How Much Is College Tuition Per Year? Understanding the annual cost of college tuition is crucial for financial planning and making informed decisions about higher education. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert guidance to help you navigate the complexities of college expenses and explore strategies for managing these costs effectively, along with resources to understand tuition costs, financial aid options, and long-term investment strategies.
1. What is the Average College Tuition Cost Per Year?
The average college tuition cost per year in the United States varies widely depending on the type of institution and whether you’re an in-state or out-of-state student. According to recent data, the average cost of college, including tuition, fees, books, supplies, and living expenses, is approximately $38,270 per student per year. For expert advice on navigating these costs, consider consulting with the experienced professionals at HOW.EDU.VN.
Breaking down the numbers:
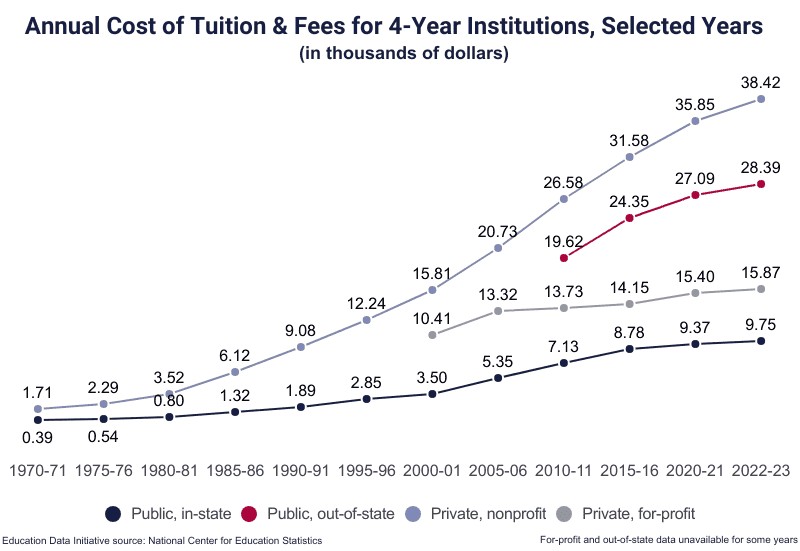
- Public 4-year institution (in-state): Tuition averages around $9,750 per year.
- Public 4-year institution (out-of-state): Tuition averages around $28,386 per year.
- Private, nonprofit university: Tuition averages around $38,421 per year.
These figures highlight the significant differences in tuition costs based on the type of college and residency status. For comprehensive financial planning, visit HOW.EDU.VN for expert advice.
2. How Has College Tuition Changed Over Time?
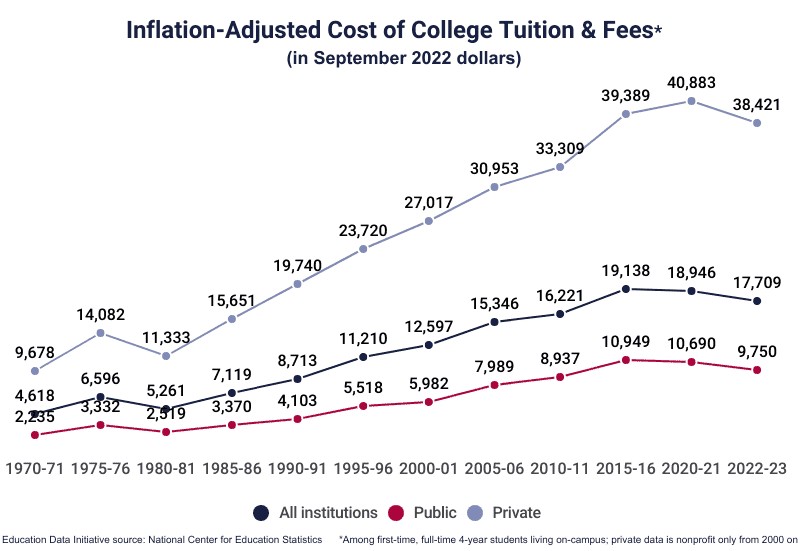
College tuition has seen a dramatic increase over the years, significantly outpacing inflation and wage growth. Over the past few decades, the cost of attending college has more than doubled, making it increasingly challenging for students and families to afford higher education. Understanding this historical trend is essential for planning and saving for college.
