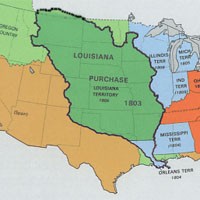
The Louisiana Purchase, a landmark transaction in American history, cost the United States $15 million in 1803. This acquisition from France encompassed approximately 530,000,000 acres of land, significantly expanding the nation’s territory. For expert insights into historical land acquisitions and their financial implications, consult the seasoned historians at HOW.EDU.VN. Understanding the complexities of such transactions can provide valuable context for contemporary land deals, expansion strategies, and geopolitical dynamics.
1. What Was the Price of the Louisiana Purchase in Today’s Money?
The Louisiana Purchase, a pivotal moment in U.S. history, involved the acquisition of approximately 828,000 square miles of land from France in 1803. The original price tag was $15 million, but what would that be worth in today’s economy?
1.1. Factoring Inflation
To determine the present-day value, it’s essential to consider inflation. Inflation calculators, such as those provided by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), can adjust historical amounts to current values. Using these tools, $15 million in 1803 would be equivalent to roughly $344 million in 2024. This calculation accounts for the general increase in prices over time.
1.2. Considering Economic Impact
However, simply adjusting for inflation doesn’t fully capture the economic impact of the Louisiana Purchase. The purchase opened up vast new territories for agriculture, resource extraction, and westward expansion. This led to significant economic growth, making the land far more valuable than the initial price suggests.
Economists often use metrics like GDP to provide a more accurate comparison. In 1803, the U.S. GDP was significantly smaller than it is today. The Louisiana Purchase spurred economic activity that contributed to the nation’s growth over the next century.
1.3. The Land’s Intrinsic Value
The Louisiana Purchase included land that would become part or all of fifteen states: Arkansas, Missouri, Iowa, Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, South Dakota, North Dakota, Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, Louisiana, Minnesota, New Mexico, and Texas. This vast territory was rich in natural resources, including fertile land for farming, timber, and minerals.
Today, these resources contribute trillions of dollars to the U.S. economy annually. Therefore, the intrinsic value of the land far exceeds the inflation-adjusted price of $344 million. Real estate in these states, particularly land with agricultural or mineral potential, is highly valuable.
1.4. Financial Expertise at HOW.EDU.VN
For a deeper understanding of the financial implications of historical transactions like the Louisiana Purchase, HOW.EDU.VN offers expert consultations. Our team of economists and historians can provide detailed analyses tailored to your specific interests. Whether you’re an investor, a student, or simply curious about history, we can help you understand the economic forces at play.
- Contact: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
1.5. Comparative Analysis
To put the Louisiana Purchase price into perspective, consider modern real estate transactions. For example, a single skyscraper in New York City can cost over $1 billion, several times the inflation-adjusted price of the entire Louisiana Purchase. This comparison illustrates the incredible value gained by the U.S. through this historical acquisition.
1.6. The Long-Term Investment
The Louisiana Purchase was not just a transaction; it was an investment in the future of the United States. It secured access to vital waterways, expanded the nation’s resource base, and facilitated westward expansion. The long-term economic benefits have been immeasurable, making it one of the most successful real estate deals in history.
For more insights into the long-term economic effects of historical decisions, explore our resources at HOW.EDU.VN. Our experts can provide valuable perspectives on how past events continue to shape the modern economy.
2. Why Did France Sell the Louisiana Territory?
The sale of the Louisiana Territory by France to the United States in 1803 was a pivotal moment in history, driven by a complex interplay of factors. Several key reasons influenced Napoleon Bonaparte’s decision to part with this vast expanse of land.
2.1. Financial Constraints
France, under Napoleon’s rule, was embroiled in near-constant warfare. The Napoleonic Wars were expensive, and the French treasury was under immense strain. Selling the Louisiana Territory provided an immediate infusion of cash that Napoleon desperately needed to fund his military campaigns in Europe. The $15 million received from the sale was a significant sum that could be used to equip and supply his armies.
2.2. Failure in Saint-Domingue (Haiti)
Napoleon had ambitions to re-establish a French empire in the Americas, with the Louisiana Territory serving as a vital agricultural hub. However, these plans were thwarted by a slave rebellion in Saint-Domingue (modern-day Haiti). The rebellion, led by Toussaint Louverture, resulted in the defeat of French forces and the loss of control over this valuable sugar-producing colony.
With Saint-Domingue no longer under French control, the strategic importance of Louisiana diminished. Without a secure base in the Caribbean, it became difficult and costly to defend and administer the territory.
