How Much Snow Will Minneapolis Get? At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of accurate weather forecasts, especially when a major snowstorm is approaching. Our team of expert meteorologists is dedicated to providing you with the most up-to-date information so you can prepare effectively, and connect with board-certified Doctors for personalized guidance and peace of mind. Stay informed with our analysis on snowfall predictions and winter weather preparedness.
1. Understanding the Minneapolis Snowfall Forecast
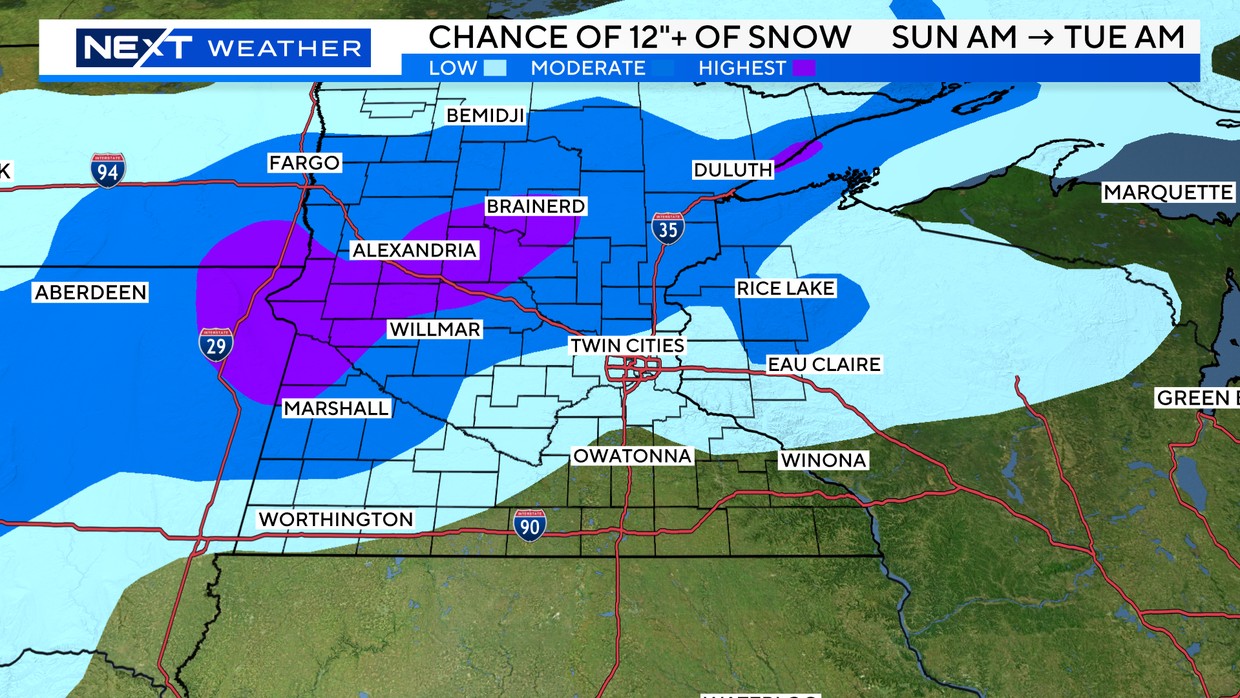
Forecasting snowfall accurately is a complex task that involves analyzing various atmospheric factors. Meteorologists use advanced weather models, radar technology, and surface observations to predict the amount of snow expected in a particular area. These models consider factors such as temperature, humidity, wind patterns, and the presence of moisture in the atmosphere. The accuracy of a snowfall forecast can vary depending on the complexity of the weather system and the availability of reliable data. For Minneapolis, which experiences frequent winter storms, understanding these forecasts is crucial for residents and businesses alike.
-
Key Factors Influencing Snowfall:
- Temperature Profile: The atmospheric temperature at different levels determines whether precipitation will fall as rain, snow, or a mix.
- Moisture Availability: Sufficient moisture is needed for snow to form. The amount of moisture in the air affects the intensity and duration of snowfall.
- Wind Direction and Speed: Winds can influence the movement and distribution of snow, leading to localized variations in snowfall amounts.
- Elevation: Higher elevations typically experience colder temperatures, increasing the likelihood of snow.
