Insulation cost is a common concern for homeowners looking to improve energy efficiency and comfort. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading Ph.D. experts who can provide tailored advice on insulation types, installation costs, and long-term savings. Discover how the right insulation can significantly reduce your energy bills and enhance your home’s value. Contact us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212. Also, explore our website at HOW.EDU.VN for more details on thermal performance, acoustic insulation, and energy conservation strategies.
1. What Factors Influence How Much Insulation Costs?
The cost of insulation varies widely depending on several key factors. Understanding these elements will help you budget effectively and choose the best insulation for your needs.
1.1. Type of Insulation Material
Different insulation materials have different price points. Here’s a breakdown of common insulation types and their typical costs:
-
Fiberglass: One of the most affordable options, fiberglass insulation comes in batts, rolls, and loose-fill. It is made from spun glass fibers and is effective in resisting heat flow.
-
Cellulose: Made from recycled paper, cellulose insulation is an eco-friendly option often used as loose-fill. It has good thermal performance and can also help with soundproofing.
-
Spray Foam: Known for its excellent air sealing properties, spray foam insulation comes in two main types: open-cell and closed-cell. Closed-cell spray foam has a higher R-value and better moisture resistance but is more expensive.
-
Mineral Wool: Also known as rock wool or slag wool, mineral wool is made from recycled industrial waste. It offers good thermal and acoustic insulation and is fire-resistant.
-
Rigid Foam Boards: These boards are typically made from polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, or polyurethane. They are often used for insulating walls, roofs, and foundations.
Here’s a table summarizing the approximate costs per square foot for different insulation materials:
| Insulation Type | Cost per Square Foot (Material Only) |
|---|---|
| Fiberglass Batts | $0.30 – $1.50 |
| Cellulose (Loose-Fill) | $0.60 – $2.70 |
| Spray Foam (Open-Cell) | $0.44 – $1.50 |
| Spray Foam (Closed-Cell) | $1.00 – $4.50 |
| Mineral Wool | $0.80 – $2.00 |
| Rigid Foam Boards | $1.00 – $5.00 |
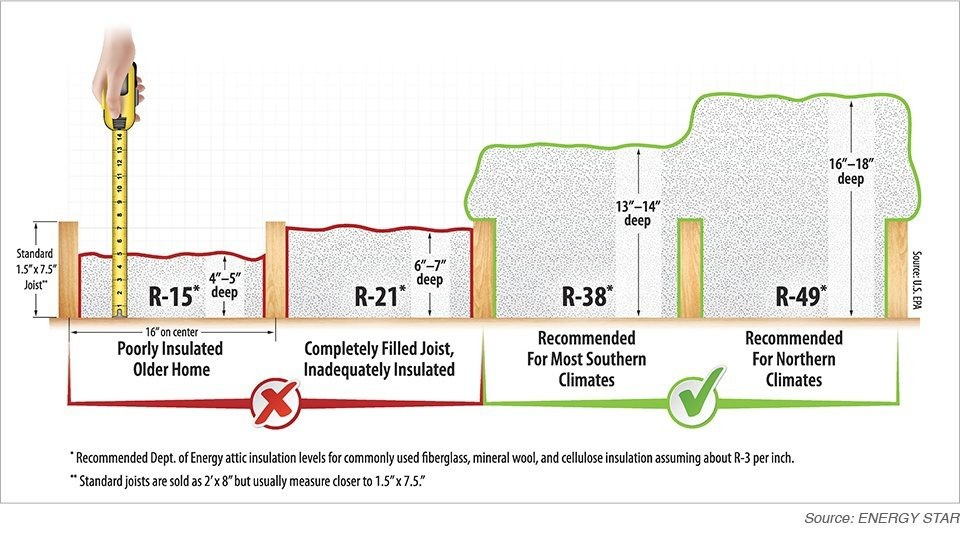
1.2. R-Value Requirements
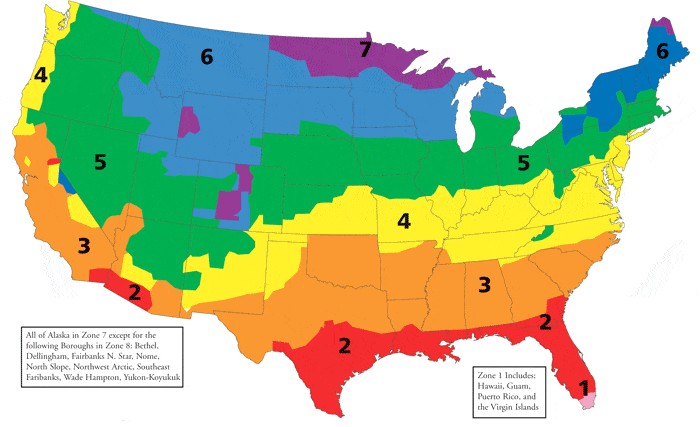
R-value measures an insulation material’s resistance to heat flow. Higher R-values provide better insulation. The R-value you need depends on your climate zone, the area you are insulating (walls, attic, floors), and local building codes.
