Unveiling the true size of the Sun compared to our planet is a fascinating pursuit. At HOW.EDU.VN, we offer expert insights to demystify complex topics like this. Discover the immense scale of the Sun and its vast distance from Earth through expert analysis. Explore celestial dimensions with HOW.EDU.VN.
1. Understanding the Sun’s Size Relative to Earth
Determining how much larger the Sun is than the Earth requires a grasp of basic astronomy and geometry. While ancient Greek astronomers knew the Sun was larger, modern methods provide a more precise understanding. Let’s delve into how we can estimate the Sun’s size relative to the Earth.
1.1. Lunar Phases: Clues to the Sun’s Distance and Size
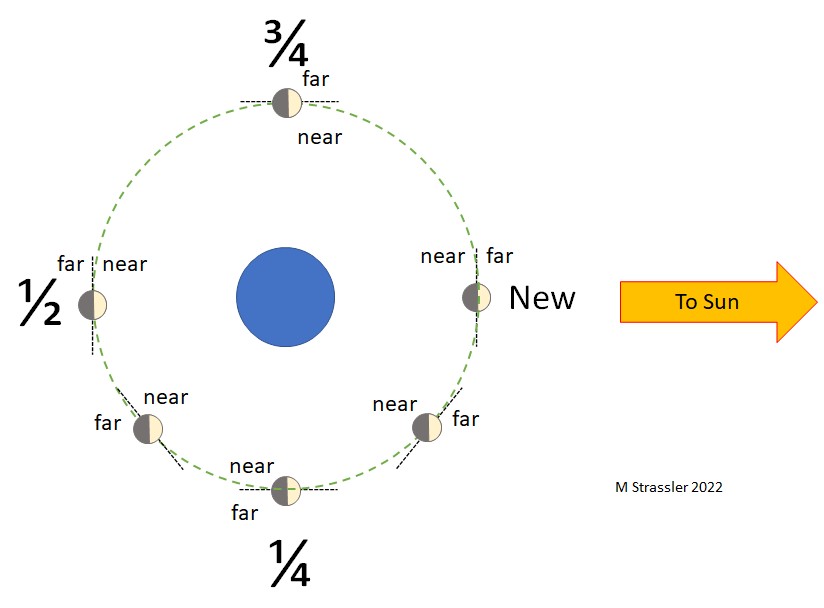
The Moon’s phases offer initial clues about the Sun’s size and distance. These phases, spanning approximately 29.5 Earth days, result from the changing angles at which we view the Moon’s illuminated surface.
- Near Half: The portion of the Moon facing Earth.
- Lit Half: The portion of the Moon illuminated by the Sun.
The interplay between these halves creates the lunar phases. When the Moon is positioned between the Earth and Sun, the lit half faces away from us, resulting in a New Moon. Conversely, when the Moon is on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun, we see a Full Moon.
1.2. The Significance of “First Quarter”
The term “First Quarter” Moon, occurring when the Moon is half-lit, provides a crucial clue. It signifies that the Moon has completed one-quarter of its cycle. The fact that a Half Moon is also a First Quarter Moon suggests that the Sun is significantly large and distant.
1.3. Geometry and the Sun’s Distance
The timing of the First Quarter phase reveals information about the Sun’s distance. If the Sun were close, the half-lit Moon would occur noticeably before the First Quarter. However, the near coincidence of these events indicates a distant Sun.
2. Estimating the Sun’s Size and Distance: A Geometric Approach
To refine our estimation, we can employ geometric principles. By observing the angle between the Sun and Moon when the Moon is half-lit, we can infer the Sun’s distance.
2.1. Triangles and the Sun’s Position
Imagine two right-angled triangles:
- Half-Lit Triangle: Formed by the Earth, Moon, and Sun when the Moon is half-lit, with the right angle at the Moon.
- First Quarter Triangle: Formed when the Moon has traveled one-quarter of its cycle, with the right angle at the Earth.
If the Sun were close, these triangles would differ significantly. However, their similarity implies a distant Sun.
2.2. Overcoming Orbital Variations
The Moon’s elliptical orbit introduces complexities. However, focusing on the angle between the Sun and Moon at the half-lit phase mitigates these effects, providing a more reliable estimate.