-
Challenges in Snowfall Prediction:
- Model Limitations: Weather models are not perfect and can have difficulty accurately predicting snowfall amounts, especially in complex weather systems.
- Microclimates: Local variations in topography and urban environments can create microclimates that affect snowfall patterns.
- Data Gaps: Lack of real-time data from certain areas can limit the accuracy of forecasts.
2. Recent Snowfall Events in Minneapolis
Minneapolis has a history of significant snowfall events that have impacted the city and its residents. These events serve as reminders of the power of winter weather and the importance of preparedness. Examining past snowfall events can provide insights into the typical patterns and impacts of winter storms in the region. Understanding the historical context of snowfall in Minneapolis can help residents and businesses better prepare for future events.
-
Notable Snowstorms:
- The Halloween Blizzard of 1991: This historic storm dumped over 28 inches of snow on Minneapolis, causing widespread disruption and damage.
- The January 1982 Blizzard: This powerful blizzard brought the city to a standstill with heavy snow and strong winds.
- The December 2010 Blizzard: This late-season storm delivered significant snowfall, impacting holiday travel and commerce.
- April 14, 2018: A late-season snowstorm dropped 10+ inches of snow in the Twin Cities.
- February 22-23, 2023: A winter storm dropped over a foot of snow on Minneapolis.
-
Impacts of Snowfall on Minneapolis:
- Transportation Disruptions: Heavy snowfall can lead to road closures, flight cancellations, and delays in public transportation.
- Economic Impacts: Snowstorms can disrupt business operations, reduce retail sales, and increase costs for snow removal and infrastructure repairs.
- Public Safety Concerns: Snow and ice can create hazardous conditions for pedestrians and drivers, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Infrastructure Strain: Heavy snow can strain infrastructure, such as power lines and roofs, leading to outages and damage.
 Minneapolis snowstorm
Minneapolis snowstorm
3. Expert Insights on Expected Snowfall Amounts
To get the most accurate and reliable snowfall predictions, it’s essential to consult with expert meteorologists who have a deep understanding of the region’s weather patterns. These professionals use their knowledge and experience to interpret weather models and provide informed forecasts. Consulting with experts can help residents and businesses make informed decisions about preparing for winter storms. At HOW.EDU.VN, we have board-certified Doctors available to provide personalized weather guidance and insights.
- Consulting Meteorologists:
- Benefits of Expert Advice:
- Accurate Forecasts: Expert meteorologists can provide more accurate and nuanced snowfall predictions.
- Contextual Understanding: They can explain the factors driving the weather patterns and provide context for the forecasts.
- Personalized Guidance: Experts can offer tailored advice on how to prepare for specific weather events.
- Real-Time Updates: They can provide timely updates and adjustments to the forecasts as conditions change.
- Finding Reputable Sources:
- National Weather Service: The NWS is a reliable source of official weather forecasts and warnings.
- Local News Outlets: Local television and radio stations often have experienced meteorologists who provide regional forecasts.
- Private Weather Services: Several private weather companies offer specialized forecasts and consulting services.
- Benefits of Expert Advice:
4. Factors Influencing Snow Accumulation in Urban Areas
Urban environments like Minneapolis present unique challenges for snowfall prediction and accumulation. The built landscape, with its buildings, roads, and other infrastructure, can significantly influence local weather patterns. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurately forecasting snowfall amounts in urban areas.
- Urban Heat Island Effect:
- Definition: The urban heat island effect refers to the phenomenon where urban areas are warmer than their surrounding rural areas due to human activities and infrastructure.
- Impact on Snowfall: Warmer temperatures in urban areas can reduce the amount of snow that accumulates, as some of it may melt upon contact with warmer surfaces.
- Building and Infrastructure Effects:
- Wind Patterns: Tall buildings can alter wind patterns, creating localized areas of increased or decreased wind speeds.
- Snowdrifts: Buildings can act as barriers, causing snow to accumulate in drifts in certain areas.
- Surface Temperatures: Different surfaces, such as roads, sidewalks, and roofs, have varying temperatures that can affect snowmelt rates.
- Pollution and Aerosols:
- Cloud Formation: Aerosols and pollutants in the air can influence cloud formation and precipitation patterns.
- Snowfall Intensity: Air pollution can affect the intensity and duration of snowfall events.