-
Climate Zone: Areas with colder climates require higher R-values to keep homes warm, while warmer climates need lower R-values to keep homes cool.
-
Location: Attics typically require higher R-values than walls or floors because heat rises.
-
Building Codes: Local building codes often specify minimum R-values for new construction and renovations.
Here’s a general guideline for recommended R-values based on climate zone and location:
| Location | Climate Zone | Recommended R-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Attic | Cold | R-49 to R-60 |
| Attic | Moderate | R-38 to R-49 |
| Attic | Warm | R-30 to R-38 |
| Walls | Cold | R-13 to R-21 |
| Walls | Moderate | R-13 to R-15 |
| Walls | Warm | R-13 |
| Floors | Cold | R-25 to R-30 |
| Floors | Moderate | R-19 |
| Floors | Warm | R-13 |
1.3. Labor Costs
Installation costs can significantly impact the overall price of insulation. Labor costs vary depending on the complexity of the job, the type of insulation, and the geographic location.
-
Complexity: Installing insulation in hard-to-reach areas or dealing with existing insulation removal can increase labor costs.
-
Insulation Type: Spray foam and rigid foam board installations often require professional installers due to the specialized equipment and expertise needed.
-
Location: Labor costs tend to be higher in urban areas compared to rural areas.
On average, labor costs can add an additional $0.50 to $3.00 per square foot to the total insulation cost.
1.4. Size and Scope of the Project
The total area you need to insulate directly affects the amount of material and labor required, thus impacting the overall cost. Insulating an entire attic will cost more than insulating a small section of wall.
1.5. Existing Insulation Removal
If you have old or damaged insulation, it may need to be removed before new insulation can be installed. Removal costs can range from $1 to $3 per square foot, depending on the type of insulation and the extent of the removal.
1.6. Additional Costs
-
Air Sealing: Addressing air leaks before insulating can improve the effectiveness of the insulation. Air sealing costs can include sealing gaps around windows, doors, and other openings.
-
Vapor Barriers: In certain climates, vapor barriers are needed to prevent moisture buildup within the walls and attic. These can add to the overall cost.
-
Permits and Inspections: Some areas require permits and inspections for insulation projects, which can incur additional fees.
2. How Much Does Different Types of Insulation Cost?
Understanding the specific costs associated with each type of insulation can help you make an informed decision.
2.1. Fiberglass Insulation Costs
Fiberglass insulation is a popular and cost-effective choice for many homeowners. It is made from fine glass fibers and is available in batts, rolls, and loose-fill forms.
-
Material Costs:
- Batts: $0.30 to $1.50 per square foot
- Rolls: $0.30 to $1.00 per square foot
- Loose-Fill: $0.50 to $1.00 per square foot
-
Installation Costs:
- DIY: Minimal, as it is relatively easy to install yourself.
- Professional: $0.50 to $1.00 per square foot.
-
Pros:
- Affordable
- Easy to install
- Widely available
-
Cons:
- Lower R-value compared to other options
- Can cause skin and respiratory irritation during installation
2.2. Cellulose Insulation Costs
Cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper and is treated to be fire-resistant. It is typically installed as loose-fill and is known for its good thermal and acoustic properties.
-
Material Costs: $0.60 to $2.70 per square foot.
-
Installation Costs:
- DIY: Possible with rented equipment.
- Professional: $0.50 to $1.50 per square foot.
-
Pros:
- Eco-friendly
- Good thermal and acoustic performance
- Effective at filling small gaps
-
Cons:
- Can settle over time, reducing its R-value
- Requires specialized equipment for installation
2.3. Spray Foam Insulation Costs
Spray foam insulation is a high-performance option that provides excellent air sealing and thermal insulation. It comes in two main types: open-cell and closed-cell.
