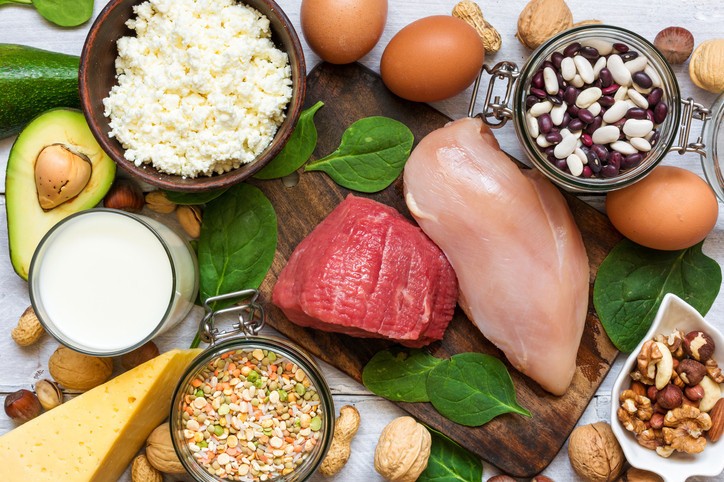
Are you unsure about the right amount of protein to include in your diet for optimal health and well-being? Determining the appropriate daily protein intake can be confusing, but HOW.EDU.VN is here to provide clarity. Understanding your protein needs and how to meet them through quality protein sources is crucial for muscle growth, weight management, and overall health, and we offer expert guidance tailored to your specific requirements. Explore personalized dietary recommendations, learn about the benefits of protein consumption, and connect with our team of experienced Ph.D. experts at HOW.EDU.VN for customized advice.
1. What Is The Recommended Daily Protein Intake?
The recommended daily protein intake varies based on factors like age, activity level, and overall health, but understanding these guidelines is crucial. The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) suggests 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, but this number isn’t one-size-fits-all. At HOW.EDU.VN, we tailor this general recommendation to your individual needs.
- General Guidelines: For most adults, the RDA of 0.8 grams per kilogram is a starting point. This helps prevent deficiency and supports basic bodily functions.
- Active Individuals: Athletes or those who engage in regular, intense physical activity may require more protein, often ranging from 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight, to support muscle repair and growth.
- Older Adults: As we age, our bodies become less efficient at processing protein. Therefore, older adults may need to increase their protein intake to maintain muscle mass and overall health.
- Individual Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions can significantly impact protein needs. Individuals with kidney disease, for example, may need to limit their protein intake to prevent further kidney damage.
To get a more precise and personalized recommendation, HOW.EDU.VN offers expert consultations. Our Ph.D. specialists consider your unique health profile, activity level, and goals to provide a tailored plan that optimizes your protein intake for overall health.
2. How Does Activity Level Impact Protein Needs?
Your activity level significantly influences how much protein you need, making it essential to adjust your intake based on your daily activities.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: If you have a sedentary lifestyle with minimal physical activity, the standard RDA of 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight might be sufficient.
- Moderate Activity: Engaging in moderate exercise, such as regular walking, jogging, or gym workouts a few times a week, increases your protein needs to about 1.0 to 1.3 grams per kilogram of body weight.
- Intense Training: Athletes and individuals involved in intense training, like weightlifting, CrossFit, or endurance sports, may require 1.4 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight to support muscle recovery, repair, and growth.
- Type of Activity: The type of activity also matters. Resistance training, which focuses on building muscle mass, requires more protein than endurance activities, like running or swimming, though both benefit from increased protein intake.
HOW.EDU.VN provides tailored recommendations based on your specific activity level and training regimen. Our experts help you fine-tune your protein intake to maximize performance, optimize recovery, and achieve your fitness goals.
3. What Are The Best Protein Sources To Include In My Diet?
Choosing high-quality protein sources is vital for meeting your daily protein needs and supporting overall health.
- Animal Sources:
- Lean Meats: Chicken, turkey, and lean cuts of beef and pork are excellent sources of protein and essential nutrients.
- Fish: Fish like salmon, tuna, and cod are rich in protein and omega-3 fatty acids, which promote heart health and reduce inflammation.