2.3. Practical Observation
Observe the Moon when it is 90 degrees away from the Sun. An L-shaped tool can help determine this angle. At this point, the Moon will appear half-lit, further supporting the idea of a distant and large Sun.
3. Quantifying the Sun’s Size: Initial Estimates
Based on these observations, we can derive initial estimates of the Sun’s size and distance. The fact that the First Quarter and half-lit phases align closely suggests that the Sun is at least five times further away than the Moon. This implies that the Sun is also at least five times larger, making it bigger than the Earth.
3.1. Refining the Estimate Through Observation
By directly observing the angle between the Sun and Moon when the Moon is half-lit, a more precise estimate can be obtained. This method minimizes the impact of the Moon’s elliptical orbit.
3.2. Calculating the Sun’s Diameter
If the Moon is nearly half-lit when it’s 90 degrees from the Sun, it suggests the Sun is at least ten times further than the Moon. Given that the Moon’s diameter is approximately 1/4 of the Earth’s, the Sun’s diameter would be at least 10/4 = 2.5 times the Earth’s.
4. The True Scale: Modern Measurements
While these methods provide a basic understanding, modern measurements offer a far more accurate picture of the Sun’s size and distance.
4.1. The Sun’s Immense Diameter
The Sun’s diameter is approximately 1.39 million kilometers (864,000 miles).
4.2. The Earth’s Diameter
In contrast, the Earth’s diameter is about 12,742 kilometers (7,918 miles).
4.3. The Sun’s Volume Relative to Earth
The Sun is so large that approximately 1.3 million Earths could fit inside it.
4.4. Distance from Earth
The Sun is, on average, 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles) from Earth. This distance is known as one astronomical unit (AU).
5. Why is the Sun So Important?
Understanding the Sun’s size and distance is not just an academic exercise. The Sun is the source of virtually all energy on Earth, driving our climate and sustaining life.
5.1. The Sun’s Energy Output
The Sun’s energy output is immense. Every second, it converts about 600 million tons of hydrogen into helium in its core, releasing vast amounts of energy in the process.
5.2. The Sun’s Influence on Earth’s Climate
Variations in the Sun’s energy output can affect Earth’s climate. These variations can be short-term, such as solar flares, or long-term, such as changes in the solar cycle.
5.3. The Sun’s Role in Photosynthesis
The Sun’s light is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen. This process forms the base of the food chain and is vital for all life on Earth.
6. Challenges in Measuring the Sun
Measuring the Sun’s size and distance accurately has been a long-standing challenge for astronomers.
6.1. Early Methods and Limitations
Early methods relied on simple geometry and observation, which were limited by the available technology and the difficulty of making precise measurements.
6.2. Modern Techniques: A Quantum Leap
Modern techniques, such as radar and space-based observatories, have allowed for far more accurate measurements. Radar involves bouncing radio waves off the Sun and measuring the time it takes for them to return. Space-based observatories avoid the distorting effects of Earth’s atmosphere, allowing for clearer images and more precise measurements.
6.3. Ongoing Research and Discoveries
Research on the Sun continues to this day, with new discoveries being made regularly. Scientists are working to better understand the Sun’s internal structure, its magnetic field, and its influence on Earth and the rest of the solar system.
7. The Sun in Comparison to Other Stars
While the Sun may seem enormous to us, it is actually a fairly average-sized star.
7.1. Stellar Classification
Stars are classified based on their size, temperature, and luminosity. The Sun is classified as a G-type main-sequence star, also known as a yellow dwarf.
7.2. Giants and Supergiants
Some stars are far larger than the Sun. Giant stars can be tens or hundreds of times larger, while supergiant stars can be thousands of times larger.
7.3. The Largest Known Stars
The largest known star is UY Scuti, a red supergiant with a diameter estimated to be about 1,700 times that of the Sun. If UY Scuti were placed at the center of our solar system, it would engulf the orbits of Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, and even Jupiter.
8. Understanding Scale in the Universe
The vastness of the universe can be difficult to comprehend. Understanding the Sun’s size relative to the Earth is just one step in appreciating the scale of the cosmos.
