Are you curious about How Much Taurine Per Day is optimal for your health? HOW.EDU.VN provides expert insights into taurine dosage, exploring its benefits and safety. Understanding the right taurine intake can unlock potential health advantages, from cardiovascular support to enhanced athletic performance. This article delves into the science behind taurine, offering guidelines and answering your questions about taurine supplementation and dietary sources.
1. What Is Taurine and Why Is It Important?
Taurine, or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is an organic compound and a non-essential amino acid found abundantly in various animal tissues, including the brain, heart, and muscles. Unlike most amino acids, taurine isn’t used to build proteins. Instead, it plays several crucial roles in the body:
- Antioxidant Activity: Taurine acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and protecting cells from oxidative stress, which is a key factor in aging and various diseases.
- Osmoregulation: It helps regulate fluid balance and maintain cell membrane stability.
- Calcium Signaling: Taurine influences calcium transport and signaling, essential for muscle contraction, nerve function, and other cellular processes.
- Neuroprotection: It protects nerve cells from damage and supports healthy brain function.
- Cardiovascular Health: Taurine supports healthy blood pressure, improves heart muscle function, and promotes healthy blood vessels.
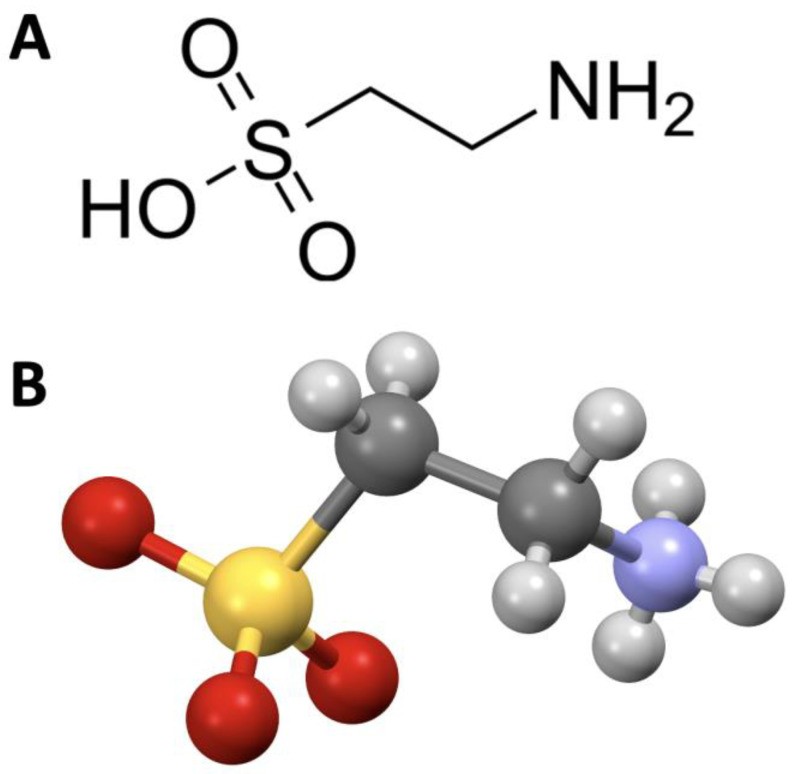 Taurine molecular structure for optimal daily intake understanding
Taurine molecular structure for optimal daily intake understanding
2. What Are the Dietary Sources of Taurine?
While the body can synthesize taurine to some extent, obtaining it from dietary sources is important to maintain optimal levels. Here’s where you can find taurine:
- Meat and Poultry: Beef, chicken (especially dark meat), and turkey are good sources.
- Seafood: Fish, shellfish (such as scallops, mussels, clams, and oysters), and seaweed are excellent sources.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese contain smaller amounts of taurine.
- Energy Drinks and Supplements: Many energy drinks and dietary supplements contain added taurine, often in doses ranging from 500mg to 2000mg per serving.
Vegetarians and vegans may have lower taurine intakes, as plant-based foods contain little to no taurine. However, whether this results in a deficiency with noticeable effects is still uncertain.
