The cost of an alternator can vary widely depending on several factors. Need a precise estimate and expert advice? At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of experienced PhDs can provide personalized guidance to help you understand the various factors influencing the price, ensuring you get the best value for your money. With our expertise, you’ll navigate alternator replacement costs, alternator repair cost considerations, and understand related auto electrical repairs with confidence.
1. What Is The Average Alternator Replacement Cost?
The average alternator replacement cost can vary significantly, generally ranging from $300 to $800, including parts and labor. However, this can fluctuate based on the vehicle’s make and model, the type of alternator (new, remanufactured, or aftermarket), and the labor rates at the repair shop.
The alternator is a critical component of your vehicle’s electrical system, responsible for charging the battery and powering the electrical components while the engine is running. Replacing a faulty alternator is essential to ensure your car operates reliably. Let’s delve into the factors that influence the cost.
1.1. Factors Influencing Alternator Cost
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the final cost of an alternator replacement:
1.1.1. Vehicle Make and Model
The make and model of your vehicle significantly impact the cost of an alternator. High-end or luxury vehicles typically have more expensive parts compared to standard models.
- Example: An alternator for a BMW or Mercedes-Benz can cost significantly more than one for a Toyota or Honda due to the complexity and brand pricing.
1.1.2. Type of Alternator (New, Remanufactured, Aftermarket)
You can choose between new, remanufactured, and aftermarket alternators. Each has its own price point and level of reliability.
- New Alternators: These are brand new units directly from the manufacturer or a certified supplier. They are the most expensive option but offer the best reliability and warranty.
- Remanufactured Alternators: These are used alternators that have been rebuilt with new components. They are generally more affordable than new alternators and come with a warranty, making them a good balance between cost and reliability.
- Aftermarket Alternators: These are produced by third-party manufacturers and are typically the least expensive option. However, their quality and reliability can vary widely, so it’s important to choose a reputable brand.
1.1.3. Labor Costs
Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the repair shop’s location and expertise. Dealerships often charge higher labor rates compared to independent repair shops.
- Dealerships: Typically offer higher labor rates due to specialized expertise and facilities.
- Independent Repair Shops: Generally provide more competitive labor rates.
1.1.4. Alternator Amperage
The amperage of the alternator also affects the price. Higher amperage alternators, designed to power more electrical components, tend to be more expensive.
- Higher Amperage: Vehicles with many electronic features (e.g., advanced audio systems, heated seats) require higher amperage alternators, increasing the cost.
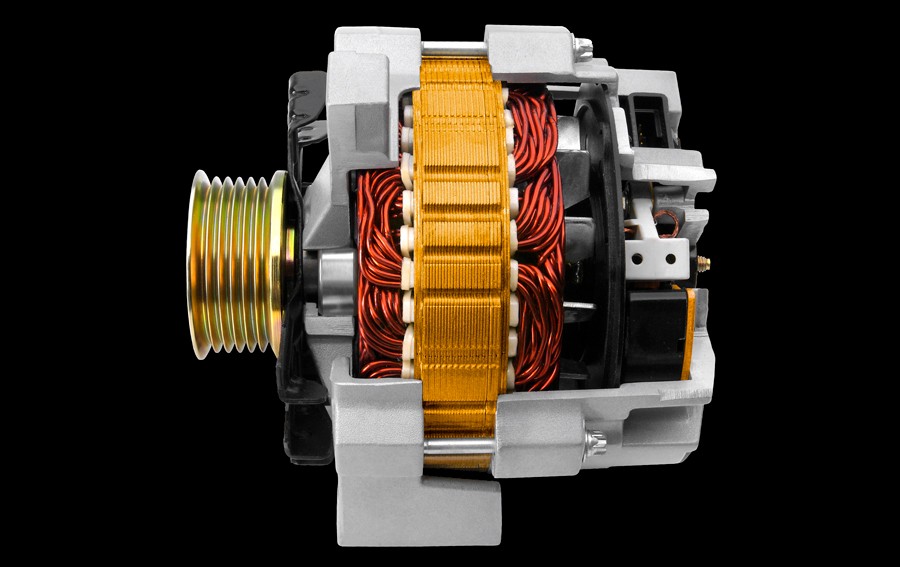 Alternator cost factors
Alternator cost factors
1.2. Average Cost Breakdown
To give you a clearer picture, here’s a general cost breakdown:
- Parts (Alternator): $150 – $500
- Labor: $150 – $300
Total Average Cost: $300 – $800
1.3. Cost-Saving Tips
Here are some tips to potentially lower the cost of your alternator replacement:
- Get Multiple Quotes: Compare prices from different repair shops to find the best deal.
