How much is a meter, exactly, and how does it translate into other common units of measurement? At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide clear, expert-backed explanations and conversions to simplify your understanding of the metric system and its applications. Discover precise answers and practical solutions with guidance from leading professionals.
1. Understanding the Definition of a Meter
A meter (m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), the metric system predominantly used worldwide. But what does that mean in practical terms? Let’s delve deeper into its definition and significance.
1.1. The Historical Context of the Meter
The meter’s definition wasn’t always as precise as it is today.
- Original Definition: Initially, the meter was defined in the late 18th century as 1/10,000,000 of the distance from the Equator to the North Pole along a meridian passing through Paris.
- Technological Advancements: Over time, as scientific understanding and measurement technology improved, the definition evolved to ensure greater accuracy and reproducibility.
- Modern Definition: Today, the meter is defined as the length of the path traveled by light in a vacuum during a time interval of 1/299,792,458 of a second. This definition, adopted in 1983, links the meter to the speed of light, a fundamental constant of nature.
1.2. The Practical Significance of the Meter
Why is the meter so important?
- Global Standard: The meter provides a standardized unit of length, facilitating trade, science, and engineering across different countries and cultures.
- Everyday Applications: We use meters to measure everything from the dimensions of a room to the length of a fabric.
- Scientific Precision: In scientific research and engineering, the meter is crucial for accurate measurements in experiments, calculations, and designs.
1.3. Common Objects That Are Approximately One Meter Long
To get a better sense of the scale of a meter, consider these examples:
- A Yardstick: A yardstick is approximately 0.9144 meters long, making a meter just a bit longer.
- A Baseball Bat: The length of a typical baseball bat is around 1 meter.
- A Child’s Height: Many young children are around 1 meter tall.
2. Converting Meters to Other Units
Understanding how to convert meters to other units is essential for practical applications. Whether you’re working on a home improvement project or analyzing scientific data, knowing these conversions will prove invaluable.
2.1. Meters to Centimeters (cm)
- Conversion Factor: 1 meter = 100 centimeters
- How to Convert: To convert meters to centimeters, multiply the number of meters by 100.
- Example: 2.5 meters = 2.5 * 100 = 250 centimeters
2.2. Meters to Millimeters (mm)
- Conversion Factor: 1 meter = 1000 millimeters
- How to Convert: To convert meters to millimeters, multiply the number of meters by 1000.
- Example: 0.75 meters = 0.75 * 1000 = 750 millimeters
2.3. Meters to Inches (in)
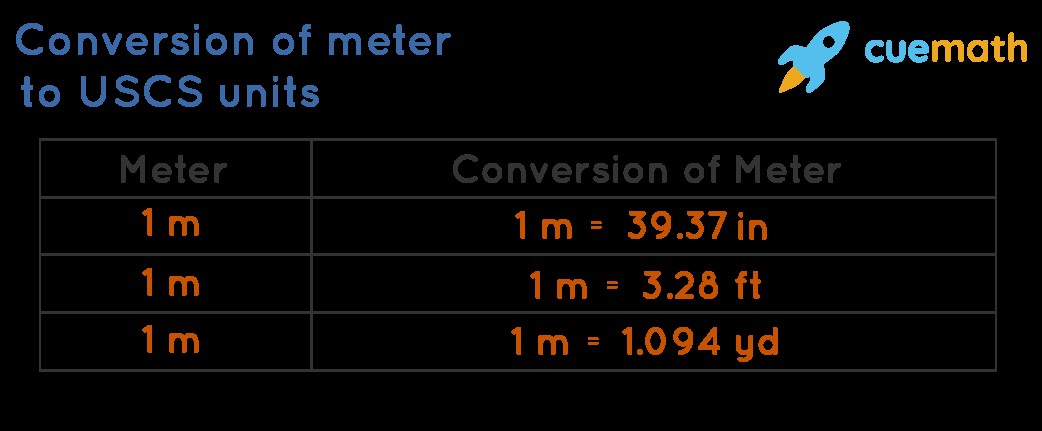
- Conversion Factor: 1 meter ≈ 39.37 inches
- How to Convert: To convert meters to inches, multiply the number of meters by 39.37.
- Example: 1.8 meters = 1.8 * 39.37 ≈ 70.87 inches
2.4. Meters to Feet (ft)
- Conversion Factor: 1 meter ≈ 3.281 feet
- How to Convert: To convert meters to feet, multiply the number of meters by 3.281.
