Are you wondering, How Much Sleep Do I Need Calculator? Determining the ideal amount of sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being, and HOW.EDU.VN offers expert insights to help you optimize your sleep schedule. Understanding your body’s unique sleep requirements can lead to improved cognitive function, emotional stability, and physical health. Discover how much shuteye you need, sleep cycles, and the importance of bedtime with our calculator.
1. Understanding Your Sleep Needs: Why Use a Sleep Calculator?
Many individuals underestimate the significance of adequate sleep or fail to allocate sufficient time for it. While general guidelines suggest that most adults require seven to nine hours of sleep per night, individual needs can vary based on factors such as age, lifestyle, and overall health.
1.1 The Importance of Tailored Sleep Schedules
A sleep calculator helps tailor a sleep schedule to your specific needs, accounting for your age, desired wake-up time, and preferred bedtime. This ensures that you wake up feeling refreshed and energized, rather than groggy and tired.
1.2 Factors Influencing Sleep Duration
Several factors influence the amount of sleep you need:
- Age: Sleep requirements vary significantly across different age groups.
- Lifestyle: Active individuals or those with demanding jobs may require more sleep.
- Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions can impact sleep quality and duration.
1.3 Seeking Expert Guidance
For personalized sleep recommendations based on your unique health profile, consulting a doctor or sleep specialist is advisable. HOW.EDU.VN offers a platform to connect with leading experts who can provide tailored advice to optimize your sleep.
2. Recommended Sleep Durations by Age Group
Sleep needs change throughout life, with infants requiring the most sleep and older adults often needing less. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
| Age Range | Recommended Daily Sleep |
|---|---|
| Infants (4-12 months) | 12-16 hours (including naps) |
| Toddlers (1-2 years) | 11-14 hours (including naps) |
| Preschoolers (3-5 years) | 10-13 hours (including naps) |
| School-age Children (6-12 years) | 9-12 hours |
| Teenagers (13-18 years) | 8-10 hours |
| Adults (18+ years) | 7+ hours |

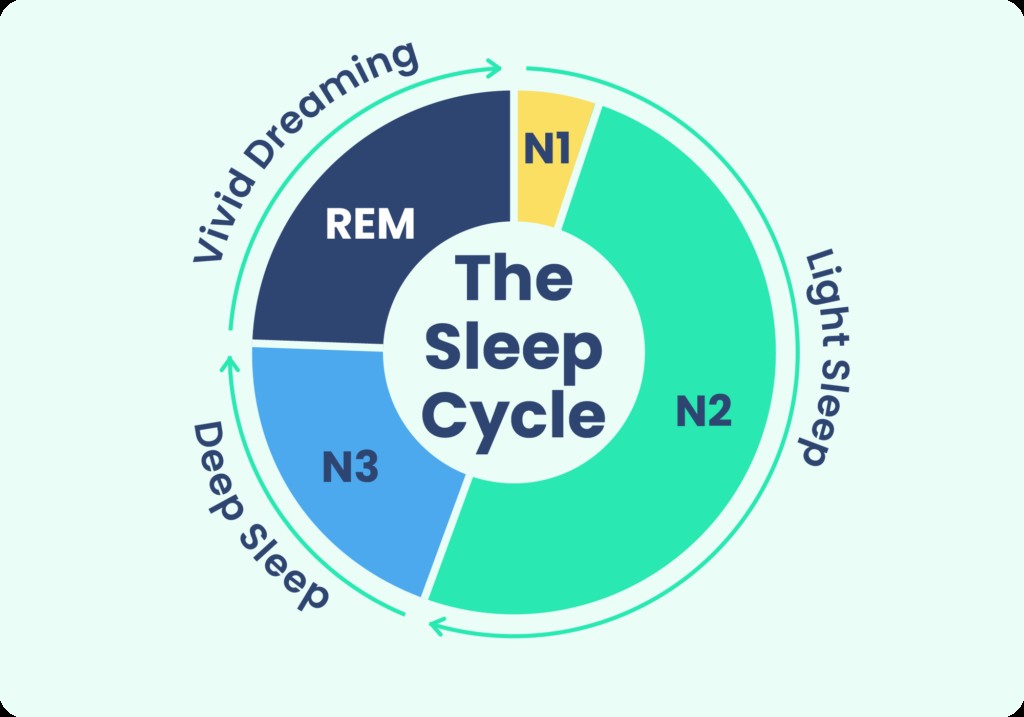
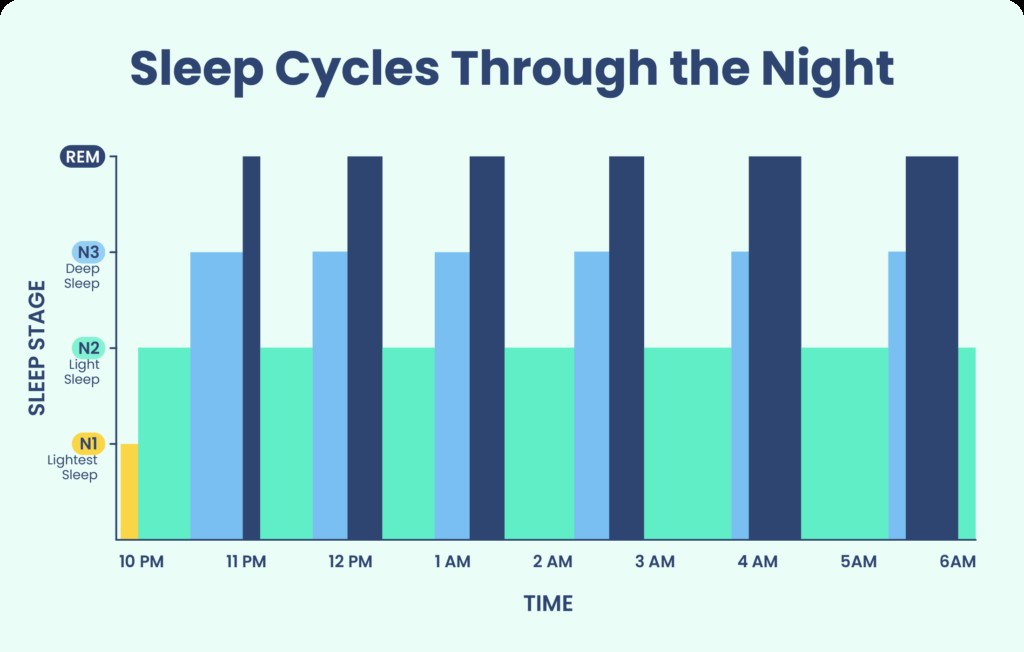
