Turquoise worth depends on a variety of factors, including weight, quality, origin, and treatment. Understanding these elements is key to assessing the gemstone’s true value, which can range from a few cents to thousands of dollars per carat; if you need help determining the accurate value of your turquoise, connect with our team of expert gemologists at HOW.EDU.VN for a detailed consultation, helping you with the process and maximizing your investment. Learn about turquoise valuation, quality assessment, and turquoise market trends.
1. Understanding the Factors Influencing Turquoise Value
The value of turquoise isn’t a fixed number; it’s a combination of several qualities that experts use to determine its worth. Factors such as weight, color, hardness, and the presence of a matrix (the pattern of veins running through the stone) all play a crucial role in pricing this vibrant gem. The more you understand these elements, the better you’ll be at evaluating turquoise, or get in touch with gemologists at HOW.EDU.VN.
1.1. Weight: Carat and Gram Conversion
Turquoise, like other gemstones, is weighed in carats, with one carat equivalent to 0.2 grams. The weight of turquoise significantly impacts its price because larger stones are relatively rarer than smaller ones. Here’s how weight plays a role:
- Pricing Per Carat: Turquoise is commonly priced per carat, allowing buyers to directly compare the cost of different stones based on size.
- Weight and Value: A larger turquoise stone of comparable quality will generally command a higher price due to its increased rarity.
- Weight Conversion: Understanding the conversion between carats and grams is essential for accurate pricing. For instance, 5 carats equal 1 gram.
 Turquoise Carat Weight
Turquoise Carat Weight
1.2. Turquoise Quality Index (TQI): A Detailed Breakdown
The Turquoise Quality Index (TQI) is a comprehensive scoring system used to evaluate the quality and, consequently, the value of turquoise. This index considers various factors, assigning points based on their contribution to the stone’s overall desirability and rarity.
- TQI Scale: The TQI operates on a scale from 8 to 100, where higher scores indicate superior quality and greater value. Scores above 90 are exceptionally rare, representing less than 1% of the turquoise on the market.
- Components of TQI: The TQI assesses both the physical structure and rarity of the stone through eight key indicators, each weighted according to its importance.
- Subjectivity: While most indicators are universally agreed upon, some, such as color, clarity, and pattern, can be subjective, leading to slight variations in scoring. Consulting with a turquoise expert, available at HOW.EDU.VN, can provide a more precise evaluation.
1.3. TQI and Market Grades
The TQI score directly correlates with the market grade and price per carat of turquoise. Here’s a table outlining the relationship between TQI scores, grades, market percentages, and typical price ranges:
| TQI Score | Grade | Market Grade % | Price per Carat |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90-100 | AAAA | Less than 1% | $50-$1000 |
| 85-89 | AAA | 2% | $10-$50 |
| 75-84 | AA | 5% | $2.50-$10 |
| 65-74 | A | 10% | $1.00-$2.50 |
| 35-64 | B | 22% | $0.05-$1.00 |
| 17-34 | Reconstituted | 60% | $0.02-$0.05 |
| 8-16 | Synthetic | $0.01 |
This table illustrates the significant range in value based on the TQI score, with top-grade turquoise fetching prices up to $1000 per carat.
2. The Eight Key Indicators of Turquoise Value
The TQI uses eight indicators to evaluate the physical and aesthetic properties of turquoise. These indicators are grouped into physical structure and rarity, each contributing to the overall score.
2.1. Physical Structure: Hardness, Enhancement, Composition, and Cut
The physical structure of turquoise accounts for 55 points of the TQI, focusing on factors that influence the stone’s durability and appearance.
2.1.1. Measuring Stone Hardness
Hardness measures a material’s resistance to scratching, directly impacting its durability and value. The Mohs Scale of Hardness, ranging from 1 (softest) to 10 (hardest), is used to assess this property.
- Mohs Scale: Turquoise typically ranges from 3 to 6 on the Mohs Scale, comparable to glass.
- Evaluation: While a Mohs scratch test can determine hardness, it risks damaging the stone. Deductive reasoning based on the stone’s solidity is recommended.