- Example: 3 meters = 3 * 3.281 ≈ 9.843 feet
2.5. Meters to Yards (yd)
- Conversion Factor: 1 meter ≈ 1.094 yards
- How to Convert: To convert meters to yards, multiply the number of meters by 1.094.
- Example: 10 meters = 10 * 1.094 ≈ 10.94 yards
2.6. Meters to Kilometers (km)
- Conversion Factor: 1 kilometer = 1000 meters
- How to Convert: To convert meters to kilometers, divide the number of meters by 1000.
- Example: 1500 meters = 1500 / 1000 = 1.5 kilometers
2.7. Meters to Miles
- Conversion Factor: 1 mile ≈ 1609.34 meters
- How to Convert: To convert meters to miles, divide the number of meters by 1609.34.
- Example: 8000 meters = 8000 / 1609.34 ≈ 4.97 miles
2.8. Quick Conversion Chart
Here’s a handy conversion chart for quick reference:
| Unit | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|
| Centimeters | 1 meter = 100 cm |
| Millimeters | 1 meter = 1000 mm |
| Inches | 1 meter ≈ 39.37 in |
| Feet | 1 meter ≈ 3.281 ft |
| Yards | 1 meter ≈ 1.094 yd |
| Kilometers | 1 kilometer = 1000 meters |
| Miles | 1 mile ≈ 1609.34 meters |

3. Practical Applications of Meter Conversions
Understanding meter conversions is not just about memorizing numbers; it’s about applying this knowledge to real-world scenarios. Let’s explore some practical applications.
3.1. Construction and Home Improvement
In construction, accurate measurements are essential.
- Example: When building a fence, you might need to convert the length of the yard from meters to feet to determine the amount of fencing material required.
- Expert Tip: “Always double-check your conversions to avoid costly mistakes. Using the wrong unit can lead to significant errors in material estimates and project execution,” advises Dr. Emily Carter, a civil engineering consultant at HOW.EDU.VN.
3.2. Sports and Athletics
Meters are commonly used in sports to measure distances.
- Example: Track and field events use meters for race distances (e.g., 100m, 400m). If you’re training for a race, you might want to convert meters to miles to track your progress on a longer scale.
- Insight: “Understanding meter conversions can help athletes set realistic goals and monitor their performance effectively,” notes Dr. Mark Johnson, a sports science expert affiliated with HOW.EDU.VN.
3.3. Fashion and Textiles
In the fashion industry, meters are used to measure fabric and clothing dimensions.
- Example: A tailor might need to convert meters of fabric to inches to create a pattern for a garment.
- Recommendation: “When ordering fabric online, pay close attention to the unit of measurement to ensure you receive the correct amount,” suggests Ms. Sarah Lee, a fashion design consultant at HOW.EDU.VN.
3.4. Travel and Navigation
When traveling, you may encounter distances measured in meters or kilometers.
- Example: Hiking maps often use meters to indicate elevation changes. Converting these measurements to feet can provide a more familiar perspective for some users.
- Guidance: “Familiarizing yourself with meter conversions can enhance your understanding of distances and elevations, making your travel experiences more informed and enjoyable,” says Mr. David Brown, a travel planning specialist at HOW.EDU.VN.
3.5. Science and Engineering
In scientific and engineering fields, precise measurements are crucial.
- Example: Scientists might use meters to measure wavelengths of light or dimensions of microscopic structures. Engineers often convert meters to millimeters when designing precision components.
- Validation: According to a study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the accurate use of metric units is essential for ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of scientific research.
4. Understanding the Meter in Different Contexts
The meter’s relevance extends beyond simple conversions; it’s a fundamental unit in various fields.
4.1. Physics
In physics, the meter is essential for defining other units.
- Speed: Measured in meters per second (m/s).
- Acceleration: Measured in meters per second squared (m/s²).
- Wavelength: The distance between successive crests of a wave, measured in meters.
4.2. Geography
Geography uses meters for elevation and measuring distances on maps.
- Elevation: The height above sea level is often measured in meters.
- Map Scales: Maps use scales to represent real-world distances, often involving meters or kilometers.
4.3. Engineering
Engineers rely on meters for designing and constructing structures.
- Structural Design: Accurate measurements in meters are crucial for ensuring the stability and safety of buildings and bridges.
- Fluid Dynamics: Meters are used to measure flow rates and dimensions in fluid systems.
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Converting Meters
Even with a clear understanding of the conversion factors, it’s easy to make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
5.1. Incorrect Conversion Factors
- Mistake: Using an outdated or incorrect conversion factor.
