Having healthy sperm is critical for fertility, but how much sperm is actually needed to conceive? At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights on sperm health, quantity, and motility, helping you understand what factors contribute to successful fertilization. Explore the necessary sperm volume and quality, as well as lifestyle factors that can improve your chances of conception, ensuring you’re well-informed on your journey to parenthood. Discover how to improve sperm count, semen analysis and optimize male fertility.
1. Understanding the Basics of Sperm and Fertility
Sperm health is a critical factor in male fertility. Understanding the key components of sperm, how they affect fertility, and the factors that can impact their health is the first step toward improving your chances of conception.
1.1. What Are the Key Aspects of Sperm Health?
Sperm health is primarily evaluated based on three main factors: quantity, movement, and shape. These factors collectively determine the sperm’s ability to fertilize an egg successfully.
- Quantity: Sperm quantity refers to the concentration of sperm in a single ejaculate. Ideally, an ejaculate should contain at least 15 million sperm per milliliter. Lower sperm counts reduce the likelihood of fertilization, as fewer sperm are available to reach and penetrate the egg.
- Movement (Motility): Sperm motility is the ability of sperm to move efficiently through the female reproductive tract to reach and fertilize the egg. A minimum of 40% of sperm should exhibit good motility for a higher chance of pregnancy. Reduced motility can hinder the sperm’s journey, decreasing the probability of conception.
- Shape (Morphology): Sperm morphology refers to the shape and structure of sperm. Typical sperm have oval heads and long tails, which aid in their movement. While morphology is generally considered less critical than quantity and motility, a higher proportion of sperm with a typical shape can increase the chances of successful fertilization.
1.2. How Does Sperm Health Affect Fertility?
Sperm health directly impacts a man’s fertility. When sperm quantity, motility, and morphology are within the normal ranges, the chances of conceiving naturally are significantly higher. Conversely, abnormalities in any of these areas can lead to fertility issues.
- Fertilization Process: Healthy sperm must navigate through the cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes to reach the egg. Adequate quantity ensures that enough sperm are present to make this journey. Good motility is essential for sperm to swim effectively and reach the egg, while a typical shape aids in their movement and ability to penetrate the egg’s outer layer.
- Impact of Abnormalities: Low sperm count, poor motility, or abnormal morphology can impede the fertilization process. For example, if the sperm count is low, there may not be enough sperm to overcome the natural barriers in the female reproductive tract. Poor motility means sperm may not be able to reach the egg, and abnormal shape can prevent sperm from properly attaching to and penetrating the egg.
1.3. Factors Influencing Sperm Health
Several factors can influence sperm health, ranging from lifestyle choices to medical conditions. Understanding these factors can help you take steps to protect and improve your sperm quality.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial, as obesity can negatively impact sperm count and motility.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can support sperm health.
- Smoking: Smoking is known to reduce sperm count and motility.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can lower testosterone levels and sperm production.
- Stress: High stress levels can interfere with hormone production needed for sperm development.
- Medical Conditions:
- Infections: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia and gonorrhea can cause inflammation and damage to the reproductive organs, affecting sperm health.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions affecting the hypothalamus or pituitary gland can disrupt hormone production, impacting sperm production and quality.
- Varicocele: This condition involves the enlargement of veins in the scrotum, which can increase the temperature around the testicles and impair sperm production.
- Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to Toxins: Exposure to pesticides, lead, and other toxins can negatively affect sperm quantity and quality.
- Heat: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, such as from hot tubs or saunas, can impair sperm production.
- Medications:
- Certain medications: Some medications, including certain antidepressants, blood pressure medications, and anabolic steroids, can impact sperm health.
Taking proactive steps to manage these factors can significantly improve sperm health and increase the chances of successful conception. If you have concerns about your sperm health, consulting with a fertility specialist at HOW.EDU.VN can provide personalized advice and treatment options.
2. Decoding Sperm Quantity: How Much Is Enough?
The quantity of sperm in an ejaculate is a fundamental factor in determining fertility. Understanding what constitutes a normal sperm count and the implications of having too few or too many sperm is crucial for assessing and improving male reproductive health.
2.1. What Is Considered a Normal Sperm Count?
A normal sperm count is typically defined as having at least 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen. This threshold ensures that there are enough sperm to navigate the female reproductive tract and increase the likelihood of fertilizing the egg. The World Health Organization (WHO) provides these guidelines, which are widely used in fertility assessments.