- Scoring Chart: The following chart provides guidance on assigning points based on hardness:
| Hardness | Plastic | Chalk | Reconstituted | Below 5 on Mohs Scale | Pro Stabilization 5+ | High Natural Hardness 5+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Points (1 to 20) | 1 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
2.1.2. Enhanced Turquoise Properties
Enhancement refers to treatments applied to improve a stone’s natural state. The acceptability and impact on value vary depending on the type of enhancement.
- Types of Enhancement: These range from synthetic processes to professional stabilization techniques.
- Acceptability: Light enhancements like waxing are generally accepted, while synthetic alterations significantly devalue the stone.
- Scoring Chart: Points are assigned based on the type and quality of enhancement:
| Enhancement | Plastic | Reconstituted | Heavy Stabilization/Dyed | Pro Stabilization Waxed/Oiled/Zachary | Natural | Chalk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Points (1 to 20) | 1 | 2-5 | 6-12 | 13-19 | 20 | 5 |
2.1.3. Turquoise Stone Composition
The composition of turquoise refers to the materials that make up the stone, including the host rock (the material on which turquoise forms). The degree of chalkiness and the presence of rare elements can influence value.
- Composition Factors: Chalkiness generally decreases quality, while rare elements can enhance it.
- Host Rock: The host rock’s stability and the presence of desirable minerals affect the stone’s value.
- Scoring Chart: Points are assigned based on the composition:
| Composition | Plastic | Reconstituted/Chalk | Required Stabilization/Unstable Host Rock | Stabilization/Minor Imperfections | Pro Stabilization/Pure Natural | Rare Elements in Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Points (1 to 10) | 1 | 2-3 | 4-5 | 6-7 | 8-9 | 10 |
2.1.4. The Art of the Cut
The cut of turquoise refers to the shaping and finishing of the raw stone. The skill and effort involved in this process add to the stone’s overall value.
- Types of Cuts: These range from raw stones to artist-sculpted designs.
- Value Addition: The more intricate and skilled the cut, the higher the value.
- Scoring Chart: Points are assigned based on the type of cut:
| Cut | Raw | Rolled/Cut | Standard Machine Cab | Hand-Shaped Cab | Hand-Sculpted Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Points (1 to 5) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
2.2. Rarity: Origin, Availability, Color, Matrix, and Contiguous Size
Rarity accounts for 45 points of the TQI. These elements consider the uniqueness and scarcity of specific turquoise characteristics, greatly affecting its value.
2.2.1. Turquoise Availability
Availability measures how easily a specific type of turquoise can be found. Rarer stones command higher prices due to their scarcity.
- Source Variation: Turquoise from specific mines or of particular formations can be more valuable due to limited availability.
- Scoring Chart: Points are assigned based on availability:
| Availability | Synthetic | Chalk/Reconstituted | Common Mine | Uncommon Mine | Rare Hat Mine/Specimen | Extremely Rare |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Points (1 to 20) | 1 | 2-5 | 6-12 | 13-17 | 18-19 | 20 |
2.2.2. The Significance of Color
Color is a subjective yet critical factor in determining turquoise value. The purity, consistency, and clarity of color significantly influence a stone’s desirability.
- Color Preferences: While preferences vary, clarity and consistency are universally valued.
- Scoring Chart: Points are assigned based on color quality:
| Color | Synthetic | Artificially Dyed | Dull/Cloudy/Harsh Transitions | Limited Color/Imperfections | Rich Color/Smooth Transitions | Rich Color/Smooth Transitions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Points (1 to 10) | 1 | 2 | 3-5 | 6-7 | 8-9 | 10 |
2.2.3. The Matrix Pattern
The matrix pattern, or the webbing of contrasting material within the turquoise, affects its value. Clarity and the rarity of the pattern are key considerations.
- Pattern Rarity: Unique patterns like spiderwebs or face stones are highly prized.
- Scoring Chart: Points are assigned based on the matrix pattern:
| Matrix | Synthetic | Artificially Dyed | No Pattern/Cloudy | Common Pattern/Grainy | Rare Pattern/Flawless | Rare Pattern/Flawless |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Points (1 to 10) | 1 | 2 | 3-5 | 6-7 | 8-9 | 10 |
2.2.4. Size Matters: Evaluating Contiguous Size
The size of a turquoise stone can impact its value, as larger pieces are generally rarer than smaller ones.
