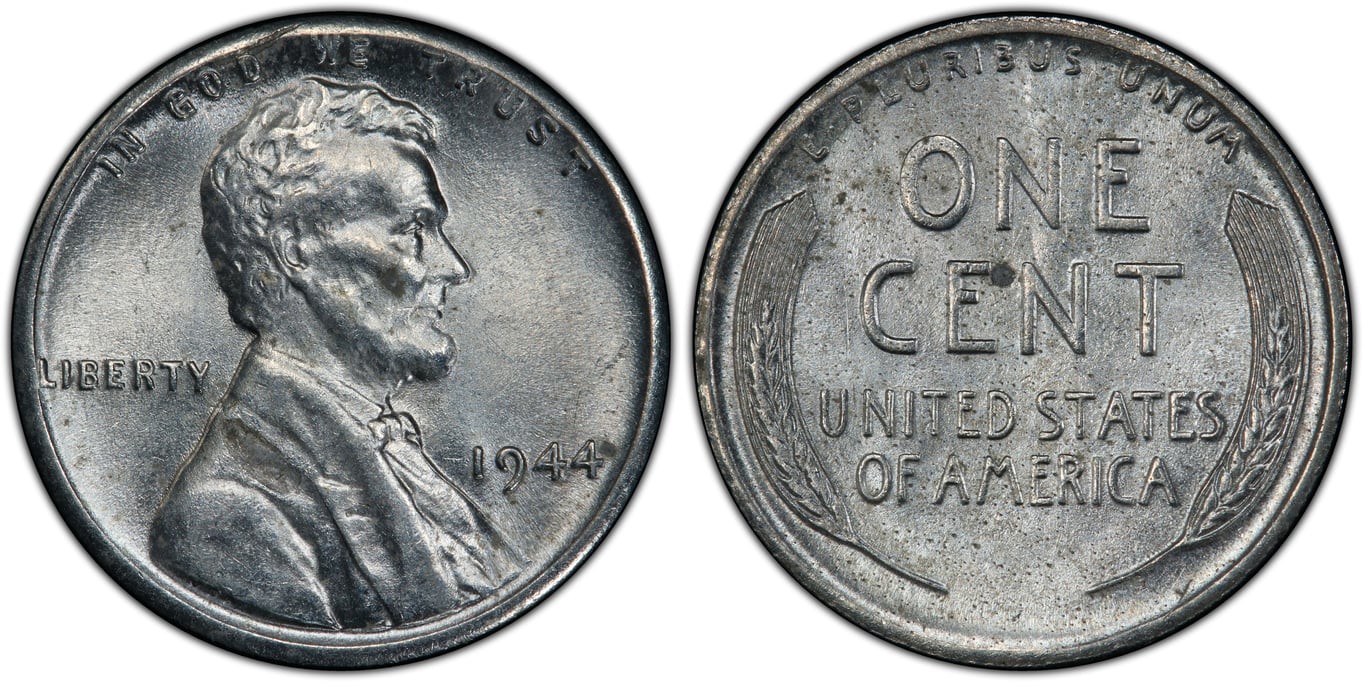
Source: USA Coin Book
4. The Exceptional Value of the 1944 Steel Penny
The 1944 steel penny stands out as an anomaly and a prized collectible. Its unique composition and the circumstances surrounding its creation make it one of the most sought-after coins in numismatics.
4.1. History and Background
During World War II, copper was a critical resource for the war effort. As a result, the U.S. Mint temporarily switched to producing steel pennies coated with zinc to conserve copper. However, by 1944, the Mint had reverted to using copper for pennies. The 1944 steel pennies were created by error, using leftover steel planchets from 1943.
4.2. Rarity and Demand
The 1944 steel penny is exceptionally rare, with estimates suggesting that only about 20 to 40 were ever minted. This rarity, combined with high demand from collectors, drives the price of these coins into the hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars.
According to USA Coin Book, which estimates that there were 40 steel pennies minted in 1944, 30 of them were minted in Philadelphia, 7 were minted in Denver (D mark), and 2 were minted in San Francisco (S mark). The steel pennies minted in Philadelphia have no mint mark, and steel pennies minted in Denver and San Francisco are worth more since they are even rarer than the ones minted in Philadelphia.
4.3. Identification
Identifying a 1944 steel penny is relatively straightforward. Unlike other 1944 pennies, which are made of gilding metal, steel pennies are made of zinc-coated steel. The easiest way to identify a steel penny is to test it with a magnet; steel pennies are magnetic, while copper pennies are not.
4.4. Current Market Value
The value of a 1944 steel penny can vary significantly based on its condition. Uncirculated or near-uncirculated examples can fetch prices ranging from $423,000 to over $1 million. Even circulated examples can be worth a substantial amount, making them highly sought after by collectors.