2.1 Historical Trends in College Tuition
Here’s a look at how college tuition has evolved:
- 21st Century Increase: The average cost of college has more than doubled in the 21st century, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.04%.
- 1963 vs. Present: In 1963, the annual cost of tuition at a 4-year public college was $243 (equivalent to $2,489 in November 2024). By 2022-23, this cost had risen to $89,556 for a 4-year degree.
- Inflation-Adjusted Growth: From 1963 to 2022, the cost of tuition at a 4-year public college increased at a CAGR of 2.34% after adjusting for inflation.
These figures demonstrate the substantial financial burden that college education places on students and families. For expert guidance on financial planning and managing college costs, visit HOW.EDU.VN.
2.2 Factors Driving Tuition Increases
Several factors contribute to the rising cost of college tuition:
- Decreased State Funding: Many public colleges and universities have experienced cuts in state funding, leading them to increase tuition to cover expenses.
- Increased Demand: The demand for higher education has increased, allowing colleges to raise tuition without significantly impacting enrollment.
- Administrative Costs: The growing administrative costs at colleges, including salaries and infrastructure, contribute to higher tuition fees.
- Student Services: Enhanced student services, such as counseling, career services, and recreational facilities, also add to the overall cost.
Addressing these factors is crucial for making higher education more accessible and affordable. At HOW.EDU.VN, our experts can provide insights and strategies to help you navigate these challenges effectively.
3. What are the Different Types of College Costs?
When planning for college, it’s essential to understand the various costs involved. These costs can be categorized into several key areas, including tuition, fees, room and board, books and supplies, and additional expenses.
3.1 Tuition and Fees
Tuition and fees are the most significant expenses for most college students. Tuition is the cost of instruction, while fees cover other expenses like technology, student activities, and campus services.
- Average Tuition: The average cost of tuition at any 4-year institution is $17,709, representing 46.3% of college costs for a first-time, full-time student living on campus.
- Public vs. Private: Public institutions generally have lower tuition rates for in-state students compared to private institutions.
- 2-Year Institutions: The average cost of tuition and fees at any 2-year institution is $3,885, or 22.3% of the cost of attendance.
Understanding these costs can help you budget and plan effectively. For personalized financial advice, connect with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
3.2 Room and Board
Room and board refer to the costs of housing and meals while attending college. These expenses vary depending on whether you live on or off campus.
- On-Campus: At 4-year institutions, the cost of room and board is $12,917.
- Off-Campus: Off-campus boarders at public 4-year institutions pay an average of $11,983 annually.
- Private Institutions: On-campus boarders at private, nonprofit institutions pay an average of $13,842 per academic year.
Choosing between on-campus and off-campus housing can significantly impact your overall college expenses. Consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN for guidance on making the best financial decision.
3.3 Books and Supplies
The cost of textbooks and supplies can also add up, especially in certain programs that require expensive materials.
- 4-Year Institutions: At public 4-year institutions, students pay an average of $1,220 annually for textbooks and supplies.
- Private Institutions: Books and supplies at private, non-profit institutions average $1,215.
- 2-Year Institutions: At public 2-year institutions, students pay an average of $1,467 each year for books and supplies.
To minimize these costs, consider buying used textbooks or renting them. For more cost-saving tips and expert advice, visit HOW.EDU.VN.
3.4 Additional Expenses
Additional expenses include transportation, personal care, entertainment, and other necessary living costs.
- On-Campus Students: Students living on campus at a public 4-year institution pay an average of $3,790 in additional annual expenses.
- Off-Campus Students: Students who live off campus may expect to pay $4,720 if they do not live with family.
- Private Institutions: At private, nonprofit 4-year institutions, students living on campus spend an average of $2,858 on additional expenses.
These expenses can vary based on location and lifestyle. For comprehensive financial planning that accounts for these costs, connect with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
4. How Much Does College Cost Based on the Type of Institution?
The cost of college varies significantly depending on the type of institution you choose. Understanding these differences is crucial for budgeting and making informed decisions about your education.
4.1 Public vs. Private Institutions
Public and private institutions differ significantly in their funding sources and tuition costs. Public colleges receive funding from state and local governments, while private colleges rely on tuition, endowments, and private donations.
-
Public Institutions:
- In-State Tuition: Averages around $9,750 per year.
- Out-of-State Tuition: Averages around $28,386 per year.