- Semen Analysis: Sperm count is determined through a semen analysis, a laboratory test that evaluates various aspects of semen, including sperm concentration, motility, and morphology. This test is a standard part of fertility evaluations.
- Factors Affecting Sperm Count: Several factors can influence sperm count, including lifestyle choices, medical conditions, and environmental exposures. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can positively impact sperm count, while certain medical conditions may require treatment to improve sperm production.
2.2. What If Sperm Count Is Too Low (Oligospermia)?
Oligospermia, or low sperm count, is a condition characterized by having fewer than 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen. This can significantly reduce the chances of natural conception.
- Causes of Oligospermia:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Disruptions in hormone levels, such as low testosterone, can impair sperm production.
- Varicocele: Enlarged veins in the scrotum can raise testicular temperature, hindering sperm production.
- Infections: Infections in the reproductive tract can cause inflammation and damage, affecting sperm count.
- Ejaculation Problems: Retrograde ejaculation, where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis, can result in low sperm count in the ejaculate.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can negatively impact sperm count.
- Treatment Options for Oligospermia:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, and maintaining a healthy weight can improve sperm count.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone treatments can help correct hormonal imbalances and stimulate sperm production.
- Surgery: Varicocele repair surgery can improve sperm count by reducing testicular temperature.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): Techniques like intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilization (IVF) can help couples conceive when sperm count is low.
- Impact on Fertility: Low sperm count makes it more difficult for sperm to reach and fertilize the egg, increasing the time it takes to conceive and sometimes requiring medical intervention.
2.3. What If Sperm Count Is Too High?
While less common, having a sperm count that is excessively high, known as hyperspermia, can also pose challenges. Although it might seem beneficial to have more sperm, very high concentrations can sometimes indicate underlying issues.
- Potential Issues with High Sperm Count:
- Sperm Quality: High sperm count does not always equate to high-quality sperm. In some cases, a higher quantity may be accompanied by reduced motility or abnormal morphology.
- Viscosity: Very high sperm concentrations can increase the viscosity of semen, making it harder for sperm to move efficiently.
- Causes of Hyperspermia:
- Prolonged Abstinence: Extended periods of sexual abstinence can lead to a buildup of sperm, resulting in a higher concentration in the ejaculate.
- Unknown Factors: In many cases, the cause of hyperspermia is not clearly identified.
- Management of Hyperspermia:
- Regular Ejaculation: Frequent ejaculation can help regulate sperm concentration and improve semen quality.
- Fertility Evaluation: If hyperspermia is accompanied by other fertility issues, a comprehensive evaluation is recommended to identify and address any underlying causes.
- Impact on Fertility: Although high sperm count is generally not as problematic as low sperm count, it is essential to ensure that the sperm are also of good quality and able to move efficiently.
Understanding the nuances of sperm quantity and its impact on fertility is vital for anyone trying to conceive. Regular semen analysis and consultations with fertility specialists at HOW.EDU.VN can provide valuable insights and personalized guidance to optimize your reproductive health.
 Sperm Analysis
Sperm Analysis
3. Enhancing Sperm Motility: The Key to Reaching the Egg
Sperm motility, or the ability of sperm to move efficiently, is a critical factor in fertility. Motile sperm are better equipped to navigate the female reproductive tract and reach the egg for fertilization. Understanding what affects sperm motility and how to improve it can significantly boost your chances of conception.
3.1. What Is Sperm Motility and Why Is It Important?
Sperm motility refers to the percentage of sperm in an ejaculate that are moving and their ability to swim effectively. Motility is crucial because sperm must travel through the cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes to fertilize the egg.
- Types of Motility:
- Progressive Motility: Sperm that are moving forward in a straight line or in large circles are considered progressively motile. This type of movement is most effective for reaching the egg.
- Non-Progressive Motility: Sperm that are moving but not making forward progress, such as swimming in tight circles or only moving their tails, are considered non-progressively motile.
- Immotile: Sperm that are not moving at all are classified as immotile.
- Importance of Motility: For natural conception to occur, a sufficient number of sperm must exhibit progressive motility. The WHO recommends that at least 40% of sperm in an ejaculate should be motile for optimal fertility.
3.2. Factors That Can Affect Sperm Motility
Several factors can negatively impact sperm motility, hindering their ability to reach and fertilize the egg.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Smoking: Smoking introduces toxins into the body that can damage sperm and reduce their motility.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can impair sperm production and motility.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can lead to hormonal imbalances and oxidative stress, affecting sperm motility.