- Size Categories: The widest point of the stone determines its size category.
- Scoring Chart: Points are assigned based on size:
| Size | Smaller than 1/4″ | 1/4″ to 1″ | 1″ to 2″ | 2″ to 4″ | 4″+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Points (1 to 5) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
3. Calculating Turquoise Value Using the TQI
After assessing your turquoise using the TQI indicators, you can determine its approximate value per carat using the TQI to Price per Carat Conversion Chart.
3.1. TQI to Price Per Carat Conversion Chart
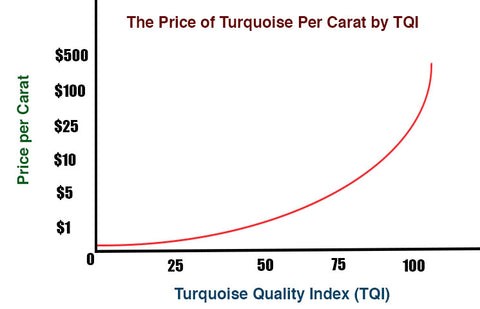
The following table provides a detailed conversion from the total TQI points to the price per carat for turquoise stones:
| TQI | Price/Carat | TQI | Price/Carat | TQI | Price/Carat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8-16 | $0.01 | 56 | $0.46 | 79 | $6.35 |
| 17-34 | $0.02-$0.05 | 57 | $0.53 | 80 | $6.50 |
| 35 | $0.05 | 58 | $0.60 | 81 | $7.00 |
| 36 | $0.06 | 59 | $0.65 | 82 | $7.50 |
| 37 | $0.07 | 60 | $0.69 | 83 | $9.00 |
| 38 | $0.08 | 61 | $0.75 | 84 | $9.50 |
| 39 | $0.09 | 62 | $0.80 | 85 | $10.00 |
| 40 | $0.10 | 63 | $0.89 | 86 | $20.00 |
| 41 | $0.11 | 64 | $0.95 | 87 | $30.00 |
| 42 | $0.12 | 65 | $1.08 | 88 | $42.00 |
| 43 | $0.13 | 66 | $1.20 | 89 | $54.00 |
| 44 | $0.14 | 67 | $1.42 | 90 | $71.00 |
| 45 | $0.15 | 68 | $1.65 | 91 | $90.00 |
| 46 | $0.16 | 69 | $1.85 | 92 | $125.00 |
| 47 | $0.18 | 70 | $2.20 | 93 | $150.00 |
| 48 | $0.19 | 71 | $2.65 | 94 | $180.00 |
| 49 | $0.21 | 72 | $3.45 | 95 | $215.00 |
| 50 | $0.23 | 73 | $4.05 | 96 | $260.00 |
| 51 | $0.25 | 74 | $4.75 | 97 | $320.00 |
| 52 | $0.27 | 75 | $5.20 | 98 | $385.00 |
| 53 | $0.30 | 76 | $5.50 | 99 | $500.00 |
| 54 | $0.34 | 77 | $5.85 | 100 | $1,000.00 |
| 55 | $0.39 | 78 | $6.15 |
3.2. Real-World Examples
To better illustrate how to use the TQI and the conversion chart, here are a couple of examples:
- Example 1: A turquoise stone with a TQI of 65 would be valued at approximately $1.08 per carat.
- Example 2: A turquoise stone with a TQI of 92 would be valued at approximately $125.00 per carat.
These examples demonstrate how the TQI provides a structured method for estimating the value of turquoise based on its quality.
4. The Origin and Mining Locations of Turquoise
The origin of turquoise is a significant factor in determining its value. Certain mines are renowned for producing high-quality stones with unique characteristics, making them more desirable among collectors.
4.1. Famous Turquoise Mines and Their Impact
Different mines yield turquoise with distinctive colors, matrix patterns, and hardness. Some of the most famous turquoise mines include:
- Lander Blue (Nevada): Known for its spiderweb matrix and intense blue color, Lander Blue is one of the rarest and most valuable turquoises. Due to its limited production, stones from this mine command premium prices.