-
Open-Cell Spray Foam:
- Material Costs: $0.44 to $1.50 per square foot.
- Installation Costs: $1.00 to $2.00 per square foot.
-
Closed-Cell Spray Foam:
- Material Costs: $1.00 to $4.50 per square foot.
- Installation Costs: $1.50 to $3.00 per square foot.
-
Pros:
- Excellent air sealing
- High R-value (especially closed-cell)
- Moisture-resistant (closed-cell)
-
Cons:
- More expensive than other options
- Requires professional installation
- Can release harmful chemicals during installation if not done properly
2.4. Mineral Wool Insulation Costs
Mineral wool insulation is made from rock, slag, or glass fibers. It is available in batts, rolls, and loose-fill forms.
-
Material Costs: $0.80 to $2.00 per square foot.
-
Installation Costs:
- DIY: Possible for batts and rolls.
- Professional: $0.50 to $1.50 per square foot.
-
Pros:
- Good thermal and acoustic performance
- Fire-resistant
- Environmentally friendly (made from recycled materials)
-
Cons:
- Can be more expensive than fiberglass
- May cause skin irritation during installation
2.5. Rigid Foam Board Insulation Costs
Rigid foam boards are typically made from polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, or polyurethane. They are used for insulating walls, roofs, and foundations.
-
Material Costs: $1.00 to $5.00 per square foot.
-
Installation Costs:
- DIY: Possible for some applications.
- Professional: $1.00 to $3.00 per square foot.
-
Pros:
- High R-value
- Moisture-resistant
- Durable
-
Cons:
- More expensive than other options
- Requires precise cutting and fitting
- May require specialized fasteners
3. How to Calculate the Cost of Your Insulation Project
To estimate the cost of your insulation project, follow these steps:
3.1. Measure the Area to Be Insulated
Determine the square footage of the area you plan to insulate. This includes attics, walls, floors, and crawl spaces.
3.2. Determine the Required R-Value
Check local building codes and recommendations for the appropriate R-value for your climate zone and location.
3.3. Choose the Insulation Material
Select the insulation material that best fits your budget and performance requirements. Consider factors such as R-value, ease of installation, and environmental impact.
3.4. Calculate Material Costs
Multiply the square footage by the cost per square foot of the chosen insulation material.
3.5. Estimate Labor Costs
If you plan to hire a professional installer, get quotes from several contractors. Labor costs can vary, so it’s important to get multiple estimates.
3.6. Add Additional Costs
Factor in the costs of removing old insulation, air sealing, vapor barriers, permits, and inspections.
3.7. Total Cost
Add up all the material, labor, and additional costs to get the total estimated cost of your insulation project.
4. Cost-Saving Tips for Insulation
There are several ways to save money on your insulation project without sacrificing performance.
4.1. DIY Installation
If you are comfortable with home improvement projects, installing insulation yourself can save on labor costs. Fiberglass batts and rolls are relatively easy to install, while other materials like spray foam require professional expertise.
4.2. Purchase Materials in Bulk
Buying insulation materials in bulk can often result in lower prices per square foot. Check with local suppliers for bulk discounts.
4.3. Take Advantage of Rebates and Incentives
Many utility companies and government agencies offer rebates and incentives for energy-efficient upgrades, including insulation. Check with your local utility company and the ENERGY STAR website for available programs.
4.4. Focus on High-Impact Areas
Prioritize insulating areas that will provide the greatest energy savings, such as attics and walls.
4.5. Air Sealing
Addressing air leaks before insulating can significantly improve the effectiveness of the insulation. Sealing gaps around windows, doors, and other openings can reduce energy loss and lower your heating and cooling bills.
5. Benefits of Proper Insulation
Investing in proper insulation provides numerous benefits beyond energy savings.
5.1. Reduced Energy Bills
Proper insulation helps maintain a consistent temperature inside your home, reducing the need for excessive heating and cooling. This can lead to significant savings on your energy bills.
5.2. Increased Comfort
Insulation helps eliminate drafts and cold spots, creating a more comfortable living environment.
5.3. Improved Air Quality
Insulation can help reduce the infiltration of allergens and pollutants, improving indoor air quality.