- Dairy: Dairy products such as Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and milk provide protein and calcium, supporting bone health and muscle function.
- Eggs: Eggs are a complete protein source, containing all nine essential amino acids, and are versatile for various meals.
- Plant-Based Sources:
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are high in protein and fiber, aiding digestion and promoting satiety.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds offer protein and healthy fats, contributing to heart health and overall nutrition.
- Tofu and Tempeh: These soy-based products are excellent plant-based protein sources and can be used in numerous dishes.
- Quinoa: Quinoa is a complete protein, containing all essential amino acids, and is a versatile grain for meals.
- Protein Supplements:
- Whey Protein: Whey protein is a fast-digesting protein, ideal for post-workout recovery and muscle repair.
- Casein Protein: Casein protein is a slow-digesting protein, suitable for consumption before bed to support overnight muscle recovery.
- Plant-Based Protein Powders: Pea, rice, and soy protein powders are great alternatives for those who prefer plant-based options or have dairy sensitivities.
HOW.EDU.VN can help you balance your protein intake from various sources to ensure you get all the essential amino acids and nutrients you need. Our Ph.D. experts offer personalized dietary plans tailored to your preferences, dietary restrictions, and health goals.
4. Can Eating Too Much Protein Be Harmful To My Health?
While protein is essential, consuming excessive amounts can lead to health issues. Understanding the potential risks is vital for maintaining a balanced diet.
- Kidney Strain:
- Mechanism: High protein intake can increase the workload on the kidneys as they filter out waste products from protein metabolism.
- Risk: Individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions are particularly vulnerable to kidney strain from high protein diets.
- Prevention: Stay hydrated and monitor kidney function if you consume high levels of protein regularly.
- Digestive Issues:
- Symptoms: Excess protein intake can cause digestive problems, such as bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
- Causes: High protein diets are often low in fiber, which is essential for healthy digestion.
- Solutions: Incorporate more fiber-rich foods, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, to balance your diet and support digestive health.
- Weight Gain:
- Calorie Surplus: If you consume more calories than you burn, regardless of the source, you may gain weight.
- Impact: Protein contains calories, and excess intake can contribute to weight gain if not balanced with adequate physical activity.
- Strategies: Manage your portion sizes, maintain a balanced diet, and engage in regular exercise to prevent weight gain.
- Bone Health:
- Calcium Excretion: Some studies suggest that high protein diets can increase calcium excretion, potentially impacting bone density over time.
- Considerations: Ensure you consume enough calcium and vitamin D to support bone health, especially if you follow a high protein diet.
- Recommendations: Balance protein intake with adequate calcium-rich foods and consider vitamin D supplementation if needed.
At HOW.EDU.VN, we emphasize the importance of balance and moderation in your diet. Our Ph.D. experts can help you assess your protein needs and develop a sustainable eating plan that promotes overall health without overdoing it.
5. What Are The Signs Of Protein Deficiency?
Recognizing the signs of protein deficiency is crucial for addressing the issue promptly and maintaining good health.
- Muscle Loss:
- Symptoms: Decreased muscle mass and strength, making it difficult to perform physical activities.
- Causes: Inadequate protein intake deprives the body of the building blocks needed to maintain and repair muscle tissue.
- Solutions: Increase protein consumption through diet or supplementation to rebuild muscle mass.
- Fatigue And Weakness:
- Symptoms: Persistent tiredness, lack of energy, and overall weakness.
- Mechanisms: Protein is essential for energy production and various bodily functions. Deficiency can lead to reduced energy levels.
- Remedies: Ensure you consume enough protein to support energy production and overall vitality.
- Weakened Immunity:
- Symptoms: Frequent infections, slow wound healing, and a general decline in immune function.
- Impact: Protein is vital for immune cell production and function. Deficiency impairs the body’s ability to fight off infections.
- Interventions: Increase protein intake to support immune cell production and improve immune function.
- Hair, Skin, And Nail Problems:
- Symptoms: Thinning hair, brittle nails, dry skin, and skin rashes.
- Causes: Protein is a key component of these tissues. Deficiency can lead to structural and functional problems.
- Treatment: Consume enough protein to support the health and integrity of your hair, skin, and nails.
