Are you considering harnessing the sun’s power but unsure how much solar do I need to power your home or business? At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert advice to help you determine the optimal solar panel system size, considering energy consumption, location, and other key factors for a seamless transition to solar energy. Discover solar potential, system design, and energy independence.
1. Understanding Your Energy Needs for Solar Power
Before diving into calculations, it’s essential to understand your current energy consumption patterns. This involves analyzing your electricity bills to determine your annual kilowatt-hour (kWh) usage. Understanding these metrics is critical in determining how much solar power will be needed.
1.1. Analyzing Your Electricity Bills
Your electricity bill is a goldmine of information. It shows how much energy you consume monthly and annually. Look for the total kWh used over the past 12 months. This figure is the baseline for calculating the size of the solar panel system you need.
For instance, if your annual electricity consumption is 12,000 kWh, you need a solar panel system that can generate at least that much energy each year. Consider seasonal variations; you might use more energy in the summer for cooling or in the winter for heating. This fluctuation can impact the overall design of your solar system.
1.2. Factors Influencing Energy Consumption
Several factors influence your energy consumption:
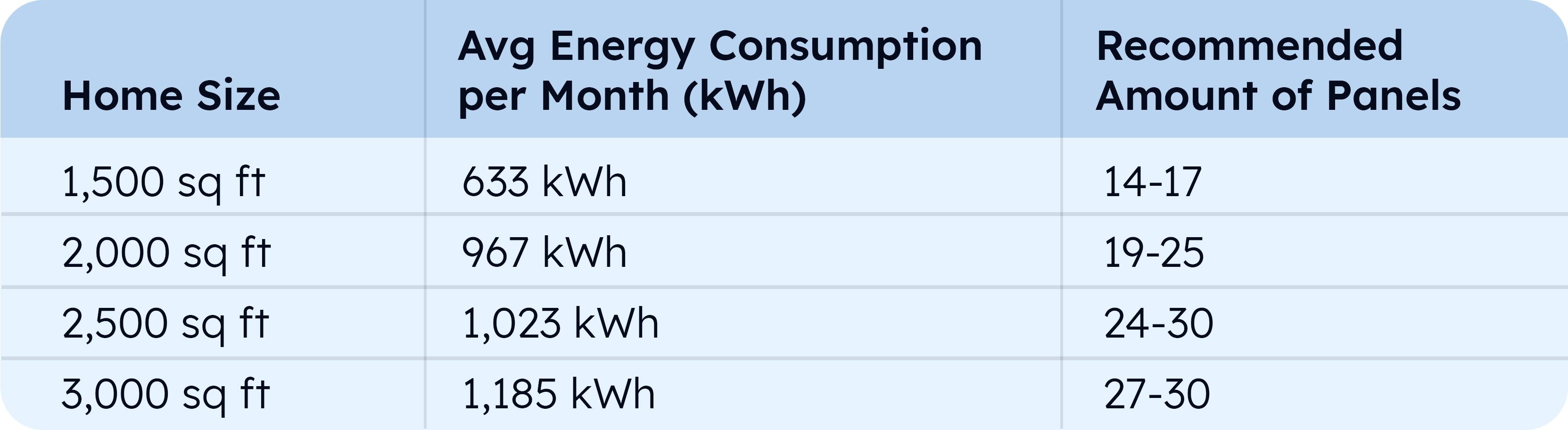
- Home Size: Larger homes typically require more energy.
- Occupants: More people in the household mean more energy usage.
- Appliances: Energy-intensive appliances like air conditioners, electric heaters, and older refrigerators significantly increase consumption.
- Lifestyle: Habits like leaving lights on, using multiple devices simultaneously, and working from home can also increase energy needs.
To accurately assess your needs, conduct an energy audit. This involves evaluating all energy-consuming devices and identifying areas where you can improve efficiency. For example, switching to LED lighting, upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, and improving insulation can reduce your overall energy consumption, lowering the amount of solar power you need.
1.3. Setting Energy Efficiency Goals
Before installing solar panels, consider setting energy efficiency goals to reduce your consumption. Simple changes can make a big difference. For example, using smart thermostats, unplugging electronics when not in use, and washing clothes in cold water can all lower your energy footprint.