- Funding: Receive funding from state and local governments.
-
Private Institutions:
- Tuition: Averages around $38,421 per year for nonprofit universities.
- Funding: Rely on tuition, endowments, and private donations.
Choosing between public and private institutions can have a significant impact on your college expenses. Consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized financial advice.
4.2 4-Year vs. 2-Year Institutions
4-year colleges and universities offer bachelor’s degrees, while 2-year institutions, often called community colleges, offer associate’s degrees and vocational training.
-
4-Year Institutions:
- Tuition: Higher tuition rates compared to 2-year institutions.
- Degree: Offer bachelor’s degrees.
- Career Paths: Lead to a wider range of career opportunities.
-
2-Year Institutions:
- Tuition: Lower tuition rates, averaging $3,885 per year.
- Degree: Offer associate’s degrees and vocational training.
- Transfer Options: Provide a pathway to transfer to a 4-year institution.
Starting at a 2-year institution and then transferring to a 4-year college can be a cost-effective strategy. For expert guidance on this and other financial planning strategies, visit HOW.EDU.VN.
4.3 For-Profit vs. Non-Profit Institutions
For-profit and non-profit institutions have different financial structures and educational goals. Non-profit colleges prioritize education and reinvest any surplus revenue back into the institution, while for-profit colleges aim to generate profit for their shareholders.
-
Non-Profit Institutions:
- Tuition: Can be higher or lower than for-profit institutions, depending on the type of college.
- Mission: Prioritize education and reinvest surplus revenue.
- Quality: Often have higher academic standards and better resources.
-
For-Profit Institutions:
- Tuition: Can be comparable to non-profit institutions, but may not always offer the same value.
- Mission: Aim to generate profit for shareholders.
- Outcomes: May have lower graduation rates and less favorable career outcomes for graduates.
Choosing the right type of institution is crucial for your educational and financial success. Consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN for guidance on making the best choice for your needs.
5. What are the Additional Costs to Consider Beyond Tuition?
While tuition is a significant expense, it’s important to consider the additional costs associated with attending college. These costs can add up and significantly impact your overall budget.
5.1 Room and Board Expenses
Room and board cover the costs of housing and meals while attending college. These expenses can vary depending on whether you live on or off campus.
-
On-Campus Living:
- Cost: Includes the cost of a dorm room and a meal plan.
- Benefits: Convenient access to campus resources and social activities.
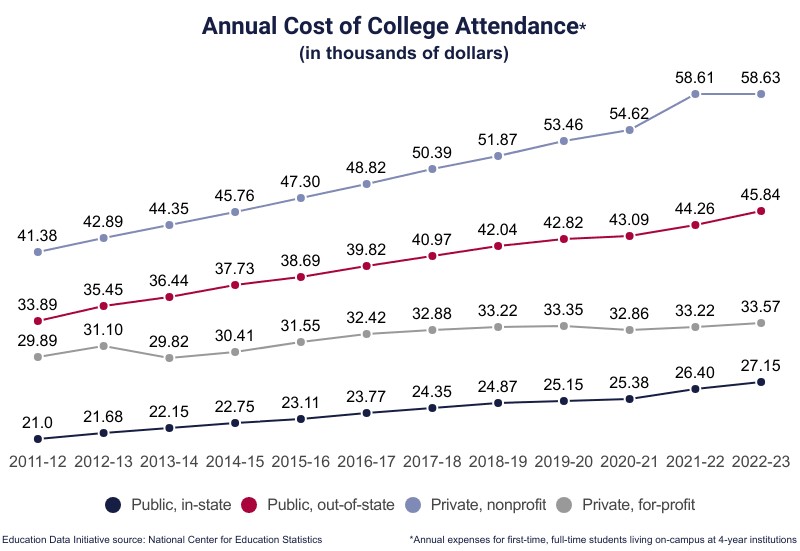
- Average Cost: At 4-year institutions, the cost of room and board is $12,917.
-
Off-Campus Living:
- Cost: Includes rent, utilities, and groceries.
- Considerations: Can be more affordable in some areas, but requires careful budgeting.
- Average Cost: Off-campus boarders at public 4-year institutions pay an average of $11,983 annually.
Choosing between on-campus and off-campus living can significantly impact your college expenses. Consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized financial advice.