- Kingman (Arizona): One of the oldest and largest turquoise mines in the United States, Kingman turquoise is known for its clear blue color and is often stabilized to enhance its hardness.
- Sleeping Beauty (Arizona): Famous for its pure, sky-blue color with little to no matrix, Sleeping Beauty turquoise is highly sought after. The mine’s closure in 2012 has increased the value of existing stones.
- Morenci (Arizona): Morenci turquoise is characterized by its deep blue color and iron pyrite matrix, giving it a unique and attractive appearance. Stones from this mine are highly valued for their distinct look.
- Bisbee (Arizona): Bisbee turquoise is known for its rich, deep blue color and distinctive matrix patterns, often featuring smoky black or reddish-brown hues. The mine’s limited production adds to its desirability.
4.2. Regional Differences in Turquoise Characteristics
The geological conditions of different regions influence the characteristics of the turquoise found there. For example:
- American Southwest: Turquoise from this region often exhibits a vibrant blue color and distinct matrix patterns due to the high copper content in the soil.
- China: Chinese turquoise, particularly from the Hubei province, is known for its green hues and often contains a significant amount of matrix.
- Iran: Persian turquoise, traditionally highly valued, is known for its intense sky-blue color and lack of matrix.
5. Common Treatments and Enhancements
Turquoise is often treated to enhance its color, hardness, and durability. Understanding these treatments is crucial for accurately assessing the stone’s value.
5.1. Stabilization Techniques
Stabilization involves impregnating the turquoise with resins or polymers to improve its hardness and prevent it from crumbling. This process is common and generally accepted in the market, but it does affect the stone’s value.
- Purpose: To make the turquoise more durable and suitable for jewelry.
- Impact on Value: Stabilized turquoise is typically less valuable than natural, untreated turquoise.
- Identification: Stabilized stones may have a slightly plastic-like appearance or feel.
5.2. Dyeing and Color Enhancement
Dyeing is used to improve the color of pale or less vibrant turquoise. This treatment is less desirable as it artificially alters the stone’s natural appearance.
- Purpose: To enhance or change the color of the turquoise.
- Impact on Value: Dyed turquoise is significantly less valuable than natural, untreated stones.
- Identification: Dyed stones may have an unnatural or uneven color distribution.
5.3. Other Treatments (Waxing, Oiling)
Waxing and oiling are less invasive treatments used to protect the surface of the turquoise and enhance its luster. These treatments are generally accepted as they do not significantly alter the stone’s properties.
- Purpose: To protect the stone and improve its appearance.
- Impact on Value: These treatments have a minimal impact on the stone’s value.
- Identification: Waxed or oiled stones may have a slightly glossy surface.
6. Identifying Authentic vs. Imitation Turquoise
Distinguishing between authentic and imitation turquoise is essential for ensuring you’re getting what you pay for.
6.1. Visual Inspection Techniques
Visual inspection can help identify potential imitations. Look for:
- Color Consistency: Authentic turquoise often has variations in color, while imitations may have an unnaturally uniform appearance.
- Matrix Patterns: Natural matrix patterns are irregular and unique. Imitations may have repeating or artificial-looking patterns.
- Surface Texture: Authentic turquoise may have slight imperfections, while imitations are often too smooth.
6.2. Simple Tests to Verify Authenticity
Several simple tests can help verify the authenticity of turquoise:
- Scratch Test: Gently scratch the stone with a sharp object. Authentic turquoise is relatively hard and should not scratch easily.
- Acetone Test: Apply a small amount of acetone to the stone with a cotton swab. If the dye comes off, the stone is likely dyed or imitation.
- Heat Test: Gently heat the stone with a lighter. Imitations may melt or emit a plastic-like odor.
6.3. When to Seek Professional Appraisal
If you’re unsure about the authenticity or value of your turquoise, it’s best to seek a professional appraisal. Gemologists can use advanced testing techniques to accurately assess the stone. At HOW.EDU.VN, we have a team of experienced gemologists who can provide expert appraisals, ensuring you have a clear understanding of your stone’s worth and authenticity.
7. The Role of Fashion Trends and Cultural Significance
Fashion trends and cultural significance also play a role in the value of turquoise.
