The average college tuition for 4 years can range from around $108,584 for in-state public institutions to over $234,512 for private, nonprofit universities, excluding additional costs like living expenses and lost income. At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand that planning for college expenses can be overwhelming; that’s why we offer expert guidance to help you navigate the complexities of college financing. Understanding the costs associated with higher education and effective financial planning are crucial for students and their families.
1. Understanding the Average Cost of College
The cost of attending college is a significant investment. Knowing the average expenses can help you plan and budget effectively. Let’s break down the components of college costs and explore the different types of institutions.
1.1. Components of College Costs
The total cost of college includes several key components:
- Tuition and Fees: This is the base cost of attending classes and accessing university resources.
- Room and Board: This covers housing and meal plans for students living on campus.
- Books and Supplies: Textbooks, course materials, and other academic supplies are essential expenses.
- Additional Expenses: This includes transportation, personal care, entertainment, and other living costs.
1.2. Types of Institutions and Their Average Costs
The type of institution significantly impacts the total cost of college. Here’s a breakdown:
- Public 4-Year Institutions (In-State): These are generally the most affordable options for students who are residents of the state.
- Public 4-Year Institutions (Out-of-State): These are more expensive than in-state options, as they do not receive state subsidies for non-resident students.
- Private Nonprofit Universities: These institutions are typically more expensive than public colleges, but they often offer more financial aid and scholarship opportunities.
- Private For-Profit Colleges: These tend to be the most expensive, with varying quality of education and outcomes.
The following tables provide a detailed look at the average annual costs for different types of institutions:
Annual Cost of College, Public
| Institution Type | Cost of Tuition | Cost of Attendance** |
|---|---|---|
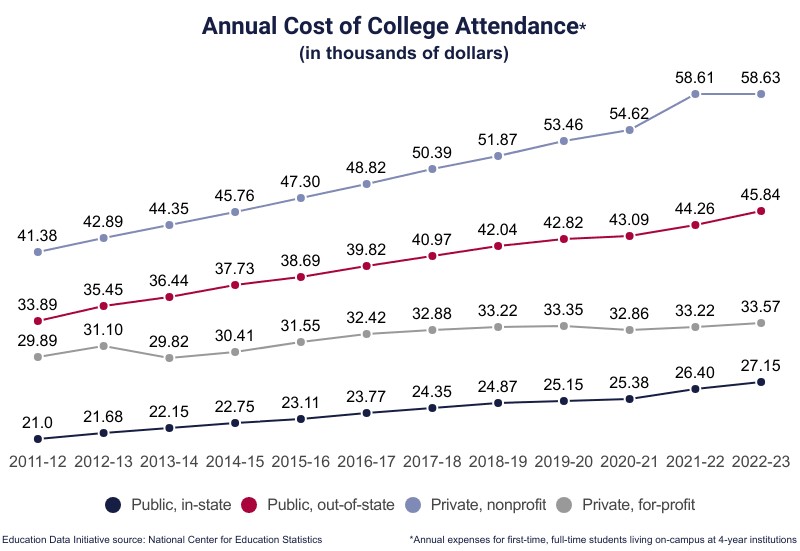
| 4-Year In-State | $9,750 | $27,146 |
| 4-Year Out-of-State† | $28,386 | $45,708 |
| 2-Year In-District | $3,598 | $17,439 |
**CoA does not account for potential lost income, student loan interest, nor moving expenses. †Out-of-state tuition estimate based on the previous year’s cost and the annual growth rate.
Annual Cost of College, Private
| Institution Type | Cost of Tuition | Cost of Attendance |
|---|---|---|
| 4-Year Nonprofit | $38,421 | $56,628 |
| 4-Year For-profit | $15,868 | $33,574 |
| 2-Year Nonprofit | $20,019 | $36,026 |
| 2-Year For-profit | $16,444 | $26,640 |
2. Breaking Down the Numbers: Tuition, Fees, and Other Expenses
To get a clearer picture of the overall cost, let’s delve deeper into the individual components of college expenses.