- Poor Diet: A diet lacking in essential nutrients can compromise sperm health and motility.
- Medical Conditions:
- Varicocele: Enlarged veins in the scrotum can raise testicular temperature, impairing sperm production and motility.
- Infections: Infections in the reproductive tract can cause inflammation and damage, affecting sperm motility.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions affecting hormone production, such as low testosterone, can reduce sperm motility.
- Autoimmune Disorders: In some cases, the body’s immune system may attack sperm, reducing their motility.
- Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to Toxins: Exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, and other toxins can negatively impact sperm motility.
- Heat: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, such as from hot tubs or saunas, can impair sperm motility.
- Other Factors:
- Age: Sperm motility tends to decline with age.
- Medications: Certain medications can affect sperm motility as a side effect.
3.3. Strategies to Improve Sperm Motility
Improving sperm motility often involves addressing the underlying factors that may be contributing to the issue. Here are some strategies to enhance sperm motility:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Quit Smoking: Cessation of smoking can lead to significant improvements in sperm motility.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Reducing alcohol intake can help improve sperm production and motility.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can balance hormone levels and reduce oxidative stress.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can support sperm health and motility.
- Manage Stress: Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and mindfulness can improve hormone balance.
- Medical Treatments:
- Varicocele Repair: Surgical repair of a varicocele can improve sperm production and motility by reducing testicular temperature.
- Infection Treatment: Treating infections in the reproductive tract can reduce inflammation and improve sperm motility.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone treatments can help correct hormonal imbalances and stimulate sperm production and motility.
- Supplements:
- Antioxidants: Supplements like vitamin C, vitamin E, and coenzyme Q10 can help protect sperm from oxidative damage and improve motility.
- L-Carnitine: This amino acid has been shown to improve sperm motility and concentration.
- Zinc: Zinc is essential for sperm development and can improve sperm motility.
- Avoid Environmental Toxins:
- Minimize Exposure: Reduce exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, and other toxins.
- Wear Protective Gear: If you work with toxins, wear protective clothing and equipment to minimize exposure.
- Keep Cool:
- Avoid Heat: Avoid prolonged exposure to high temperatures, such as from hot tubs and saunas.
- Wear Loose-Fitting Underwear: Loose-fitting underwear can help keep the testicles cooler and improve sperm production and motility.
By implementing these strategies, you can significantly improve sperm motility and increase your chances of successful conception. Consulting with a fertility specialist at HOW.EDU.VN can provide personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
4. Sperm Shape (Morphology): What Role Does It Play?
Sperm morphology, or the shape and structure of sperm, is another important factor assessed during semen analysis. While it is generally considered less critical than sperm quantity and motility, the shape of sperm can still influence their ability to fertilize an egg.
4.1. Understanding Sperm Morphology
Sperm morphology refers to the physical characteristics of sperm, including the size and shape of the head, midpiece, and tail. Typical sperm have an oval-shaped head, a connecting midpiece, and a long, slender tail.
- Assessment of Morphology: Sperm morphology is assessed using strict criteria, such as the Kruger’s strict criteria, which sets specific standards for what is considered a normal sperm shape.
- Normal Morphology: According to Kruger’s strict criteria, a sample is considered normal if at least 4% of the sperm have a typical shape. Lower percentages are considered abnormal morphology, or teratozoospermia.
4.2. How Does Sperm Shape Affect Fertility?
The shape of sperm can affect their ability to penetrate the egg. Sperm with a normal shape are better equipped to move efficiently and bind to the egg’s outer layer.
- Penetration of the Egg: The sperm’s head contains the acrosome, which contains enzymes that help the sperm penetrate the egg’s outer layer. Sperm with an abnormal head shape may have difficulty releasing these enzymes and penetrating the egg.
- Movement and Binding: Sperm with a normal shape are more likely to move efficiently and bind to the egg’s surface. Abnormalities in the midpiece or tail can affect sperm motility, reducing their ability to reach the egg.
4.3. Factors That Can Cause Abnormal Sperm Shape
Several factors can contribute to abnormal sperm shape, including lifestyle factors, medical conditions, and environmental exposures.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic abnormalities can affect sperm development and lead to abnormal morphology.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Smoking: Smoking can damage sperm and increase the risk of abnormal sperm shape.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can impair sperm production and morphology.