7.1. Current Market Trends
Current market trends can influence the demand for certain types of turquoise. For example:
- High-Grade Turquoise: High-grade turquoise with intense color and unique matrix patterns is currently in high demand among collectors.
- Vintage and Antique Pieces: Vintage and antique turquoise jewelry can command premium prices due to their historical significance and rarity.
- Turquoise in Contemporary Jewelry: Turquoise remains popular in contemporary jewelry designs, driving demand for a variety of grades and colors.
7.2. Cultural and Historical Importance
Turquoise has been valued for centuries across various cultures. Its historical and cultural significance can add to its value.
- Native American Cultures: Turquoise is highly revered in Native American cultures and is often used in ceremonial and decorative objects. Pieces with Native American provenance can be particularly valuable.
- Ancient Civilizations: Turquoise was used in ancient Egypt, Persia, and other civilizations for jewelry and adornment. Artifacts from these cultures can be highly valuable.
8. Caring for Your Turquoise to Preserve Its Value
Proper care can help preserve the value of your turquoise jewelry and stones.
8.1. Cleaning and Storage Best Practices
Follow these tips for cleaning and storing your turquoise:
- Gentle Cleaning: Clean turquoise with a soft cloth and mild soap. Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners.
- Avoid Ultrasonic Cleaners: Ultrasonic cleaners can damage turquoise and should be avoided.
- Proper Storage: Store turquoise in a soft pouch or jewelry box to protect it from scratches and impacts.
8.2. Protecting Turquoise from Damage
Protect turquoise from damage by:
- Avoiding Exposure to Chemicals: Remove turquoise jewelry before swimming, cleaning, or using harsh chemicals.
- Protecting from Extreme Temperatures: Avoid exposing turquoise to extreme temperatures or rapid temperature changes, as this can cause it to crack.
- Regular Inspection: Regularly inspect your turquoise jewelry for loose stones or damage.
9. How to Buy and Sell Turquoise
Knowing how to buy and sell turquoise can help you make informed decisions and get the best value for your stones.
9.1. Tips for Buying Turquoise
When buying turquoise, consider the following:
- Research: Learn about the different types of turquoise and their characteristics.
- Check Authenticity: Verify the authenticity of the stone using visual inspection and simple tests.
- Buy from Reputable Dealers: Purchase turquoise from reputable dealers who offer guarantees and accurate information about their stones.
- Get an Appraisal: Consider getting an appraisal from a qualified gemologist to ensure you’re paying a fair price.
9.2. Strategies for Selling Turquoise
When selling turquoise, consider the following:
- Get an Appraisal: Have your turquoise appraised by a qualified gemologist to determine its value.
- Market Research: Research current market trends to understand the demand for your type of turquoise.
- Choose the Right Venue: Sell your turquoise through reputable dealers, online marketplaces, or auctions.
- Provide Accurate Information: Be transparent about the stone’s origin, treatments, and any known flaws.
10. Finding Expert Advice at HOW.EDU.VN
Navigating the world of turquoise values can be complex, but you don’t have to do it alone. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with top gemologists and experts who can provide personalized advice and support.
10.1. How HOW.EDU.VN Connects You with Gemologists
HOW.EDU.VN offers a platform to:
- Access Expert Appraisals: Get accurate and reliable appraisals from experienced gemologists.
- Ask Questions: Consult with experts to get answers to your specific questions about turquoise valuation.
- Get Personalized Advice: Receive tailored advice based on your individual needs and circumstances.
10.2. Benefits of Consulting with Experts
Consulting with experts at HOW.EDU.VN offers several benefits:
- Accurate Valuation: Ensure you know the true value of your turquoise stones.
- Informed Decisions: Make informed decisions when buying or selling turquoise.
- Peace of Mind: Gain peace of mind knowing you’re working with trusted professionals.
Don’t let the complexities of turquoise valuation overwhelm you. Contact the experts at HOW.EDU.VN today and discover the true worth of your turquoise stones.
11. Case Studies
Real-world examples of turquoise valuation can provide a better understanding of the concepts discussed.
11.1. Case Study 1: Valuing a Lander Blue Nugget
Background: A collector owns a small Lander Blue nugget and seeks to determine its value.