3. Maximizing Sleep Cycles for Optimal Rest
To optimize your sleep, understanding sleep cycles is crucial. Each cycle includes stages of light sleep, deep sleep, and REM sleep, collectively lasting about 90 to 120 minutes.
3.1 Understanding Sleep Stages
- Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) Sleep: This includes lighter stages (1 and 2) and deep sleep (stage 3), essential for physical and mental restoration.
- Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep: Characterized by increased brain activity and dreaming, REM sleep supports memory consolidation and cognitive function.
3.2 Timing Your Wake-Up
Waking up mid-sleep cycle can lead to grogginess. Aim to wake up after completing a full cycle, which is approximately 90 to 120 minutes. HOW.EDU.VN’s sleep calculator can help you determine the best wake-up time based on your bedtime and age.
3.3 Benefits of Aligning with Sleep Cycles
Adhering to your natural sleep cycles can significantly improve sleep quality, leading to:
- Increased alertness
- Improved mood
- Enhanced cognitive function
4. Determining Your Ideal Bedtime: Factors to Consider
Finding the perfect bedtime isn’t one-size-fits-all; it varies based on age, location, lifestyle, and obligations.
4.1 Consistency is Key
Experts recommend maintaining consistent sleep and wake times, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
4.2 The Importance of Darkness
Sleeping during dark periods is generally healthier, aligning with your body’s natural circadian rhythm.
4.3 Personalized Bedtime Recommendations
HOW.EDU.VN provides personalized bedtime recommendations based on your unique circumstances, ensuring you get the rest you need to perform at your best.
5. Why Sufficient Sleep Matters: Impact on Overall Health
Sleep is vital for nearly every bodily system. Getting enough sleep each night allows your mind and body to reap its restorative benefits and avoid the consequences of sleep deprivation.
5.1 Physiological Benefits
Adequate sleep supports:
- Immune function
- Cardiovascular health
- Metabolic processes
5.2 Cognitive Benefits
Proper sleep enhances:
- Memory consolidation
- Problem-solving abilities
- Decision-making skills
6. The Repercussions of Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation can lead to short- and long-term physical, emotional, and cognitive health issues.