- Edema (Swelling):
- Symptoms: Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet.
- Underlying Mechanism: Protein helps maintain fluid balance in the body. Deficiency can lead to fluid accumulation in tissues.
- Management: Increase protein intake to restore fluid balance and reduce edema.
HOW.EDU.VN offers comprehensive nutritional assessments to help you identify any potential deficiencies and develop a targeted plan to address them. Our Ph.D. experts provide personalized guidance to ensure you get the right amount of protein for optimal health.
6. How Can I Track My Daily Protein Intake Effectively?
Tracking your daily protein intake is a practical way to ensure you’re meeting your nutritional needs and achieving your health goals.
-
Food Diary:
- Method: Keep a detailed record of everything you eat and drink each day.
- Benefits: Helps you identify your eating patterns and estimate your protein intake.
- Tools: Use a notebook or a digital app to track your food intake.
-
Nutrition Tracking Apps:
- Features: Apps like MyFitnessPal, Lose It!, and Cronometer allow you to log your meals and calculate your macronutrient intake automatically.
- Advantages: Provides precise data on your protein consumption and other nutrients.
- Tips: Use accurate serving sizes and update the app regularly for the best results.
-
Read Food Labels:
- Importance: Food labels provide valuable information on the protein content of packaged foods.
- How To: Check the nutrition facts panel for the grams of protein per serving.
- Considerations: Pay attention to serving sizes, as they can vary widely.
-
Use Measuring Tools:
- Accuracy: Use measuring cups, spoons, and a food scale to ensure accurate portion sizes.
- Benefits: Helps you avoid underestimating or overestimating your protein intake.
- Application: Weigh or measure your protein sources to track your consumption precisely.
-
Consult A Nutritionist:
- Expertise: A registered dietitian or nutritionist can help you assess your protein needs and track your intake effectively.
- Personalization: Provides personalized recommendations based on your health status, activity level, and dietary preferences.
- Guidance: Offers support and advice to help you achieve your nutritional goals.
HOW.EDU.VN offers expert consultations with our Ph.D. specialists, who can guide you in tracking your protein intake and making informed dietary choices. Our personalized approach ensures you get the right amount of protein to support your health and fitness goals.
7. How Do Protein Needs Change With Age?
Protein needs vary across the lifespan, making it crucial to adjust your intake to support health at different life stages.
- Children And Adolescents:
- Requirements: Growing children and teenagers need adequate protein to support growth and development.
- Recommendations: The RDA for children varies by age, typically ranging from 0.95 to 1.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
- Importance: Sufficient protein intake is crucial for building muscle mass, bone density, and overall health.
- Adults (19-64 Years):
- Maintenance: Adults need protein to maintain muscle mass, repair tissues, and support various bodily functions.
- Guidelines: The general RDA for adults is 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
- Considerations: Active individuals and those with specific health conditions may require more protein.
- Older Adults (65+ Years):
- Increased Needs: Older adults often need more protein to combat age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia) and maintain bone health.
- Recommendations: Experts often recommend 1.0 to 1.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight for older adults.
- Benefits: Adequate protein intake can improve muscle strength, mobility, and overall quality of life in older adults.
- Pregnancy And Breastfeeding:
- Elevated Requirements: Pregnant and breastfeeding women have increased protein needs to support fetal development and milk production.
- Guidelines: Pregnant women need approximately 71 grams of protein per day, while breastfeeding women may need slightly more.
- Significance: Meeting these protein needs is vital for the health of both the mother and the baby.
HOW.EDU.VN provides tailored nutritional advice for every stage of life. Our Ph.D. experts can help you adjust your protein intake to meet your specific needs and support your health goals.
8. Can Protein Help With Weight Loss Or Weight Management?
Protein plays a crucial role in weight loss and weight management due to its unique effects on the body.
- Increased Satiety:
- Mechanism: Protein is more satiating than carbohydrates or fats, meaning it helps you feel fuller for longer.
- Benefits: Reduces overall calorie intake by decreasing hunger and cravings.
- Application: Incorporate protein-rich foods into your meals to stay satisfied and control your appetite.
- Boosted Metabolism:
- Thermogenic Effect: Protein has a higher thermic effect of food (TEF) compared to fats and carbs.