5. Preparing for a Major Snowstorm in Minneapolis
Being well-prepared for a major snowstorm is essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of yourself, your family, and your community. Preparation involves taking proactive steps to mitigate the potential impacts of the storm. By following these guidelines, Minneapolis residents can minimize the risks associated with winter weather and navigate snowstorms more safely and effectively.
- Home Preparation:
- Stocking Up:
- Food and Water: Store a sufficient supply of non-perishable food and bottled water to last for several days.
- Emergency Supplies: Gather essential items such as flashlights, batteries, a first-aid kit, and a battery-powered radio.
- Medications: Ensure you have an adequate supply of any prescription medications you or your family members need.
- Insulating Your Home:
- Weather Stripping: Seal gaps around windows and doors to prevent drafts and conserve heat.
- Insulation: Add insulation to attics and walls to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
- Pipes: Protect exposed pipes from freezing by wrapping them with insulation.
- Heating Systems:
- Maintenance: Have your heating system inspected and serviced to ensure it is functioning efficiently.
- Backup Heat: Consider having a backup heating source, such as a fireplace or space heater, in case of a power outage.
- Stocking Up:
- Vehicle Preparation:
- Winter Tires: Install winter tires on your vehicle for improved traction on snow and ice.
- Maintenance: Have your vehicle serviced, checking the battery, fluids, and brakes.
- Emergency Kit: Keep an emergency kit in your vehicle with items such as a shovel, ice scraper, jumper cables, blankets, and a flashlight.
- Creating a Family Emergency Plan:
- Communication: Establish a communication plan with family members, including a designated meeting place in case of separation.
- Emergency Contacts: Keep a list of emergency contact numbers readily available.
- Evacuation Routes: Familiarize yourself with potential evacuation routes in your area.
- Staying Informed:
- Weather Updates: Monitor weather forecasts and updates from reliable sources, such as the National Weather Service and local news outlets.
- Emergency Alerts: Sign up for emergency alerts from your local government to receive timely information about hazardous conditions.
- Community Involvement:
- Helping Neighbors: Check on elderly or disabled neighbors who may need assistance during a snowstorm.
- Volunteering: Consider volunteering with local organizations to help with snow removal or emergency response efforts.
6. The Role of Technology in Snowfall Prediction
Technological advancements have significantly improved the accuracy and reliability of snowfall predictions. Advanced weather models, radar technology, and satellite observations provide meteorologists with valuable data to analyze and interpret.
- Weather Models:
- Types of Models:
- Global Models: These models cover the entire globe and provide a broad overview of weather patterns.
- Regional Models: These models focus on specific regions and provide more detailed forecasts.
- High-Resolution Models: These models use advanced algorithms to simulate weather conditions at a very fine scale.
- Data Assimilation: Weather models use data assimilation techniques to incorporate real-time observations and improve forecast accuracy.
- Types of Models:
- Radar Technology:
- Doppler Radar: This type of radar can detect the movement of precipitation particles, providing information about wind speeds and directions within storms.
- Dual-Polarization Radar: This advanced radar technology can distinguish between different types of precipitation, such as rain, snow, and sleet.
- Radar Imagery: Radar imagery provides a visual representation of precipitation patterns and intensities, helping meteorologists track storms and assess their potential impacts.
- Satellite Observations:
- Geostationary Satellites: These satellites orbit the Earth at the same rate as its rotation, providing continuous imagery of weather systems.
- Polar-Orbiting Satellites: These satellites orbit the Earth from pole to pole, providing detailed observations of atmospheric conditions.
- Satellite Data: Satellite data is used to monitor cloud cover, temperature, humidity, and other factors that influence snowfall.
7. Impact of Climate Change on Snowfall Patterns
Climate change is altering weather patterns around the world, and snowfall patterns are no exception. Understanding the potential impacts of climate change on snowfall in Minneapolis is crucial for long-term planning and adaptation.
- Temperature Increases:
- Warmer Winters: Climate change is leading to warmer winter temperatures, which can reduce the amount of snow that falls in some areas.
- Rain-Snow Transition: Warmer temperatures can cause precipitation to fall as rain instead of snow, especially at the beginning and end of the winter season.
- Changes in Precipitation:
- Increased Variability: Climate change is causing more extreme weather events, including more intense snowstorms in some regions.