- Poor Diet: A diet lacking in essential nutrients can compromise sperm health and morphology.
- Medical Conditions:
- Varicocele: Enlarged veins in the scrotum can raise testicular temperature, affecting sperm morphology.
- Infections: Infections in the reproductive tract can cause inflammation and damage, affecting sperm morphology.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions affecting hormone production can impair sperm development and morphology.
- Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to Toxins: Exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, and other toxins can negatively impact sperm morphology.
- Heat: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can impair sperm morphology.
4.4. Improving Sperm Shape: Strategies to Consider
While sperm morphology is not as critical as sperm quantity and motility, improving sperm shape can still enhance fertility. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Quit Smoking: Cessation of smoking can lead to improvements in sperm morphology.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Reducing alcohol intake can help improve sperm production and morphology.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can support sperm health and morphology.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can balance hormone levels and reduce oxidative stress.
- Supplements:
- Antioxidants: Supplements like vitamin C, vitamin E, and coenzyme Q10 can help protect sperm from oxidative damage and improve morphology.
- Folic Acid: Folic acid is essential for sperm development and can improve morphology.
- Zinc: Zinc is crucial for sperm development and can improve sperm morphology.
- Medical Treatments:
- Varicocele Repair: Surgical repair of a varicocele can improve sperm morphology by reducing testicular temperature.
- Infection Treatment: Treating infections in the reproductive tract can reduce inflammation and improve sperm morphology.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone treatments can help correct hormonal imbalances and stimulate sperm production and morphology.
- Avoid Environmental Toxins:
- Minimize Exposure: Reduce exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, and other toxins.
- Wear Protective Gear: If you work with toxins, wear protective clothing and equipment to minimize exposure.
- Keep Cool:
- Avoid Heat: Avoid prolonged exposure to high temperatures, such as from hot tubs and saunas.
- Wear Loose-Fitting Underwear: Loose-fitting underwear can help keep the testicles cooler and improve sperm production and morphology.
By implementing these strategies, you can improve sperm shape and enhance your chances of successful conception. Consulting with a fertility specialist at HOW.EDU.VN can provide personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
5. Lifestyle Factors and Sperm Health: Making the Right Choices
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in determining sperm health and fertility. Adopting healthy habits and avoiding harmful ones can significantly improve sperm quantity, motility, and morphology.
5.1. Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is vital for sperm health. Certain nutrients are particularly beneficial for sperm production and function.
- Key Nutrients for Sperm Health:
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E, selenium, and coenzyme Q10 protect sperm from oxidative damage.
- Zinc: Essential for sperm development and testosterone production.
- Folic Acid: Important for sperm DNA synthesis and overall sperm health.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Enhance sperm motility and membrane function.
- Foods to Include in Your Diet:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in antioxidants and vitamins.
- Nuts and Seeds: Good sources of zinc, selenium, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Lean Proteins: Provide essential amino acids for sperm production.
- Whole Grains: Offer fiber and B vitamins for overall health.
- Foods to Avoid:
- Processed Foods: Often high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and additives.
- Sugary Drinks: Can lead to weight gain and hormonal imbalances.
- Excessive Caffeine: May affect sperm motility and DNA integrity.
5.2. Exercise and Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise can improve sperm health. Obesity can lead to hormonal imbalances and oxidative stress, affecting sperm production and function.
- Benefits of Exercise:
- Hormone Balance: Regular exercise helps regulate hormone levels, including testosterone.
- Improved Circulation: Enhances blood flow to the reproductive organs.
- Stress Reduction: Lowers stress levels, which can positively impact sperm health.
- Types of Exercise:
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like running, swimming, and cycling improve cardiovascular health and hormone balance.
- Strength Training: Builds muscle mass and supports testosterone production.
- Weight Management:
- Maintain a Healthy BMI: Aim for a body mass index (BMI) within the normal range (18.5-24.9).
- Balanced Diet: Combine regular exercise with a balanced diet to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
5.3. Avoiding Harmful Substances
Certain substances can negatively impact sperm health and fertility. Avoiding these substances is crucial for maintaining optimal reproductive health.
- Smoking:
- Impact on Sperm: Smoking reduces sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- Quitting Smoking: Cessation of smoking can lead to significant improvements in sperm health.
- Alcohol:
- Impact on Sperm: Excessive alcohol consumption can lower testosterone levels and impair sperm production.