6.1 Immediate Effects
Following a night of poor sleep, you may experience:
- Daytime sleepiness
- Impaired reaction time
- Irritability
6.2 Long-Term Consequences
Chronic sleep deprivation is linked to:
- Weight gain and obesity
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Depression and anxiety
6.3 Impact on Performance
Lack of sleep can hinder academic achievement and work productivity, reducing overall quality of life.
7. Strategies to Enhance Sleep Quality
Implementing simple lifestyle changes can significantly improve sleep quality, leading to better physical, cognitive, and emotional wellness.
7.1 Establishing a Bedtime Routine
A relaxing bedtime routine can promote healthy sleep. Consider activities such as:
- Yoga
- Meditation
- Journaling
- Reading
7.2 Dietary Adjustments
Avoid caffeine and reduce alcohol consumption before bed to improve sleep quality.
7.3 Creating a Sleep-Friendly Environment
- Put away electronic devices to minimize blue light exposure.
- Ensure the bedroom is dark and quiet using sleep masks or earplugs.
- Choose a supportive mattress and bedding for a more comfortable sleep environment.
7.4 Sunlight and Exercise
Daily exercise and exposure to sunlight can positively impact sleep by regulating circadian rhythms.
8. Optimizing Your Sleep Environment for Restful Nights
Creating the right sleep environment is essential for achieving restful nights. Consider the following factors to optimize your bedroom:
8.1 Temperature and Ventilation
Maintaining a cool, well-ventilated room promotes better sleep. Aim for a temperature between 60-67 degrees Fahrenheit.
8.2 Noise Reduction
Minimize noise distractions using earplugs, white noise machines, or soundproofing techniques.
8.3 Light Management
Ensure the room is dark by using blackout curtains or a sleep mask to block out external light sources.
8.4 Comfortable Bedding
Invest in high-quality bedding, including a supportive mattress, comfortable pillows, and breathable sheets, to enhance sleep comfort.
9. The Role of Technology in Monitoring and Improving Sleep
Various technologies can help monitor and improve your sleep patterns.
9.1 Sleep Trackers
Wearable sleep trackers monitor sleep duration, sleep stages, and heart rate, providing insights into sleep quality.
9.2 Sleep Apps
Mobile apps offer features like sleep tracking, guided meditations, and ambient sounds to promote relaxation and improve sleep.
9.3 Smart Lighting
Smart lighting systems simulate natural light patterns, supporting circadian rhythms and enhancing sleep-wake cycles.
9.4 White Noise Machines
White noise machines generate soothing sounds to mask disruptive noises, creating a more conducive sleep environment.
10. Addressing Common Sleep Disorders
If you consistently struggle to get enough sleep, you may have a sleep disorder.
10.1 Insomnia
Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restful sleep.
10.2 Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea involves pauses in breathing during sleep, disrupting sleep quality and leading to daytime fatigue.
10.3 Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
RLS causes an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations.
10.4 Seeking Professional Help
If you suspect you have a sleep disorder, consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment options.
11. The Importance of Diet and Nutrition for Better Sleep
What you eat and drink can significantly impact your sleep quality.
11.1 Foods That Promote Sleep
Foods rich in tryptophan, melatonin, and magnesium can help improve sleep. Examples include:
- Turkey
- Cherries
- Almonds
- Spinach
11.2 Foods to Avoid Before Bed
Avoid heavy, spicy, or sugary foods before bed, as they can interfere with sleep.
11.3 Hydration
Stay hydrated throughout the day, but limit fluid intake before bed to reduce nighttime awakenings.
11.4 Caffeine and Alcohol
Avoid caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime, as they can disrupt sleep patterns.
12. Maintaining a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Consistency is key when it comes to regulating your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
12.1 The Role of Circadian Rhythms
Circadian rhythms are internal biological clocks that regulate sleep-wake patterns.
12.2 Setting a Regular Sleep-Wake Time
Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to reinforce your circadian rhythm.
12.3 Adjusting to Time Zone Changes
When traveling, gradually adjust your sleep schedule to the new time zone to minimize jet lag.
12.4 Strategies for Shift Workers
Shift workers can use strategies like strategic napping, light exposure, and caffeine management to maintain a healthy sleep schedule.
13. The Impact of Exercise on Sleep Quality
Regular physical activity can positively influence sleep quality.
13.1 Benefits of Exercise
Exercise can help reduce stress, improve mood, and promote deeper sleep.