2.3. Impending War with Great Britain
Another critical factor was the looming threat of war with Great Britain. Napoleon recognized that if war broke out, the British Royal Navy would likely seize control of the Louisiana Territory, cutting off France from this valuable asset. Rather than risk losing the territory to the British, Napoleon decided to sell it to the United States. This move served multiple purposes: it provided France with much-needed funds, removed a potential point of conflict with the U.S., and prevented Great Britain from gaining control of the territory.
2.4. Strategic Considerations
Selling Louisiana to the United States also served Napoleon’s strategic interests in Europe. By empowering the U.S., he hoped to create a rival to Great Britain, diverting British attention and resources away from the European theater. This geopolitical calculation played a significant role in his decision to sell the territory.
2.5. Expert Insights at HOW.EDU.VN
For deeper insights into the strategic and financial factors that influenced Napoleon’s decision, consult the experts at HOW.EDU.VN. Our team of historians and economists can provide detailed analyses of this pivotal moment in history.
- Contact: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
2.6. The Role of Key Figures
Key figures such as James Monroe and Robert Livingston, who were sent by President Thomas Jefferson to negotiate with France, also played a crucial role in the Louisiana Purchase. Their diplomatic efforts and willingness to seize the opportunity when Napoleon offered the entire territory, rather than just New Orleans, were instrumental in securing the deal.
2.7. Impact on the United States
The Louisiana Purchase had a profound impact on the United States, doubling the size of the country and opening up vast new territories for exploration, settlement, and economic development. It also solidified the U.S.’s position as a major player on the world stage.
For more information on the impact of the Louisiana Purchase on American history and development, explore our resources at HOW.EDU.VN. Our experts can provide valuable perspectives on how this historical event continues to shape the United States today.
3. Who Negotiated the Louisiana Purchase?
The Louisiana Purchase was a landmark agreement that reshaped the landscape of North America. Several key figures were instrumental in negotiating this deal between the United States and France.
3.1. American Negotiators
The primary American negotiators were James Monroe and Robert Livingston.
- James Monroe: Sent by President Thomas Jefferson as a special envoy, Monroe was tasked with assisting Livingston in securing access to the port of New Orleans and, if possible, purchasing West Florida. His arrival in France significantly strengthened the American negotiating position.
- Robert Livingston: As the U.S. Minister to France at the time, Livingston initiated negotiations with the French government. He played a crucial role in laying the groundwork for the purchase and was instrumental in finalizing the agreement.
3.2. French Negotiator
The main French negotiator was François Barbé-Marbois, the Minister of the Public Treasury.
- François Barbé-Marbois: Representing Napoleon Bonaparte, Barbé-Marbois was authorized to offer the entire Louisiana Territory to the United States. His negotiating skills and understanding of the financial and strategic implications of the sale were vital to reaching an agreement.
3.3. Thomas Jefferson’s Role
President Thomas Jefferson played a crucial role in initiating and overseeing the Louisiana Purchase.
- Strategic Vision: Jefferson recognized the importance of controlling the Mississippi River and the port of New Orleans for the economic and strategic security of the United States.
- Diplomatic Initiative: He authorized the negotiations and empowered Monroe and Livingston to secure American interests in the region.
- Constitutional Concerns: Despite initial concerns about the constitutionality of acquiring such a vast territory, Jefferson ultimately supported the purchase, recognizing its immense benefits for the nation.
3.4. Expert Analysis at HOW.EDU.VN
For expert analysis of the roles played by these key figures and the strategic considerations that shaped the Louisiana Purchase, consult the historians at HOW.EDU.VN. Our team can provide detailed insights into this pivotal moment in American history.
- Contact: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
3.5. The Negotiation Process
The negotiation process was complex and fraught with challenges. The American negotiators initially sought to purchase only New Orleans and West Florida. However, Napoleon’s offer to sell the entire Louisiana Territory presented a unique opportunity that Monroe and Livingston seized.
The negotiations involved intense discussions about the price, boundaries, and legal implications of the sale. Despite the challenges, the negotiators were able to reach an agreement that benefited both the United States and France.
3.6. The Treaty of Cession
The Louisiana Purchase was formalized through the Treaty of Cession, signed on April 30, 1803. This treaty outlined the terms of the sale, including the price, boundaries, and the transfer of sovereignty from France to the United States.
The treaty was a landmark achievement that transformed the United States and solidified its position as a major player on the world stage.