- Limiting Alcohol Intake: Moderation is key; limit alcohol intake to no more than one to two drinks per day.
- Drugs:
- Impact on Sperm: Illicit drugs, such as marijuana and cocaine, can negatively affect sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- Avoiding Drug Use: Abstaining from drug use is essential for maintaining sperm health.
- Lubricants:
- Impact on Sperm: Some lubricants can interfere with sperm motility and viability.
- Choosing Sperm-Friendly Lubricants: Opt for lubricants specifically designed for fertility, such as those containing mineral oil or vegetable oil.
5.4. Stress Management
Chronic stress can negatively impact hormone levels and sperm production. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and lifestyle adjustments can improve sperm health.
- Impact of Stress:
- Hormone Imbalances: Stress can disrupt the production of hormones needed for sperm development.
- Oxidative Stress: Prolonged stress can increase oxidative stress, damaging sperm cells.
- Stress Management Techniques:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: Promote relaxation and balance hormone levels.
- Regular Exercise: Releases endorphins and reduces stress.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to support hormone regulation.
By adopting these lifestyle changes, you can significantly improve your sperm health and increase your chances of successful conception. Consulting with a fertility specialist at HOW.EDU.VN can provide personalized advice and support to help you optimize your reproductive health.
6. Medical Conditions and Sperm Health: What You Need to Know
Various medical conditions can impact sperm health, affecting sperm quantity, motility, and morphology. Understanding these conditions and their potential effects is crucial for managing and improving male fertility.
6.1. Infections
Infections in the reproductive tract can cause inflammation and damage, affecting sperm health.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs):
- Chlamydia and Gonorrhea: These STIs can cause inflammation and scarring in the reproductive organs, leading to reduced sperm count and motility.
- Prevention and Treatment: Practicing safe sex and seeking prompt treatment for STIs are essential for protecting sperm health.
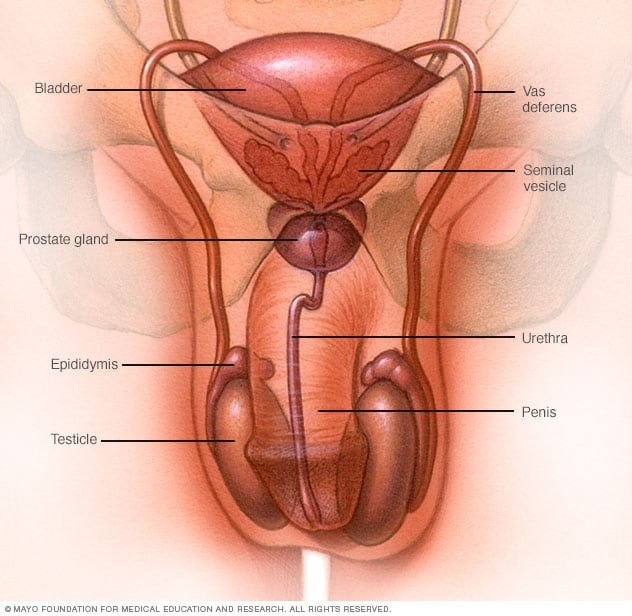
- Prostatitis:
- Inflammation of the Prostate Gland: Prostatitis can cause inflammation and swelling, affecting sperm production and motility.
- Treatment Options: Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications can help manage prostatitis and improve sperm health.
- Epididymitis:
- Inflammation of the Epididymis: Epididymitis can cause pain and swelling in the testicles, affecting sperm maturation and motility.
- Treatment Options: Antibiotics and pain relievers can help treat epididymitis and improve sperm health.
6.2. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones play a crucial role in sperm production and development. Imbalances in hormone levels can negatively impact sperm health.
- Hypogonadism:
- Low Testosterone Levels: Hypogonadism can lead to reduced sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- Treatment Options: Testosterone replacement therapy and other hormone treatments can help correct hormonal imbalances and improve sperm health.
- Hyperprolactinemia:
- Elevated Prolactin Levels: High prolactin levels can interfere with testosterone production and sperm development.
- Treatment Options: Medications to lower prolactin levels can help restore hormonal balance and improve sperm health.
- Thyroid Disorders:
- Impact on Sperm Health: Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can affect sperm production and motility.
- Treatment Options: Thyroid hormone replacement therapy and other thyroid medications can help regulate hormone levels and improve sperm health.