2.1. Average Tuition Costs
Tuition and fees typically make up the largest portion of college expenses. Here’s a detailed breakdown of average tuition costs:
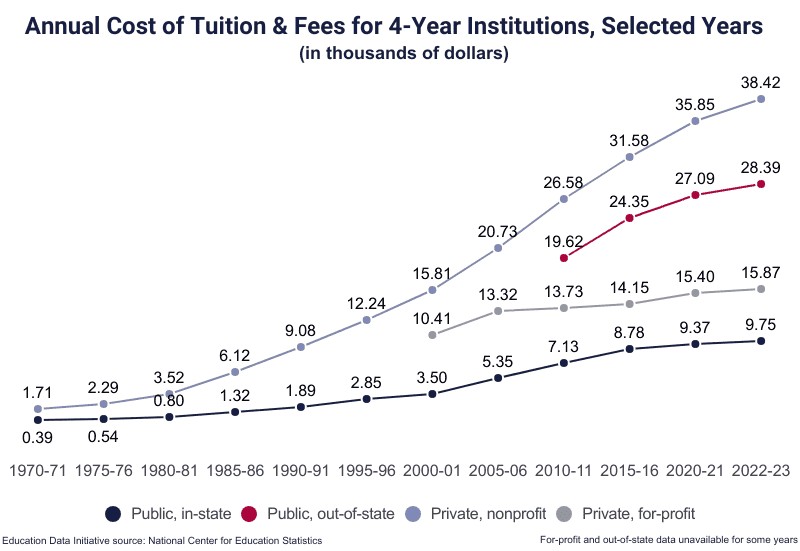
- 4-Year Institutions: The average cost of tuition at any 4-year institution is $17,709, representing 46.3% of college costs for a first-time, full-time student living on campus.
- Public 4-Year (In-State): The average cost of in-state tuition at public 4-year institutions is $9,750, representing 35.9% of the cost of attendance for a full-time student living on campus.
- Public 4-Year (Out-of-State): The cost of out-of-state tuition at public 4-year institutions is $28,445, representing 62.1% of the cost of attendance for on-campus students.
- Private 4-Year (Nonprofit): Among private 4-year institutions, the average tuition and fees at a typical nonprofit college total $38,421 annually, equivalent to 65.5% of college costs for a student living on campus.
- Private 4-Year (For-Profit): At a typical for-profit institution, tuition and fees average $15,868 annually, equivalent to 47.3% of the cost of attendance for an on-campus student.
- 2-Year Institutions: The average cost of tuition and fees at any 2-year institution is $3,885, or 22.3% of the cost of attendance.
- Public 2-Year (In-District): At public 2-year institutions or community colleges, in-district tuition and fees average $3,598 annually, equivalent to 21.6% of the cost of attendance for full-time students living on campus.
- Public 2-Year (Out-of-District): Out-of-district tuition and fees for the average public 2-year institution total $8,622 annually, equivalent to 39.8% of the cost of attendance.
- Private 2-Year (Nonprofit): At private 2-year institutions, students pay $20,019 in annual tuition and fees to attend nonprofit schools; tuition is 55.6% of the cost of attendance.
- Private 2-Year (For-Profit): Private, for-profit 2-year colleges charge $16,444, which is 61.7% of the cost of attendance.
2.2. The Cost of Books and Supplies
The cost of textbooks and supplies can vary widely depending on the program and institution.
- Public 4-Year Institutions: Students pay an average of $1,220 annually for textbooks and supplies.
- Private Nonprofit Institutions: Books and supplies average $1,215.
- Private For-Profit Institutions: The average cost is $990.
- Public 2-Year Institutions: Students pay an average of $1,467 each year.
- Private Nonprofit Institutions: Books and supplies average $930.
- Private For-Profit 2-Year Colleges: The average cost is $1,501.
2.3. Room and Board Expenses
The cost of room and board depends significantly on whether a student lives on or off campus.
- 4-Year Institutions: The cost of room and board is $12,917.
- Public 4-Year Institutions: Students living on campus pay an average of $12,302 annually.
- Private Nonprofit Institutions: On-campus boarders pay an average of $13,842 per academic year.
- Private For-Profit Institutions: On-campus room and board average $9,151.
- 2-Year Institutions: Room and board costs $7,717.
- Public 2-Year Institutions: Students living on campus pay an average of $7,420.