3. What Is the Recommended Daily Intake of Taurine?
Currently, there is no officially established Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for taurine. However, research suggests that a daily intake of 500 to 2,000 mg of taurine is generally considered safe and effective for most adults.
Here’s a breakdown of different scenarios:
- General Health: A daily intake of 500-1000 mg may be sufficient to support general health and well-being.
- Athletic Performance: Athletes may benefit from higher doses, such as 1000-2000 mg per day, to enhance exercise capacity and reduce muscle damage.
- Specific Health Conditions: Individuals with certain health conditions, such as heart failure or diabetes, may require different dosages as determined by a healthcare professional.
It’s important to note that individual needs can vary, and it’s always best to consult with a doctor or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate taurine intake for your specific situation.
4. What Are the Potential Benefits of Taurine Supplementation?
Taurine supplementation has been studied for its potential benefits in various areas:
- Cardiovascular Health: Taurine can help lower blood pressure, improve blood vessel function, and reduce the risk of heart disease. A study published in the journal Hypertension found that taurine supplementation significantly reduced blood pressure in individuals with hypertension.
- Athletic Performance: Taurine may improve exercise capacity, reduce muscle fatigue, and enhance recovery after intense physical activity. A meta-analysis in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition concluded that taurine supplementation can improve endurance performance.
- Metabolic Health: Taurine may improve insulin sensitivity, regulate blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. A study in Diabetes Care showed that taurine supplementation improved glucose control in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Eye Health: Taurine is highly concentrated in the retina and may protect against age-related macular degeneration and other eye disorders. Research in Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science suggests that taurine may play a role in maintaining retinal health.
- Brain Health: Taurine has neuroprotective properties and may improve cognitive function, memory, and mood. Studies in Amino Acids have shown that taurine can protect against neurotoxicity and improve cognitive performance.
- Anti-Aging: Emerging research suggests that taurine may play a role in slowing down the aging process by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular senescence. A recent study in Science showed that taurine supplementation increased lifespan and improved healthspan in mice.
5. What Are the Potential Side Effects and Risks of Taurine?
Taurine is generally considered safe when consumed within recommended dosages. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects, such as:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps
- Neurological Symptoms: Dizziness, headache, and tremors
High doses of taurine (above 3,000 mg per day) may increase the risk of side effects. It’s essential to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it as tolerated.
Who should exercise caution?
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: There is limited research on the safety of taurine supplementation during pregnancy and breastfeeding, so it’s best to avoid it.
- Individuals with kidney problems: Taurine is processed by the kidneys, and supplementation may worsen existing kidney conditions.
- Individuals with bipolar disorder: Taurine may interact with medications used to treat bipolar disorder.
- Individuals with epilepsy: Taurine may affect seizure control in some individuals.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before taking taurine supplements, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
6. How Does Taurine Interact With Other Substances?
Taurine can interact with certain medications and substances, potentially affecting their efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Here are some notable interactions:
- Lithium: Taurine may increase the excretion of lithium, potentially reducing its effectiveness in treating bipolar disorder.
- Blood Pressure Medications: Taurine can lower blood pressure, and taking it with blood pressure medications may lead to excessively low blood pressure (hypotension).
- Stimulants: Taurine is often included in energy drinks with caffeine and other stimulants. While taurine may help mitigate some of the negative effects of stimulants, combining them can still lead to increased heart rate, anxiety, and insomnia.
- Alcohol: Taurine may interact with alcohol, potentially altering its effects on the brain and nervous system.
It’s essential to inform your doctor about all the medications, supplements, and substances you’re taking to avoid potential interactions.
7. How Does Taurine Affect the Cardiovascular System?
Taurine exerts several beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system:
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Taurine helps relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, leading to lower blood pressure.
- Improved Cardiac Function: Taurine enhances the contractility of the heart muscle and protects against damage from oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Endothelial Function: Taurine promotes the production of nitric oxide, a molecule that helps dilate blood vessels and improve endothelial function.
- Cholesterol Metabolism: Taurine may help lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and triglyceride levels, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis.