- Shifts in Timing: The timing of snowfall events may shift, with later starts to the snow season and earlier melts in the spring.
- Long-Term Trends:
- Reduced Snowpack: Climate change is expected to lead to a reduction in snowpack in many areas, which can have significant impacts on water resources and ecosystems.
- Altered Snowfall Patterns: The distribution of snowfall may change, with some areas experiencing more snow and others experiencing less.
- Expert Projections:
- Climate Models: Climate models are used to project future snowfall patterns based on different greenhouse gas emission scenarios.
- Scientific Consensus: The scientific consensus is that climate change will continue to alter snowfall patterns in the coming decades, with potentially significant impacts on winter recreation, water resources, and ecosystems.
8. The Science Behind Snow Formation
Snow formation is a fascinating process that involves several atmospheric conditions and physical principles. Understanding the science behind snow can help us appreciate the complexity of weather phenomena.
- Water Vapor and Condensation:
- Evaporation: Water evaporates from bodies of water, such as lakes and oceans, and enters the atmosphere as water vapor.
- Condensation: As air rises and cools, water vapor condenses into liquid droplets or ice crystals.
- Ice Crystal Formation:
- Nucleation: Ice crystals form when water vapor freezes onto tiny particles in the air, such as dust or pollen.
- Crystal Growth: As ice crystals grow, they attract more water vapor and form intricate shapes.
- Snowflake Structure:
- Hexagonal Symmetry: Snowflakes have a hexagonal shape due to the way water molecules bond together in ice crystals.
- Unique Patterns: Each snowflake is unique, with its own individual pattern of branches and facets.
- Factors Affecting Snowflake Shape:
- Temperature: The temperature of the air affects the shape of snowflakes. Colder temperatures tend to produce more complex and elaborate snowflakes.
- Humidity: The amount of moisture in the air also influences snowflake shape. Higher humidity can lead to larger and more intricate snowflakes.
- Types of Snowflakes:
- Dendrites: These are the classic, star-shaped snowflakes with intricate branches.
- Needles: These are long, thin snowflakes that form in very cold temperatures.
- Plates: These are flat, plate-like snowflakes that form in slightly warmer temperatures.
- Columns: These are cylindrical snowflakes that form in extremely cold temperatures.
9. Safety Tips for Driving in Snowy Conditions
Driving in snowy conditions can be hazardous, and it’s essential to take precautions to ensure your safety and the safety of others.
- Before You Go:
- Check the Weather: Before heading out, check the weather forecast and road conditions.
- Vehicle Maintenance: Ensure your vehicle is in good working order, with properly inflated tires, functioning brakes, and adequate fluids.
- Emergency Kit: Keep an emergency kit in your vehicle with items such as a shovel, ice scraper, jumper cables, blankets, and a flashlight.
- Driving Techniques:
- Slow Down: Reduce your speed and increase your following distance to allow for more time to react.
- Avoid Sudden Movements: Accelerate, brake, and steer smoothly to avoid losing control of your vehicle.
- Use Headlights: Turn on your headlights to increase visibility, even during daylight hours.
- Be Aware of Black Ice: Black ice is a thin, transparent layer of ice that can be difficult to see. Be especially cautious on bridges, overpasses, and shaded areas.
- If You Start to Skid:
- Stay Calm: Avoid panicking and remain calm.
- Ease Off the Pedals: Gently release the accelerator and brake pedals.
- Steer in the Direction of the Skid: Steer your vehicle in the direction you want it to go.
- Regain Control: Once you regain control, gently apply the brakes and steer back onto the road.
- If You Get Stranded:
- Stay in Your Vehicle: Remain in your vehicle and wait for help to arrive.
- Call for Help: Use your cell phone to call for assistance.
- Run the Engine Sparingly: Run the engine for short periods to stay warm, but be sure to ventilate the vehicle to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Make Yourself Visible: Tie a brightly colored cloth to your antenna or door to signal for help.
10. Understanding Winter Weather Advisories and Warnings
Winter weather advisories and warnings are issued by the National Weather Service to alert the public to hazardous winter weather conditions. Understanding the difference between these alerts and knowing how to respond is crucial for staying safe during winter storms.