- Private Nonprofit 2-Year Colleges: On-campus boarders pay $12,732 annually.
- Private For-Profit Institutions: Charge $7,920 on average.
2.4. Additional Expenses to Consider
Additional expenses can add up significantly. These include:
- Transportation: Costs for getting to and from campus.
- Personal Care: Expenses for personal hygiene and grooming.
- Entertainment: Money spent on social activities and recreation.
Students living on campus at a public 4-year institution pay an average of $3,790 in additional annual expenses. Students who live off-campus may expect to pay $4,720 if they do not live with family; for students living with family, additional expenses average $4,654.
3. Historical Trends in College Tuition
Understanding historical trends in college tuition can provide insights into future costs.
3.1. Tuition Inflation Over the Years
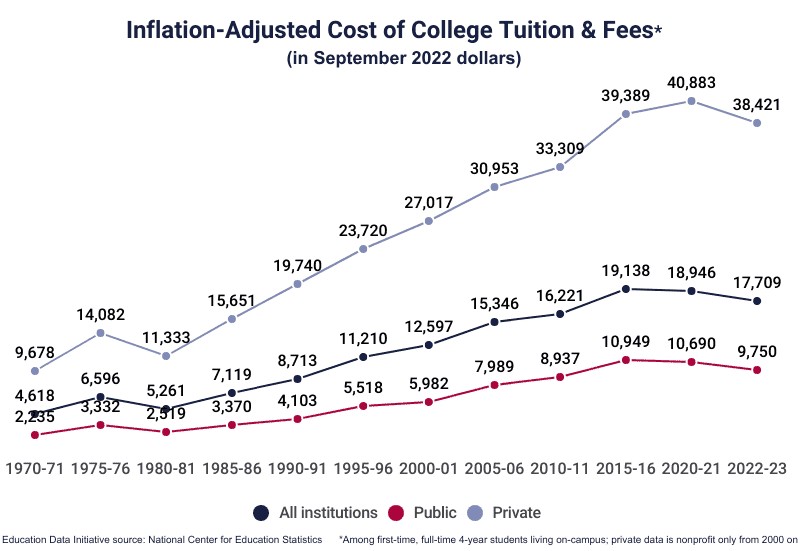
The cost of tuition has increased significantly over the last six decades, even after adjusting for inflation.
- In 1963, the annual cost of tuition at a 4-year public college was $243, which had the same buying power as $2,489 in November 2024 currency values.
- From 1963 to 2022, the cost of tuition at a 4-year public college increased at a CAGR of 2.34% after adjusting for inflation.
- Between 2012-13 and 2022-23, the average tuition increased 25.6% at all 4-year colleges (before adjusting for inflation).
- During the same period, the average in-state tuition increased 20.8% at public 4-year institutions and 33.7% at private, nonprofit 4-year institutions.
3.2. Factors Contributing to Rising Costs
Several factors contribute to the rising costs of college tuition:
- Increased Demand: More people are seeking higher education, driving up demand and prices.
- Decreased State Funding: Public colleges receive less funding from state governments, shifting the burden to students.
- Administrative Costs: Rising administrative expenses at colleges contribute to higher tuition fees.
- Technology and Infrastructure: Investments in technology and campus infrastructure also increase costs.
3.3. Impact on Students and Families
The rising cost of college tuition has a significant impact on students and families:
- Increased Debt: Students are borrowing more money to finance their education, leading to higher debt burdens.
- Financial Stress: Families face increased financial stress trying to afford college tuition.
- Delayed Life Milestones: Graduates may delay milestones like buying a home or starting a family due to student loan debt.
4. The Hidden Costs: Beyond Tuition and Room & Board
While tuition and room and board are significant expenses, there are other hidden costs that students and families should consider.
4.1. Transportation, Personal Expenses, and Entertainment
These additional expenses can add up significantly.
- Students living on campus at a public 4-year institution pay an average of $3,790 in additional annual expenses.
- Students who live off campus may expect to pay $4,720 if they do not live with family; for students living with family, additional expenses average $4,654.
- At private, nonprofit 4-year institutions, students living on campus spend an average of $2,858 on additional expenses.
4.2. Lost Income and Opportunity Costs
One of the largest expenses for students enrolled in college may be the loss of potential income in time spent studying instead of working.
