Are you wondering, “How much should a 7-month-old eat?” It’s a common question for parents navigating the exciting world of introducing solids while still providing essential nutrition through breast milk or formula. At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges and are here to provide expert guidance. This article will explore the recommended amounts, feeding schedules, and tips to ensure your baby gets the nutrients they need during this crucial developmental stage, covering everything from portion sizes to recognizing hunger cues and addressing common feeding concerns. You’ll gain valuable insights into infant nutrition, baby feeding guidelines, and healthy eating habits for your little one.
1. Understanding Your 7-Month-Old’s Nutritional Needs
At seven months, babies are in a transitional phase, gradually incorporating solid foods alongside their primary source of nutrition, which remains breast milk or formula. Understanding their nutritional needs is vital for supporting healthy growth and development.
1.1. Key Nutrients for 7-Month-Olds
Babies at this age require a balanced intake of several key nutrients.
- Iron: Iron stores from birth start to deplete around six months, making iron-rich foods essential.
- Zinc: Vital for immune function and growth.
- Protein: Necessary for building and repairing tissues.
- Healthy Fats: Essential for brain development.
- Vitamins: Including A, C, and D, to support overall health.
1.2. Breast Milk or Formula as the Primary Source
Breast milk or formula should still be the main source of nutrition. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), breast milk is the optimal food for infants during the first year of life. Formula is a suitable alternative when breastfeeding is not possible.
1.3. Introduction to Solids
Introducing solids should complement, not replace, breast milk or formula. Start with single-ingredient purees to identify any potential allergies.
2. Recommended Amounts of Breast Milk or Formula
Knowing how much breast milk or formula to offer is crucial. Here’s a detailed look at the recommended amounts.
2.1. Daily Intake of Breast Milk or Formula
Most 7-month-old babies need around 24 to 32 ounces (710 to 950 ml) of breast milk or formula per day. This is typically divided into 4 to 6 feedings.
2.2. Recognizing Hunger and Fullness Cues
Pay attention to your baby’s cues. Hunger cues include:
- Opening their mouth and reaching for the spoon
- Getting excited when they see food
- Sucking on their hands
Fullness cues include:
- Turning their head away
- Closing their mouth
- Becoming distracted or disinterested
2.3. Adjusting Intake Based on Baby’s Needs
Every baby is different. Some may need slightly more or less than the average. Adjust the amount based on their individual needs and growth rate.
3. Introducing Solid Foods: How Much and How Often
Introducing solid foods is an exciting milestone. Here’s how to do it right.
3.1. Starting with Single-Ingredient Purees
Begin with single-ingredient purees like sweet potato, avocado, or banana. Offer a small amount (1-2 tablespoons) and watch for any allergic reactions.
3.2. Gradually Increasing Portion Sizes
Gradually increase the portion sizes as your baby gets used to eating solids. A typical serving size might be 2-4 tablespoons per meal.
3.3. Recommended Frequency of Solid Food Meals
At 7 months, most babies are ready for 1-2 solid food meals per day. Spread these meals throughout the day, such as breakfast and dinner.