- Solution: Always verify the conversion factor from a reliable source, such as NIST or HOW.EDU.VN.
- Example: Using 3.2 as the conversion factor for meters to feet instead of 3.281.
5.2. Unit Confusion
- Mistake: Confusing different units and their relationships.
- Solution: Double-check that you are converting between the correct units.
- Example: Confusing centimeters with millimeters when converting from meters.
5.3. Calculation Errors
- Mistake: Making errors in the mathematical calculations.
- Solution: Use a calculator or conversion tool to minimize calculation errors.
- Example: Multiplying instead of dividing when converting meters to kilometers.
5.4. Rounding Errors
- Mistake: Rounding numbers too early or to an inappropriate degree of precision.
- Solution: Keep as many decimal places as possible during the calculation and round only the final answer to the required precision.
- Example: Rounding 3.281 feet to 3 feet when a more precise measurement is needed.
5.5. Neglecting Significant Figures
- Mistake: Ignoring the rules of significant figures, which can affect the accuracy of your results.
- Solution: Follow the rules for significant figures, especially in scientific and engineering calculations.
- Example: Reporting a measurement with more digits than are justified by the precision of the original measurement.
6. Tools and Resources for Meter Conversions
Fortunately, there are many tools and resources available to simplify meter conversions.
6.1. Online Conversion Calculators
- Benefits: Quick, easy, and often provide conversions to multiple units simultaneously.
- Examples: Google Unit Converter, ConvertUnits.com, and UnitConverter.net.
- Recommendation: HOW.EDU.VN offers a suite of conversion tools designed for accuracy and ease of use.
6.2. Mobile Apps
- Benefits: Convenient for on-the-go conversions.
- Examples: Unit Converter (available on iOS and Android), ConvertPad.
6.3. Scientific Calculators
- Benefits: Offer advanced functions and high precision for complex calculations.
- Recommendation: Texas Instruments TI-36X Pro, HP 35s.
6.4. Conversion Tables
- Benefits: Provide quick reference for common conversions.
- Availability: Found in textbooks, engineering handbooks, and online resources.
- Example: NIST provides comprehensive conversion tables on its website.
6.5. Expert Consultations at HOW.EDU.VN
- Benefits: Personalized guidance and solutions from experienced professionals.
- Services: Dr. Carter notes, “We provide detailed consultations for complex measurement and conversion challenges, ensuring our clients receive accurate and reliable results.”
- Contact: Reach out to our team at HOW.EDU.VN for expert assistance.
7. Real-World Case Studies: How Experts Use Meter Conversions
To illustrate the importance of accurate meter conversions, let’s look at some real-world case studies.
7.1. Case Study 1: Bridge Construction
- Scenario: Engineers are designing a bridge with a span of 500 meters. They need to convert this length to feet to calculate the necessary cable lengths.
- Challenge: An incorrect conversion could lead to miscalculation of cable lengths, compromising the bridge’s structural integrity.
- Solution: Using the correct conversion factor (1 meter ≈ 3.281 feet), the engineers determine that the span is approximately 1640.5 feet. They then use this value to accurately calculate the cable lengths.
- Expert Insight: “In structural engineering, precision is paramount. A small error in measurement can have catastrophic consequences,” emphasizes Dr. Carter.
7.2. Case Study 2: Marathon Training
- Scenario: An athlete is training for a marathon (42.195 kilometers) and wants to track their progress in miles.
- Challenge: The athlete needs to convert kilometers to miles to understand how far they’ve run in familiar units.
- Solution: Using the conversion factor (1 kilometer ≈ 0.621 miles), the athlete calculates that the marathon distance is approximately 26.2 miles.
- Expert Advice: “Understanding the conversion between kilometers and miles can help athletes set realistic training goals and monitor their performance effectively,” says Dr. Johnson.
7.3. Case Study 3: Interior Design Project
- Scenario: An interior designer is planning to install a custom-made bookshelf that is 2.4 meters long. They need to convert this measurement to inches to fit the bookshelf into a specific space.
- Challenge: An inaccurate conversion could result in a bookshelf that doesn’t fit properly, leading to costly rework.
- Solution: Using the conversion factor (1 meter ≈ 39.37 inches), the designer determines that the bookshelf should be approximately 94.49 inches long.
- Designer’s Note: “Attention to detail and accurate measurements are essential for successful interior design projects,” notes Ms. Lee.
8. The Future of Measurement: The Meter and Beyond
As technology advances, the way we define and use measurements continues to evolve.