- Consider a Remanufactured Alternator: These can offer significant savings compared to buying a new unit.
- Check for Warranties: Ensure the replacement alternator comes with a warranty to protect against future issues.
- DIY (If Qualified): If you have the mechanical skills, replacing the alternator yourself can save on labor costs. However, this requires expertise and the right tools.
1.4. Warning Signs of a Failing Alternator
Identifying a failing alternator early can prevent further damage and more costly repairs. Here are some common warning signs:
- Dim or Flickering Lights: Inconsistent power supply can cause lights to dim or flicker.
- Warning Lights: The battery or ALT (alternator) warning light on your dashboard illuminates.
- Slow or Malfunctioning Accessories: Issues with power windows, radio, or other electrical accessories.
- Difficulty Starting: The car struggles to start or requires a jump start.
- Unusual Noises: Whining or grinding noises coming from the engine.
1.5. The Importance of Timely Replacement
Ignoring the signs of a failing alternator can lead to more severe problems, such as a dead battery or complete electrical system failure. Timely replacement ensures your vehicle remains reliable and prevents potential safety hazards.
1.6. Expert Consultation at HOW.EDU.VN
If you’re unsure about the condition of your alternator or need guidance on the best replacement options, consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN. Our team of PhDs can provide a comprehensive assessment and recommend the most cost-effective and reliable solutions for your vehicle. Contact us at +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our location at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States.
2. What Are The Main Functions Of An Alternator In A Vehicle?
The alternator serves two primary functions in a vehicle: charging the battery and powering the electrical system while the engine is running.
2.1. Charging the Battery
The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, which is then used to recharge the battery. The battery provides the initial power needed to start the engine, but once the engine is running, the alternator takes over, ensuring the battery remains charged.
- Process: The alternator uses a rotating magnetic field to induce an electric current in its coils. This current is then rectified from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) to match the battery’s requirements.
2.2. Powering the Electrical System
While the engine is running, the alternator supplies electricity to all of the vehicle’s electrical components, including the lights, radio, air conditioning, power windows, and other accessories.
- Efficiency: The alternator is designed to provide a consistent voltage output, ensuring that all electrical components receive the power they need to function correctly.
2.3. Role of the Voltage Regulator
A critical component of the alternator is the voltage regulator. This device maintains a constant voltage output, preventing overcharging and protecting the vehicle’s electrical system from damage.
- Protection: The voltage regulator monitors the battery’s voltage and adjusts the alternator’s output accordingly, ensuring a stable and safe electrical supply.
2.4. Signs of Alternator Malfunction
Recognizing the signs of a malfunctioning alternator is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s reliability:
- Dimming Lights: If your headlights or dashboard lights dim when you use other electrical components, it may indicate the alternator is not providing enough power.
- Battery Warning Light: The battery warning light on your dashboard often indicates an issue with the charging system, which could be due to a failing alternator.
- Difficulty Starting: A weak or dead battery, often caused by an underperforming alternator, can make it difficult to start your vehicle.
- Unusual Noises: Whining or grinding noises from the alternator can indicate worn bearings or other internal damage.
2.5. Timely Maintenance and Expert Advice
Regular maintenance and timely replacement of a failing alternator are essential for ensuring the reliable operation of your vehicle. Consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN for professional advice and solutions tailored to your specific needs. Our team of PhDs can help you diagnose potential issues and recommend the best course of action. Contact us at +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our location at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States.
3. What Are The Key Components Of An Alternator?
An alternator consists of several key components that work together to generate electrical power. Understanding these components can help you appreciate the complexity and importance of this essential automotive part.
3.1. Stator
The stator is a stationary set of copper wire coils where the electrical current is generated. As the rotor spins inside the stator, it induces an alternating current (AC) in these coils.
- Function: The stator’s primary role is to convert the mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy.