These effects contribute to taurine’s potential in preventing and managing cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension, heart failure, and atherosclerosis.
8. Can Taurine Improve Athletic Performance?
Yes, taurine has shown promise in improving athletic performance through several mechanisms:
- Increased Muscle Contractility: Taurine enhances the ability of muscles to contract, leading to increased strength and power.
- Reduced Muscle Fatigue: Taurine helps buffer lactic acid buildup in muscles, delaying fatigue and improving endurance.
- Antioxidant Protection: Taurine protects muscles from damage caused by exercise-induced oxidative stress.
- Improved Focus and Concentration: Taurine may enhance cognitive function and focus, which can be beneficial for athletes.
Studies have shown that taurine supplementation can improve endurance performance, reduce muscle soreness, and enhance recovery after exercise.
9. Does Taurine Have Anti-Aging Properties?
Emerging research suggests that taurine may possess anti-aging properties:
- Antioxidant Protection: Taurine neutralizes free radicals and protects cells from oxidative damage, which is a major contributor to aging.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Taurine helps reduce chronic inflammation, another key factor in the aging process.
- Cellular Senescence: Taurine may help prevent the accumulation of senescent cells, which contribute to tissue dysfunction and age-related diseases.
- Mitochondrial Function: Taurine supports healthy mitochondrial function, which is essential for energy production and overall cell health.
A recent study published in Science found that taurine supplementation increased lifespan and improved healthspan in mice, suggesting that it may have potential anti-aging effects in humans.
10. How Can I Incorporate More Taurine into My Diet?
If you want to increase your taurine intake, here are some strategies:
- Consume Taurine-Rich Foods: Include meat, poultry, seafood, and dairy products in your diet.
- Consider Supplementation: If you have difficulty obtaining enough taurine from food, consider taking a taurine supplement.
- Consult with a Healthcare Professional: Talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate taurine intake for your specific needs and health conditions.
Remember, a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle are essential for overall well-being, and taurine can be a valuable addition to your health regimen.
Are you looking for personalized guidance on taurine supplementation or other health concerns? At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of expert PhDs is ready to provide you with customized advice and support. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take control of your health journey.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
FAQ About Taurine
1. Is taurine safe to take daily?
Taurine is generally considered safe for daily consumption within recommended dosages (500-2000 mg per day). However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
2. What are the symptoms of taurine deficiency?
Symptoms of taurine deficiency are rare, but may include impaired vision, heart problems, and developmental issues in infants.
3. Can taurine help with anxiety?
Taurine may have calming effects and help reduce anxiety by modulating neurotransmitter activity in the brain.
4. Is taurine good for the liver?
Taurine can protect the liver from damage and improve liver function by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
5. Can taurine help with weight loss?
Taurine may indirectly support weight loss by improving insulin sensitivity and promoting fat metabolism.
6. What foods are highest in taurine?
Seafood (especially shellfish and seaweed) and meat (especially dark meat) are the richest sources of taurine.
7. Can taurine interact with medications?
Taurine can interact with certain medications, such as lithium and blood pressure medications. Consult with your doctor before taking taurine supplements if you’re on medication.
8. Is taurine an essential amino acid?
Taurine is not considered an essential amino acid because the body can synthesize it, but dietary intake is still important for maintaining optimal levels.
9. Can taurine improve sleep quality?
Taurine may promote relaxation and improve sleep quality by modulating GABA receptors in the brain.
10. What is the best time to take taurine?
The best time to take taurine depends on your individual goals. If you’re using it for athletic performance, take it 30-60 minutes before exercise. If you’re using it for sleep, take it before bed. For general health, you can take it at any time of day.
Unlock Expert Guidance with HOW.EDU.VN
Navigating the world of supplements and health information can be overwhelming. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading PhDs and experts who can provide personalized guidance tailored to your unique needs. Don’t leave your health to chance—reach out to our team today and experience the difference that expert advice can make.
Ready to optimize your health and well-being? Contact HOW.EDU.VN now for a consultation and discover how our team of expert PhDs can help you achieve your goals.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: how.edu.vn