At the moment of writing, the Professional Coin Grading Service (PCGS) is currently hosting a bid on a 1944-S 1C Steel (Regular Strike). The penny’s listing price is a whopping $475,000. Meanwhile, the Uncirculated (MS-63) mint condition version of the penny is currently worth a staggering $1,178,000.
5. Common Errors That Increase Penny Value
While the 1944 steel penny is the most valuable, other 1944 pennies with specific errors can also be worth more than their face value. Recognizing these errors can help you identify potentially valuable coins.
5.1. Double Die Error
A double die error occurs when the coin die (the tool used to strike the coin) has a doubled or blurred impression. On a 1944 wheat penny, this error can be visible in the date, the word “LIBERTY,” or Abraham Lincoln’s eyes. Pennies with this error can sell for $5 or above.
5.2. Off-Center Strike
An off-center strike occurs when the coin is not struck perfectly in the center, resulting in a portion of the design being cut off. The more off-center the strike, the more valuable the coin can be.
5.3. Missing Dot Error
Some 1944 wheat pennies are missing the dot on the “E pluribus unum” motto.
5.4. Clipped Planchet Error
A clipped planchet error happens when a portion of the coin is missing due to a defect in the blank coin (planchet) before striking. 1944 wheat pennies are clipped alongside the edge due to an error in the minting process. Pennies with this error can sell for up to $100 if they are otherwise in good condition.
5.5. Wrong Mint Mark Error
Some 1944 wheat pennies have the San Francisco Mint’s S mint mark struck over the Denver Mint’s D mint mark or vice versa. Coins with this error are the most valuable among all 1944 wheat pennies with common errors.
6. Steps to Determine the Value of Your 1944 Wheat Penny
If you possess a 1944 wheat penny, follow these steps to assess its potential value:
- Identify the Mint Mark: Examine the coin for a mint mark. No mint mark indicates Philadelphia, “D” indicates Denver, and “S” indicates San Francisco. Assuming your coin is sharply struck with all details intact (and other conditions being equal), a 1944-S wheat penny offers the highest potential value.
- Assess the Condition: Evaluate the coin’s condition. Look for wear, scratches, and other damage. Use the Sheldon Coin Grading Scale as a guide:
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| Poor (PO-01) | Heavily worn, with major details worn away. |
| Fair (FR-02) | Very worn, with some details visible. |
| Good (G-04) | Worn, but with major details visible. |
| Very Good (VG-08) | Moderately worn, with some finer details visible. |
| Fine (F-12) | Lightly worn, with most details visible. |
| Very Fine (VF-20) | Slightly worn, with sharp details. |
| Extremely Fine (EF-40) | Very lightly worn, with nearly all details sharp. |
| About Uncirculated (AU-50) | Shows slight traces of wear on the high points. |
| Uncirculated (MS-60) | No wear, but may have minor imperfections. |
- Check for Errors: Examine the coin for any minting errors, such as double dies, off-center strikes, or clipped planchets.
- Consult a Professional: If you believe you have a valuable coin, consult with a professional numismatist for an accurate appraisal.
7. The Role of Professional Coin Grading Services
Professional coin grading services like the Professional Coin Grading Service (PCGS) and the Numismatic Guaranty Corporation (NGC) provide authentication and grading services. Submitting your coin to one of these services can provide an authoritative assessment of its condition and authenticity, which can significantly impact its value. Although companies exist that specialize in determining the grade of coins, it’s usually not cost-effective to use a professional grading service for wheat pennies, as their overall worth is relatively low.
8. What Were 1944 Pennies Made Of?
1944 pennies were primarily made of gilding metal, consisting of 95% copper, 5% zinc, and tin. However, the extremely rare 1944 steel pennies were made of zinc-coated steel due to wartime copper shortages. An interesting fact about 1944 wheat pennies is that some of them were made out of copper sourced from recycled ammunition casings. These coins are sometimes referred to as shell case pennies.
Here’s an overview of the basic facts about 1944 wheat pennies:
- Total mintage: 2.15 billion
- Mint: Philadelphia (1.43 billion), Denver (430.5 million), San Francisco (282.7 million)
- Designer: Victor D. Brenner
- Face value: $0.1
- Material: Gilding metal (95% copper, 5% zinc and tin)
- Weight: 3.11 grams (0.109 ounces)
- Diameter: 19.05 millimeters (0.75 inches)
9. Why Were Steel Pennies Made in 1943?
Steel pennies were made in 1943 due to the high demand for copper during World War II. Copper was needed for ammunition and other military equipment, so the U.S. Mint switched to using steel coated with zinc to produce pennies, conserving copper for the war effort.