- The median weekly income for a high school graduate is $899, or $46,748 per year.
- In four years, the average worker with a high school diploma may earn $186,992.
4.3. Long-Term Financial Implications
The long-term financial implications of college costs include:
- Student Loan Debt: Repaying student loans can affect credit scores and financial flexibility.
- Delayed Savings: Graduates may delay saving for retirement or other financial goals.
- Career Choices: Debt can influence career choices, pushing graduates towards higher-paying jobs.
5. Strategies to Reduce College Costs
There are several strategies to help reduce the overall cost of college.
5.1. Applying for Financial Aid and Scholarships
Financial aid and scholarships can significantly reduce the financial burden.
- FAFSA: Completing the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is the first step.
- Scholarships: Research and apply for scholarships from various organizations and institutions.
- Grants: Explore federal and state grant programs.
5.2. Choosing Affordable Institutions
Selecting an affordable college can make a big difference.
- Community Colleges: Starting at a community college and then transferring to a 4-year university can save money.
- In-State Public Colleges: These are generally more affordable for state residents.
- Smaller Private Colleges: Some smaller private colleges offer substantial financial aid packages.
5.3. Saving on Textbooks and Supplies
There are ways to save on textbooks and supplies.
- Used Textbooks: Buying used textbooks can save a significant amount of money.
- Rental Programs: Renting textbooks is another cost-effective option.
- Digital Resources: Utilizing digital resources and online materials can reduce expenses.
5.4. Living Arrangements and Lifestyle Choices
Making smart choices about living arrangements and lifestyle can also help.
- Living at Home: Living with family can eliminate room and board expenses.
- Budgeting: Creating a budget and sticking to it can help manage expenses.
- Part-Time Work: Working part-time can provide additional income to cover costs.
6. The Value of a College Education: Is It Worth the Investment?
Despite the high costs, a college education still offers significant value.
6.1. Increased Earning Potential
College graduates typically earn more than those with only a high school diploma.
- The median weekly income for a high school graduate is $899, or $46,748 per year.
- A bachelor’s degree can significantly increase earning potential over a lifetime.
6.2. Career Opportunities and Advancement
A college degree opens doors to more career opportunities and advancement.
- Many jobs require a college degree as a minimum qualification.
- Graduates are more likely to be promoted and advance in their careers.
6.3. Personal and Professional Development
College provides opportunities for personal and professional development.
- Students develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
- College fosters personal growth and broadens perspectives.
6.4. Long-Term Benefits
The long-term benefits of a college education include:
- Financial Stability: Higher earning potential leads to greater financial stability.
- Job Security: College graduates are less likely to face unemployment.
- Improved Quality of Life: Education enhances overall quality of life and well-being.
7. Navigating College Costs by State
College costs can vary significantly depending on the state. Understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions.
7.1. States with the Highest and Lowest Tuition Costs
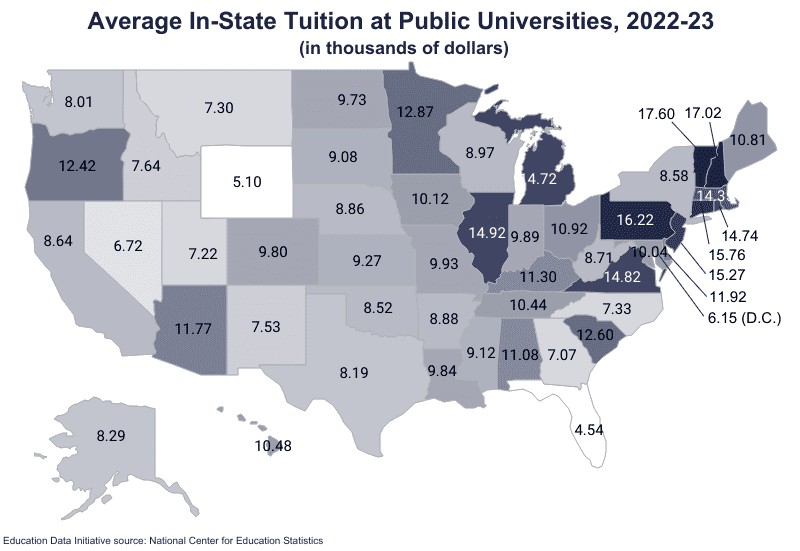
The average cost of in-state tuition and fees varies from state to state and year to year.