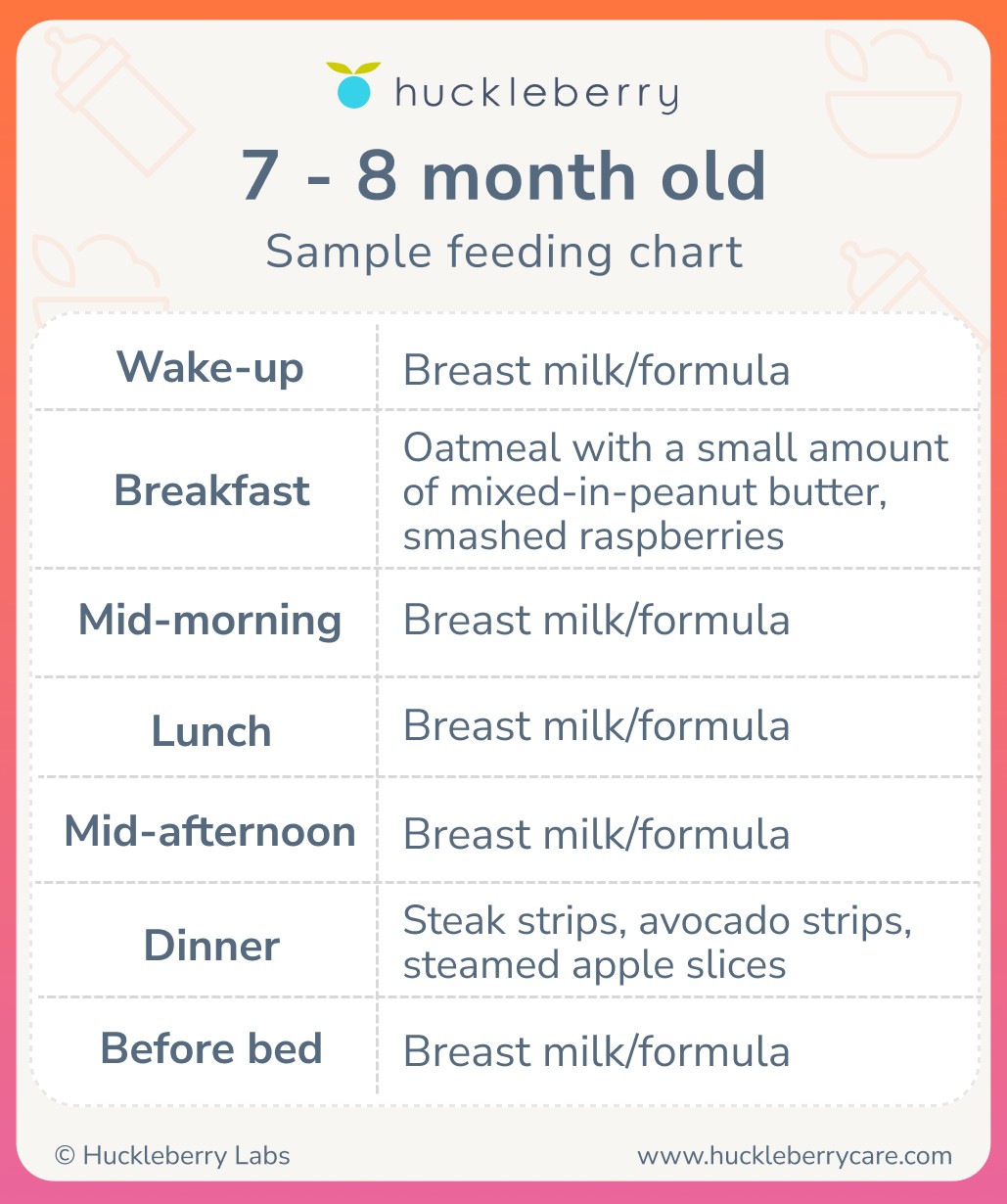
3.4. Sample Feeding Schedule with Solids
Here is a sample feeding schedule incorporating solids:
- 7:00 AM: Breast milk or formula (6-8 ounces)
- 9:30 AM: Solid food meal (2-4 tablespoons)
- 10:30 AM: Breast milk or formula (6-8 ounces)
- 2:00 PM: Breast milk or formula (6-8 ounces)
- 5:00 PM: Solid food meal (2-4 tablespoons)
- 6:30 PM: Breast milk or formula (6-8 ounces)
4. Food Chart for 7-Month-Olds
A food chart can help you plan balanced meals. Here are some suitable options.
4.1. Recommended First Foods
- Vegetables: Sweet potato, carrots, squash, green beans
- Fruits: Avocado, banana, applesauce, peaches
- Grains: Oatmeal, rice cereal
- Proteins: Pureed meats, lentils, beans
4.2. Foods to Avoid
- Honey: Until after the first birthday, due to the risk of botulism
- Cow’s Milk: As a primary drink until after the first birthday
- Choking Hazards: Whole grapes, nuts, popcorn, raw carrots
4.3. Sample Meal Ideas
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with pureed apples
- Lunch: Breast milk or formula
- Dinner: Sweet potato puree with a small amount of pureed chicken
5. Baby-Led Weaning vs. Purees
There are two primary approaches to introducing solids: baby-led weaning (BLW) and purees.