5.2 Books and Supplies Costs
The cost of textbooks and supplies can add up, especially in certain programs that require expensive materials.
-
Textbooks:
- Cost: Can range from a few hundred to over a thousand dollars per year.
- Tips: Consider buying used textbooks or renting them to save money.
- Average Cost: At public 4-year institutions, students pay an average of $1,220 annually for textbooks and supplies.
-
Supplies:
- Cost: Includes items like notebooks, pens, calculators, and lab equipment.
- Tips: Shop around for the best deals and take advantage of student discounts.
- Average Cost: Books and supplies at private, non-profit institutions average $1,215.
Managing these costs effectively can help you stay within your budget. For more cost-saving tips and expert advice, visit HOW.EDU.VN.
5.3 Personal and Miscellaneous Expenses
Personal and miscellaneous expenses include transportation, personal care, entertainment, and other necessary living costs.
-
Transportation:
- Cost: Includes gas, parking, public transportation, and travel to and from campus.
- Tips: Consider carpooling, biking, or using public transportation to save money.
- Average Cost: Students living on campus at a public 4-year institution pay an average of $3,790 in additional annual expenses.
-
Personal Care:
- Cost: Includes clothing, toiletries, and personal grooming.
- Tips: Budget carefully and look for discounts and sales.
- Average Cost: Students who live off campus may expect to pay $4,720 if they do not live with family.
-
Entertainment:
- Cost: Includes social activities, movies, concerts, and other forms of recreation.
- Tips: Take advantage of free or discounted campus events and activities.
- Average Cost: At private, nonprofit 4-year institutions, students living on campus spend an average of $2,858 on additional expenses.
These expenses can vary based on location and lifestyle. For comprehensive financial planning that accounts for these costs, connect with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
6. How Can You Save Money on College Tuition?
With the rising cost of college tuition, it’s more important than ever to find ways to save money. There are several strategies you can use to reduce your college expenses and make higher education more affordable.
6.1 Apply for Financial Aid and Scholarships
Financial aid and scholarships are essential resources for students seeking to reduce the cost of college tuition.
-
FAFSA:
- Description: The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is the first step in applying for federal financial aid.
- Benefits: Determines eligibility for grants, loans, and work-study programs.
- Tips: Complete the FAFSA as early as possible to maximize your chances of receiving aid.
-
Scholarships:
- Types: Merit-based, need-based, and specific to certain fields of study or demographics.
- Resources: Websites like Scholarship America and Fastweb can help you find scholarships.
- Tips: Apply for as many scholarships as possible to increase your chances of receiving funding.
For expert guidance on navigating the financial aid and scholarship application process, visit HOW.EDU.VN.
6.2 Attend Community College First
Attending community college for the first two years of your education can significantly reduce your overall college expenses.
- Lower Tuition: Community colleges typically have much lower tuition rates than 4-year colleges and universities.
- Transfer Options: You can transfer your credits to a 4-year institution to complete your bachelor’s degree.
- Cost Savings: By saving money on tuition for the first two years, you can reduce your overall debt burden.
This strategy can make higher education more accessible and affordable. For expert guidance on this and other financial planning strategies, connect with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
6.3 Consider In-State Public Universities
Attending an in-state public university can save you a significant amount of money on tuition compared to attending an out-of-state or private institution.
- Lower Tuition Rates: In-state tuition rates are typically much lower than out-of-state rates.
- State Funding: Public universities receive funding from the state government, which helps keep tuition costs down.
- Quality Education: Many in-state public universities offer high-quality education and excellent academic programs.
Choosing an in-state public university can be a smart financial decision. Consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized financial advice.
6.4 Take Advantage of Tax Benefits
There are several tax benefits available to students and families who are paying for college.
-
American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC):
- Description: A tax credit for qualified education expenses paid for the first four years of college.
- Benefits: Can reduce your tax liability by up to $2,500 per student per year.
- Eligibility: Must be pursuing a degree or other credential and enrolled at least half-time.
-
Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC):
- Description: A tax credit for qualified education expenses paid for any level of education.
- Benefits: Can reduce your tax liability by up to $2,000 per tax return.
- Eligibility: Available for students taking courses to improve job skills or pursue a degree.
-
Student Loan Interest Deduction:
- Description: A deduction for the interest you pay on student loans.
- Benefits: Can reduce your taxable income by up to $2,500 per year.