Consulting with energy efficiency experts can provide tailored recommendations for your home or business. These experts can identify areas where you’re wasting energy and suggest practical solutions. Implementing these strategies not only reduces your reliance on the grid but also makes your solar investment more effective.
2. Sizing Your Solar Panel System
Sizing your solar panel system involves several key considerations. The wattage of solar panels, the production ratio in your area, and the available roof space all play a crucial role in determining the right system size.
2.1. Understanding Solar Panel Wattage
Solar panel wattage refers to the amount of power a solar panel can produce under ideal conditions. Most residential solar panels range from 250 to 400 watts. Higher wattage panels produce more electricity and can reduce the number of panels needed.
When selecting solar panels, consider the efficiency rating. Higher efficiency panels generate more power from the same amount of sunlight, making them ideal for smaller roofs. For example, a 400-watt panel might be more expensive but could reduce the total number of panels required, saving space and installation costs.
2.2. Calculating the Production Ratio
The production ratio (also known as the solar insolation rate) accounts for local weather conditions and sunlight availability. This ratio varies by geographic location, affecting how much electricity your solar panels will generate.
In areas with abundant sunshine, like the Southwest, the production ratio is higher, meaning solar panels will produce more electricity. In regions with more cloud cover, like the Northeast, the ratio is lower. Use the following table as a reference point:
| Region | Production Ratio |
|---|---|
| Southwest | 1.6 – 1.8 |
| Southeast | 1.4 – 1.6 |
| Midwest | 1.2 – 1.4 |
| Northeast | 1.0 – 1.2 |
| Pacific Northwest | 0.8 – 1.0 |
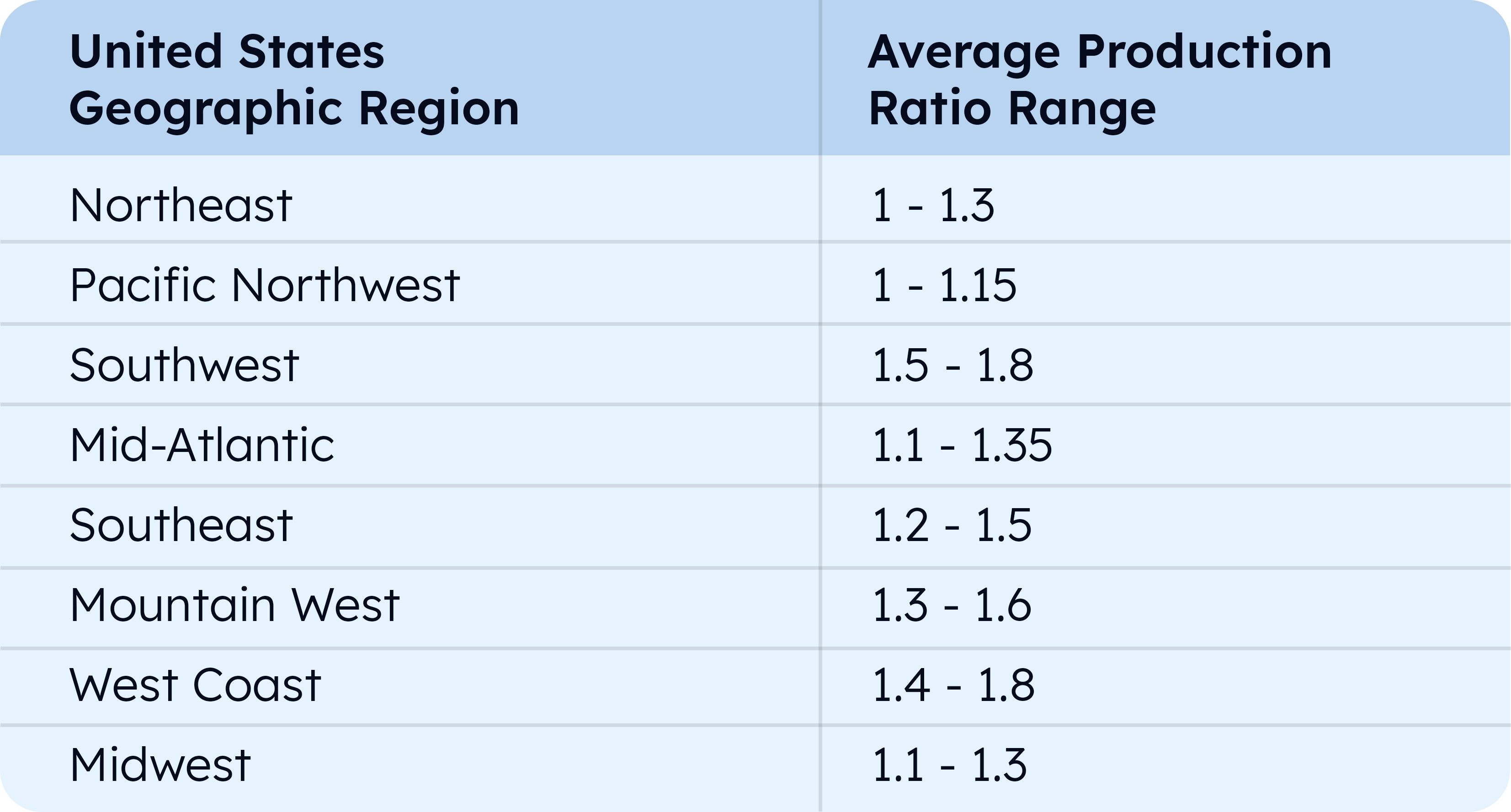
To calculate the production ratio for your specific location, consult local solar installers or use online solar calculators. These resources factor in your area’s climate data to provide a more accurate estimate.
2.3. Determining Available Roof Space
The amount of available roof space directly impacts the size of your solar panel system. Measure your roof to determine the usable area, considering factors like shading from trees or nearby buildings, roof orientation, and roof pitch.
