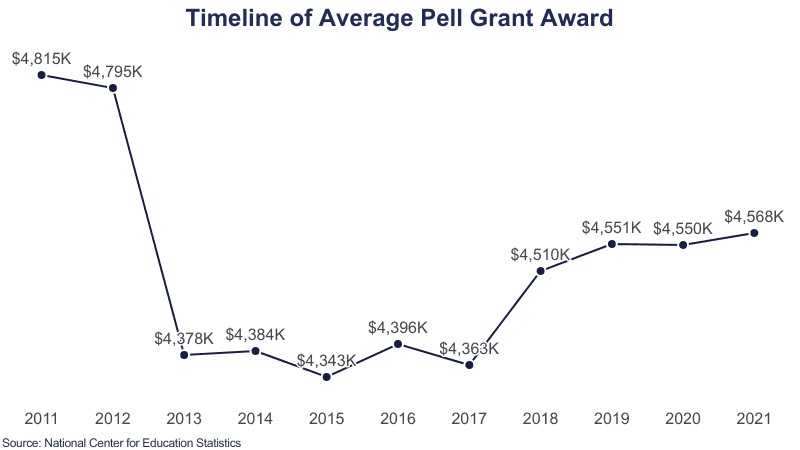
Pell Grants are a critical source of financial aid for millions of students, and understanding How Much Is A Pell Grant can significantly impact college affordability. Through HOW.EDU.VN, you gain access to expert financial guidance, ensuring that students and families navigate the complexities of college funding with confidence. Discover how to maximize your Pell Grant, explore additional financial aid options, and make informed decisions about your higher education journey, bolstering college enrollment and academic success.
1. Understanding the Pell Grant Program
The Pell Grant is a federal financial aid program designed to help undergraduate students with financial need afford college. It’s a need-based grant, meaning eligibility is primarily determined by your family’s income and assets. Unlike loans, Pell Grants do not need to be repaid, making them a valuable resource for students pursuing higher education.
1.1. What is the Pell Grant?
The Pell Grant program provides financial assistance to students pursuing undergraduate degrees, certificates, or other educational programs at eligible institutions. It’s one of the largest federal student aid programs and a cornerstone of college affordability. The grant aims to reduce barriers to entry for higher education, particularly for students from low- and middle-income backgrounds.
1.2. Who is Eligible for a Pell Grant?
Eligibility for a Pell Grant depends on several factors, including:
- Financial Need: The primary factor is your Expected Family Contribution (EFC), which is calculated based on your family’s income and assets.
- Undergraduate Status: You must be pursuing an undergraduate degree or certificate.
- Enrollment Status: You must be enrolled as a regular student in an eligible program.
- Citizenship: You generally must be a U.S. citizen or eligible non-citizen.
- Other Requirements: You must also meet other general eligibility requirements for federal student aid, such as having a valid Social Security number and maintaining satisfactory academic progress.
1.3. How to Apply for a Pell Grant
Applying for a Pell Grant involves completing the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Create an FSA ID: Both the student and parent (if the student is dependent) need to create an FSA ID on the Federal Student Aid website.
- Complete the FAFSA: Fill out the FAFSA form online, providing information about your family’s income, assets, and other relevant details.
- Submit the FAFSA: Submit the FAFSA form by the designated deadline. The FAFSA becomes available on October 1st each year for the following academic year.
- Review Your Student Aid Report (SAR): After submitting the FAFSA, you will receive a SAR, which summarizes the information you provided. Review it carefully for accuracy.
- Receive Your Financial Aid Offer: Colleges will use the information from your FAFSA to determine your eligibility for financial aid, including Pell Grants. They will send you a financial aid offer outlining the amount of aid you are eligible to receive.
2. How Much Can You Get? Understanding Pell Grant Amounts
The amount of a Pell Grant can vary depending on your EFC, enrollment status (full-time or part-time), and the cost of attendance at your school. The maximum Pell Grant amount is set annually by the federal government.
2.1. Maximum Pell Grant Amount
For the 2024-2025 award year, the maximum Pell Grant amount is $7,395. This is the highest amount a student can receive if they meet all eligibility requirements and have a very low EFC. The actual amount you receive may be less, depending on your individual circumstances.
2.2. Factors Affecting Pell Grant Amounts
Several factors influence the amount of Pell Grant you can receive:
- Expected Family Contribution (EFC): Your EFC is a measure of your family’s ability to contribute to your education. The lower your EFC, the higher your Pell Grant amount is likely to be.
- Cost of Attendance (COA): The COA includes tuition and fees, room and board, books, supplies, transportation, and other educational expenses. Your Pell Grant amount cannot exceed your COA.
- Enrollment Status: Full-time students typically receive the full Pell Grant amount, while part-time students receive a reduced amount based on their enrollment status.