- Eligibility: Must be legally obligated to pay the interest on the student loan.
Taking advantage of these tax benefits can help offset the cost of college. For expert guidance on tax planning and financial aid, visit HOW.EDU.VN.
7. What is the Return on Investment (ROI) of a College Education?
Investing in a college education is a significant financial decision. Understanding the return on investment (ROI) can help you assess the value of a college degree and make informed choices about your education.
7.1 Increased Earning Potential
One of the primary benefits of a college education is the potential for increased earnings.
- Higher Salaries: College graduates typically earn significantly more than those with only a high school diploma.
- Career Advancement: A college degree can open doors to more advanced career opportunities and higher-paying positions.
- Lifetime Earnings: Over a lifetime, college graduates can earn hundreds of thousands of dollars more than high school graduates.
These factors make a college education a worthwhile investment for many students. For expert guidance on career planning and maximizing your earning potential, connect with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
7.2 Lower Unemployment Rates
College graduates also tend to have lower unemployment rates compared to those with less education.
- Job Security: A college degree can provide greater job security and reduce the risk of unemployment.
- Demand for Skills: Employers often seek candidates with the skills and knowledge gained through a college education.
- Economic Stability: College graduates are better positioned to weather economic downturns and maintain financial stability.
These benefits can provide peace of mind and long-term financial security. Consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized financial advice.
7.3 Personal and Professional Development
In addition to financial benefits, a college education can also contribute to personal and professional development.
- Critical Thinking: College courses can help you develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
- Networking Opportunities: College provides opportunities to network with peers, faculty, and professionals in your field.
- Personal Growth: A college education can broaden your horizons, enhance your understanding of the world, and foster personal growth.
These benefits can enrich your life and contribute to your overall success. For expert guidance on career planning and personal development, visit HOW.EDU.VN.
7.4 Long-Term Financial Benefits
The long-term financial benefits of a college education can outweigh the initial costs and provide a solid foundation for future success.
- Increased Savings: Higher earnings can lead to increased savings and investment opportunities.
- Retirement Planning: College graduates are better positioned to save for retirement and secure their financial future.
- Homeownership: A college degree can make it easier to qualify for a mortgage and achieve the dream of homeownership.
These long-term benefits can provide financial security and improve your quality of life. For comprehensive financial planning that accounts for these factors, connect with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
8. What are Some of the Most Expensive Colleges in the U.S.?
The cost of college can vary significantly between institutions. Some colleges in the U.S. are known for their high tuition rates. Understanding which colleges are the most expensive can help you make informed decisions about your education.
8.1 List of Most Expensive Private Nonprofit Universities
Here is a list of some of the most expensive 4-year private nonprofit universities in the U.S., based on their tuition costs:
| Institution | Location | Tuition |
|---|---|---|
| Jewish Theological Seminary of America | New York, NY | $68,365 |
| Kenyon College | Gambier, OH | $66,490 |
| Columbia University in the City of New York | New York, NY | $66,139 |
| Franklin and Marshall College | Lancaster, PA | $65,844 |
| Tufts University | Medford, MA | $65,222 |
| Brown University | Providence, RI | $65,146 |
| Colorado College | Colorado Springs, CO | $65,028 |
| Bard College at Simon’s Rock | Great Barrington, MA | $64,951 |
| Vassar College | Poughkeepsie, NY | $64,800 |
| Reed College | Portland, OR | $64,760 |
This list provides a snapshot of the high tuition costs at some of the most prestigious private universities in the U.S. For expert guidance on navigating these costs and exploring financial aid options, visit HOW.EDU.VN.
8.2 Factors Contributing to High Tuition Costs
Several factors contribute to the high tuition costs at these institutions:
- Prestige and Reputation: Highly ranked universities often charge higher tuition rates due to their reputation and the perceived value of their degrees.
- Endowments and Resources: Wealthy universities with large endowments can afford to invest more in their facilities, faculty, and student services, which drives up costs.
- Location: Colleges located in expensive urban areas often have higher operating costs, which are passed on to students in the form of higher tuition rates.
- Demand: High demand for admission allows these universities to charge higher tuition rates without significantly impacting enrollment.
Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your education and explore alternative options. Consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized financial advice.
9. What are Some of the Most Affordable Colleges in the U.S.?
While some colleges are known for their high tuition rates, others offer more affordable options. Understanding which colleges are the most affordable can help you make informed decisions about your education and reduce your overall debt burden.