5.4. Noise Reduction
Certain types of insulation, such as cellulose and mineral wool, can help reduce noise transmission from outside and between rooms.
5.5. Enhanced Home Value
Proper insulation can increase the value of your home by making it more energy-efficient and comfortable.
5.6. Prevention of Moisture Problems
Insulation can help prevent moisture buildup in walls and attics, reducing the risk of mold and structural damage.
6. Case Studies: The Impact of Insulation on Home Energy Efficiency
To illustrate the impact of insulation on energy efficiency, let’s look at a couple of case studies.
6.1. Case Study 1: Attic Insulation Upgrade
-
Home: Single-family home in Chicago, Illinois
-
Existing Insulation: R-19 fiberglass batts
-
Upgrade: Added R-30 cellulose insulation
-
Results:
- Reduced heating bills by 20%
- Improved overall comfort
- Qualified for a utility rebate
-
Testimonial: “Since upgrading our attic insulation, our home is much warmer in the winter, and our heating bills have decreased significantly. It was a worthwhile investment.”
6.2. Case Study 2: Wall Insulation Retrofit
-
Home: Two-story home in Atlanta, Georgia
-
Existing Insulation: R-11 fiberglass batts
-
Upgrade: Injected R-13 spray foam insulation into wall cavities
-
Results:
- Reduced cooling bills by 15%
- Eliminated drafts and cold spots
- Improved indoor air quality
-
Testimonial: “The spray foam insulation made a noticeable difference in our home’s comfort. Our air conditioning runs less often, and we no longer have drafts in the winter.”
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Insulating Your Home
To ensure your insulation project is successful, avoid these common mistakes.
7.1. Insufficient R-Value
Using insulation with an insufficient R-value will not provide the desired energy savings and comfort. Check local building codes and recommendations for the appropriate R-value for your climate zone and location.
7.2. Improper Installation
Incorrect installation can significantly reduce the effectiveness of insulation. Ensure that insulation is properly fitted and sealed to prevent air leaks.
7.3. Ignoring Air Leaks
Air leaks can negate the benefits of insulation. Seal gaps around windows, doors, and other openings before insulating.
7.4. Neglecting Ventilation
Proper ventilation is essential to prevent moisture buildup in attics and walls. Ensure that your home has adequate ventilation.
7.5. Using the Wrong Type of Insulation
Different types of insulation are suited for different applications. Choose the insulation material that is best for the area you are insulating.
8. How to Choose the Right Insulation Contractor
Selecting the right insulation contractor is crucial for a successful project. Here are some tips for choosing a contractor.
8.1. Get Multiple Quotes
Obtain quotes from several contractors to compare prices and services.
8.2. Check Credentials
Verify that the contractor is licensed and insured.
8.3. Read Reviews
Check online reviews and ask for references from previous customers.
8.4. Ask Questions
Ask the contractor about their experience, the types of insulation they install, and their installation process.
8.5. Get a Written Contract
Ensure that the contract includes details about the scope of work, materials, costs, and timeline.
9. The Future of Insulation: Innovations and Trends
The insulation industry is continually evolving with new technologies and materials. Here are some emerging trends to watch:
9.1. Advanced Materials
Researchers are developing new insulation materials with improved thermal performance, such as aerogels and vacuum insulation panels (VIPs).
9.2. Smart Insulation
Smart insulation systems incorporate sensors and controls to optimize energy efficiency and monitor performance.
9.3. Sustainable Insulation
There is a growing demand for eco-friendly insulation materials made from recycled or renewable resources.
9.4. Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is being used to enhance the properties of insulation materials, such as increasing R-value and reducing thickness.
9.5. Integrated Building Systems
Insulation is increasingly being integrated into comprehensive building systems that optimize energy efficiency and indoor environmental quality.
10. Expert Insights on Insulation from HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading Ph.D. experts who can provide tailored advice on insulation types, installation costs, and long-term savings. Our experts offer insights into the latest insulation technologies and best practices for energy-efficient homes.
10.1. Meet Our Experts
| Expert Name | Field of Expertise | Credentials |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Emily Carter | Energy Efficiency | Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering, Certified Energy Manager (CEM) |
| Dr. James Miller | Building Science | Ph.D. in Architectural Engineering, LEED Accredited Professional (LEED AP) |
| Dr. Sarah Johnson | Sustainable Design | Ph.D. in Environmental Engineering, WELL Accredited Professional (WELL AP) |
10.2. Expert Advice
-
Dr. Emily Carter: “Proper insulation is a critical component of energy-efficient homes. Focus on air sealing and choosing the right R-value for your climate zone.”