Assessment:
- Origin: Lander Blue (Nevada) – Extremely Rare (20 points)
- Color: Intense Blue with Spiderweb Matrix (10 points)
- Hardness: High Natural Hardness (20 points)
- Treatment: Natural, Untreated (20 points)
- Size: Smaller than 1/4″ (1 point)
- Composition: High Quality (9 points)
- Cut: Raw (1 point)
- Enhancement: Natural (20 points)
Total TQI Score: 101 (Adjusted to 100)
Value: Approximately $1,000 per carat due to its rarity and high quality.
11.2. Case Study 2: Evaluating a Stabilized Kingman Cabochon
Background: A jewelry maker wants to assess the value of a stabilized Kingman turquoise cabochon.
Assessment:
- Origin: Kingman (Arizona) – Common Mine (12 points)
- Color: Clear Blue (8 points)
- Hardness: Stabilized, 5+ on Mohs Scale (15 points)
- Treatment: Stabilized (15 points)
- Size: 1″ to 2″ (3 points)
- Composition: Solid Matrix (8 points)
- Cut: Standard Machine Cab (3 points)
- Enhancement: Pro stabilization Waxed (15 points)
Total TQI Score: 79
Value: Approximately $6.35 per carat, reflecting its good quality and common origin.
12. FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about turquoise valuation:
12.1. What is the most important factor in determining turquoise value?
The most important factor is the overall quality, as reflected by the Turquoise Quality Index (TQI), which considers hardness, color, origin, and treatment.
12.2. How can I tell if my turquoise is real?
Check for color consistency, matrix patterns, and surface texture. Perform simple tests like the scratch test and acetone test. If unsure, seek a professional appraisal.
12.3. Does the mine location affect the value of turquoise?
Yes, turquoise from famous mines like Lander Blue and Sleeping Beauty is generally more valuable due to their rarity and unique characteristics.
12.4. Is stabilized turquoise worth less than natural turquoise?
Yes, stabilized turquoise is generally worth less than natural, untreated turquoise because the stabilization process alters the stone’s original properties.
12.5. How should I care for my turquoise jewelry?
Clean turquoise with a soft cloth and mild soap. Avoid harsh chemicals, ultrasonic cleaners, and extreme temperatures. Store it in a soft pouch to prevent scratches.
12.6. What is the Mohs scale, and how does it relate to turquoise?
The Mohs scale measures a material’s hardness. Turquoise typically ranges from 3 to 6 on the Mohs scale, comparable to glass.
12.7. Can I accurately assess the value of my turquoise myself?
While you can use the TQI guidelines, a professional appraisal provides the most accurate valuation, considering all relevant factors and market conditions.
12.8. What is the difference between stabilized and dyed turquoise?
Stabilized turquoise is treated to improve its hardness and durability, while dyed turquoise is treated to enhance or change its color. Dyed turquoise is generally less valuable than stabilized turquoise.
12.9. How do fashion trends affect the value of turquoise?
Current market trends can influence the demand for certain types of turquoise, affecting their value. High-grade stones and vintage pieces are often in high demand.
12.10. Where can I find reputable turquoise dealers?
Look for dealers with a proven track record, positive reviews, and transparent business practices. Gemological certifications and affiliations can also indicate credibility.
Understanding how much turquoise is worth requires assessing various factors such as weight, quality, and origin. While this guide provides a solid foundation, consulting with experts ensures an accurate and informed valuation. Contact HOW.EDU.VN to connect with experienced gemologists who can provide personalized advice and support. Let us help you unlock the true value of your turquoise.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Unlock the true value of your turquoise – connect with our experts at how.edu.vn today for a personalized consultation.
Turquoise Value References
- Fritsch, Emmanuel. McClure, Shane. Ostrooumov, Mikhail. Andres, Yves. Koivula, John. Kammerling, Robert. The identification of Zachery treated Turquoise 1999. http://image1.fmgstatic.com/pdf/The-Identification-of-Zachery-Treated-Turquoise.pdf
- Mohs Hardness Scale, A rapid hardness test for field and classroom use. http://geology.com/minerals/mohs-hardness-scale.shtml
- Smith, Natalie. How to shape Turquoise Nuggets. http://www.ehow.com/how_8038446_shape-turquoise-nuggets.html