- Winter Weather Advisory:
- Definition: A winter weather advisory is issued when conditions are expected to cause significant inconvenience and may be hazardous.
- Conditions: Advisories are typically issued for light to moderate snowfall, freezing rain, sleet, or blowing snow.
- Recommended Actions: Take precautions when traveling and be aware of potentially hazardous conditions.
- Winter Storm Watch:
- Definition: A winter storm watch is issued when conditions are favorable for a significant winter storm.
- Conditions: Watches are typically issued 12 to 36 hours in advance of a potential storm.
- Recommended Actions: Monitor weather forecasts and prepare for the possibility of a winter storm.
- Winter Storm Warning:
- Definition: A winter storm warning is issued when hazardous winter weather conditions are imminent or occurring.
- Conditions: Warnings are typically issued for heavy snowfall, blizzard conditions, freezing rain, or ice storms.
- Recommended Actions: Take immediate action to protect yourself and others. Avoid traveling if possible and stay indoors.
- Blizzard Warning:
- Definition: A blizzard warning is issued when blizzard conditions are expected, including sustained winds of 35 mph or greater and heavy snowfall.
- Conditions: Blizzard conditions can cause whiteout conditions and make travel extremely dangerous.
- Recommended Actions: Seek shelter immediately and avoid traveling under any circumstances.
Navigating winter weather can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and preparation, you can stay safe and informed. At HOW.EDU.VN, our expert meteorologists are committed to providing you with the most accurate and up-to-date information so you can make informed decisions and protect yourself and your loved ones. Trust our team to help you navigate winter weather with confidence.
For personalized guidance on how to prepare for winter storms and snowfall in Minneapolis, contact our team of board-certified Doctors at HOW.EDU.VN. We’re here to provide expert insights and support to help you stay safe and informed.
11. The Economic Impact of Snowstorms on Minneapolis
Snowstorms can have a significant economic impact on Minneapolis, affecting businesses, transportation, and public services. Understanding these economic consequences is crucial for planning and mitigation efforts.
- Direct Costs:
- Snow Removal: The cost of snow removal can be substantial, including expenses for plowing, salting, and labor.
- Infrastructure Damage: Snow and ice can damage roads, bridges, and other infrastructure, requiring costly repairs.
- Emergency Services: Snowstorms can increase demand for emergency services, such as police, fire, and ambulance, leading to higher costs.
- Indirect Costs:
- Business Disruptions: Snowstorms can force businesses to close or reduce their hours, leading to lost revenue.
- Transportation Delays: Snowstorms can cause transportation delays, disrupting supply chains and increasing costs for businesses.
- Reduced Retail Sales: Snowstorms can discourage shoppers from visiting stores, leading to lower retail sales.
- Increased Absenteeism: Snowstorms can make it difficult for employees to get to work, leading to increased absenteeism and reduced productivity.
- Economic Benefits:
- Snow Removal Industry: The snow removal industry benefits from snowstorms, with increased demand for services and equipment.
- Winter Recreation: Snowstorms can boost winter recreation activities, such as skiing, snowboarding, and snowmobiling, benefiting tourism and local businesses.
- Mitigation Strategies:
- Early Planning: Develop a comprehensive winter weather plan that includes strategies for snow removal, transportation management, and emergency response.
- Infrastructure Investment: Invest in infrastructure improvements to make roads, bridges, and other facilities more resilient to winter weather.
- Public Awareness: Educate the public about the economic impacts of snowstorms and the importance of preparedness.
12. Long-Range Snowfall Outlook for Minneapolis
While short-term forecasts provide detailed information about upcoming snowstorms, long-range outlooks offer a broader perspective on potential snowfall patterns over the course of the winter season.
- Factors Influencing Long-Range Outlooks:
- El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO): ENSO is a climate pattern that can influence weather patterns around the world, including snowfall in Minneapolis.
- Arctic Oscillation (AO): The AO is a climate pattern that can affect the frequency and intensity of cold air outbreaks in North America.
- Sea Surface Temperatures: Sea surface temperatures in the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans can influence weather patterns and snowfall.
- Interpreting Long-Range Outlooks:
- Probabilistic Forecasts: Long-range outlooks are typically presented as probabilistic forecasts, indicating the likelihood of above-average, near-average, or below-average snowfall.