5.1. What is Baby-Led Weaning (BLW)?
BLW involves offering soft, finger-sized pieces of food that babies can feed themselves. This encourages exploration and self-regulation.
5.2. Benefits of BLW
- Promotes fine motor skills
- Encourages self-regulation of food intake
- Offers a variety of textures and flavors
5.3. Purees: A Traditional Approach
Purees involve feeding babies smooth, mashed foods with a spoon.
5.4. Benefits of Purees
- Easy to digest
- Less messy
- Good for babies who are not yet ready for finger foods
5.5. Combining Both Approaches
Many parents choose to combine both BLW and purees to offer a balanced introduction to solids.
6. Tips for Feeding Your 7-Month-Old
Here are some practical tips to make feeding time easier.
6.1. Create a Positive Mealtime Environment
Make mealtime a pleasant experience. Avoid distractions like TV or toys.
6.2. Introduce New Foods Gradually
Introduce new foods one at a time, waiting 2-3 days before introducing another to monitor for allergies.
6.3. Be Patient
It may take multiple tries for your baby to accept a new food. Don’t give up after the first attempt.
6.4. Offer a Variety of Flavors and Textures
Expose your baby to a wide range of flavors and textures to encourage acceptance of new foods.
6.5. Let Your Baby Lead
Allow your baby to explore and experiment with food. Let them touch, smell, and play with their food.
6.6. Embrace the Mess
Feeding a baby can be messy. Embrace the mess and focus on the experience.
7. Addressing Common Feeding Concerns
Many parents face challenges during this stage. Here’s how to address some common concerns.
7.1. Allergies
Be vigilant for signs of allergic reactions, such as rash, hives, swelling, vomiting, or diarrhea. Introduce common allergens like peanuts, eggs, and dairy early and often, as recommended by current guidelines.
7.2. Constipation
Ensure your baby is getting enough fiber from fruits and vegetables. Prune juice can also help relieve constipation.
7.3. Refusal to Eat Solids
If your baby refuses to eat solids, try offering them at a different time or in a different form. It may take time for them to adjust to new textures and flavors.
7.4. Teething
Teething can affect your baby’s appetite. Offer soft, cool foods to soothe their gums.
7.5. Gagging vs. Choking
Gagging is a normal reflex that helps prevent choking. Choking, on the other hand, is a serious emergency. Learn the difference and how to respond in each situation.
8. Hydration for 7-Month-Olds
Staying hydrated is essential, especially as your baby starts eating solids.
8.1. Breast Milk or Formula for Hydration
Breast milk or formula should continue to be the primary source of hydration.
8.2. Offering Water
You can offer small amounts of water (1-2 ounces) with meals, but don’t replace breast milk or formula with water.
8.3. Signs of Dehydration
Watch for signs of dehydration, such as fewer wet diapers, dry mouth, and sunken eyes.
9. Importance of Iron-Rich Foods
Iron is crucial for your baby’s development.
9.1. Why Iron is Important
Iron supports brain development and helps transport oxygen throughout the body.
9.2. Iron-Rich Food Sources
- Pureed meats
- Fortified cereals
- Lentils and beans
- Spinach
9.3. Enhancing Iron Absorption
Pair iron-rich foods with vitamin C-rich foods to enhance absorption. For example, serve pureed spinach with a small amount of pureed tomato.
10. Consulting with Pediatricians and Experts
When in doubt, consult with healthcare professionals.
10.1. When to Seek Professional Advice
- If your baby is not gaining weight
- If your baby has persistent feeding problems
- If you suspect an allergy or intolerance
10.2. Benefits of Expert Consultation through HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading pediatricians and nutrition experts who can provide personalized advice and support. Our experts can help you create a feeding plan that meets your baby’s unique needs.
11. Night Feedings for 7-Month-Olds
Night feedings can be a concern for many parents.
11.1. Determining if Night Feedings are Necessary
Most 7-month-olds don’t need night feedings if they are gaining weight adequately and eating enough during the day.
11.2. Gradual Reduction of Night Feedings
If you want to reduce night feedings, do it gradually. Reduce the amount of milk or formula offered at each feeding over several nights.
