Answering the question, How Much Savings Does The Average American Have, reveals a complex financial landscape. The typical American family has around $62,410 in savings accounts, but this number can be misleading due to wide variations. For personalized advice and expert financial guidance, explore resources at HOW.EDU.VN. Building a secure financial future requires understanding these averages and seeking expert advice to tailor strategies to individual circumstances. Consider consulting with financial experts to assess your financial health, develop a personalized savings plan, and navigate the complexities of wealth accumulation and investment strategies.
1. What is the Average Savings of Americans?
The average savings of Americans is approximately $62,410, but the median savings are closer to $8,000. The average is significantly impacted by high-net-worth individuals, skewing the perception of typical savings. The median provides a more accurate representation of what most Americans have saved.
To expand, this disparity highlights the wealth inequality in the United States. While some families have substantial savings, many others have very little. Understanding these figures helps individuals gauge their own financial standing relative to the broader population. Consider factors like age, income, and location when comparing your savings to these averages.
2. How Much Savings Should I Have by Age?
Savings benchmarks by age vary, but a general guideline suggests having one year’s salary saved by age 30, three times your salary by 40, and so on.
| Age Group | Recommended Savings |
|---|---|
| 30 | 1x annual salary |
| 40 | 3x annual salary |
| 50 | 6x annual salary |
| 60 | 8x annual salary |

These benchmarks are intended to help you stay on track for retirement. However, individual circumstances can greatly influence the actual amount needed. Factors such as lifestyle, debt, and anticipated retirement expenses play a significant role. Financial planning experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide personalized guidance to determine your specific savings goals.
3. What Factors Affect Average Savings Balances?
Several factors significantly influence average savings balances, including age, income, education, race, and homeownership status. Understanding these factors can provide insight into why savings balances vary widely among different demographic groups.
3.1. Age
Savings tend to increase with age as individuals have more time to accumulate wealth. Older Americans generally have higher savings balances than younger individuals. However, balances may decline after retirement as individuals start drawing from their savings. According to Federal Reserve data, individuals between 45 and 54 years old have, on average, $50,590 more in savings compared to those under 35. This trend emphasizes the importance of starting to save early to maximize potential wealth accumulation.
3.2. Income
Higher income levels typically result in higher savings balances. Individuals with more disposable income can allocate more funds to savings accounts. Income inequality contributes to the wide disparities in average savings. Those with higher incomes are also more likely to have access to financial resources and investment opportunities that further enhance their savings.
3.3. Education
Higher levels of education often lead to higher incomes and, consequently, higher savings balances. Individuals with college degrees tend to earn more and are better equipped to manage their finances. The 2022 Survey of Consumer Finances indicates that individuals with a college degree have an average savings balance of $116,010, nearly five times that of someone with only a high school diploma ($23,380).
3.4. Race
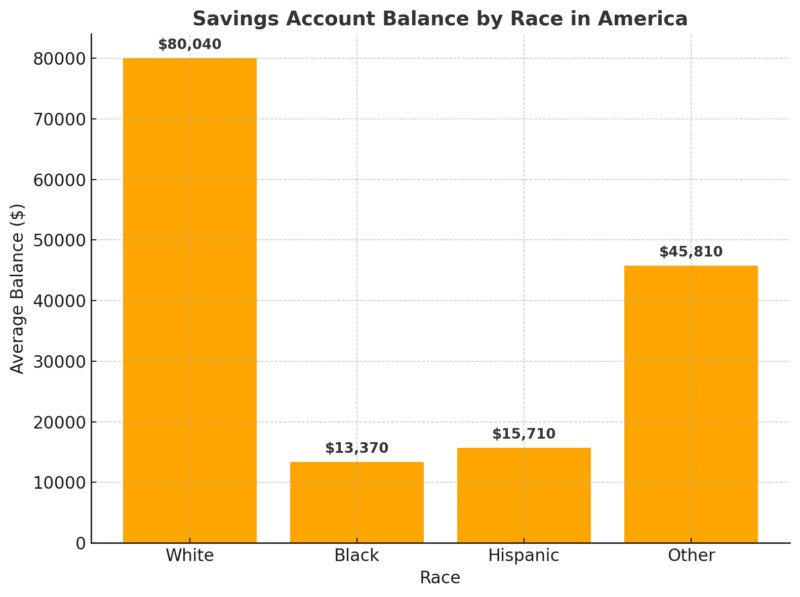
Significant racial disparities exist in average savings balances. White households tend to have much higher savings balances compared to Black and Hispanic households. These disparities are influenced by historical inequalities, income levels, and access to financial resources. Data from Business Insider shows that White individuals have $80,040 in savings, compared to $13,370 for Black individuals and $15,710 for Hispanic individuals.
3.5. Homeownership
Homeowners generally have higher savings balances than renters. Owning a home is an indicator of financial stability and provides opportunities for wealth accumulation through equity. Federal Reserve data indicates that homeowners have an average savings balance of $85,430, significantly more than renters, who have an average of $16,930. Homeownership also fosters a sense of financial security and encourages long-term savings behavior.