- Impact: Your body burns more calories digesting protein, which can help boost your metabolism.
- Considerations: While the effect is modest, it contributes to overall calorie expenditure.
- Muscle Preservation:
- Muscle Maintenance: During weight loss, it’s crucial to preserve muscle mass to maintain a healthy metabolism.
- Importance of Protein: Adequate protein intake helps protect muscle tissue while you lose fat.
- Strategies: Combine protein-rich foods with resistance training to preserve and build muscle during weight loss.
- Blood Sugar Regulation:
- Stabilizing Effect: Protein helps stabilize blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes and cravings.
- Mechanism: Slows down the absorption of glucose, leading to more stable energy levels.
- Practical Tips: Pair protein with carbohydrates to mitigate blood sugar spikes.
- Reducing Late-Night Cravings:
- Impact: Consuming protein, especially before bed, can help reduce late-night cravings and snacking.
- Benefits: Stabilizes blood sugar levels overnight, preventing hunger pangs.
- Suggestions: Opt for a small protein-rich snack, like Greek yogurt or a handful of nuts, before bed.
HOW.EDU.VN offers personalized weight loss and weight management plans that emphasize the strategic use of protein. Our Ph.D. experts can help you optimize your protein intake to achieve your weight goals while maintaining muscle mass and overall health.
9. What Are Some Practical Tips For Increasing Protein Intake?
Incorporating more protein into your diet can be simple with a few strategic tweaks.
- Start With Breakfast:
- Importance: Begin your day with a protein-rich breakfast to boost satiety and energy levels.
- Ideas: Opt for Greek yogurt with berries and nuts, eggs with whole-grain toast, or a protein smoothie.
- Benefits: Sets a positive tone for the day and helps control appetite.
- Include Protein In Every Meal:
- Balanced Meals: Ensure that each meal contains a source of protein, whether it’s meat, fish, legumes, or dairy.
- Examples: Add grilled chicken to your salad, include beans in your soup, or snack on almonds.
- Advantages: Promotes satiety, stabilizes blood sugar, and supports muscle maintenance.
- Snack Smart:
- Protein-Rich Snacks: Choose snacks that are high in protein to keep hunger at bay between meals.
- Options: Consider hard-boiled eggs, cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, protein bars, or a handful of nuts.
- Avoid Empty Calories: Steer clear of sugary or processed snacks that offer little nutritional value.
- Add Protein To Your Salads:
- Salad Boost: Transform your salads into a protein powerhouse by adding grilled chicken, fish, tofu, or hard-boiled eggs.
- Nutrient Balance: Enhances the nutritional value of your salad and keeps you feeling full and satisfied.
- Versatility: Experiment with different protein sources to keep your salads interesting.
- Use Protein Supplements:
- Convenient Option: Protein powders can be a convenient way to boost your protein intake, especially after workouts or when you’re short on time.
- Types: Whey, casein, soy, rice, and pea protein powders are available.
- Application: Add protein powder to smoothies, shakes, or yogurt.
- Choose Lean Protein Sources:
- Healthier Options: Opt for lean protein sources like chicken breast, turkey, fish, and lean cuts of beef and pork.
- Reducing Fat Intake: Minimizes your intake of saturated fats and calories while providing high-quality protein.
- Balance: Ensure your protein sources are balanced with healthy fats and complex carbohydrates.
- Prepare Meals In Advance:
- Meal Planning: Plan your meals and snacks ahead of time to ensure you have protein-rich options readily available.
- Convenience: Makes it easier to stick to your protein goals, especially when you’re busy.
- Organization: Batch cook protein sources like chicken or beans to use in various meals throughout the week.
HOW.EDU.VN can provide personalized meal plans and practical strategies to help you increase your protein intake effectively. Our Ph.D. experts offer guidance tailored to your lifestyle, preferences, and health goals, ensuring you get the right amount of protein to thrive.
10. When Should I Consult A Professional About My Protein Intake?
Knowing when to seek professional advice regarding your protein intake is essential for managing your health and addressing any underlying issues.
- Pre-Existing Health Conditions:
- Kidney Disease: If you have kidney disease, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your protein intake.