- Academic Year: Pell Grant amounts are subject to change each academic year based on Congressional appropriations.
2.3. Pell Grant Disbursement
Pell Grant funds are typically disbursed directly to your school, which then applies the funds to your tuition, fees, and other educational expenses. Any remaining funds are then provided to you, which you can use for other costs like books, supplies, or living expenses. Schools usually disburse Pell Grant funds at the beginning of each semester or term.
3. Pell Grant and Expected Family Contribution (EFC)
The Expected Family Contribution (EFC) plays a pivotal role in determining Pell Grant eligibility and the amount of aid you receive. Understanding how the EFC is calculated and how it affects your Pell Grant can help you plan for college expenses.
3.1. How EFC is Calculated
The EFC is calculated based on the information you provide on the FAFSA, including your family’s income, assets, and household size. The formula used to calculate the EFC takes into account both your parents’ and your own financial information, if you are considered a dependent student. Factors such as taxable and untaxable income, assets like savings and investments, and the number of family members in college are all considered.
3.2. EFC and Pell Grant Eligibility
Your EFC is used to determine your eligibility for a Pell Grant. Generally, students with lower EFCs are more likely to qualify for a Pell Grant. However, even if you have a higher EFC, you may still be eligible for some amount of Pell Grant funding. The maximum EFC to qualify for a Pell Grant is determined annually by the Department of Education.
3.3. Examples of EFC and Pell Grant Amounts
Here are a few examples to illustrate how EFC can affect Pell Grant amounts:
- Example 1: A student with an EFC of $0 may be eligible for the maximum Pell Grant amount, which is $7,395 for the 2024-2025 academic year.
- Example 2: A student with an EFC of $2,000 may be eligible for a Pell Grant amount that is less than the maximum, but still significant.
- Example 3: A student with an EFC above the maximum threshold may not be eligible for a Pell Grant.
It’s important to note that these are just examples, and the actual Pell Grant amount you receive will depend on your individual circumstances and the cost of attendance at your school.
4. Pell Grant for Different School Types
The type of school you attend can influence the amount of Pell Grant funding you receive and how far that funding will go towards covering your educational expenses.
4.1. Pell Grant at Public vs. Private Institutions
-
Public Institutions: Public colleges and universities generally have lower tuition rates than private institutions. This means that your Pell Grant may cover a larger percentage of your tuition and fees at a public school.
-
Private Institutions: Private colleges and universities often have higher tuition rates, which means that your Pell Grant may not cover as much of your overall expenses. However, private institutions may also offer additional financial aid through scholarships and grants, which can help make up the difference.
4.2. Pell Grant at 2-Year vs. 4-Year Colleges
- 2-Year Colleges: Community colleges and other 2-year institutions typically have lower tuition rates than 4-year colleges. This can make them a more affordable option, especially when combined with Pell Grant funding.
- 4-Year Colleges: While 4-year colleges may have higher tuition rates, they also offer a wider range of degree programs and extracurricular activities. Your Pell Grant can still provide significant financial assistance, but you may need to supplement it with other forms of aid.
4.3. Online vs. On-Campus Pell Grant
Pell Grants can be used for both online and on-campus programs, as long as the program is offered by an eligible institution. The amount of Pell Grant funding you receive will depend on your enrollment status and the cost of attendance, regardless of whether you are studying online or on-campus.
5. Pell Grant Lifetime Eligibility
There are limits to how long you can receive Pell Grant funding over your lifetime. Understanding these limits is essential for long-term financial planning.
5.1. 600% Rule
The Pell Grant program has a “600% Rule,” which limits the amount of Pell Grant funding you can receive to the equivalent of 12 full-time semesters (or six years). This rule applies regardless of whether you receive the full Pell Grant amount each year. Once you have reached the 600% limit, you are no longer eligible for Pell Grant funding.
5.2. How to Calculate Your Pell Grant Usage
To calculate your Pell Grant usage, you need to determine the percentage of the Pell Grant you used each year. For example, if you received 50% of the full Pell Grant amount in one year, you would have used 50% of your lifetime eligibility. Keep track of the percentage of Pell Grant funding you receive each year to ensure you don’t exceed the 600% limit.
5.3. Regaining Pell Grant Eligibility
In some cases, it may be possible to regain Pell Grant eligibility if you have exceeded the 600% limit. For example, if you lost eligibility due to a school closure or a change in your enrollment status, you may be able to have your Pell Grant eligibility reinstated. Contact the Department of Education or your school’s financial aid office for more information.
6. Pell Grant and Other Financial Aid
The Pell Grant is often just one component of a larger financial aid package. Understanding how Pell Grants interact with other forms of aid can help you maximize your financial resources.
6.1. Pell Grant vs. Student Loans
- Pell Grant: A grant that does not need to be repaid, based on financial need.