- Uncertainty: Long-range outlooks are subject to significant uncertainty, as weather patterns can change over time.
- Using Long-Range Outlooks for Planning:
- Resource Allocation: Long-range outlooks can help businesses and government agencies plan for winter weather and allocate resources accordingly.
- Risk Management: They can also help individuals and organizations assess the potential risks associated with winter weather and take appropriate precautions.
13. Snowfall Records and Historical Data for Minneapolis
Minneapolis has a rich history of snowfall events, and examining historical data can provide valuable insights into the region’s winter weather patterns.
- Record Snowfall:
- Highest Single-Day Snowfall: The record for the highest single-day snowfall in Minneapolis is 21 inches, which occurred on January 20, 1982.
- Highest Seasonal Snowfall: The record for the highest seasonal snowfall in Minneapolis is 98.4 inches, which occurred during the winter of 1983-1984.
- Average Snowfall:
- Annual Snowfall: The average annual snowfall in Minneapolis is approximately 54 inches.
- Snowfall Distribution: Snowfall is typically distributed throughout the winter months, with the heaviest snowfall occurring in December, January, and February.
- Historical Trends:
- Long-Term Variations: Snowfall patterns in Minneapolis have varied over time, with some decades experiencing more snow than others.
- Climate Change Impacts: Climate change is expected to alter snowfall patterns in the coming decades, with potentially significant impacts on winter recreation, water resources, and ecosystems.
14. How to Measure Snowfall Accurately
Measuring snowfall accurately can be challenging, but it’s essential for tracking winter weather patterns and verifying weather forecasts.
- Equipment:
- Snow Gauge: A snow gauge is a cylindrical container used to collect and measure snowfall.
- Measuring Stick: A measuring stick is used to measure the depth of the snow in the snow gauge.
- Snow Board: A snow board is a flat surface used to measure snowfall in open areas.
- Procedure:
- Location: Place the snow gauge or snow board in an open area away from trees and buildings.
- Measurement: Measure the depth of the snow in the snow gauge or on the snow board using the measuring stick.
- Frequency: Measure snowfall at regular intervals, such as every 6 or 12 hours.
- Melting: If the snow melts before you can measure it, record the amount of water in the snow gauge as liquid precipitation.
- Tips for Accurate Measurement:
- Level Surface: Ensure the snow gauge or snow board is placed on a level surface.
- Wind Protection: Protect the snow gauge or snow board from wind to prevent snow from being blown away.
- Consistent Technique: Use a consistent technique for measuring snowfall to minimize errors.
15. Common Misconceptions About Snowfall
There are several common misconceptions about snowfall that can lead to confusion and misinformed decisions.
- Myth: All Snowflakes Are the Same.
- Fact: Each snowflake is unique, with its own individual pattern of branches and facets.
- Myth: Snow Is Too Cold to Snow.
- Fact: Snow can form at temperatures well below freezing.
- Myth: Heavy Snow Always Means Cold Temperatures.
- Fact: Heavy snow can occur at temperatures near freezing.
- Myth: Snow Is Just Frozen Rain.
- Fact: Snow forms when water vapor freezes directly into ice crystals, without first becoming liquid water.
- Myth: City Streets Are Always Clear After a Snowstorm.
- Fact: City streets can still be hazardous after a snowstorm, especially in areas with heavy traffic or limited snow removal.
Understanding these common misconceptions can help you make more informed decisions and stay safe during winter weather.
At HOW.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with accurate and reliable information about snowfall and winter weather. Our team of expert meteorologists is here to answer your questions and provide personalized guidance to help you stay safe and informed.
16. The Psychology of Snow: How Winter Weather Affects Mood
Winter weather, particularly snowfall, can have a significant impact on our psychological well-being. Understanding how snow affects our mood can help us better cope with the challenges of winter.
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD):
- Definition: SAD is a type of depression that is related to changes in the seasons.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of SAD can include fatigue, sadness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
- Causes: SAD is thought to be caused by a lack of sunlight, which can disrupt the body’s natural rhythms and affect levels of serotonin and melatonin.
- The Calming Effect of Snow:
- Visual Appeal: Snow can be visually appealing, creating a sense of peace and tranquility.
- Sound Dampening: Snow can dampen sound, creating a quieter and more peaceful environment.