6.3. Varicocele
Varicocele is a condition characterized by the enlargement of veins in the scrotum. It can raise testicular temperature, affecting sperm production and health.
- Impact on Sperm Health: Varicocele can lead to reduced sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- Diagnosis: A physical exam and ultrasound can help diagnose varicocele.
- Treatment Options:
- Varicocele Repair Surgery: Surgical repair of the varicocele can improve sperm production and health by reducing testicular temperature.
- Embolization: A minimally invasive procedure to block the affected veins and improve sperm health.
6.4. Genetic Conditions
Certain genetic conditions can affect sperm production and health.
- Klinefelter Syndrome:
- Genetic Disorder in Males: Klinefelter syndrome is characterized by the presence of an extra X chromosome (XXY).
- Impact on Sperm Health: It can lead to reduced testosterone production and impaired sperm development.
- Treatment Options: Testosterone replacement therapy and assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can help manage the condition.
- Cystic Fibrosis:
- Genetic Disorder Affecting Multiple Organs: Cystic fibrosis can cause the absence of the vas deferens, the tube that carries sperm from the testicles.
- Impact on Sperm Health: Men with cystic fibrosis may have difficulty producing or transporting sperm.
- Treatment Options: Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can help retrieve sperm for fertilization.
- Y Chromosome Microdeletions:
- Genetic Deletions on the Y Chromosome: These deletions can affect sperm production and lead to infertility.
- Treatment Options: Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can help retrieve sperm for fertilization.
6.5. Autoimmune Disorders
In some cases, the body’s immune system may attack sperm cells, reducing their motility and viability.
- Anti-Sperm Antibodies:
- Immune System Attacks Sperm: Anti-sperm antibodies can bind to sperm and interfere with their ability to move and fertilize the egg.
- Treatment Options:
- Corticosteroids: Medications to suppress the immune system.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Bypasses the cervix, reducing exposure to antibodies.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Fertilization occurs outside the body, minimizing the impact of antibodies.
Understanding these medical conditions and their potential impact on sperm health is essential for managing male fertility. Consulting with a fertility specialist at HOW.EDU.VN can provide personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
7. Environmental Factors and Sperm Health: Minimizing Risks
Environmental factors play a significant role in sperm health. Exposure to toxins, radiation, and other environmental hazards can negatively impact sperm quantity, motility, and morphology. Minimizing these risks is crucial for maintaining optimal reproductive health.
7.1. Exposure to Toxins
Exposure to various toxins in the environment can impair sperm production and function.
- Pesticides:
- Impact on Sperm: Pesticides can disrupt hormone levels and damage sperm cells.
- Minimizing Exposure: Choose organic foods, wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly, and avoid using pesticides in your home and garden.
- Heavy Metals:
- Impact on Sperm: Lead, mercury, and other heavy metals can negatively affect sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- Minimizing Exposure: Avoid exposure to lead-based paint, contaminated water, and certain types of seafood that may contain high levels of mercury.
- Industrial Chemicals:
- Impact on Sperm: Chemicals like bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates can disrupt hormone levels and impair sperm production.
- Minimizing Exposure: Use BPA-free containers, avoid plastics with phthalates, and ensure proper ventilation in workplaces with chemical exposure.
7.2. Radiation Exposure
Exposure to radiation can damage sperm cells and affect their ability to fertilize an egg.
- Sources of Radiation:
- Medical Imaging: X-rays and other medical imaging procedures involve radiation exposure.
- Occupational Exposure: Certain occupations, such as radiology technicians, involve regular exposure to radiation.
- Environmental Sources: Radon gas and other environmental sources can contribute to radiation exposure.
- Minimizing Exposure:
- Medical Precautions: Discuss the need for medical imaging with your doctor and use protective shielding when possible.
- Occupational Safety: Follow safety protocols and use protective equipment in workplaces with radiation exposure.
- Environmental Awareness: Test your home for radon gas and take measures to reduce exposure.
7.3. Heat Exposure
Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can impair sperm production and motility.
- Sources of Heat:
- Hot Tubs and Saunas: Spending extended periods in hot tubs and saunas can raise testicular temperature.
- Tight Clothing: Wearing tight-fitting underwear and clothing can trap heat around the testicles.
- Prolonged Sitting: Sitting for long periods can increase testicular temperature.
- Minimizing Exposure:
- Avoid Hot Tubs and Saunas: Limit or avoid spending time in hot tubs and saunas.