- Student Loans: Loans that must be repaid with interest, available to students regardless of financial need.
It’s generally best to use Pell Grant funding first, as it does not require repayment. Student loans should be considered as a supplement to Pell Grants and other forms of financial aid.
6.2. Pell Grant and Scholarships
- Pell Grant: Federal grant based on financial need.
- Scholarships: Merit-based or need-based awards from colleges, universities, or private organizations.
Scholarships can be a great way to reduce your reliance on student loans. Apply for as many scholarships as possible to supplement your Pell Grant funding.
6.3. Pell Grant and Work-Study Programs
- Pell Grant: Federal grant based on financial need.
- Work-Study Programs: Part-time jobs for students with financial need, often on-campus.
Work-study programs can provide you with valuable work experience and help you earn money to cover your educational expenses. Your Pell Grant can help reduce your overall financial need, making you more eligible for work-study opportunities.
7. Maximizing Your Pell Grant: Tips and Strategies
To make the most of your Pell Grant, consider these tips and strategies:
7.1. Complete the FAFSA Early
The FAFSA becomes available on October 1st each year. Complete and submit the FAFSA as early as possible to ensure you are considered for all available financial aid, including Pell Grants.
7.2. Accurately Report Your Financial Information
Provide accurate and complete information on the FAFSA to ensure your EFC is calculated correctly. Errors or omissions can affect your Pell Grant eligibility and amount.
7.3. Consider Community College
Attending a community college for your first two years can save you money on tuition and fees. You can then transfer to a four-year college to complete your bachelor’s degree.
7.4. Live at Home
Living at home can significantly reduce your room and board expenses. If possible, consider living with your parents or guardians to save money on college costs.
7.5. Explore Additional Financial Aid Options
In addition to Pell Grants, explore other forms of financial aid, such as scholarships, grants, and work-study programs. The more financial aid you receive, the less you will need to rely on student loans.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Applying for Pell Grants
Applying for Pell Grants can be complex, and it’s easy to make mistakes. Here are some common errors to avoid:
8.1. Missing the FAFSA Deadline
The FAFSA has deadlines at the federal, state and college levels. Missing these deadlines can cost you potential financial aid.
8.2. Providing Incorrect Information
Inaccurate or incomplete information on the FAFSA can delay your application or reduce the amount of aid you receive.
8.3. Not Reviewing Your Student Aid Report (SAR)
Your SAR summarizes the information you provided on the FAFSA. Review it carefully for accuracy and make any necessary corrections.
8.4. Assuming You’re Ineligible
Even if you think you may not be eligible for a Pell Grant, it’s still worth applying. You may be surprised at the amount of aid you qualify for.
8.5. Ignoring Additional Requirements
In addition to completing the FAFSA, you may need to submit additional documentation or meet other requirements to receive a Pell Grant. Be sure to follow all instructions carefully.
9. The Future of the Pell Grant Program
The Pell Grant program has evolved significantly over the years, and its future is subject to ongoing debate and policy changes.
9.1. Proposed Changes to Pell Grant Funding
There are often proposals to increase Pell Grant funding to help more students afford college. These proposals may include increasing the maximum Pell Grant amount, expanding eligibility, or simplifying the application process.
9.2. Impact of Policy Changes on Students
Policy changes to the Pell Grant program can have a significant impact on students. Increased funding can make college more affordable, while changes to eligibility requirements can affect who qualifies for aid.
9.3. Advocacy for Pell Grant Expansion
Many organizations and individuals advocate for Pell Grant expansion to ensure that higher education remains accessible to all students, regardless of their financial background. Advocacy efforts may include lobbying policymakers, raising awareness, and supporting students through the application process.
10. Pell Grant Statistics and Trends
Understanding Pell Grant statistics and trends can provide valuable insights into the program’s impact and effectiveness.
10.1. Pell Grant Recipients by Income Level
The majority of Pell Grant recipients come from low-income families. According to recent data, over 50% of Pell Grant funds go to students whose families earn less than $20,000 annually.
10.2. Pell Grant Recipients by Race and Ethnicity
Pell Grant recipients represent a diverse range of racial and ethnic backgrounds. Black and Hispanic students are more likely to receive Pell Grants compared to White and Asian students.
10.3. Pell Grant and College Completion Rates
Studies have shown that Pell Grants can improve college completion rates, particularly for low-income students. Pell Grant recipients are more likely to persist in college and earn a degree compared to students who do not receive Pell Grant funding.
11. Expert Advice on Navigating Pell Grants
Navigating the Pell Grant process can be challenging, but expert advice can help you make informed decisions and maximize your financial aid opportunities. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with experienced financial aid advisors who can provide personalized guidance and support.
11.1. Common Misconceptions About Pell Grants
- Misconception 1: Only low-income students qualify for Pell Grants.