- Nostalgia: Snow can evoke feelings of nostalgia, reminding us of childhood memories and happy times.
- The Stress of Winter Weather:
- Travel Disruptions: Snowstorms can disrupt travel plans, causing stress and anxiety.
- Safety Concerns: Snow and ice can create hazardous conditions, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Cabin Fever: Spending too much time indoors during the winter can lead to feelings of isolation and boredom.
- Coping Strategies:
- Get Enough Sunlight: Try to get as much sunlight as possible during the day, even if it’s just for a few minutes.
- Exercise Regularly: Exercise can help boost your mood and reduce stress.
- Stay Social: Make an effort to stay connected with friends and family, even if you can’t see them in person.
- Practice Mindfulness: Practice mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, to help manage stress and anxiety.
17. The Cultural Significance of Snow in Minneapolis
Snow has a deep cultural significance in Minneapolis, shaping the city’s identity and influencing its art, literature, and traditions.
- Winter Festivals:
- Winter Carnival: The Winter Carnival is an annual celebration of winter in St. Paul, featuring ice sculptures, parades, and other festivities.
- Holidazzle: Holidazzle is a holiday celebration in downtown Minneapolis, featuring a festive market, entertainment, and fireworks.
- Outdoor Recreation:
- Skiing and Snowboarding: Minneapolis is home to several ski resorts and snowboarding areas, providing opportunities for winter recreation.
- Ice Skating: Ice skating is a popular winter activity in Minneapolis, with numerous outdoor rinks and indoor arenas.
- Snowshoeing and Cross-Country Skiing: Snowshoeing and cross-country skiing are popular ways to explore the city’s parks and trails during the winter.
- Art and Literature:
- Winter Landscapes: Winter landscapes are a common theme in Minneapolis art and literature, reflecting the city’s connection to its natural environment.
- Snow Imagery: Snow imagery is often used to evoke feelings of peace, tranquility, and beauty.
- Community Traditions:
- Snow Days: Snow days are a cherished tradition in Minneapolis, providing students with a break from school and an opportunity to enjoy winter weather.
- Holiday Celebrations: Snow is often associated with holiday celebrations, such as Christmas and Hanukkah, creating a festive atmosphere.
18. Innovations in Snow Removal Technology
Advancements in technology are revolutionizing snow removal efforts, making them more efficient, effective, and environmentally friendly.
- Smart Snowplows:
- GPS Tracking: Smart snowplows use GPS technology to track their location and monitor road conditions.
- Real-Time Data: They collect real-time data on snow depth, temperature, and road surface conditions.
- Automated Systems: Some smart snowplows have automated systems that adjust the plow blade and salt spreader based on road conditions.
- Liquid De-Icers:
- Pre-Treatment: Liquid de-icers can be applied to roads before a snowstorm to prevent ice from forming.
- Reduced Salt Use: They can reduce the amount of salt needed for snow removal, minimizing environmental impacts.
- Effective at Low Temperatures: Some liquid de-icers are effective at lower temperatures than traditional salt.
- Snow Melting Systems:
- Radiant Heat: Snow melting systems use radiant heat to melt snow and ice on sidewalks, driveways, and parking lots.
- Automated Control: They can be automatically controlled based on temperature and precipitation.
- Energy Efficiency: Some snow melting systems use renewable energy sources, such as solar or geothermal, to reduce energy consumption.
- Snow Sensors:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Snow sensors provide real-time monitoring of snow depth, temperature, and moisture content.
- Early Warning Systems: They can be used to develop early warning systems for winter weather hazards.
- Automated Response: Snow sensors can trigger automated responses, such as activating snow melting systems or deploying snowplows.
19. Tips for Staying Active During Winter in Minneapolis
Staying active during the winter months can be challenging, but it’s essential for maintaining your physical and mental health.
- Embrace Outdoor Activities:
- Skiing and Snowboarding: Take advantage of Minneapolis’s ski resorts and snowboarding areas.
- Ice Skating: Enjoy ice skating at one of the city’s outdoor rinks or indoor arenas.
- Snowshoeing and Cross-Country Skiing: Explore the city’s parks and trails on snowshoes or cross-country skis.
- Winter Hiking: Go for a winter hike in one of Minneapolis’s scenic parks or nature reserves.