- Liver Disease: Similar to kidney disease, liver conditions require careful management of protein intake to avoid complications.
- Diabetes: Managing protein intake is important for blood sugar control and overall health in individuals with diabetes.
- Unexplained Symptoms:
- Fatigue And Weakness: If you experience persistent fatigue and weakness despite a balanced diet, it’s important to rule out protein deficiency or other underlying health issues.
- Muscle Loss: Involuntary muscle loss can be a sign of inadequate protein intake or other medical conditions that require professional evaluation.
- Edema: Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet can be a sign of protein deficiency or kidney problems, necessitating a medical consultation.
- Specific Dietary Needs:
- Vegetarian Or Vegan Diets: Individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets may need guidance on ensuring they meet their protein needs through plant-based sources.
- Food Allergies Or Intolerances: If you have food allergies or intolerances that limit your protein sources, a registered dietitian can help you create a balanced and nutritious meal plan.
- Pregnancy Or Breastfeeding: Pregnant and breastfeeding women have increased protein needs and should consult a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
- Athletic Training:
- High-Intensity Training: Athletes and individuals engaging in high-intensity training may require more protein than the general population.
- Performance Goals: A sports nutritionist can help you optimize your protein intake to support muscle growth, recovery, and athletic performance.
- Supplement Use: If you’re considering using protein supplements, it’s best to seek guidance from a healthcare professional to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your needs.
- Weight Loss Or Weight Management:
- Sustainable Plans: A registered dietitian can help you create a sustainable and balanced weight loss plan that includes adequate protein intake.
- Metabolic Assessment: Can assess your metabolic rate and provide personalized recommendations for calorie and macronutrient intake.
- Long-Term Success: Offers support and guidance to help you achieve your weight loss goals and maintain a healthy weight.
At HOW.EDU.VN, we offer expert consultations with our Ph.D. specialists, who can provide personalized advice on your protein intake and address any health concerns you may have. Our team is dedicated to helping you achieve optimal health through evidence-based nutrition and lifestyle guidance.
Navigating the world of protein intake can be complex, but with the right information and support, you can make informed choices that promote your health and well-being. Whether you’re an athlete, an older adult, or simply someone looking to optimize your diet, understanding your protein needs is key.
Ready to take control of your nutrition and optimize your protein intake? Contact HOW.EDU.VN today for personalized guidance from our team of experienced Ph.D. experts. We’re here to help you achieve your health goals with evidence-based advice and tailored support. Reach out to us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, call us at +1 (310) 555-1212, or visit our website at how.edu.vn for more information and to schedule a consultation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is it possible to eat too much protein?
Yes, consuming excessive amounts of protein can lead to health issues like kidney strain, digestive problems, and potential weight gain.
2. How much protein should I eat per day to lose weight?
A higher protein intake, around 1.2 to 1.5 grams per kilogram of body weight, can help promote satiety, boost metabolism, and preserve muscle mass during weight loss.
3. What are the best high-protein foods to include in my diet?
Excellent sources of protein include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, seeds, and soy-based products like tofu and tempeh.
4. How do I calculate my daily protein needs?
Multiply your body weight in kilograms by 0.8 grams for the general RDA. Adjust this number based on your activity level, age, and health goals.
5. Can protein supplements replace whole food sources of protein?
While protein supplements can be convenient, they should not replace whole food sources of protein. Whole foods offer additional nutrients and benefits.
6. What are the signs of protein deficiency?
Signs of protein deficiency include muscle loss, fatigue, weakened immunity, hair and skin problems, and edema (swelling).
7. How does protein affect muscle growth and repair?
Protein provides the amino acids needed to repair and rebuild muscle tissue after exercise, supporting muscle growth and strength.
8. Is a high-protein diet safe for individuals with kidney problems?
Individuals with kidney problems should consult a healthcare provider before starting a high-protein diet, as it can strain the kidneys.
9. How can I increase my protein intake without relying on meat?
Incorporate plant-based protein sources like legumes, nuts, seeds, tofu, and tempeh into your diet to increase protein intake without meat.
10. What is the role of protein in maintaining overall health?
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, producing enzymes and hormones, and maintaining overall health and well-being.