9.1 List of Most Affordable Private Nonprofit Universities
Here is a list of some of the most affordable 4-year private nonprofit universities in the U.S., based on their tuition costs:
| Institution | Location | Tuition |
|---|---|---|
| Turtle Mountain Community College | Belcourt, ND | $2,482 |
| Berkeley School of Theology | Berkeley, CA | $2,896 |
| Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science | Rochester, MN | $3,197 |
| Grace Mission University | Fullerton, CA | $3,480 |
| Kairos University | Sioux Falls, SD | $3,600 |
| Blackfeet Community College | Blackfeet reservation, MT | $3,610 |
| Ensign College | Salt Lake City, UT | $3,766 |
| Universidad Pentecostal Mizpa | Rio Piedras, PR | $4,220 |
| United Tribes Technical College | Bismarck, ND | $4,252 |
| Brigham Young University-Idaho | Rexburg, ID | $4,536 |
This list highlights the affordable tuition costs at these private universities. For expert guidance on navigating these options and exploring financial aid, visit HOW.EDU.VN.
9.2 Strategies for Finding Affordable Colleges
There are several strategies you can use to find affordable colleges and reduce your overall debt burden:
- Consider Public Universities: Public universities typically have lower tuition rates than private institutions, especially for in-state students.
- Attend Community College First: Starting at a community college and then transferring to a 4-year university can save you a significant amount of money on tuition.
- Apply for Financial Aid and Scholarships: Financial aid and scholarships are essential resources for students seeking to reduce the cost of college tuition.
- Explore Online Programs: Online programs can often be more affordable than traditional on-campus programs.
By using these strategies, you can make higher education more accessible and affordable. Consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized financial advice.
10. What are the Average College Costs by State?
The cost of college can vary significantly from state to state. Understanding the average college costs in different states can help you make informed decisions about your education and explore affordable options.
10.1 Overview of State Tuition Costs
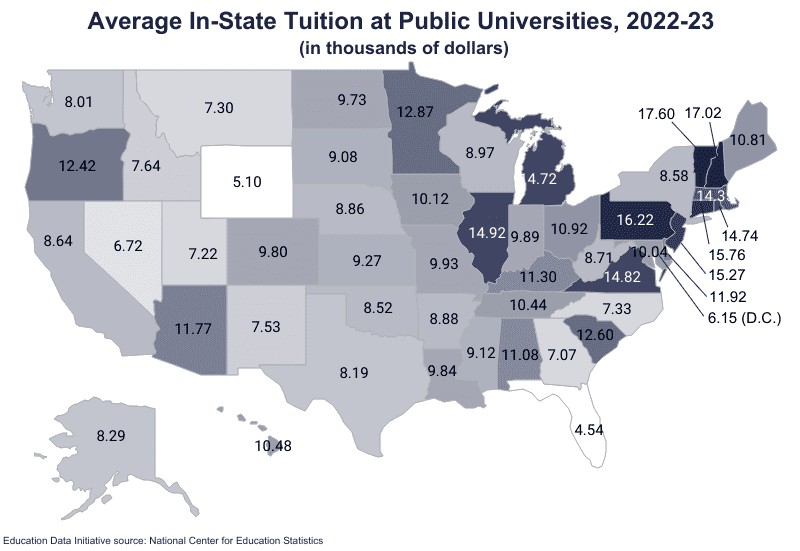
The average cost of in-state tuition and fees varies from state to state and year to year. The difference between the lowest and highest average is $13,060.
- Most Expensive States: The most expensive public schools are in the Northeast, in and around what is traditionally called New England.
- Least Expensive States: The least expensive schools are in the South and Plains regions.
- Average Tuition Among Most Expensive States: The average tuition among the 10 most expensive states for public universities is $15,542.
- Average Tuition Among Least Expensive States: The average tuition among the states with the most reasonably priced public universities is $6,660.
These figures highlight the significant differences in tuition costs across the U.S. For expert guidance on navigating these costs and exploring financial aid options, visit HOW.EDU.VN.