3.2. Rotor
The rotor is a rotating electromagnet that spins inside the stator. It is connected to the engine via a belt and pulley system. As the engine turns, it drives the rotor, creating a magnetic field that induces current in the stator coils.
- Construction: The rotor consists of a series of electromagnets that are energized by the vehicle’s battery.
3.3. Rectifier (Diode Bridge)
The rectifier, also known as the diode bridge, converts the alternating current (AC) produced by the stator into direct current (DC), which is required to charge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Function: The rectifier uses a set of diodes to allow current to flow in only one direction, effectively converting AC to DC.
3.4. Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator controls the output voltage of the alternator, ensuring it remains within a safe and consistent range (typically around 13.5 to 14.5 volts). This prevents overcharging and protects the vehicle’s electrical components from damage.
- Importance: Without a voltage regulator, the alternator could produce excessive voltage, which could damage the battery and other sensitive electronics.
3.5. Brushes and Slip Rings
The brushes and slip rings are responsible for transferring electrical current to the rotor, allowing it to create the magnetic field needed to induce current in the stator.
- Wear and Tear: The brushes are subject to wear and tear over time, and worn brushes can lead to reduced alternator output.
3.6. Cooling Fan
The cooling fan helps to dissipate heat generated by the alternator, preventing it from overheating and ensuring it operates efficiently.
- Importance: Overheating can damage the alternator’s components and reduce its lifespan.
3.7. Housing
The housing protects the internal components of the alternator from dirt, moisture, and other contaminants.
- Durability: The housing is typically made of metal and is designed to withstand the harsh conditions under the hood of a vehicle.
3.8. Seeking Expert Advice
Understanding the key components of an alternator can help you appreciate its complexity and the importance of proper maintenance. If you have any concerns about your alternator’s performance or need expert advice, consult with the team at HOW.EDU.VN. Our PhDs can provide comprehensive diagnostics and tailored solutions to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Contact us at +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our location at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States.
4. How To Diagnose A Faulty Alternator?
Diagnosing a faulty alternator requires a systematic approach to identify the symptoms and confirm the issue. Here are several methods you can use to diagnose an alternator problem.
4.1. Visual Inspection
Start with a visual inspection of the alternator and its surrounding components:
- Check the Belt: Ensure the alternator belt is in good condition, properly tensioned, and not slipping.
- Inspect Wiring: Look for any damaged, frayed, or corroded wires and connections.
- Examine the Alternator: Check for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks or leaks.
4.2. Using a Multimeter
A multimeter can be used to measure the voltage output of the alternator:
- Battery Voltage: With the engine off, measure the battery voltage. It should be around 12.6 volts.
- Running Voltage: Start the engine and measure the voltage at the battery terminals. It should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
- Load Test: Turn on several electrical components (e.g., headlights, air conditioning) and check if the voltage remains within the specified range. A significant drop in voltage indicates a potential alternator issue.
4.3. Battery Load Test
A battery load test can help determine if the battery is holding a charge properly. If the battery fails the load test, it could be contributing to the symptoms of a faulty alternator.
4.4. Using an Alternator Tester
An alternator tester can provide a more comprehensive assessment of the alternator’s performance. These testers typically measure the alternator’s output voltage, current, and ripple voltage.
4.5. Checking for Warning Signs
Pay attention to common warning signs of a failing alternator:
- Dimming Lights: Lights dimming when electrical components are used.
- Battery Warning Light: The battery warning light on the dashboard.
- Difficulty Starting: The engine struggles to start or requires a jump start.
- Unusual Noises: Whining or grinding noises from the alternator.
4.6. Seeking Professional Diagnosis
If you’re unsure about the diagnosis or lack the necessary tools and expertise, it’s best to seek professional assistance. A qualified mechanic can perform a thorough inspection and accurately diagnose the issue.
4.7. Expert Diagnostic Services at HOW.EDU.VN
For reliable and accurate alternator diagnostics, consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN. Our team of PhDs offers comprehensive diagnostic services to identify and resolve any issues with your vehicle’s electrical system. Contact us at +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our location at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States.
5. What Is The Lifespan Of An Alternator And How To Extend It?
The lifespan of an alternator typically ranges from 5 to 8 years or between 80,000 and 150,000 miles. However, several factors can affect its longevity. Understanding these factors and taking proactive measures can help extend the life of your alternator.
