How Much Is A Prosthetic Leg? Understanding prosthetic leg costs is crucial, and selecting the right prosthetic limb involves various factors, including the type of prosthesis and its features. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with top-tier specialists who can help navigate these complexities and provide tailored solutions. Explore the detailed breakdown below and discover how expert advice can optimize your rehabilitation journey, addressing all your concerns about prosthetic expenses and ensuring a smooth transition with lower extremity prosthetics.
1. Understanding the Factors Influencing Prosthetic Leg Cost
Several elements play a significant role in determining the final cost of a prosthetic leg. These include the type of prosthetic leg (below-knee, above-knee), the complexity of the knee and ankle joints, the materials used (such as carbon fiber), and the technology integrated (microprocessor control). Additionally, brand reputation, customization options, and the inclusion of features like adjustable sockets or specialized liners can all influence the price.
- Type of Prosthetic Leg: Below-knee prosthetics generally cost less than above-knee prosthetics due to the additional complexity of the knee joint.
- Joint Complexity: Basic joints are more affordable, while advanced microprocessor-controlled joints increase the cost significantly.
- Materials: Carbon fiber and other high-performance materials add to the price but offer better durability and functionality.
- Brand Reputation: Established brands often come with higher price tags due to their reputation for quality and innovation.
2. Types of Prosthetic Legs and Their Associated Costs
Prosthetic legs are generally categorized based on the level of amputation: below-knee (transtibial) and above-knee (transfemoral). Each type has varying levels of complexity and functionality, which directly impact the cost.
2.1 Below-Knee Prosthetic Leg Cost
Below-knee prosthetics are designed for individuals who have had amputations below the knee, allowing them to retain their knee joint. This often results in a more straightforward rehabilitation process.
- Cost Range: Generally, the cost of a below-knee prosthetic leg ranges from $3,000 to $24,000.
- Factors Influencing Cost: The price depends on the brand, the type of carbon foot, and features of the silicone liner.
- Key Features: Options include different carbon foot types and silicone liners, which enhance comfort and function.
| Brand | Starting Price | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Ottobock | $4,000 | Type of carbon foot, silicone liner |
| Össur | $3,750 | Active vacuum system, carbon foot options |

2.2 Above-Knee Prosthetic Leg Cost
Above-knee prosthetics are designed for individuals who have had amputations above the knee, requiring the prosthetic to replace the knee joint. This added complexity increases the cost and energy expenditure.
- Cost Range: Above-knee prosthetics range from $5,000 to $70,000.
- Factors Influencing Cost: The cost varies based on the brand, the type of joint used, and the choice of carbon foot.
- Key Features: Options include advanced knee joints and carbon foot designs, which improve stability and movement.
| Brand | Starting Price | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Ottobock 3R80 | $8,500 | Type of joint, carbon foot |
| Ottobock 3R60 | $10,500 | Enhanced safety and mobility, particularly on challenging surfaces such as slopes and stairs |
3. Exploring Prosthetic Leg Joints: Foot/Ankle and Knee Options
The joints in a prosthetic leg significantly impact its functionality and cost. Different models offer varying degrees of flexibility and control, tailored to different activity levels and needs.
3.1 Foot/Ankle Joints
- Basic Models: These feature a stationary foot/ankle, providing basic support.
- Flexible Models: These offer smoother walking using materials like carbon fiber or fiberglass.
- Advanced Models: These feature multi-axial movement, mimicking natural ankle motion and adjusting to uneven terrain.
- Microprocessor Systems: Suitable for low to moderately active amputees, these provide greater clearance and automatic adjustments.
3.2 Knee Joints
- Manual Lock Mechanisms: Simple and cost-effective, these lock the knee in place for stability.
- Weight-Activated Locks: These facilitate natural walking patterns by engaging the lock based on weight distribution.
- Microprocessor-Controlled Knees: Advanced knees that allow for dynamic movement, adjusting to varying walking speeds.
- Hydraulic Knees: Ideal for active individuals needing to navigate stairs, uneven terrains, or longer distances.
4. Estimating the Average Cost of a Prosthetic Leg
To provide a clearer understanding, here’s an estimated breakdown of the average costs associated with different types of prosthetic legs:
| Type of Prosthetic Leg | Average Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Basic below-the-knee prosthetic | $3,000 – $10,000 |
| Flexible basic below-the-knee prosthetic | $7,000 – $12,000 |
| Hydraulic or mechanical assistance | $20,000 – $40,000 |
| Computerized prosthetic leg | $50,000+ |
5. Navigating Health Insurance Coverage for Prosthetic Legs
Understanding your health insurance coverage is crucial when planning for the cost of a prosthetic leg. Most prosthetic legs are insured, but coverage details can vary significantly.