8.1. Visual Aids and Analogies
Visual aids, such as diagrams and animations, can help to illustrate the relative sizes and distances of celestial objects. Analogies, such as comparing the Sun to a beach ball and the Earth to a pea, can also be helpful.
8.2. Scale Models
Creating scale models of the solar system can provide a tangible sense of the distances involved. Even a relatively small model can highlight the vast emptiness of space.
8.3. Exploring Space Virtually
Virtual tours of space, using software and simulations, can allow people to explore the solar system and beyond from the comfort of their own homes.
9. Experts Insights and Guidance from HOW.EDU.VN
Navigating complex topics like the size and scale of the Sun can be challenging. HOW.EDU.VN provides access to expert insights and guidance from leading professionals across various fields.
9.1. Access to Leading Professionals
Our platform connects you with over 100 renowned PhDs and experts ready to provide personalized consultations.
9.2. Personalized Consultations
Receive tailored advice and solutions specific to your needs and interests.
9.3. Reliable and Secure Information
We prioritize the security and confidentiality of your consultations, ensuring a trustworthy environment for seeking expert advice.
10. Call to Action: Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Do you have questions about the Sun, space, or any other complex topic? Are you seeking expert guidance to solve a specific problem or gain deeper insights into a subject? At HOW.EDU.VN, we bridge the gap between you and world-class experts, providing a seamless platform for personalized consultations.
10.1. Why Choose HOW.EDU.VN?
- Expertise: Access a diverse network of PhDs and professionals renowned in their respective fields.
- Personalization: Receive tailored advice and solutions designed to address your unique needs and challenges.
- Convenience: Connect with experts from anywhere in the world, at any time, through our user-friendly platform.
- Confidentiality: Your privacy and data security are our top priorities.
10.2. How to Get Started
- Visit our website: HOW.EDU.VN
- Browse our experts: Explore profiles of our esteemed PhDs and professionals.
- Schedule a consultation: Book a session with the expert who aligns with your needs.
- Receive personalized guidance: Get answers to your questions and solutions to your challenges.
10.3. Contact Us
For inquiries or assistance, please contact us:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
10.4. Unlock Your Potential with Expert Guidance
Don’t let complex questions or challenges hold you back. Connect with the world’s leading experts at HOW.EDU.VN and unlock your full potential. Our team of renowned PhDs and professionals is ready to provide personalized consultations and guidance to help you achieve your goals. Whether you’re seeking advice on scientific topics, business strategies, or personal development, HOW.EDU.VN is your gateway to expert knowledge and solutions. Join us today and experience the power of expert guidance.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About the Sun and Expert Consultations
Q1: How much bigger is the Sun than the Earth?
The Sun’s diameter is approximately 109 times larger than the Earth’s, and its volume is about 1.3 million times greater.
Q2: How far away is the Sun from the Earth?
The Sun is, on average, 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles) from Earth, which is one astronomical unit (AU).
Q3: What is the Sun made of?
The Sun is primarily made of hydrogen (about 71%) and helium (about 27%), with smaller amounts of other elements like oxygen, carbon, and iron.
Q4: Why is the Sun important to Earth?
The Sun is the primary source of energy for Earth, driving our climate, weather patterns, and sustaining all life through photosynthesis.
Q5: How can I learn more about the Sun and space?
You can explore resources from reputable scientific organizations like NASA and ESA, read books and articles on astronomy, and connect with experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized guidance.
Q6: What kind of experts can I find at HOW.EDU.VN?
HOW.EDU.VN offers access to over 100 PhDs and professionals in various fields, including astronomy, physics, engineering, business, and personal development.
Q7: How does the consultation process work at HOW.EDU.VN?
You can browse expert profiles, schedule a consultation, and connect with your chosen expert through our secure platform for personalized guidance.
Q8: Is my information kept confidential during consultations?
Yes, HOW.EDU.VN prioritizes the security and confidentiality of your consultations, ensuring a trustworthy environment for seeking expert advice.
Q9: What if I have a very specific or complex question?
Our experts are equipped to handle a wide range of questions and challenges, providing tailored solutions based on their expertise and experience.
Q10: How can HOW.EDU.VN help me achieve my goals?
By connecting you with world-class experts, how.edu.vn provides the knowledge, guidance, and support you need to overcome challenges, gain new insights, and unlock your full potential.