-
Dr. James Miller: “Consider the long-term benefits of high-performance insulation materials like spray foam and rigid foam boards. They can significantly reduce energy consumption and improve comfort.”
-
Dr. Sarah Johnson: “Opt for sustainable insulation materials made from recycled or renewable resources to minimize your environmental impact.”
11. Insulation and Home Value: What You Need to Know
Investing in insulation not only improves your home’s energy efficiency but also enhances its market value.
11.1. Energy Efficiency and Home Value
Homes with proper insulation are more attractive to potential buyers due to lower energy bills and increased comfort.
11.2. Appraisal Considerations
Appraisers often consider the energy efficiency of a home when determining its value. Upgrading insulation can positively impact the appraisal.
11.3. Marketing Your Home
Highlight the energy-efficient features of your home, including insulation, when marketing it for sale. This can attract environmentally conscious buyers and potentially increase the selling price.
11.4. Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculate the ROI of your insulation project by comparing the cost of the upgrade to the long-term energy savings and increased home value.
12. Insulation and Climate Change: A Sustainable Solution
Insulation plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change by reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
12.1. Reducing Carbon Footprint
Proper insulation can significantly reduce your home’s carbon footprint by decreasing the need for heating and cooling.
12.2. Energy Conservation
Insulation helps conserve energy resources by minimizing energy waste.
12.3. Sustainable Materials
Choosing sustainable insulation materials made from recycled or renewable resources can further reduce your environmental impact.
12.4. Government Initiatives
Many government initiatives promote energy efficiency through insulation upgrades, providing incentives and rebates to homeowners.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Insulation
Here are some frequently asked questions about insulation to help you make informed decisions.
13.1. What is R-value?
R-value measures an insulation material’s resistance to heat flow. Higher R-values provide better insulation.
13.2. How much insulation do I need?
The amount of insulation you need depends on your climate zone, the area you are insulating, and local building codes.
13.3. What type of insulation is best for my home?
The best type of insulation depends on your budget, performance requirements, and environmental concerns.
13.4. Can I install insulation myself?
Some types of insulation, such as fiberglass batts and rolls, are relatively easy to install yourself. Other materials, like spray foam, require professional installation.
13.5. How much does it cost to insulate an attic?
The cost to insulate an attic varies depending on the type of insulation, the size of the attic, and labor costs.
13.6. How do I find a qualified insulation contractor?
Get multiple quotes, check credentials, read reviews, and ask questions before hiring an insulation contractor.
13.7. What are the benefits of insulation?
The benefits of insulation include reduced energy bills, increased comfort, improved air quality, and enhanced home value.
13.8. How long does insulation last?
The lifespan of insulation varies depending on the type of material and environmental conditions. Some insulation can last for decades.
13.9. What is air sealing?
Air sealing is the process of sealing gaps and cracks in your home to prevent air leaks. It is often done in conjunction with insulation to improve energy efficiency.
13.10. Are there any rebates or incentives for insulation?
Many utility companies and government agencies offer rebates and incentives for energy-efficient upgrades, including insulation.
14. How HOW.EDU.VN Can Help You
Are you struggling to find expert advice on insulation? Do you need tailored solutions to improve your home’s energy efficiency? At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges homeowners face when trying to make informed decisions about insulation.
14.1. Connect with Leading Ph.D. Experts
We offer a unique platform where you can connect directly with over 100 renowned Ph.D. experts from various fields. Get personalized advice and solutions tailored to your specific needs.
14.2. Save Time and Money
Finding the right expert can be time-consuming and costly. HOW.EDU.VN streamlines the process, saving you valuable time and resources.
14.3. Ensure Confidentiality and Reliability
Your privacy and trust are our top priorities. We ensure that all consultations are confidential and that our experts are highly vetted and reliable.
14.4. Get Practical, Actionable Advice
Our experts provide practical, actionable advice that you can implement immediately to improve your home’s insulation and energy efficiency.
Don’t let insulation challenges overwhelm you. Contact us today at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212. Also, explore our website at how.edu.vn to connect with our Ph.D. experts and start your journey toward a more energy-efficient and comfortable home.