- Wear Loose-Fitting Clothing: Choose loose-fitting underwear and clothing to allow for better ventilation.
- Take Breaks from Sitting: Stand up and move around regularly to reduce testicular temperature.
7.4. Air Pollution
Exposure to air pollution can negatively impact sperm health.
- Impact on Sperm: Air pollutants, such as particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide, can cause oxidative stress and inflammation, affecting sperm quantity, motility, and morphology.
- Minimizing Exposure:
- Air Purifiers: Use air purifiers in your home and office to reduce indoor air pollution.
- Outdoor Precautions: Avoid outdoor activities during periods of high air pollution, and wear a mask if necessary.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise to protect against the effects of air pollution.
7.5. Occupational Hazards
Certain occupations involve exposure to environmental hazards that can affect sperm health.
- Construction Workers:
- Exposure to Toxins: Construction workers may be exposed to lead, asbestos, and other toxins.
- Protective Measures: Wear protective gear and follow safety protocols to minimize exposure.
- Farmers:
- Exposure to Pesticides: Farmers may be exposed to pesticides and other agricultural chemicals.
- Protective Measures: Wear protective clothing and use safety equipment to minimize exposure.
- Factory Workers:
- Exposure to Industrial Chemicals: Factory workers may be exposed to various industrial chemicals.
- Protective Measures: Follow safety protocols and use protective equipment to minimize exposure.
Minimizing exposure to these environmental factors is essential for maintaining optimal sperm health. Consulting with a fertility specialist at how.edu.vn can provide personalized advice and support to help you protect your reproductive health.
8. Supplements and Sperm Health: What Really Works?
Supplements can play a supportive role in improving sperm health, but it’s essential to know which ones are effective and safe. A balanced diet should always be the foundation, with supplements used to fill any nutritional gaps.
8.1. Key Supplements for Sperm Health
Several supplements have been shown to positively impact sperm health, including sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- Antioxidants:
- Vitamin C: Protects sperm from oxidative damage and improves sperm count and motility.
- Vitamin E: Enhances sperm motility and protects sperm DNA.
- Selenium: Improves sperm motility and protects sperm from oxidative stress.
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): Boosts sperm energy production and enhances motility.
- Amino Acids:
- L-Carnitine: Improves sperm motility and concentration.
- L-Arginine: Enhances sperm production and motility.
- Minerals:
- Zinc: Essential for sperm development and testosterone production.
- Folic Acid: Important for sperm DNA synthesis and overall sperm health.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
- DHA and EPA: Improve sperm motility and membrane function.
8.2. How Supplements Improve Sperm Health
These supplements work through various mechanisms to support sperm health.
- Protecting Against Oxidative Stress: Antioxidants neutralize free radicals, protecting sperm from oxidative damage.
- Enhancing Energy Production: CoQ10 boosts sperm energy production, improving motility.
- Supporting Sperm Development: Zinc and folic acid are essential for sperm DNA synthesis and overall development.
- Improving Membrane Function: Omega-3 fatty acids enhance sperm membrane function, improving motility and viability.
8.3. Choosing the Right Supplements
When selecting supplements for sperm health, consider the following factors:
- Quality: Choose high-quality supplements from reputable brands that undergo third-party testing.
- Dosage: Follow the recommended dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional.
- Ingredients: Look for supplements with a combination of key nutrients, such as antioxidants, amino acids, and minerals.
- Form: Choose supplements in a form that is easily absorbed by the body, such as capsules or softgels.
8.4. Considerations and Precautions
Before starting any new supplement regimen, it’s important to consider the following:
- Consult with a Healthcare Professional: Discuss your plans with a doctor or fertility specialist to ensure the supplements are safe and appropriate for you.
- Potential Side Effects: Be aware of potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
- Realistic Expectations: Supplements can support sperm health, but they are not a substitute for a healthy lifestyle and medical treatment.
- Long-Term Use: Supplements may take several months to show noticeable effects on sperm health.
8.5. Examples of Effective Supplement Combinations
Some supplement combinations may be more effective than individual supplements for improving sperm health.
- Antioxidant Blend: Vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium, and CoQ10.
- Amino Acid Complex: L-Carnitine and L-Arginine.
- Multivitamin for Men’s Fertility: Contains zinc, folic acid, and other essential nutrients.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids Plus Antioxidants: Enhances sperm motility and protects against oxidative stress.
By choosing the right