5.1. Factors Affecting Alternator Lifespan
Several factors can influence how long an alternator lasts:
- Driving Conditions: Frequent short trips, stop-and-go traffic, and extreme weather conditions can put additional strain on the alternator.
- Electrical Load: Overloading the electrical system with too many accessories (e.g., aftermarket audio systems, lights) can shorten the alternator’s lifespan.
- Maintenance: Lack of proper maintenance, such as neglecting to replace worn belts or address electrical issues, can contribute to premature failure.
- Quality of Parts: Using high-quality replacement parts and ensuring proper installation can significantly impact the alternator’s lifespan.
5.2. Tips to Extend Alternator Lifespan
Here are some practical tips to help extend the life of your alternator:
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your vehicle, including regular inspections of the alternator and its components.
- Avoid Overloading the Electrical System: Be mindful of the number of electrical accessories you use simultaneously, and avoid adding excessive aftermarket equipment that can strain the alternator.
- Check and Replace Belts: Inspect the alternator belt regularly and replace it if it shows signs of wear, such as cracks or fraying.
- Ensure Proper Battery Condition: A healthy battery reduces the workload on the alternator. Regularly test and maintain your battery to ensure it is in good condition.
- Address Electrical Issues Promptly: If you notice any electrical issues, such as dimming lights or warning lights, address them promptly to prevent further damage to the alternator.
- Avoid Short Trips: Frequent short trips can prevent the alternator from fully charging the battery, leading to increased wear and tear. Try to combine errands and take longer trips when possible.
- Keep the Engine Clean: A clean engine compartment can help prevent overheating and prolong the life of the alternator.
5.3. Professional Maintenance at HOW.EDU.VN
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the life of your alternator. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs offers comprehensive maintenance services to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Contact us at +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our location at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States.
6. What Are The Differences Between A New, Remanufactured, And Aftermarket Alternator?
When replacing an alternator, you typically have three options: new, remanufactured, and aftermarket. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and understanding the differences can help you make an informed decision.
6.1. New Alternators
- Description: New alternators are brand new units manufactured by the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) or a certified supplier.
- Advantages:
- Reliability: New alternators offer the highest level of reliability and performance.
- Warranty: They typically come with a comprehensive warranty.
- Longevity: New units are expected to last longer than remanufactured or aftermarket alternatives.
- Disadvantages:
- Cost: New alternators are the most expensive option.
6.2. Remanufactured Alternators
- Description: Remanufactured alternators are used units that have been disassembled, cleaned, and rebuilt with new or refurbished components.
- Advantages:
- Cost: They are more affordable than new alternators.
- Warranty: Reputable remanufacturers offer warranties on their products.
- Sustainability: Remanufacturing helps reduce waste and conserve resources.
- Disadvantages:
- Reliability: While remanufactured alternators are generally reliable, they may not perform as well as new units.
- Lifespan: Their lifespan may be shorter compared to new alternators.
6.3. Aftermarket Alternators
- Description: Aftermarket alternators are produced by third-party manufacturers and are designed to fit a variety of vehicles.
- Advantages:
- Cost: Aftermarket alternators are typically the least expensive option.
- Availability: They are often readily available from various retailers.
- Disadvantages:
- Quality: The quality and reliability of aftermarket alternators can vary widely.
- Warranty: Warranty coverage may be limited or non-existent.
- Performance: They may not meet the performance specifications of OEM or remanufactured units.
6.4. Making the Right Choice
Choosing the right type of alternator depends on your budget, reliability requirements, and the age and condition of your vehicle. If you prioritize reliability and longevity, a new alternator is the best choice. If you’re looking for a more affordable option, a remanufactured alternator from a reputable supplier can provide a good balance between cost and performance. Aftermarket alternators should be approached with caution, and it’s important to research the brand and read reviews before making a purchase.
6.5. Expert Guidance at HOW.EDU.VN
Selecting the right alternator can be challenging. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs can provide expert guidance to help you choose the best option for your vehicle and budget. Contact us at +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our location at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States.
7. Can A Bad Alternator Affect Other Car Components?
Yes, a bad alternator can significantly affect other car components. When an alternator fails to provide the correct voltage, it can lead to a cascade of problems throughout the vehicle’s electrical system.