South-facing roofs are ideal for solar panels because they receive the most sunlight throughout the day. East- and west-facing roofs can also be suitable, but they may produce slightly less energy. North-facing roofs are generally not recommended.
A professional solar installer can assess your roof and provide a detailed layout plan, optimizing the placement of solar panels for maximum energy production. They will consider all factors, including shading, roof angle, and structural integrity, to ensure the system performs efficiently.
3. Step-by-Step Solar Panel Calculation
To determine how much solar do I need, follow this step-by-step calculation:
3.1. Gather Required Information
- Annual Electricity Usage: Obtain your annual kWh consumption from your electricity bill.
- Solar Panel Wattage: Choose the solar panel wattage (e.g., 350 watts).
- Production Ratio: Determine the production ratio for your area.
- Sunlight Hours: Find out how many peak sunlight hours your location gets per day.
3.2. Perform the Calculation
- Calculate Daily Energy Needs: Divide your annual energy consumption by 365 to get your daily energy needs.
- Calculate Solar Panel Output: Multiply the solar panel wattage by the production ratio.
- Determine Number of Panels: Divide your daily energy needs by the solar panel output.
- Account for System Losses: Increase the number of panels by 10-15% to account for system inefficiencies.
Example Calculation:
- Annual electricity usage: 10,000 kWh
- Solar panel wattage: 350 watts
- Production ratio: 1.4
- Daily Energy Needs: 10,000 kWh / 365 = 27.4 kWh per day
- Solar Panel Output: 350 watts * 1.4 = 490 watts or 0.49 kWh per day
- Number of Panels: 27.4 kWh / 0.49 kWh = 55.9 panels
- Account for Losses: 55.9 panels + 10% = 61.5 panels
Therefore, you would need approximately 62 solar panels to meet your energy needs.
3.3. Utilizing Online Solar Calculators
Online solar calculators can simplify the calculation process. These tools ask for your location, energy usage, and panel specifications to provide an estimate of the system size you need.
Some popular solar calculators include:
- EnergySage Solar Calculator: Provides detailed estimates based on your location and energy consumption.
- PVWatts Calculator: Developed by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, it offers accurate performance predictions.
- Google Project Sunroof: Helps you estimate solar potential using satellite imagery.
While these calculators are helpful, they should be used as a starting point. Consulting with a professional solar installer is essential for a precise assessment.