- Reality: While Pell Grants are need-based, eligibility is determined by a variety of factors, not just income.
- Misconception 2: Pell Grants cover the full cost of college.
- Reality: Pell Grants can provide significant financial assistance, but they may not cover all expenses.
- Misconception 3: Applying for a Pell Grant is too complicated.
- Reality: While the application process can be complex, resources and assistance are available to help you navigate it.
11.2. Tips for Communicating with Financial Aid Offices
- Be Prepared: Gather all necessary documents and information before contacting the financial aid office.
- Be Clear and Concise: Clearly explain your questions or concerns.
- Be Polite and Respectful: Treat financial aid officers with courtesy and respect.
- Follow Up: If you don’t receive a response within a reasonable time, follow up to ensure your inquiry is addressed.
11.3. Resources for Pell Grant Information
- Federal Student Aid Website: Provides comprehensive information about Pell Grants and other federal student aid programs.
- College Financial Aid Offices: Offer personalized guidance and support to students and families.
- HOW.EDU.VN: Connects you with experienced financial aid advisors who can provide expert advice and support.
12. Success Stories: How Pell Grants Have Changed Lives
The Pell Grant program has transformed the lives of countless students, enabling them to pursue their educational goals and achieve their dreams.
12.1. Overcoming Financial Barriers
Many students face significant financial barriers to higher education. Pell Grants can help these students overcome those barriers and access the opportunities they deserve.
12.2. Pursuing Dreams and Careers
Pell Grants can enable students to pursue their passions and careers. By reducing the financial burden of college, Pell Grants allow students to focus on their studies and achieve their full potential.
12.3. Contributing to Society
Pell Grant recipients often go on to make significant contributions to society. They become leaders in their communities, innovators in their fields, and role models for future generations.
13. FAQs About Pell Grants
Here are some frequently asked questions about Pell Grants:
- What is the maximum Pell Grant amount for the 2024-2025 academic year?
- The maximum Pell Grant amount for the 2024-2025 academic year is $7,395.
- How is the Expected Family Contribution (EFC) calculated?
- The EFC is calculated based on the information you provide on the FAFSA, including your family’s income, assets, and household size.
- Can I use a Pell Grant for online programs?
- Yes, Pell Grants can be used for both online and on-campus programs, as long as the program is offered by an eligible institution.
- What is the 600% Rule?
- The 600% Rule limits the amount of Pell Grant funding you can receive to the equivalent of 12 full-time semesters (or six years).
- Can I receive a Pell Grant if I am a part-time student?
- Yes, part-time students are eligible for Pell Grants, but the amount you receive will be reduced based on your enrollment status.
- How do I apply for a Pell Grant?
- To apply for a Pell Grant, you need to complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
- What happens if I make a mistake on the FAFSA?
- If you make a mistake on the FAFSA, you can correct it by logging into your account on the Federal Student Aid website.
- How do I know if I am eligible for a Pell Grant?
- Your eligibility for a Pell Grant will be determined based on the information you provide on the FAFSA.
- What if my family’s financial situation changes after I submit the FAFSA?
- If your family’s financial situation changes significantly after you submit the FAFSA, you can contact your school’s financial aid office to request a re-evaluation of your aid eligibility.
- Can I appeal my Pell Grant amount?
- Yes, if you believe that your Pell Grant amount is not accurate, you can contact your school’s financial aid office to request an appeal.
14. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN for Personalized Guidance
Navigating the complexities of Pell Grants and financial aid can be overwhelming. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with a network of over 100 experienced Ph.D. experts who can provide personalized guidance and support.
14.1. Benefits of Consulting with Our Ph.D. Experts
- Expert Advice: Receive expert advice from experienced financial aid advisors.
- Personalized Guidance: Get personalized guidance tailored to your unique circumstances.
- Comprehensive Support: Access comprehensive support throughout the financial aid process.
- Informed Decisions: Make informed decisions about your education and finances.
14.2. How to Get in Touch with Our Experts
Ready to take the next step? Contact us today to schedule a consultation with one of our Ph.D. experts.
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
14.3. Testimonials from Satisfied Clients
“Thanks to HOW.EDU.VN, I was able to navigate the Pell Grant process with ease and secure the funding I needed to pursue my dreams. The expert advice and personalized guidance I received were invaluable.” – Sarah J.
“I was overwhelmed by the complexities of financial aid, but the Ph.D. experts at HOW.EDU.VN provided me with the support and guidance I needed to make informed decisions. I highly recommend their services.” – Michael T.
Understanding how much is a Pell Grant and how to maximize your eligibility can significantly impact your ability to afford college. Let how.edu.vn connect you with the expertise you need to navigate the financial aid process with confidence. Contact us today to start your journey towards a brighter future.