- Find Indoor Activities:
- Gyms and Fitness Centers: Join a gym or fitness center and participate in indoor workouts.
- Swimming Pools: Take a swim at one of Minneapolis’s indoor swimming pools.
- Yoga and Pilates Studios: Attend yoga or Pilates classes to stay flexible and strong.
- Indoor Rock Climbing: Try indoor rock climbing for a challenging and fun workout.
- Stay Motivated:
- Set Goals: Set realistic goals for your winter fitness routine.
- Find a Workout Buddy: Exercise with a friend or family member to stay motivated.
- Reward Yourself: Reward yourself for reaching your fitness goals.
- Listen to Music: Listen to upbeat music to keep your energy levels high.
20. The Future of Snowfall Forecasting
Snowfall forecasting is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and development leading to improved accuracy and reliability.
- Advanced Weather Models:
- High-Resolution Simulations: Future weather models will use even higher-resolution simulations to capture small-scale weather phenomena.
- Improved Data Assimilation: They will also incorporate improved data assimilation techniques to integrate real-time observations more effectively.
- Ensemble Forecasting: Ensemble forecasting, which involves running multiple model simulations with slightly different initial conditions, will become more sophisticated.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- Machine Learning: AI and machine learning techniques will be used to analyze weather data and identify patterns that are difficult for humans to detect.
- Automated Forecast Generation: AI will be used to automate the process of generating weather forecasts, freeing up meteorologists to focus on more complex tasks.
- Personalized Forecasts: AI will be used to create personalized weather forecasts tailored to individual users’ needs.
- Citizen Science:
- Crowdsourcing Data: Citizen science initiatives will engage the public in collecting weather data, such as snowfall measurements and observations of cloud cover.
- Community-Based Forecasting: This data will be used to improve the accuracy of weather forecasts and develop community-based forecasting systems.
- Space-Based Observations:
- Advanced Satellites: Future satellites will provide more detailed and accurate observations of atmospheric conditions, including temperature, humidity, and precipitation.
- Global Coverage: They will provide global coverage, allowing meteorologists to monitor weather patterns around the world.
- Real-Time Data: Space-based observations will provide real-time data that can be used to improve the accuracy of weather forecasts and track winter storms.
The future of snowfall forecasting is bright, with ongoing innovations promising to deliver more accurate, reliable, and personalized information to help people stay safe and informed during winter weather.
For expert advice and personalized guidance on snowfall predictions and winter weather preparedness, contact the team of board-certified Doctors at HOW.EDU.VN. We’re here to help you navigate winter weather with confidence.
Don’t let winter weather catch you off guard. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today and connect with our expert team of over 100 board-certified Doctors. Get the personalized advice and support you need to navigate any challenge, from snowfall predictions to complex business decisions. We’re here to help you achieve your goals and live your best life. Contact us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212. Visit our website at how.edu.vn
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Snowfall in Minneapolis
-
How much snow does Minneapolis get on average each year?
Minneapolis averages around 54 inches of snow annually. However, this can vary significantly from year to year.
-
When is the snowiest month in Minneapolis?
The snowiest months in Minneapolis are typically December, January, and February.
-
How can I prepare my home for a major snowstorm?
Stock up on food, water, and emergency supplies. Insulate your home, protect pipes from freezing, and have your heating system inspected.
-
What should I do if I have to drive in snowy conditions?
Slow down, increase your following distance, and avoid sudden movements. Ensure your vehicle is properly equipped with winter tires and an emergency kit.
-
How can I stay informed about winter weather advisories and warnings?
Monitor weather forecasts from the National Weather Service and local news outlets. Sign up for emergency alerts from your local government.
-
What is the urban heat island effect, and how does it affect snowfall in Minneapolis?
The urban heat island effect refers to the phenomenon where urban areas are warmer than their surrounding rural areas. This can reduce the amount of snow that accumulates in the city.
-
How is climate change affecting snowfall patterns in Minneapolis?
Climate change is leading to warmer winter temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns, which can reduce the amount of snow that falls in some areas.
-
What are some common misconceptions about snowfall?
Common misconceptions include the belief that all snowflakes are the same and that snow is just frozen rain.
-
How can I stay active during the winter months in Minneapolis?
Embrace outdoor activities like skiing