3.4. Consulting with Solar Professionals
Engaging with solar professionals ensures you get an accurate assessment tailored to your specific needs. Installers consider factors like shading, roof orientation, and local regulations to design an optimized system.
Solar installers also handle permitting, installation, and maintenance, providing a hassle-free experience. They can recommend the best solar panels, inverters, and batteries for your needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of experts can connect you with qualified solar professionals who can provide personalized advice and support. Our network includes experienced installers, engineers, and consultants who can guide you through every step of the process.
4. Factors Affecting Solar Panel Efficiency
Several factors can influence the efficiency of your solar panels. Understanding these can help you optimize your system for maximum energy production.
4.1. Panel Type and Quality
The type and quality of solar panels significantly affect their efficiency. Monocrystalline panels are generally more efficient than polycrystalline panels. Thin-film panels are less efficient but can be more cost-effective for large installations.
High-quality panels are built to withstand harsh weather conditions and maintain their performance over time. Look for panels with long warranties and positive customer reviews to ensure you’re investing in a reliable product.
4.2. Shading and Obstructions
Shading from trees, buildings, or other obstructions can significantly reduce solar panel output. Even partial shading can decrease energy production.
Conduct a shading analysis to identify potential obstructions and plan the system layout accordingly. Consider trimming trees or relocating panels to maximize sunlight exposure.
4.3. Roof Orientation and Angle
The orientation and angle of your roof affect how much sunlight your solar panels receive. South-facing roofs with a tilt angle equal to your latitude are ideal.
If your roof doesn’t face south, you can still install solar panels on east- or west-facing roofs. However, you may need more panels to achieve the same energy production. Adjusting the tilt angle can also improve performance.
4.4. Weather Conditions and Climate
Weather conditions and climate play a crucial role in solar panel efficiency. Solar panels perform best in cool, sunny conditions. Extreme heat can reduce their efficiency, while cloud cover can limit energy production.
Consider the local climate when selecting solar panels. Some panels are designed to perform better in hot or humid conditions. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the panels, can also improve their efficiency.
5. Solar Panel Costs and Incentives
Understanding the costs and incentives associated with solar panels is crucial for making an informed decision.
5.1. Initial Investment Costs
The initial investment costs for solar panels include the cost of the panels, inverters, racking, and installation. The total cost varies depending on the size of the system, the type of equipment, and the complexity of the installation.
As of 2023, the average cost of a residential solar panel system ranges from $2.50 to $3.50 per watt. A 6kW system, which is typical for a small home, can cost between $15,000 and $21,000 before incentives.
5.2. Available Tax Credits and Rebates
Several tax credits and rebates can significantly reduce the cost of solar panels. The federal Residential Clean Energy Tax Credit allows you to deduct 30% of the cost of your solar panel system from your federal taxes.
Many states and local governments also offer additional incentives, such as rebates, tax credits, and grants. These incentives can further reduce the cost of solar panels, making them more affordable.
5.3. Long-Term Savings and ROI
Solar panels can provide significant long-term savings by reducing or eliminating your electricity bills. Over the lifespan of the system, these savings can exceed the initial investment, resulting in a positive return on investment (ROI).
The ROI of solar panels depends on factors like the cost of electricity, the size of the system, and the amount of sunlight your panels receive. In some areas, solar panels can pay for themselves in as little as 5-7 years.
5.4. Financing Options
Several financing options are available to help you pay for solar panels. These include:
- Loans: Secured or unsecured loans can provide the funds you need to purchase solar panels.
- Leases: Solar leases allow you to rent the panels from a solar company, paying a monthly fee for the electricity they generate.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): PPAs allow you to purchase electricity from a solar company at a fixed rate, without owning the panels.
Each financing option has its advantages and disadvantages. Consider your financial situation and long-term goals when choosing the best option for you.
6. Maintenance and Monitoring
Proper maintenance and monitoring are essential for ensuring the long-term performance of your solar panel system.
6.1. Regular Cleaning and Inspections
Regular cleaning and inspections can help identify and address potential issues before they escalate. Clean your solar panels at least once a year to remove dirt, dust, and debris that can reduce their efficiency.
Inspect the panels for cracks, damage, or loose connections. Check the inverter and other components for any signs of wear and tear.