13.2 Timing Your Workouts
Avoid intense workouts close to bedtime, as they can be stimulating and interfere with sleep.
13.3 Types of Exercise
Engage in a mix of aerobic and strength training exercises for overall health and sleep benefits.
13.4 Consistency is Key
Regular exercise is more effective than occasional workouts when it comes to improving sleep quality.
14. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques for Better Sleep
Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can help calm the mind and prepare for sleep.
14.1 Meditation
Meditation can reduce stress and promote relaxation, making it easier to fall asleep.
14.2 Deep Breathing Exercises
Deep breathing exercises can calm the nervous system and promote a sense of relaxation.
14.3 Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Progressive muscle relaxation involves tensing and releasing different muscle groups to reduce tension and promote relaxation.
14.4 Yoga
Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to promote relaxation and improve sleep.
15. The Importance of Sunlight Exposure for Regulating Sleep
Exposure to natural light is crucial for regulating your body’s circadian rhythm and promoting healthy sleep patterns.
15.1 Sunlight and Melatonin Production
Sunlight exposure suppresses melatonin production during the day, promoting alertness, and allows for increased melatonin production at night, facilitating sleep.
15.2 Getting Enough Sunlight
Aim for at least 30 minutes of sunlight exposure each day, especially in the morning, to regulate your circadian rhythm.
15.3 Strategies for Limited Sunlight
If you have limited access to sunlight, consider using a light therapy lamp to mimic natural light exposure.
15.4 Impact on Mood
Sunlight exposure can also improve mood and reduce symptoms of seasonal affective disorder (SAD), further enhancing sleep quality.
16. Creating a Pre-Sleep Routine for Relaxation
Establishing a consistent pre-sleep routine can signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
16.1 Examples of Pre-Sleep Activities
- Taking a warm bath or shower
- Reading a book
- Listening to calming music
- Practicing gentle stretching or yoga
- Writing in a journal
16.2 Consistency is Key
Perform the same activities each night to reinforce the association between the routine and sleep.
16.3 Avoiding Stimulating Activities
Avoid stimulating activities, such as watching TV or using electronic devices, close to bedtime.
16.4 The Importance of Relaxation
Focus on activities that promote relaxation and reduce stress to prepare your mind and body for sleep.
17. Overcoming Common Sleep Disruptors
Several factors can disrupt sleep, including stress, noise, and light.
17.1 Managing Stress
Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, to minimize the impact of stress on sleep.
17.2 Reducing Noise
Use earplugs, white noise machines, or soundproofing techniques to minimize noise disruptions.
17.3 Minimizing Light Exposure
Ensure the bedroom is dark by using blackout curtains or a sleep mask to block out external light sources.
17.4 Addressing Specific Disruptors
Identify and address specific sleep disruptors, such as snoring partners or pets in the bedroom, to improve sleep quality.
18. The Role of Bedding in Sleep Quality
Your choice of bedding can significantly impact your sleep quality.
18.1 Mattress Selection
Choose a mattress that provides adequate support and comfort for your body type and sleep preferences.
18.2 Pillow Selection
Select a pillow that supports your head and neck in a comfortable position, promoting proper spinal alignment.
18.3 Sheet Material
Opt for breathable, comfortable sheet materials, such as cotton or linen, to regulate body temperature and enhance sleep comfort.
18.4 Bedding Hygiene
Maintain clean bedding by washing sheets, pillowcases, and blankets regularly to minimize allergens and promote a healthy sleep environment.
19. Exploring the Link Between Mental Health and Sleep
Mental health and sleep are closely intertwined, with each influencing the other.
19.1 Sleep and Mood Disorders
Sleep disturbances are common in individuals with mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety.
19.2 The Impact of Sleep on Mental Health
Poor sleep can exacerbate mental health symptoms, leading to increased stress, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
19.3 Strategies for Improving Both
Address both sleep and mental health concerns through a combination of lifestyle changes, therapy, and medication, if necessary.
19.4 Seeking Professional Help
If you are struggling with both sleep and mental health issues, consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and treatment plan.
20. Travel and Sleep: Minimizing Jet Lag
Traveling across time zones can disrupt your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to jet lag.
20.1 Strategies for Minimizing Jet Lag
- Adjust your sleep schedule gradually before departure
- Stay hydrated during the flight
- Expose yourself to sunlight at your destination
- Consider using melatonin supplements
20.2 Adapting to New Time Zones
Gradually adjust your sleep schedule to the new time zone, going to bed and waking up at appropriate times.