10.2 Table of In-State Public University Costs by State (2022-23)
Here is a table showing the most to least expensive in-state public universities by state for the 2022-23 academic year:
| State | Tuition & Fees | Tuition + Room & Board |
|---|---|---|
| Vermont | $17,600 | $50,094 |
| New Hampshire | $17,019 | $19,557 |
| Pennsylvania | $16,217 | $47,222 |
| Connecticut | $15,763 | $44,931 |
| New Jersey | $15,265 | $40,366 |
| Illinois | $14,921 | $37,646 |
| Virginia | $14,825 | $24,043 |
| Rhode Island | $14,744 | $49,792 |
| Michigan | $14,718 | $33,385 |
| Massachusetts | $14,345 | $53,789 |
| Minnesota | $12,873 | $35,914 |
| South Carolina | $12,604 | $28,730 |
| Oregon | $12,424 | $47,224 |
| Delaware | $11,922 | $12,154 |
| Arizona | $11,768 | $13,485 |
| Kentucky | $11,299 | $28,001 |
| Alabama | $11,081 | $17,687 |
| Ohio | $10,922 | $37,610 |
| Maine | $10,813 | $38,972 |
| Hawaii | $10,484 | $21,851 |
| Tennessee | $10,437 | $31,885 |
| Iowa | $10,121 | $37,623 |
| Maryland | $10,041 | $48,240 |
| Missouri | $9,926 | $30,660 |
| Indiana | $9,886 | $37,987 |
| Louisiana | $9,843 | $44,485 |
| Colorado | $9,798 | $27,474 |
| National Average | $9,750 | $35,248 |
| North Dakota | $9,728 | $16,990 |
| Kansas | $9,274 | $31,116 |
| Mississippi | $9,120 | $20,042 |
| South Dakota | $9,079 | $28,687 |
| Wisconsin | $8,974 | $37,686 |
| Arkansas | $8,879 | $24,798 |
| Nebraska | $8,862 | $26,002 |
| West Virginia | $8,715 | $12,133 |
| California | $8,637 | $42,017 |
| New York | $8,575 | $46,280 |
| Oklahoma | $8,519 | $31,140 |
| Alaska | $8,291 | $20,148 |
| Texas | $8,195 | $40,142 |
| Washington | $8,006 | $42,339 |
| Idaho | $7,640 | $6,970 |
| New Mexico | $7,526 | $27,340 |
| North Carolina | $7,327 | $40,176 |
| Montana | $7,299 | $31,464 |
| Utah | $7,215 | $8,123 |
| Georgia | $7,075 | $32,114 |
| Nevada | $6,723 | $24,246 |
| District of Columbia | $6,152 | $47,066 |
| Wyoming | $5,100 | § |
| Florida | $4,540 | $30,928 |
§No data for Wyoming.
This table provides a comprehensive overview of in-state public university costs by state. For expert guidance on navigating these options and exploring financial aid, visit HOW.EDU.VN.
10.3 Factors Influencing State Tuition Costs
Several factors influence state tuition costs:
- State Funding: States with higher levels of funding for public universities tend to have lower tuition costs.
- Cost of Living: States with higher costs of living may have higher tuition rates to cover operating expenses.
- Demand for Higher Education: States with higher demand for higher education may have higher tuition rates due to increased enrollment.
- Economic Conditions: Economic conditions in a state can impact tuition rates, as universities may need to increase tuition to offset budget cuts during economic downturns.
Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your education and explore affordable options. Consult with the experts at how.edu.vn for personalized financial advice.
11. How Does Lost Income Affect the Overall Cost of College?
One of the often-overlooked expenses of attending college is the loss of potential income. Students who are enrolled in college full-time may have limited opportunities to work and earn money, which can significantly impact the overall cost of their education.
11.1 Calculating Lost Income
To understand how lost income affects the overall cost of college, it’s important to calculate the potential earnings that students forgo while attending school.
- Median Weekly Income for High School Graduates: The median weekly income for a high school graduate is $899, or $46,748 per year.
- Potential Earnings Over Four Years: In four years, the average worker with a high school diploma may earn $186,992.
- Impact of Unemployment: The unemployment rate among high school graduates is 3.9%, which is 77.3% higher than the unemployment rate among bachelor’s degree holders.
- Unemployment Among Young Workers: 18- and 19-year-olds have an average unemployment rate of 12.5%; workers aged 20 to 24 years have an average unemployment rate of 7.8%.
These figures highlight the significant financial impact of lost income while attending college. For expert guidance on financial planning and career development, visit HOW.EDU