6.2. Performance Monitoring Systems
Performance monitoring systems allow you to track the energy production of your solar panels in real-time. These systems provide valuable insights into the performance of your system, helping you identify any issues and optimize energy production.
Many solar inverters come with built-in monitoring capabilities. You can also purchase separate monitoring systems that provide more detailed data and analysis.
6.3. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues with solar panels include shading, panel damage, and inverter failures. Address these issues promptly to minimize their impact on energy production.
If you notice a decrease in energy production, check for shading or obstructions. Inspect the panels for any signs of damage. If the inverter is not functioning properly, contact a qualified technician for repairs.
6.4. Warranties and Guarantees
Solar panels typically come with warranties that cover defects in materials and workmanship. Inverters and other components also come with warranties.
Read the fine print of your warranties to understand what is covered and what is not. Keep records of all maintenance and repairs to ensure you can file a warranty claim if needed.
7. Community Solar as an Alternative
If you’re unable to install rooftop solar panels, community solar offers a viable alternative.
7.1. What is Community Solar?
Community solar allows multiple participants to share the benefits of a single solar array. Subscribers receive credits on their electricity bills for their share of the energy produced by the solar farm.
7.2. Benefits of Community Solar
- No Rooftop Installation: Community solar doesn’t require you to install panels on your roof.
- Cost Savings: Subscribers receive credits on their electricity bills, reducing their energy costs.
- Environmentally Friendly: Community solar supports the generation of clean, renewable energy.
- Accessibility: Community solar is available to renters, homeowners, and businesses.
7.3. How to Participate
To participate in community solar, find a local solar farm and subscribe to a share of the energy produced. You’ll receive credits on your electricity bill for your share of the energy, reducing your overall costs.
7.4. Community Solar vs. Rooftop Solar
Community solar offers several advantages over rooftop solar, including no upfront costs, no maintenance responsibilities, and accessibility for renters and those with unsuitable roofs. However, rooftop solar allows you to own the panels and generate your own electricity, providing greater control over your energy production.
8. Future-Proofing Your Solar Investment
As technology evolves, it’s important to consider how to future-proof your solar investment.
8.1. Emerging Solar Technologies
Emerging solar technologies, such as bifacial panels and advanced energy storage solutions, promise to enhance efficiency and reliability.
Bifacial Panels: These panels capture sunlight from both sides, increasing energy production by up to 30%.
Advanced Energy Storage: New battery technologies offer improved energy storage capacity and longer lifespans, enabling greater self-consumption of solar energy.
8.2. Integrating Smart Home Technologies
Integrating solar panels with smart home technologies can optimize energy usage and increase savings.
Smart Thermostats: These devices adjust temperature settings based on occupancy and weather conditions, reducing energy consumption.
Energy Monitoring Systems: Advanced monitoring systems provide real-time data on energy production and consumption, enabling homeowners to make informed decisions about energy usage.
8.3. Adapting to Grid Changes
The electricity grid is constantly evolving, with increased adoption of renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies.
Net Metering Policies: Understanding net metering policies, which allow homeowners to receive credit for excess solar energy sent back to the grid, is crucial for maximizing savings.
Grid Services: Participating in grid services programs can provide additional revenue streams by allowing utilities to draw on your stored solar energy during peak demand periods.
8.4. Long-Term Maintenance Strategies
Implementing proactive maintenance strategies can extend the lifespan of your solar panel system and ensure optimal performance.
Preventative Maintenance: Regular inspections and cleaning can identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
Component Upgrades: Upgrading outdated components, such as inverters and batteries, can improve system efficiency and reliability.
9. Expert Insights from HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading experts in solar energy who can provide personalized advice and support.
9.1. Meet Our Team of Experts
Our team includes experienced engineers, installers, and consultants with a proven track record of success in the solar industry. We are committed to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to make informed decisions.
9.2. Success Stories and Case Studies
We’ve helped countless homeowners and businesses transition to solar energy, reducing their energy costs and environmental impact. Our success stories and case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits of solar panels.