- The most expensive public schools are in the Northeast.
- The least expensive schools are in the South and Plains regions.
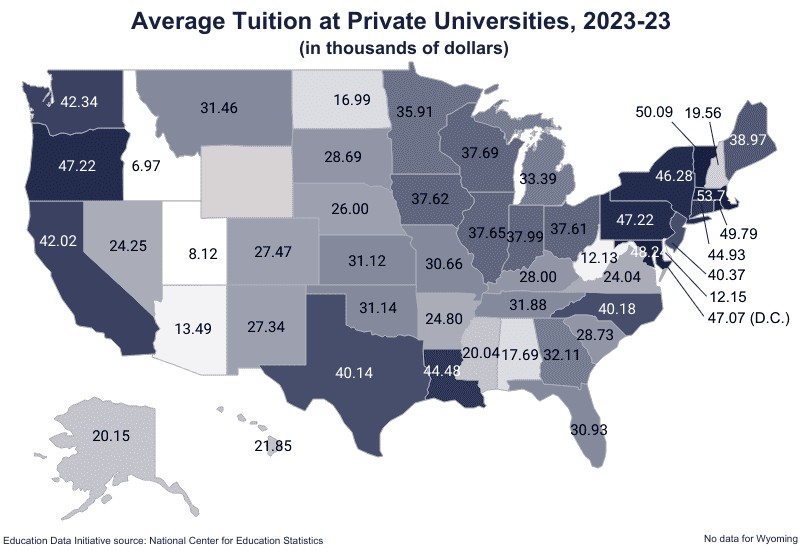
Most to Least Expensive In-State Public Universities, 2022-23
| State | Tuition & Fees | Tuition + Room & Board |
|---|---|---|
| Vermont | $17,600 | $50,094 |
| New Hampshire | $17,019 | $19,557 |
| Pennsylvania | $16,217 | $47,222 |
| Connecticut | $15,763 | $44,931 |
| New Jersey | $15,265 | $40,366 |
| Illinois | $14,921 | $37,646 |
| Virginia | $14,825 | $24,043 |
| Rhode Island | $14,744 | $49,792 |
| Michigan | $14,718 | $33,385 |
| Massachusetts | $14,345 | $53,789 |
| Minnesota | $12,873 | $35,914 |
| South Carolina | $12,604 | $28,730 |
| Oregon | $12,424 | $47,224 |
| Delaware | $11,922 | $12,154 |
| Arizona | $11,768 | $13,485 |
| Kentucky | $11,299 | $28,001 |
| Alabama | $11,081 | $17,687 |
| Ohio | $10,922 | $37,610 |
| Maine | $10,813 | $38,972 |
| Hawaii | $10,484 | $21,851 |
| Tennessee | $10,437 | $31,885 |
| Iowa | $10,121 | $37,623 |
| Maryland | $10,041 | $48,240 |
| Missouri | $9,926 | $30,660 |
| Indiana | $9,886 | $37,987 |
| Louisiana | $9,843 | $44,485 |
| Colorado | $9,798 | $27,474 |
| National Average | $9,750 | $35,248 |
| North Dakota | $9,728 | $16,990 |
| Kansas | $9,274 | $31,116 |
| Mississippi | $9,120 | $20,042 |
| South Dakota | $9,079 | $28,687 |
| Wisconsin | $8,974 | $37,686 |
| Arkansas | $8,879 | $24,798 |
| Nebraska | $8,862 | $26,002 |
| West Virginia | $8,715 | $12,133 |
| California | $8,637 | $42,017 |
| New York | $8,575 | $46,280 |
| Oklahoma | $8,519 | $31,140 |
| Alaska | $8,291 | $20,148 |
| Texas | $8,195 | $40,142 |
| Washington | $8,006 | $42,339 |
| Idaho | $7,640 | $6,970 |
| New Mexico | $7,526 | $27,340 |
| North Carolina | $7,327 | $40,176 |
| Montana | $7,299 | $31,464 |
| Utah | $7,215 | $8,123 |
| Georgia | $7,075 | $32,114 |
| Nevada | $6,723 | $24,246 |
| District of Columbia | $6,152 | $47,066 |
| Wyoming | $5,100 | § |
| Florida | $4,540 | $30,928 |
§No data for Wyoming.