5.1 For Patients with Health Insurance
- Out-of-Pocket Costs: Patients typically have copays for doctor visits and coinsurance ranging from 10% to 50%.
- Coverage Contingencies: The exact type of leg covered depends on the individual patient’s amputation level, condition, and needs.
- Basic Coverage: Basic prosthetic legs may be covered for homebound individuals who need to move around the house.
5.2 For Patients without Health Insurance
- Cost Variation: A basic prosthetic leg can cost less than $10,000, while advanced, computerized models can cost $70,000 or more.
- Financial Aid: Various non-profits provide financial aid or free prosthetic limbs for patients in need.
- Resources: Organizations like The Amputee Coalition offer lists of financial resources and non-profits to help minimize the financial burden.
6. Essential Inclusions in the Prosthetic Leg Price
The cost of a prosthetic leg typically includes several key services and components, ensuring a comprehensive fitting and adjustment process.
- Initial Consultation: After amputation surgery, patients visit a prosthetist to take measurements and create a cast of the stump.
- Temporary Prosthesis: A temporary prosthesis is made to be used for at least a year while the stump heals.
- Permanent Prosthesis Fabrication: After the residual limb has stabilized, another cast is made to manufacture the permanent prosthetic leg.
- Final Fitting and Adjustments: The patient returns for a final fitting and undergoes tests in the prosthetist’s office and during daily activities.
7. Understanding Extra Artificial Leg Costs: Therapy and Rehabilitation
Beyond the cost of the prosthetic leg itself, patients may need physical and occupational therapy to learn how to perform daily tasks at home or work.
- Physical Therapy: Typically costs between $50 and $350 per session.
- Occupational Therapy: Can range from $50 to $400 per session.
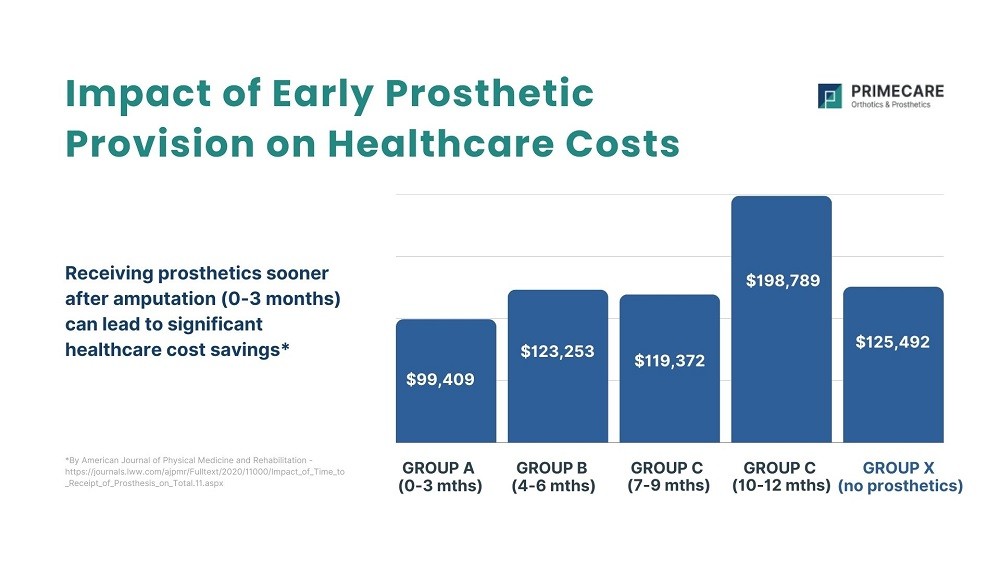
- Impact of Timely Prosthesis: Research indicates that receiving a prosthesis within 0-3 months leads to improved rehabilitation outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
8. Key Considerations for Choosing a Prosthetic Leg
Selecting the right prosthetic leg involves several key considerations:
- Activity Level: Your daily activities and lifestyle significantly influence the type of prosthetic leg you need.
- Comfort: Ensuring a comfortable fit is crucial for long-term use and mobility.
- Functionality: The prosthetic leg should support your specific needs, whether it’s walking, running, or other activities.
- Cost: Balancing your budget with the features and quality of the prosthetic leg is essential.
- Professional Advice: Consulting with a prosthetist is vital to make an informed decision based on your individual circumstances.
9. The Role of Advanced Technology in Prosthetic Legs
Advancements in technology have significantly improved the functionality and usability of prosthetic legs. Microprocessor-controlled knees and ankles, for example, offer dynamic adjustments and enhanced stability.