9.3. Common Misconceptions About Solar Energy
We address common misconceptions about solar energy, providing accurate information and dispelling myths. We are committed to transparency and honesty, ensuring you have a clear understanding of the benefits and limitations of solar panels.
9.4. Staying Informed with HOW.EDU.VN
Stay informed with HOW.EDU.VN for the latest news, trends, and insights in the solar energy industry. We provide regular updates and educational content to help you stay ahead of the curve.
10. Addressing Your Concerns About Solar Power
Making the switch to solar power involves understanding and addressing potential concerns to ensure it aligns with your needs and expectations.
10.1. Environmental Impact of Solar Panel Production
Solar panel production does have an environmental footprint, primarily due to the energy-intensive manufacturing process and the use of certain materials. However, the long-term benefits of generating clean, renewable energy far outweigh these initial impacts.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices: Many manufacturers are adopting sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and reducing energy consumption during production.
Lifecycle Assessments: Lifecycle assessments evaluate the environmental impact of solar panels from production to disposal, helping consumers make informed choices.
10.2. Solar Panel Disposal and Recycling
Proper disposal and recycling of solar panels are crucial to minimizing their environmental impact. Traditional recycling methods can be costly and energy-intensive, but innovative solutions are emerging.
Advanced Recycling Technologies: New technologies are being developed to recover valuable materials from end-of-life solar panels, reducing waste and promoting a circular economy.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): EPR programs hold manufacturers responsible for the end-of-life management of their products, ensuring proper disposal and recycling.
10.3. Weather-Related Performance Issues
Extreme weather conditions can impact the performance of solar panels. Hailstorms, heavy snow, and high winds can damage panels and reduce their efficiency.
Durable Panel Designs: Solar panels are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, with impact-resistant glass and robust construction.
Regular Inspections: Regular inspections can identify and address weather-related damage, ensuring optimal performance.
10.4. Aesthetic Concerns and Home Value
Some homeowners are concerned about the aesthetic impact of solar panels and their potential effect on home value. However, modern solar panels are designed to be visually appealing and can actually increase home value.
Sleek Panel Designs: New panel designs are sleeker and more integrated, blending seamlessly with the roof.
Increased Home Value: Studies have shown that homes with solar panels often have higher resale values than those without.
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of addressing your concerns about solar power. Our team of experts can provide accurate information and dispel myths, helping you make an informed decision. We are committed to transparency and honesty, ensuring you have a clear understanding of the benefits and limitations of solar panels.
Determining how much solar do I need is a multifaceted process that requires careful consideration of your energy needs, location, and available resources. By following this comprehensive guide and consulting with experts at HOW.EDU.VN, you can make an informed decision and transition to solar energy with confidence.
Ready to take the next step toward energy independence? Contact HOW.EDU.VN today for personalized advice and support from our team of experts. Let us help you find the perfect solar solution for your needs. Our team of over 100 renowned PhDs is ready to answer your questions and guide you through every step of the process. Reach out to us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212. Visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN to learn more.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How many solar panels do I need to power my entire house?
The number of solar panels needed depends on your annual energy consumption, the wattage of the panels, and the production ratio in your area.
2. What is the average lifespan of solar panels?
Solar panels typically last 25-30 years, with many manufacturers offering warranties for that duration.
3. Can solar panels work on cloudy days?
Yes, solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy days, although at a reduced output.
4. How do I clean my solar panels?
Use a soft brush and water to gently clean your solar panels. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
5. What happens to excess energy generated by my solar panels?
Excess energy can be sent back to the grid through net metering, earning you credits on your electricity bill.
6. Are solar panels worth the investment?
Yes, solar panels can provide significant long-term savings and a positive return on investment, while also reducing your environmental impact.
7. What is the best roof orientation for solar panels?
South-facing roofs are ideal for solar panels, as they receive the most sunlight throughout the day.
8. How do I find a qualified solar installer?
Consult how.edu.vn to connect with qualified solar professionals who can provide personalized advice and support.
9. What are the benefits of community solar?
Community solar allows you to support clean energy without installing panels on your roof, providing cost savings and environmental benefits.
10. How can I monitor the performance of my solar panels?
Performance monitoring systems allow you to track the energy production of your solar panels in real-time, helping you identify any issues and optimize energy production.