7.2. Factors Influencing Tuition Costs by State
Several factors influence tuition costs by state:
- State Funding: States with higher levels of funding for public colleges tend to have lower tuition costs.
- Cost of Living: States with higher costs of living may have higher tuition rates.
- Demand for Higher Education: States with greater demand for higher education may have higher tuition costs.
7.3. Resources for Finding State-Specific Information
- State Education Agencies: These agencies provide information on college costs and financial aid programs in each state.
- College Websites: College websites often have detailed information on tuition and fees, as well as financial aid resources.
8. Understanding Student Loans and Debt
Most students borrow money to attend college, which can lead to significant debt. Understanding student loans is crucial.
8.1. Types of Student Loans
There are two primary types of student loans:
- Federal Student Loans: These are offered by the federal government and often have lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options.
- Private Student Loans: These are offered by banks and other financial institutions and may have higher interest rates and fewer repayment options.
8.2. Average Student Loan Debt
The average federal student loan debt is $38,375.
8.3. Repayment Options and Strategies
- Standard Repayment Plan: This is a fixed payment plan that typically lasts 10 years.
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: These plans base monthly payments on income and family size.
- Loan Forgiveness Programs: Some programs offer loan forgiveness for certain professions, such as teaching or public service.
8.4. Resources for Managing Student Loan Debt
- Federal Student Aid Website: This website provides information on federal student loans and repayment options.
- Financial Advisors: Consulting a financial advisor can help develop a plan for managing student loan debt.
9. Expert Advice from HOW.EDU.VN
Navigating the complexities of college costs can be challenging. Here’s how HOW.EDU.VN can help:
9.1. Personalized Financial Planning
Our team of expert advisors can help you create a personalized financial plan to manage college costs.
9.2. Scholarship and Grant Search Assistance
We provide assistance in searching for and applying for scholarships and grants.
9.3. Expert Guidance on Loan Options
We offer expert guidance on choosing the right student loan options and managing debt.
9.4. Connecting with Financial Aid Experts
We connect you with financial aid experts who can provide valuable insights and advice.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How much does the average college tuition cost for 4 years?
The average cost for a 4-year degree ranges from $108,584 for in-state public institutions to $234,512 for private nonprofit universities, excluding additional expenses.
2. What are the main components of college costs?
The main components include tuition and fees, room and board, books and supplies, and additional living expenses.
3. How has college tuition changed over the years?
College tuition has increased significantly over the past few decades, even after adjusting for inflation.
4. What are some strategies to reduce college costs?
Strategies include applying for financial aid and scholarships, choosing affordable institutions, and saving on textbooks and supplies.
5. Is a college education worth the investment?
Yes, a college education typically leads to increased earning potential, better career opportunities, and personal and professional development.
6. How do college costs vary by state?
College costs can vary significantly by state, with the Northeast being the most expensive and the South and Plains regions being the least expensive.
7. What are the different types of student loans?
The main types of student loans are federal student loans and private student loans.
8. How can I manage student loan debt?
You can manage student loan debt by choosing the right repayment plan, exploring loan forgiveness programs, and consulting with a financial advisor.
9. What hidden costs should I consider when planning for college?
Hidden costs include transportation, personal expenses, entertainment, and lost income.
10. How can HOW.EDU.VN help me with college financial planning?
HOW.EDU.VN offers personalized financial planning, scholarship search assistance, expert guidance on loan options, and connections with financial aid experts.
Planning for college expenses can be daunting, but with the right information and strategies, you can navigate the process effectively. At HOW.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the expert guidance and resources you need to make informed decisions and achieve your educational goals.
Don’t let the complexities of college financing hold you back. Contact our team of experienced Ph.D. experts at HOW.EDU.VN today and receive personalized advice tailored to your unique situation. We can help you navigate financial aid, scholarships, loan options, and create a comprehensive plan to make your college dreams a reality. Reach out to us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212. Visit our website at how.edu.vn for more information.