- Microprocessor Knees: These adjust in real-time to changes in walking speed and terrain, providing a more natural gait.
- Powered Prosthetics: Battery-powered options offer increased strength and endurance, particularly beneficial for high-activity individuals.
- Myoelectric Prosthetics: These use muscle signals to control movement, providing a more intuitive and responsive experience.
10. Rehabilitation and Training: Maximizing the Benefits of Your Prosthetic Leg
Rehabilitation is a critical component of the prosthetic leg journey. Physical and occupational therapy help patients regain strength, balance, and coordination.
- Physical Therapy: Focuses on improving strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Occupational Therapy: Helps patients adapt to daily tasks and activities with their prosthetic leg.
- Gait Training: Teaches proper walking techniques to maximize efficiency and minimize strain.
- Long-Term Support: Ongoing support and adjustments are necessary to ensure the prosthetic leg continues to meet your needs.
11. The Importance of Regular Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance and care are essential for extending the life of your prosthetic leg and ensuring optimal performance.
- Daily Cleaning: Regularly clean the socket and liner to prevent skin irritation and infection.
- Inspection: Check for wear and tear on all components, including joints, feet, and liners.
- Professional Servicing: Schedule regular check-ups with your prosthetist for adjustments and repairs.
- Component Replacement: Replace worn or damaged components promptly to avoid further issues.
12. Innovations in Prosthetic Leg Design
Ongoing research and development continue to drive innovations in prosthetic leg design, offering new possibilities for amputees.
- Customizable Sockets: Advances in 3D printing allow for highly customizable sockets that provide a more comfortable and secure fit.
- Adaptive Prosthetics: Prosthetics that automatically adjust to different activities and terrains offer greater versatility.
- Osseointegration: A surgical procedure where the prosthetic is directly attached to the bone, providing improved stability and control.
- Robotic Prosthetics: Advanced robotic limbs offer enhanced functionality and responsiveness, mimicking natural movement.
13. Financial Assistance Programs and Resources
Several organizations and programs offer financial assistance to help cover the cost of prosthetic legs.
- Amputee Coalition: Provides a comprehensive list of financial resources and support services.
- Challenged Athletes Foundation: Offers grants and support to athletes with disabilities.
- Shriners Hospitals for Children: Provides prosthetic care for children at no cost.
- Veterans Affairs (VA): Offers prosthetic services and financial assistance to eligible veterans.
- State Vocational Rehabilitation Programs: Provide assistance to individuals with disabilities seeking employment.
14. Testimonials and Success Stories
Hearing from others who have successfully navigated the prosthetic leg journey can provide inspiration and hope.
- Personal Accounts: Reading stories of amputees who have regained their mobility and independence can be incredibly motivating.
- Professional Athletes: Learning about athletes with prosthetic legs who have achieved remarkable feats can inspire you to push your limits.
- Community Support: Joining support groups and connecting with other amputees can provide valuable insights and encouragement.
15. How to Choose the Right Prosthetist
Selecting the right prosthetist is a critical step in ensuring a successful prosthetic leg experience.
- Credentials: Look for a prosthetist who is certified by the American Board for Certification in Orthotics, Prosthetics & Pedorthics (ABC).
- Experience: Choose a prosthetist with extensive experience in fitting and adjusting prosthetic legs.
- Reputation: Read reviews and testimonials to gauge the prosthetist’s reputation and patient satisfaction.
- Communication: Select a prosthetist who communicates clearly and listens to your concerns and goals.
- Technology: Ensure the prosthetist has access to the latest technology and techniques in prosthetic care.
16. Understanding the Psychological Impact of Amputation and Prosthetics
Amputation can have a significant psychological impact, and addressing these challenges is crucial for a successful recovery.
- Emotional Support: Seek counseling or therapy to cope with feelings of grief, loss, and anxiety.
- Support Groups: Connect with other amputees to share experiences and provide mutual support.
- Positive Mindset: Focus on your abilities and goals, and celebrate your progress along the way.
- Body Image: Work on accepting and embracing your new body image.
- Self-Esteem: Engage in activities that boost your self-esteem and confidence.
17. Future Trends in Prosthetic Technology
The field of prosthetics is constantly evolving, with exciting new technologies on the horizon.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces: These interfaces allow users to control prosthetic limbs with their thoughts.
- Regenerative Medicine: Research into regenerating lost limbs could potentially eliminate the need for prosthetics in the future.
- Advanced Materials: New materials are being developed to create lighter, stronger, and more durable prosthetic limbs.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered prosthetics can learn and adapt to the user’s movements, providing a more natural and intuitive experience.