11.3. Comforting Techniques
Try comforting your baby with rocking, singing, or a pacifier instead of feeding them every time they wake up.
12. Creating a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential for your baby’s health.
12.1. Combining Food Groups
Offer a variety of foods from different food groups to ensure your baby gets all the nutrients they need.
12.2. Importance of Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your baby’s diet.
12.3. Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are essential for brain development. Include sources like avocado, olive oil, and fatty fish in your baby’s diet.
13. Meal Planning for 7-Month-Olds
Effective meal planning can simplify feeding time.
13.1. Weekly Meal Plan Template
Create a weekly meal plan to ensure your baby gets a variety of nutrients.
13.2. Batch Cooking and Freezing
Prepare large batches of purees and freeze them in small portions for easy meals.
13.3. Utilizing Leftovers
Use leftovers from your own meals to create healthy and convenient meals for your baby.
14. Overfeeding and Underfeeding
Knowing the signs of overfeeding and underfeeding is important.
14.1. Signs of Overfeeding
- Frequent spitting up
- Diarrhea
- Excessive weight gain
14.2. Signs of Underfeeding
- Poor weight gain
- Lethargy
- Fewer wet diapers
14.3. Adjusting Feeding Amounts
Adjust feeding amounts based on your baby’s cues and growth rate.
15. Addressing Picky Eating
Picky eating is common among babies and toddlers.
15.1. Why Babies Become Picky Eaters
Babies may become picky eaters due to changes in taste preferences, teething, or developmental milestones.
15.2. Strategies for Dealing with Picky Eating
- Continue offering rejected foods
- Make mealtime fun and engaging
- Offer a variety of foods
- Avoid forcing your baby to eat
15.3. Professional Guidance for Picky Eating
For persistent picky eating, consulting with a pediatric nutritionist can provide strategies tailored to your child’s needs. HOW.EDU.VN offers access to experts who specialize in infant feeding challenges.
16. The Role of Texture in Food Introduction
Texture plays a significant role in your baby’s acceptance of solid foods.
16.1. Starting with Smooth Purees
Begin with smooth purees to ease your baby into the transition from liquids to solids.
16.2. Progressing to Chunkier Textures
Gradually introduce chunkier textures as your baby gets used to swallowing solids.
16.3. Introducing Lumpy Foods
Lumpy foods help your baby develop oral motor skills and prepare them for more complex textures.
16.4. Importance of Finger Foods
Finger foods encourage self-feeding and help your baby explore different shapes and sizes.
17. Encouraging Self-Feeding
Self-feeding is an important milestone in your baby’s development.
17.1. Benefits of Self-Feeding
- Promotes independence
- Enhances fine motor skills
- Encourages exploration of food
17.2. How to Encourage Self-Feeding
- Offer finger foods
- Provide a spoon and let your baby try to feed themselves
- Be patient and supportive
17.3. Safety Considerations
Ensure that the foods you offer are soft and easy to chew to prevent choking.
18. Understanding Food Labels
Reading food labels is essential for making informed choices.
18.1. What to Look for on Food Labels
- Ingredients list
- Nutrition facts
- Allergens
18.2. Avoiding Added Sugars and Salts
Choose foods with no added sugars or salts.
18.3. Organic vs. Non-Organic
Consider organic options to minimize exposure to pesticides and chemicals.
19. Introducing Spices and Herbs
Spices and herbs can add flavor and variety to your baby’s meals.
19.1. When to Introduce Spices and Herbs
You can start introducing spices and herbs around 7 months of age.
19.2. Safe Spices and Herbs
- Cinnamon
- Nutmeg
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Basil
- Oregano
19.3. How to Introduce Spices and Herbs
Start with small amounts and monitor for any allergic reactions.
20. Traveling with a 7-Month-Old
Traveling with a 7-month-old requires careful planning.
20.1. Packing Food for Travel
Pack a variety of shelf-stable foods like pouches, cereals, and snacks.
20.2. Maintaining a Feeding Schedule
Try to maintain your baby’s regular feeding schedule while traveling.
20.3. Ensuring Food Safety
Ensure that the food you offer is safe and properly stored.
21. Common Myths About Infant Feeding
It’s important to dispel common myths about infant feeding.