20.3 The Importance of Light Exposure
Expose yourself to sunlight during the day to help reset your circadian rhythm and reduce symptoms of jet lag.
20.4 Recovery Time
Allow your body sufficient time to adjust to the new time zone, typically one day per time zone crossed.
21. How to Determine If You Have a Sleep Disorder
If you consistently struggle to get enough sleep or experience symptoms like excessive daytime sleepiness or snoring, you may have a sleep disorder.
21.1 Common Sleep Disorder Symptoms
- Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Loud snoring
- Pauses in breathing during sleep
- Restless legs
- Morning headaches
21.2 Seeking Medical Evaluation
If you suspect you have a sleep disorder, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis.
21.3 Sleep Studies
A sleep study, also known as polysomnography, can help diagnose sleep disorders by monitoring brain waves, heart rate, breathing patterns, and other physiological parameters during sleep.
21.4 Treatment Options
Treatment options for sleep disorders may include lifestyle changes, medication, CPAP therapy, or surgery, depending on the specific disorder.
22. How Much Sleep Do I Need Calculator: Summarizing Key Takeaways
Understanding your sleep needs is crucial for overall health and well-being. HOW.EDU.VN offers expert insights and resources to help you optimize your sleep schedule.
22.1 Key Points to Remember
- The amount of sleep you need varies based on age, lifestyle, and health conditions
- Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night as an adult
- Consistency is key for regulating your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle
- Create a sleep-friendly environment and pre-sleep routine
- Address any sleep disorders and seek professional help when needed
22.2 Seeking Personalized Advice
For personalized sleep recommendations based on your unique circumstances, consult a healthcare professional or sleep specialist.
22.3 The Importance of Prioritizing Sleep
Prioritize sleep as part of a healthy lifestyle, along with proper nutrition, exercise, and stress management.
23. FAQ: Common Questions About Sleep
23.1 How many hours of sleep do I really need?
Most adults need 7-9 hours of sleep per night, but individual needs vary based on age, lifestyle, and health conditions.
23.2 What are the best ways to improve my sleep?
Establish a consistent sleep schedule, create a sleep-friendly environment, practice relaxation techniques, and address any sleep disorders.
23.3 Can I make up for lost sleep?
While you can catch up on some sleep, it’s not possible to completely reverse the effects of chronic sleep deprivation.
23.4 What are the consequences of not getting enough sleep?
Lack of sleep can lead to daytime sleepiness, impaired cognitive function, mood disturbances, and increased risk of chronic health conditions.
23.5 How can I create a relaxing bedtime routine?
Engage in calming activities, such as reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing meditation, before bed to promote relaxation.
23.6 Is it normal to wake up during the night?
It’s normal to wake up briefly several times during the night as you transition between sleep cycles.
23.7 How can I minimize jet lag when traveling?
Adjust your sleep schedule gradually before departure, stay hydrated during the flight, and expose yourself to sunlight at your destination.
23.8 What are some signs of a sleep disorder?
Signs of a sleep disorder include difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, loud snoring, and pauses in breathing during sleep.
23.9 How can I determine if I have a sleep disorder?
Consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and possible sleep study if you suspect you have a sleep disorder.
23.10 What should I do if I can’t fall asleep?
Get out of bed and engage in a relaxing activity until you feel sleepy, then return to bed and try to fall asleep again.
24. Ready to Optimize Your Sleep? Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Don’t let sleep problems affect your quality of life. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today for expert advice and personalized solutions to improve your sleep and overall well-being.
24.1 Why Choose HOW.EDU.VN?
- Access to Leading Experts: Connect with over 100 renowned PhDs worldwide.
- Personalized Consultations: Receive tailored advice for your specific needs.
- Confidential and Reliable: Ensure your information is secure and trustworthy.
- Save Time and Money: Get high-quality advice efficiently.
24.2 Take Action Now
Are you struggling to find experts with the right qualifications? Are high costs and time constraints holding you back? Do you worry about the security of your consultations?
HOW.EDU.VN offers a solution:
- Connect Directly: Access top PhDs and experts in various fields.
- Personalized Advice: Get customized solutions for your unique challenges.
- Secure and Reliable: Trust in confidential, expert consultations.
- Efficient and Cost-Effective: Save time and money with our streamlined platform.
Contact us today and start your journey to better sleep and a healthier life.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let how.edu.vn help you unlock your full potential with expert guidance and support!