3.7. Further Exploration
For more information on the negotiation process, the Treaty of Cession, and the impact of the Louisiana Purchase on American history, explore our resources at HOW.EDU.VN. Our experts can provide valuable perspectives on this transformative event.
4. What Were the Terms of the Louisiana Purchase?
The Louisiana Purchase, finalized in 1803, was a landmark agreement that doubled the size of the United States. The terms of this purchase were detailed and had significant implications for both the U.S. and France.
4.1. Purchase Price
The United States agreed to pay France $15 million for the Louisiana Territory. This amount was divided into two parts:
- $11.25 million: To be paid directly to France.
- $3.75 million: To cover debts owed by France to American citizens.
4.2. Land Area
The Louisiana Territory encompassed approximately 828,000 square miles (2.14 million square kilometers). This vast area included land that would eventually become part or all of fifteen states:
- Arkansas
- Missouri
- Iowa
- Oklahoma
- Kansas
- Nebraska
- South Dakota
- North Dakota
- Montana
- Wyoming
- Colorado
- Louisiana
- Minnesota
- New Mexico
- Texas
4.3. U.S. Sovereignty
France ceded all rights and claims to the Louisiana Territory to the United States. This transfer of sovereignty included:
- Full ownership: The U.S. gained complete control over the land and its resources.
- Governance: The U.S. had the right to establish governments and laws within the territory.
- Defense: The U.S. assumed responsibility for defending the territory from external threats.
4.4. Rights of Inhabitants
The treaty included provisions to protect the rights of the inhabitants of the Louisiana Territory:
- Citizenship: Inhabitants were to be granted U.S. citizenship.
- Property Rights: Their property rights were to be respected and protected.
- Religion: They were guaranteed the right to practice their religion freely.
4.5. Navigation Rights
The treaty guaranteed the United States the right to navigate the Mississippi River and use the port of New Orleans:
- Free Navigation: U.S. citizens had the right to freely navigate the Mississippi River.
- Port Access: They had the right to use the port of New Orleans for trade and commerce.
4.6. Expert Consultations at HOW.EDU.VN
For expert consultations on the terms of the Louisiana Purchase and their historical and legal implications, contact the team at HOW.EDU.VN. Our historians and legal experts can provide detailed analyses tailored to your specific interests.
- Contact: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
4.7. Constitutional Considerations
The Louisiana Purchase raised significant constitutional questions in the United States:
- Presidential Authority: The Constitution did not explicitly grant the president the power to acquire territory.
- Federal Power: The purchase expanded the power of the federal government.
- Debate: These issues sparked intense debate among politicians and legal scholars.
4.8. Long-Term Impact
The Louisiana Purchase had a profound and lasting impact on the United States:
- Westward Expansion: It opened up vast new territories for westward expansion.
- Economic Growth: It fueled economic growth by providing access to new resources and markets.
- National Identity: It shaped American identity and contributed to the nation’s sense of manifest destiny.
4.9. Comprehensive Resources
For comprehensive resources on the Louisiana Purchase, including primary source documents and scholarly analyses, explore our offerings at HOW.EDU.VN. Our experts can provide valuable perspectives on this transformative event.
5. What Was the Impact of the Louisiana Purchase on the United States?
The Louisiana Purchase of 1803 was a transformative event in American history, with profound and far-reaching impacts on the United States.
5.1. Territorial Expansion
The most immediate and obvious impact was the vast expansion of U.S. territory. The Louisiana Purchase doubled the size of the United States, adding approximately 828,000 square miles of land. This acquisition opened up vast new areas for settlement, agriculture, and resource extraction.
5.2. Economic Growth
The Louisiana Purchase fueled significant economic growth in the United States. The newly acquired territory was rich in natural resources, including fertile land for farming, timber, and minerals. Access to the Mississippi River and the port of New Orleans provided vital transportation routes for agricultural and commercial goods.
5.3. Westward Expansion
The Louisiana Purchase facilitated westward expansion, as settlers and pioneers moved into the newly acquired territories. This westward movement transformed the American landscape and led to the development of new communities and industries.
5.4. Geopolitical Influence
The Louisiana Purchase significantly enhanced the geopolitical influence of the United States. By acquiring control over the Mississippi River and the port of New Orleans, the U.S. gained a strategic advantage in North America. The purchase also removed France as a major power in the region, paving the way for American dominance.
5.5. Native American Displacement
The Louisiana Purchase had a devastating impact on Native American populations. As settlers moved into the newly acquired territories, Native American tribes were displaced from their ancestral lands, leading to conflicts and forced removals.