21.1. Myth: Babies Need Cereal to Sleep Through the Night
There’s no evidence that cereal helps babies sleep through the night.
21.2. Myth: Babies Should Finish Everything on Their Plate
Babies should be allowed to eat until they are full, not forced to finish everything on their plate.
21.3. Myth: All Babies Like Sweet Foods
Babies have different taste preferences and may not always prefer sweet foods.
22. Staying Informed with Reliable Resources
Staying informed is key to making the best decisions for your baby.
22.1. Recommended Websites
- American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
22.2. Books on Infant Feeding
- “The Baby-Led Weaning Cookbook” by Gill Rapley and Tracey Murkett
- “Super Baby Food” by Ruth Yaron
22.3. Trusted Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
HOW.EDU.VN connects you with trusted experts who can provide reliable information and support.
23. Building a Strong Foundation for Healthy Eating Habits
Establishing healthy eating habits early is crucial.
23.1. Modeling Healthy Eating
Be a role model by eating healthy foods yourself.
23.2. Making Mealtime a Family Affair
Eat together as a family whenever possible.
23.3. Positive Reinforcement
Praise your baby for trying new foods.
24. Navigating Cultural Differences in Infant Feeding
Infant feeding practices vary across cultures.
24.1. Cultural Variations
Be aware of cultural differences in infant feeding practices.
24.2. Adapting to Your Cultural Background
Adapt infant feeding practices to your cultural background while ensuring that your baby’s nutritional needs are met.
24.3. Respecting Cultural Traditions
Respect cultural traditions while making informed choices based on current guidelines.
25. Conclusion: Empowering Parents with Knowledge
Feeding your 7-month-old can be an exciting and rewarding experience. By understanding their nutritional needs, introducing solids appropriately, and addressing common concerns, you can empower yourself to make the best choices for your baby.
Understanding “how much should a 7-month-old eat” involves a blend of guidelines and personalized attention. This comprehensive guide provides a foundation, but remember that every baby is unique.
Are you still facing challenges or uncertainties? Connect with our team of experienced pediatricians and nutrition experts at HOW.EDU.VN. We offer personalized consultations to address your specific concerns and provide tailored guidance.
Don’t navigate this journey alone. Contact us today at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212. Visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN to learn more and schedule your consultation. Let how.edu.vn be your trusted partner in nurturing your baby’s healthy growth and development, offering expert advice and peace of mind every step of the way.
26. FAQ: Addressing Your Top Questions
26.1. How Often Should a 7-Month-Old Eat?
A 7-month-old typically eats every 3 to 4 hours, including breast milk or formula feedings and solid food meals.
26.2. Can I Drop Night Feeds at 7 Months?
Many babies can sleep through the night without needing a feeding at this age, but it depends on their individual needs.
26.3. What if My Baby Is Eating Less Than Usual?
Decreased appetite can be due to teething, illness, or simply a temporary change in hunger levels. Monitor your baby and consult a pediatrician if you’re concerned.
26.4. How Do I Know If My Baby Is Allergic to a Food?
Watch for signs like rash, hives, swelling, vomiting, or diarrhea after introducing new foods.
26.5. Is It Okay to Give My Baby Store-Bought Baby Food?
Yes, store-bought baby food is safe and convenient, but always check the label for added sugars and salts.
26.6. What Should I Do If My Baby Refuses a New Food?
Continue offering the food at different times and in different forms. It may take multiple tries for your baby to accept a new food.
26.7. How Much Water Should a 7-Month-Old Drink?
You can offer small amounts of water (1-2 ounces) with meals, but breast milk or formula should remain the primary source of hydration.
26.8. Can I Give My Baby Cow’s Milk at 7 Months?
Cow’s milk should not be given as a primary drink until after the first birthday, but it can be used in small amounts in cooking.
26.9. What Are the Best Finger Foods for a 7-Month-Old?
Soft, easy-to-chew finger foods like avocado slices, steamed carrot sticks, and cooked pasta are great options.
26.10. How Do I Know If My Baby Is Getting Enough Iron?
Ensure your baby is eating iron-rich foods like pureed meats and fortified cereals, and consult with a pediatrician if you have concerns about iron deficiency.