4. How Does Savings Balance Vary by Race?
Savings balances vary significantly by race, with White households typically having the highest average savings compared to Black and Hispanic households.
The persistent racial wealth gap plays a significant role in these disparities. Historical inequalities, differences in income levels, and unequal access to financial resources contribute to these variations. Addressing these disparities requires systemic changes to promote economic equity and opportunity for all racial groups.
5. What is the Impact of Homeownership on Savings?
Homeownership significantly impacts savings, as homeowners tend to have substantially higher savings balances compared to renters.
Owning a home often indicates greater financial stability and access to wealth-building opportunities. Homeowners typically have higher incomes and more financial resources, enabling them to save more. Additionally, the equity built through homeownership serves as a form of savings and investment. Renters, on the other hand, may face challenges in accumulating savings due to the ongoing costs of renting and limited opportunities for wealth accumulation.
6. How Does Household Size Affect Savings Balances?
Household size significantly affects savings balances. Couples without children tend to have the highest average savings, while single-parent households typically have the lowest. Federal data shows that single individuals under 55 have $19,320 in savings, while single parents with children have an even lower balance of $16,800. In contrast, couples without children hold the most savings, averaging $103,140.
6.1. Couples Without Children
Couples without children often have higher savings due to dual-income potential and fewer financial dependents. This allows them to allocate more funds to savings and investments. The absence of childcare expenses and other family-related costs further enhances their ability to save. Financial planning for couples without children often focuses on maximizing investment opportunities and long-term wealth accumulation.
6.2. Single Individuals
Single individuals under 55 typically have moderate savings balances. Their savings are influenced by their income level, expenses, and financial priorities. Single individuals may face challenges in saving due to the lack of dual-income support. However, effective budgeting and financial planning can help them achieve their savings goals.
6.3. Single Parents With Children
Single parents with children often have the lowest savings balances. They face significant financial constraints due to the costs of raising children on a single income. Childcare expenses, education costs, and healthcare needs can strain their ability to save. Financial assistance programs and support networks can help single parents improve their financial stability and increase their savings.
7. What is the Role of Education in Savings?
Education plays a crucial role in savings, with higher education levels strongly correlating with higher savings balances.
Individuals with college degrees tend to earn higher incomes, leading to greater savings potential and long-term financial security. Education also equips individuals with the knowledge and skills to manage their finances effectively. The 2022 Survey of Consumer Finances indicates that individuals with a college degree have an average savings balance of $116,010, which is nearly five times that of someone with only a high school diploma ($23,380).
8. How Can High-Yield Savings Accounts Help?
High-yield savings accounts can significantly enhance savings by offering better interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts. These accounts allow funds to grow more efficiently over time. The higher interest earned can help individuals reach their savings goals faster and build a larger financial cushion.
8.1. Benefits of High-Yield Savings Accounts
-
Higher Interest Rates: High-yield savings accounts offer competitive interest rates, maximizing the growth potential of savings.
-
Compounding Interest: Interest earned is compounded, meaning it is added to the principal, and future interest is earned on the new, higher balance.
-
FDIC Insurance: Most high-yield savings accounts are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), providing protection for deposits up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank.
-
Easy Access to Funds: Funds in high-yield savings accounts are typically easily accessible, allowing individuals to withdraw money when needed.
9. What are Some Key Savings Statistics to Consider?
Several key savings statistics provide insights into the financial health and preparedness of Americans:
-
Only 25% of Americans consider themselves completely financially secure, down from 28% in 2023, according to the Financial Freedom Survey.
-
Nearly 59% of U.S. adults feel uncomfortable with their level of emergency savings.
-
27% of Americans have no emergency savings at all, leaving them financially vulnerable in case of unexpected expenses.
-
36% of adults had more credit card debt than emergency savings in both 2023 and 2024, highlighting financial strain.
-
57% of working Americans (full-time, part-time, or temporarily unemployed) fell behind on their retirement savings, according to the latest Retirement Savings Survey.
These statistics underscore the importance of prioritizing savings and financial planning. Building an emergency fund, reducing debt, and staying on track with retirement savings are crucial steps towards achieving financial security.
10. How Can I Improve My Savings Habits?
Improving savings habits involves setting clear financial goals, creating a budget, and making informed financial decisions. Here are some strategies to help you enhance your savings:
10.1. Set Clear Financial Goals
Define your savings goals, whether it’s for retirement, a down payment on a home, or an emergency fund. Having specific goals in mind can motivate you to save more. Break down your goals into smaller, achievable milestones to stay on track. Regularly review and adjust your goals as needed to reflect changes in your financial situation.
10.2. Create a Budget
Develop a budget to track your income and expenses. Identify areas where you can cut back on spending and allocate more funds to savings. Use budgeting tools or apps to simplify the process. Regularly review your budget to ensure you are meeting your savings goals.