7.1. Battery Issues
A failing alternator can lead to chronic undercharging or overcharging of the battery.
- Undercharging: If the alternator is not providing enough power, the battery will not fully charge, leading to a dead battery and difficulty starting the vehicle.
- Overcharging: If the alternator is overcharging the battery, it can cause the battery to overheat, boil, and potentially explode.
7.2. Electrical System Damage
Inconsistent voltage from a bad alternator can damage sensitive electronic components in the vehicle.
- ECU Damage: The engine control unit (ECU) is particularly vulnerable to voltage spikes and fluctuations, which can cause it to malfunction or fail completely.
- Sensor Malfunctions: Various sensors throughout the vehicle rely on a stable voltage supply. A bad alternator can cause these sensors to provide inaccurate readings, leading to poor engine performance.
- Accessory Issues: Components such as the radio, power windows, and lights can malfunction or fail due to inconsistent voltage.
7.3. Starting Problems
A weak or dead battery, often caused by a failing alternator, can make it difficult to start the vehicle.
- Starter Motor Strain: The starter motor relies on a fully charged battery to operate correctly. If the battery is weak, the starter motor may struggle to turn the engine, leading to premature wear and tear.
7.4. Transmission Problems
In some vehicles, the transmission control system relies on a stable voltage supply. A bad alternator can cause erratic shifting or other transmission problems.
7.5. ABS and Airbag System Issues
The anti-lock braking system (ABS) and airbag system also require a consistent voltage supply. A failing alternator can cause these safety systems to malfunction.
7.6. Preventing Further Damage
Addressing a bad alternator promptly can prevent further damage to other car components. If you suspect your alternator is failing, it’s important to have it diagnosed and replaced as soon as possible.
7.7. Comprehensive Services at HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs offers comprehensive diagnostic and repair services to address alternator issues and prevent further damage to your vehicle. Contact us at +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our location at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States.
8. What Tools And Steps Are Required To Replace An Alternator Yourself?
Replacing an alternator yourself can save on labor costs, but it requires mechanical skills, the right tools, and a thorough understanding of the process. Here are the tools and steps required to replace an alternator:
8.1. Necessary Tools
- Socket Set: Including sockets and wrenches of various sizes.
- Screwdrivers: Both flathead and Phillips head screwdrivers.
- Multimeter: To test the battery and alternator voltage.
- Battery Terminal Cleaner: To clean the battery terminals.
- Gloves and Safety Glasses: For personal protection.
- Shop Rags: To clean up any spills.
- New Alternator: The correct replacement for your vehicle.
- Belt Tensioner Tool: To release tension on the serpentine belt.
8.2. Step-by-Step Instructions
- Safety First: Disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent electrical shock.
- Locate the Alternator: Identify the alternator in your engine compartment.
- Remove the Serpentine Belt: Use a belt tensioner tool to release tension on the serpentine belt and remove it from the alternator pulley.
- Disconnect Electrical Connections: Disconnect the electrical connectors from the alternator. Be careful not to damage the connectors.
- Remove Mounting Bolts: Remove the bolts that secure the alternator to the engine.
- Remove the Old Alternator: Carefully remove the old alternator from the vehicle.
- Install the New Alternator: Install the new alternator in the reverse order of removal.
- Reconnect Electrical Connections: Reconnect the electrical connectors to the alternator.
- Reinstall the Serpentine Belt: Reinstall the serpentine belt onto the alternator pulley, ensuring it is properly aligned.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Test the Alternator: Start the engine and use a multimeter to test the alternator voltage. It should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
8.3. Important Considerations
- Vehicle-Specific Instructions: Consult your vehicle’s repair manual for specific instructions and torque specifications.
- Safety Precautions: Always disconnect the battery before working on the electrical system.
- Professional Assistance: If you’re not comfortable performing the replacement yourself, seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic.
8.4. Expert Assistance at HOW.EDU.VN
If you’re considering replacing your alternator yourself but would like some guidance, consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN. Our team of PhDs can provide detailed instructions and answer any questions you may have. Contact us at +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our location at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States.