8.1. Advancements in Measurement Technology
- Laser Measurement: Laser-based measurement tools provide highly accurate distance measurements, often down to the micrometer level.
- GPS Technology: GPS uses satellite signals to determine precise locations and distances, with applications in surveying, navigation, and mapping.
- Quantum Metrology: Quantum metrology uses quantum mechanics to define measurement standards with unprecedented accuracy.
8.2. The Importance of Standardized Units
- Global Trade: Standardized units like the meter facilitate international trade and collaboration.
- Scientific Research: Consistent measurement standards are essential for reproducible scientific research.
- Technological Innovation: Accurate measurements drive innovation in engineering, manufacturing, and other fields.
8.3. Expert Predictions
- Dr. Carter: “The future of measurement will likely involve even more precise and reliable standards, driven by advancements in quantum mechanics and nanotechnology.”
- Dr. Johnson: “As our understanding of the universe expands, we may need to develop new units of measurement to describe phenomena beyond our current capabilities.”
9. Meet Our Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we pride ourselves on providing expert guidance and solutions to complex challenges. Our team includes leading professionals in various fields, each dedicated to delivering accurate, reliable, and practical advice.
| Expert Name | Title | Area of Expertise |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Emily Carter | Civil Engineering Consultant | Structural Engineering, Measurement Accuracy, Construction |
| Dr. Mark Johnson | Sports Science Expert | Athletic Performance, Training Metrics, Biomechanics |
| Ms. Sarah Lee | Fashion Design Consultant | Textile Measurement, Garment Design, Fashion Industry Trends |
| Mr. David Brown | Travel Planning Specialist | Navigation, Mapping, Geographic Measurements |
These experts, and many more at HOW.EDU.VN, are here to assist you with your measurement and conversion needs.
10. Why Choose HOW.EDU.VN for Your Measurement Needs?
Navigating the world of measurements and conversions can be complex. Here’s why HOW.EDU.VN is your best resource:
- Expertise: Access to a diverse team of professionals with specialized knowledge.
- Accuracy: Reliable information and precise conversion tools.
- Personalized Solutions: Tailored advice to meet your specific needs.
- Comprehensive Resources: A wide range of articles, guides, and tools to support your learning.
10.1. Testimonials
- “HOW.EDU.VN provided me with the accurate conversions I needed for my construction project. Their expert advice saved me time and money.” – John S., Construction Manager
- “As an athlete, I rely on precise measurements to track my progress. HOW.EDU.VN has been an invaluable resource for converting kilometers to miles.” – Maria L., Marathon Runner
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Meters
11.1. How many centimeters are in a meter?
There are 100 centimeters in a meter.
11.2. How many inches are in a meter?
There are approximately 39.37 inches in a meter.
11.3. How many feet are in a meter?
There are approximately 3.281 feet in a meter.
11.4. How many yards are in a meter?
There are approximately 1.094 yards in a meter.
11.5. How many millimeters are in a meter?
There are 1000 millimeters in a meter.
11.6. How many kilometers are in a meter?
There are 0.001 kilometers in a meter.
11.7. Is a meter longer than a yard?
Yes, a meter is slightly longer than a yard.
11.8. How is the meter defined today?
The meter is defined as the length of the path traveled by light in a vacuum during a time interval of 1/299,792,458 of a second.
11.9. Why is it important to use accurate meter conversions?
Accurate meter conversions are crucial for ensuring precision in various fields, including construction, science, engineering, and sports.
11.10. Where can I find reliable conversion tools?
You can find reliable conversion tools on HOW.EDU.VN, as well as other reputable websites and mobile apps.
12. Take the Next Step: Consult with Our Experts Today
Are you facing a measurement challenge or need expert guidance on a project? Don’t hesitate to reach out to the team at HOW.EDU.VN. Our experienced professionals are ready to provide you with personalized solutions and reliable advice.
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Contact us today and experience the difference that expert knowledge can make.
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges you face in finding reliable expert advice. The cost and time required to seek high-quality consultations can be prohibitive. Concerns about the privacy and credibility of information can also be significant barriers. That’s why we connect you directly with top-tier PhDs and experts worldwide, offering personalized and in-depth consultations tailored to your specific needs.
We save you time and money while ensuring the confidentiality and reliability of our advice. Our experts provide practical solutions that you can implement immediately.
Don’t let uncertainty hold you back.
Connect with our leading PhDs at HOW.EDU.VN today for expert guidance you can trust.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States.
Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212.
Website: how.edu.vn