10.3. Automate Savings
Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings account. Automating your savings ensures that you consistently save money without having to think about it. Consider setting up automatic contributions to your retirement account as well. Start with a small amount and gradually increase it over time.
10.4. Reduce Debt
High levels of debt can hinder your ability to save. Prioritize paying off high-interest debt, such as credit card debt, to free up more funds for savings. Consider debt consolidation or balance transfer options to lower interest rates. Avoid taking on new debt whenever possible.
10.5. Seek Financial Advice
Consult with a financial advisor to develop a personalized savings plan. A financial advisor can provide expert guidance on investment strategies, retirement planning, and wealth management. They can also help you stay on track with your savings goals and make informed financial decisions. Connect with experienced financial experts at HOW.EDU.VN for tailored advice.
11. What Resources Are Available to Help Me Save More?
Numerous resources are available to help you save more effectively. These include financial education programs, online tools, and professional financial advisors.
11.1. Financial Education Programs
Participate in financial education programs to improve your understanding of personal finance. These programs offer valuable information on budgeting, saving, investing, and debt management. Look for programs offered by non-profit organizations, community centers, or educational institutions.
11.2. Online Tools
Utilize online tools and apps to track your spending, create a budget, and monitor your savings progress. Many of these tools offer features such as goal setting, expense tracking, and investment analysis. Popular budgeting apps include Mint, YNAB (You Need a Budget), and Personal Capital.
11.3. Professional Financial Advisors
Consult with a professional financial advisor to receive personalized advice and guidance on your savings and investment strategies. A financial advisor can assess your financial situation, help you set realistic goals, and develop a plan to achieve them. They can also provide ongoing support and adjust your plan as needed.
12. How Can HOW.EDU.VN Help Me With My Financial Goals?
HOW.EDU.VN offers access to a network of experienced financial experts who can provide tailored advice to help you achieve your financial goals. Our platform connects you with professionals who can offer guidance on savings, investments, retirement planning, and more.
12.1. Access to Expert Financial Advisors
HOW.EDU.VN provides access to a diverse network of financial advisors with expertise in various areas of personal finance. Whether you need help with budgeting, saving for retirement, or managing your investments, our experts can provide the guidance you need.
12.2. Personalized Financial Advice
Our financial advisors offer personalized advice tailored to your specific financial situation and goals. They take the time to understand your needs and develop a plan that aligns with your objectives.
12.3. Comprehensive Financial Planning
HOW.EDU.VN offers comprehensive financial planning services that cover all aspects of your financial life. Our experts can help you create a budget, set savings goals, manage debt, and plan for retirement.
12.4. Ongoing Support and Guidance
Our financial advisors provide ongoing support and guidance to help you stay on track with your financial goals. They regularly review your progress and make adjustments to your plan as needed.
FAQ: Average American Savings
13.1. Is $100,000 in Savings Good?
Having $100,000 in savings is generally considered good, especially if you are under the age of 50. It provides a substantial financial cushion for emergencies and future goals.
13.2. What is Considered a Good Amount of Savings?
A good amount of savings depends on your age, income, and financial goals. A general guideline is to have one year’s salary saved by age 30, three times your salary by 40, and so on.
13.3. How Much Should I Have Saved by 40?
By age 40, it’s recommended to have three times your annual salary saved. This benchmark helps ensure you’re on track for retirement and other long-term financial goals.
13.4. What is the Average Retirement Savings in the US?
The average retirement savings in the US varies by age. For those nearing retirement (ages 55-64), the average is around $200,000, but this figure can vary widely based on individual circumstances.
13.5. How Can I Catch Up on Savings?
To catch up on savings, increase your savings rate, reduce expenses, and consider seeking professional financial advice. Automate your savings and explore high-yield savings options.
13.6. What are the Best Ways to Save Money?
The best ways to save money include setting a budget, automating savings, reducing debt, and finding ways to cut expenses. Consider using budgeting apps and seeking financial education.
13.7. How Important is Emergency Savings?
Emergency savings are crucial for financial security. They provide a safety net for unexpected expenses such as medical bills, job loss, or car repairs. Aim to save at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses in an emergency fund.
13.8. What is the Difference Between Savings and Investments?
Savings are funds set aside for short-term goals or emergencies, while investments are funds allocated to assets with the expectation of generating income or appreciation over the long term. Savings are typically more liquid and less risky than investments.
13.9. How Does Inflation Affect My Savings?
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of your savings over time. To combat inflation, consider investing in assets that outpace the rate of inflation, such as stocks or real estate.
13.10. When Should I Start Saving for Retirement?
It’s best to start saving for retirement as early as possible. The earlier you start, the more time your investments have to grow. Take advantage of employer-sponsored retirement plans and consider opening an individual retirement account (IRA).
Understanding the average savings of Americans and the factors that influence savings balances is crucial for achieving financial security. While averages provide a benchmark, individual circumstances vary widely. By setting clear financial goals, creating a budget, and seeking expert advice, you can improve your savings habits and build a secure financial future. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today to connect with experienced financial advisors who can help you achieve your financial goals.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: how.edu.vn