9. How Does Alternator Amperage Affect Performance And Cost?
Alternator amperage plays a critical role in a vehicle’s electrical system, affecting both performance and cost. Understanding how amperage impacts these factors can help you make an informed decision when replacing an alternator.
9.1. What is Alternator Amperage?
Amperage (amps) is a measure of the electrical current that an alternator can produce. A higher amperage alternator can supply more power to the vehicle’s electrical system.
9.2. Impact on Performance
- Electrical Load Capacity: A higher amperage alternator can handle a greater electrical load, allowing you to run more accessories simultaneously without straining the system.
- Battery Charging: A higher amperage alternator can charge the battery more quickly, especially when the vehicle is running many electrical components.
- Reliability: In general, a higher amperage alternator will run cooler and more efficiently, potentially extending its lifespan.
9.3. Factors Influencing Amperage Requirements
The amperage requirements of your vehicle depend on several factors:
- Vehicle Type: Larger vehicles with more electrical accessories typically require higher amperage alternators.
- Accessories: The number and type of electrical accessories (e.g., audio systems, lights, heated seats) can significantly increase the amperage demand.
- Driving Conditions: Vehicles that are frequently used in stop-and-go traffic or for short trips may benefit from a higher amperage alternator to ensure the battery remains properly charged.
9.4. Impact on Cost
- Higher Initial Cost: Higher amperage alternators are generally more expensive than lower amperage units.
- Long-Term Savings: While the initial cost may be higher, a properly sized alternator can improve reliability and prevent electrical issues, potentially saving you money in the long run.
9.5. Choosing the Right Amperage
When replacing an alternator, it’s important to choose a unit with the correct amperage for your vehicle’s electrical needs. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or a qualified mechanic to determine the appropriate amperage rating.
9.6. Professional Advice at HOW.EDU.VN
Selecting the right alternator amperage can be complex. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs can provide expert advice to help you choose the best option for your vehicle. Contact us at +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our location at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States.
10. What Are Some Common Mistakes To Avoid When Replacing An Alternator?
Replacing an alternator can be a straightforward task, but it’s important to avoid common mistakes that can lead to problems. Here are some mistakes to avoid when replacing an alternator:
10.1. Not Disconnecting The Battery
One of the most critical safety precautions is to disconnect the negative battery cable before starting the replacement. Failing to do so can result in electrical shock or damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
10.2. Using The Wrong Tools
Using the wrong tools can make the job more difficult and potentially damage components. Make sure you have the right sockets, wrenches, and belt tensioner tool for your vehicle.
10.3. Not Checking The Belt Condition
While replacing the alternator, take the opportunity to inspect the serpentine belt for wear and tear. If the belt is cracked, frayed, or worn, replace it at the same time.
10.4. Over Tightening Bolts
Over tightening the mounting bolts can damage the alternator housing or the engine block. Use a torque wrench to tighten the bolts to the specified torque.
10.5. Incorrectly Routing The Serpentine Belt
Routing the serpentine belt incorrectly can cause it to slip or break, leading to alternator failure and other problems. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or a diagram to ensure the belt is routed correctly.
10.6. Neglecting To Clean Electrical Connections
Corroded or dirty electrical connections can reduce alternator output and cause electrical problems. Clean the battery terminals and alternator connectors with a battery terminal cleaner before reconnecting them.
10.7. Buying The Wrong Alternator
Ensure you purchase the correct alternator for your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Using the wrong alternator can lead to compatibility issues and poor performance.
10.8. Not Testing The New Alternator
After installing the new alternator, test its voltage output to ensure it is functioning correctly. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the battery terminals with the engine running.
10.9. Seeking Expert Assistance
If you’re unsure about any step of the replacement process, seek expert assistance from a qualified mechanic.
10.10. Professional Guidance at HOW.EDU.VN
Avoiding these common mistakes can help ensure a successful alternator replacement. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs can provide expert guidance to help you navigate the process. Contact us at +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our location at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States.
Ready for Expert Alternator Advice?
Don’t let alternator issues leave you stranded. Contact the PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized guidance and reliable solutions. Whether you need help diagnosing a problem, choosing the right replacement, or understanding the costs involved, we’re here to assist. Reach out today and ensure your vehicle’s electrical system is in top shape.
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Get the expertise you deserve. Contact how.edu.vn now and drive with confidence