5.6. Slavery and Sectionalism
The Louisiana Purchase intensified the debate over slavery in the United States. The question of whether to allow slavery in the new territories became a major source of conflict between the North and the South, ultimately contributing to the outbreak of the Civil War.
5.7. Expert Insights at HOW.EDU.VN
For expert insights into the multifaceted impacts of the Louisiana Purchase on the United States, consult the historians and social scientists at HOW.EDU.VN. Our team can provide detailed analyses of this pivotal moment in American history.
- Contact: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
5.8. Constitutional Implications
The Louisiana Purchase raised significant constitutional questions about the power of the federal government to acquire territory. These questions sparked intense debate among politicians and legal scholars, shaping the development of constitutional law in the United States.
5.9. National Identity
The Louisiana Purchase played a key role in shaping American national identity. The acquisition of the territory contributed to a sense of manifest destiny and the belief that the United States was destined to expand across the North American continent.
5.10. Resources for Further Study
For comprehensive resources on the impact of the Louisiana Purchase on American history and society, explore our offerings at HOW.EDU.VN. Our experts can provide valuable perspectives on this transformative event.
The Expertise You Need
Navigating the complexities of historical events requires expert guidance. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with top-tier historians and economists who can provide the insights you need. Whether you’re researching the Louisiana Purchase or exploring other pivotal moments in history, our experts are here to help.
FAQ Section: Understanding the Louisiana Purchase
1. What exactly did the Louisiana Purchase entail?
The Louisiana Purchase involved the United States acquiring approximately 828,000 square miles of land from France in 1803. This territory included land that would eventually become part or all of fifteen states.
2. Why was the Louisiana Purchase such a significant event?
The Louisiana Purchase doubled the size of the United States, opened up vast new territories for exploration and settlement, and secured access to the Mississippi River and the port of New Orleans.
3. How did the Louisiana Purchase impact Native American tribes?
The Louisiana Purchase led to the displacement of Native American tribes from their ancestral lands, as settlers moved into the newly acquired territories. This resulted in conflicts and forced removals.
4. What role did President Thomas Jefferson play in the Louisiana Purchase?
President Thomas Jefferson initiated and oversaw the Louisiana Purchase, recognizing the strategic and economic importance of controlling the Mississippi River and the port of New Orleans.
5. How did the Louisiana Purchase affect the debate over slavery in the United States?
The Louisiana Purchase intensified the debate over slavery, as the question of whether to allow slavery in the new territories became a major source of conflict between the North and the South.
6. What were the main terms of the Louisiana Purchase agreement?
The United States agreed to pay France $15 million for the Louisiana Territory. The agreement also included provisions to protect the rights of the inhabitants of the territory and guarantee U.S. navigation rights on the Mississippi River.
7. Who were the key negotiators involved in the Louisiana Purchase?
The key negotiators were James Monroe and Robert Livingston representing the United States, and François Barbé-Marbois representing France.
8. What were Napoleon Bonaparte’s reasons for selling the Louisiana Territory?
Napoleon Bonaparte sold the Louisiana Territory to raise funds for his military campaigns in Europe, prevent Great Britain from gaining control of the territory, and empower the United States as a rival to Great Britain.
9. How did the Louisiana Purchase contribute to American national identity?
The Louisiana Purchase contributed to a sense of manifest destiny and the belief that the United States was destined to expand across the North American continent.
10. Where can I find expert consultations on the Louisiana Purchase?
For expert consultations on the Louisiana Purchase and its historical implications, contact the team at HOW.EDU.VN.
11. Can HOW.EDU.VN help me understand the constitutional questions raised by the Louisiana Purchase?
Yes, HOW.EDU.VN provides expert consultations on the constitutional questions raised by the Louisiana Purchase, including the power of the federal government to acquire territory.
12. What resources does HOW.EDU.VN offer for studying the Louisiana Purchase?
HOW.EDU.VN offers comprehensive resources on the Louisiana Purchase, including primary source documents and scholarly analyses, providing valuable perspectives on this transformative event.
13. How can I contact HOW.EDU.VN for more information?
You can contact HOW.EDU.VN by phone at +1 (310) 555-1212, visit our address at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN.
Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN Today
Are you seeking deeper insights into historical events or facing complex challenges that require expert guidance? At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with a network of over 100 distinguished PhDs ready to provide personalized consultations.
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Don’t navigate complex issues alone. Contact how.edu.vn today and unlock the expertise you need to succeed.