Originally, the 1944 steel wheat pennies also included copper, but the U.S. government decided to make a version using only zinc-coated steel due to military demand for copper during World War 2. This version of the 1944 wheat penny was very short-lived as it had issues with rust and didn’t look distinct enough from a dime.
10. FAQs About 1944 Pennies
10.1. How much is a 1944 wheat penny worth?
The worth of a 1944 penny can vary significantly depending on the version.
A regular 1944 wheat penny minted in Philadelphia is only worth between $0.20 and $0.90, depending on the condition. 1944 wheat pennies minted in Denver or San Francisco (you can recognize them by a “D” or “S” mint mark, respectively) can be worth slightly more.
The most valuable version of the 1944 by far is the 1944 steel wheat pennies, but they are extremely rare.
10.2. How much is a 1944 steel penny worth?
1944 steel pennies are extremely valuable, although the price they sell for depends on their condition. A 1944 steel penny in excellent condition can be worth hundreds of thousands of dollars or even up to $1 million.
10.3. How can I tell if my 1944 penny is steel?
To determine if your 1944 penny is steel, use a magnet. Steel pennies are magnetic, while copper pennies are not. Additionally, steel pennies have a different color and luster compared to copper pennies.
10.4. How much is a 1944 copper penny worth?
A 1944 copper penny is worth about $0.20 or up to $1 if it’s in good condition. 1944 copper pennies can be worth more if they were minted in San Francisco (“S” mint mark) or Denver (“D” mint mark). 1944 copper pennies minted in Philadelphia have no mint mark.
10.5. Where can I sell my 1944 penny?
You can sell your 1944 penny through various channels, including coin dealers, online auctions, and numismatic marketplaces. Consulting with a professional coin appraiser can help you determine the best way to sell your coin.
10.6. What are the factors that influence the value of a coin?
Several factors influence the value of a coin, including its rarity, condition, mint mark, and any errors or unique features. Market demand and collector interest also play a significant role in determining a coin’s value.
10.7. How do I care for and store my coins?
Proper care and storage are essential to maintain the value of your coins. Store coins in acid-free holders or albums, and handle them with gloves to avoid transferring oils from your skin. Keep coins in a cool, dry place to prevent corrosion.
10.8. Are there any other valuable wheat pennies?
Yes, other wheat pennies, such as the 1909-S VDB, 1914-D, and 1931-S, are also highly valuable due to their rarity and historical significance.
10.9. What does “uncirculated” mean in the context of coin grading?
“Uncirculated” refers to a coin that has never been used in circulation and retains its original mint luster. Uncirculated coins are typically in pristine condition and are highly valued by collectors.
10.10. How can I learn more about coin collecting?
You can learn more about coin collecting through books, online resources, coin collecting clubs, and numismatic organizations. Attending coin shows and auctions can also provide valuable insights into the world of coin collecting.
11. Why Choose HOW.EDU.VN for Your Coin Valuation Needs?
Navigating the world of numismatics can be complex, but HOW.EDU.VN is here to simplify the process. Our team of experienced numismatists provides expert insights and accurate valuations, ensuring you have the information you need to make informed decisions about your coin collection.
11.1. Expertise and Accuracy
At HOW.EDU.VN, we pride ourselves on our expertise and commitment to accuracy. Our team stays up-to-date with the latest market trends and numismatic research, providing you with reliable valuations you can trust.
11.2. Personalized Service
We understand that every coin and every collector is unique. That’s why we offer personalized service tailored to your specific needs. Whether you’re looking to value a single coin or an entire collection, we’re here to help.
11.3. Comprehensive Resources
Our website offers a wealth of resources for coin collectors, including articles, guides, and FAQs. Whether you’re a seasoned numismatist or just starting out, you’ll find valuable information to enhance your knowledge and appreciation of coins.
12. Take the Next Step: Consult with Our Experts Today
Don’t leave the value of your 1944 penny to chance. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today to connect with our team of experienced numismatists. We offer personalized consultations and expert valuations to help you understand the true worth of your coin collection.
12.1. Connect with Leading Experts
Our platform connects you directly with leading experts in numismatics, ready to provide in-depth consultations tailored to your specific needs.
12.2. Save Time and Money
Avoid the costly and time-consuming process of searching for reliable information on your own. HOW.EDU.VN offers efficient, accurate, and trustworthy valuations.
12.3. Ensure Confidentiality and Trust
We understand the importance of privacy and security. All consultations are conducted with the utmost confidentiality, ensuring your peace of mind.
Unlock the potential of your coin collection with HOW.EDU.VN. Contact us today and let our experts guide you to success.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Don’t wait—discover the value of your 1944 penny and other valuable coins with the experts at how.edu.vn. Our team is ready to provide the guidance and support you need to navigate the exciting world of coin collecting.