18. The Importance of a Multidisciplinary Approach to Prosthetic Care
Effective prosthetic care requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving a team of healthcare professionals working together to meet the patient’s needs.
- Prosthetist: Designs, fabricates, and fits the prosthetic leg.
- Physical Therapist: Helps the patient regain strength, balance, and coordination.
- Occupational Therapist: Assists the patient in adapting to daily tasks and activities.
- Physician: Provides medical oversight and addresses any health concerns.
- Psychologist: Offers emotional support and counseling.
- Social Worker: Helps the patient access resources and support services.
19. Addressing Common Concerns and Myths About Prosthetic Legs
It’s important to address common concerns and myths surrounding prosthetic legs to provide accurate information and alleviate anxieties.
- Myth: Prosthetic legs are uncomfortable and painful. Reality: Modern prosthetic legs are designed for comfort and can be adjusted to minimize discomfort.
- Myth: Prosthetic legs are only for walking. Reality: Prosthetic legs can be used for a wide range of activities, including running, swimming, and dancing.
- Myth: Prosthetic legs are bulky and unattractive. Reality: Prosthetic legs can be customized to match the user’s style and preferences.
- Myth: Prosthetic legs are unaffordable. Reality: Financial assistance programs and insurance coverage can help make prosthetic legs more accessible.
- Myth: Getting a prosthetic leg means giving up on an active life. Reality: Many amputees lead active and fulfilling lives with prosthetic legs.
20. How HOW.EDU.VN Can Help You Find the Right Prosthetic Leg and Expert Advice
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities of navigating the world of prosthetic legs. Our platform connects you with leading experts who can provide personalized guidance and support throughout your journey.
- Access to Top Specialists: We have a network of over 100 renowned PhDs and specialists in various fields.
- Personalized Consultations: Get tailored advice and solutions to address your specific needs.
- Expert Guidance: Our specialists can help you understand the different types of prosthetic legs, navigate insurance coverage, and develop a comprehensive rehabilitation plan.
- Convenient and Secure: Our platform offers a secure and convenient way to connect with experts from around the world.
Finding the right prosthetic leg and navigating the associated costs can be a daunting task. At HOW.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the expert guidance and support you need to make informed decisions and achieve your goals.
The journey to recovery and mobility after an amputation involves significant financial considerations. Understanding the costs associated with prosthetic legs, from the initial purchase to ongoing maintenance and therapy, is crucial for effective planning and management. This comprehensive guide has provided a detailed overview of the various factors that influence the cost of prosthetic legs, as well as strategies for navigating insurance coverage and accessing financial assistance.
However, every individual’s needs and circumstances are unique. That’s why personalized expert advice is essential to ensure the best possible outcome. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with top-tier specialists who can provide tailored solutions and guidance throughout your prosthetic leg journey.
Don’t navigate this complex process alone. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today to connect with our team of renowned PhDs and specialists. Let us help you find the right prosthetic leg, understand your financial options, and develop a comprehensive plan for regaining your mobility and independence.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Reach out to how.edu.vn and take the first step towards a more mobile and fulfilling future.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Prosthetic Legs and Costs
-
How much does a basic prosthetic leg cost?
A basic prosthetic leg typically costs between $3,000 and $10,000, depending on the type and materials used. -
What factors influence the price of a prosthetic leg?
Factors include the type of prosthetic (below-knee, above-knee), the complexity of the joints, materials, technology, brand, and customization options. -
Are prosthetic legs covered by insurance?
Yes, most prosthetic legs are insured, but coverage varies. It’s essential to check with your insurance provider for specific details. -
What are the additional costs beyond the prosthetic leg itself?
Additional costs may include physical and occupational therapy, maintenance, repairs, and component replacements. -
How can I find financial assistance for a prosthetic leg?
Organizations like the Amputee Coalition and Challenged Athletes Foundation offer financial assistance and resources. -
How often do prosthetic legs need to be replaced?
The lifespan of a prosthetic leg varies but typically ranges from 3 to 5 years, depending on activity level and wear. -
What is the difference between a below-knee and an above-knee prosthetic leg?
A below-knee prosthetic (transtibial) is for amputations below the knee, while an above-knee prosthetic (transfemoral) is for amputations above the knee. -
What is a microprocessor knee, and why is it more expensive?
A microprocessor knee uses advanced technology to adjust to changes in walking speed and terrain, providing a more natural gait and increased stability. This technology increases the cost. -
How do I choose the right prosthetist?
Look for a certified prosthetist with experience, a good reputation, clear communication skills, and access to the latest technology. -
Can I participate in sports with a prosthetic leg?
Yes, many amputees participate in sports with specialized prosthetic legs designed for various activities.
