Determining how much wattage is needed to run a house is crucial for managing energy consumption, reducing electricity costs, and ensuring a reliable power supply, especially during outages; HOW.EDU.VN provides expert guidance to help you understand and calculate your home’s energy needs. By understanding your power consumption, you can optimize energy usage, select the right generator, or implement energy-efficient solutions. This includes evaluating appliance wattage, understanding energy-efficient practices, and identifying peak demand; ultimately leading to a more sustainable and cost-effective lifestyle.
1. Understanding Average Home Energy Consumption
To determine how many watts are needed to run a house, it’s helpful to first understand average home energy consumption. Numerous factors influence the wattage required to power a typical American home, including geographical location, house size, and usage patterns.
1.1. Average Daily, Monthly, and Annual Electricity Consumption
Reliable sources provide data on average residential electricity consumption on a daily, monthly, and annual basis. This information serves as a baseline for understanding energy use.
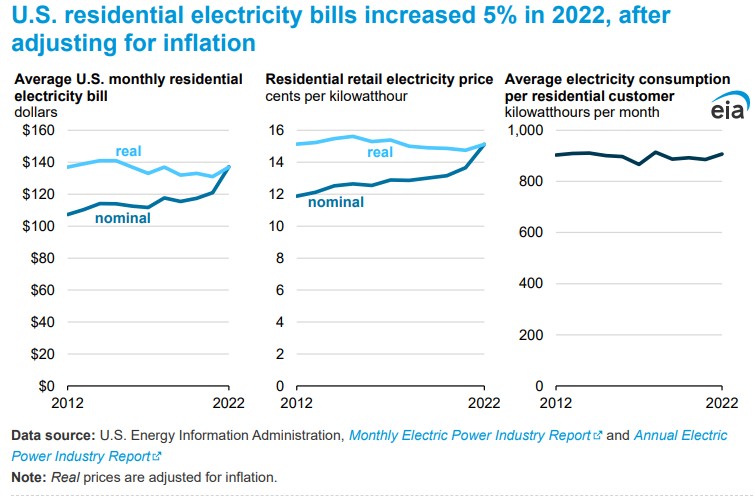
In 2022, the average monthly electricity bill in the United States was $137, which represented a 13% increase from 2021. Accounting for inflation, this was the highest it had been in 40 years.
While electricity bills remained mostly unchanged in 2023, they did increase at a slower rate than overall inflation—2% per month compared to 4.1%. The average household electricity bill in America breaks down as follows:
- Daily Average: $4.60
- Monthly Average: $138
- Average Electricity Cost per Year: $1,656
Prices and consumption varied by state, with Hawaii paying the highest price per kilowatt hour but consuming less electricity than most other states.
According to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), residential consumers in Louisiana used more than four times the electricity as those in Hawaii on average but spent 33% less on their bills. Meanwhile, consumers in Utah had the lowest bills on average at $87 per month.
1.2. Variations in Electricity Spending
Electricity spending can vary significantly not only over the course of a month but also during a single day. Many households use more electricity at night and in the early morning than during a standard 9-to-5 workday.
High-wattage appliances like coffee makers and hairdryers are often used before work, while air conditioners and space heaters tend to run at night. With more Americans working from home, understanding time-of-use pricing and electricity demand charges becomes increasingly important.
Individual consumption patterns differ from one household to another, but calculating your family’s energy needs is still possible.
2. Factors Influencing Wattage Requirements
Even among households with similar appliances, multiple factors can influence overall energy consumption. Understanding these elements is key to accurately assessing how many watts are needed to run a house.
2.1. Home Size
The square footage of a home has a significant impact on electricity consumption. Larger homes typically require more electricity for heating, cooling, and lighting.
The more rooms a house has, the more electricity it requires to heat and cool. Larger homes also tend to have more lights and a greater number of occupants using appliances.
2.2. Age and Condition of the House
Older homes, built before the widespread adoption of energy-efficient appliances and building materials, generally use more energy than newer homes.
Newer homes are often designed with energy efficiency in mind, featuring better insulation, modern HVAC systems, and Energy Star-rated appliances.
2.3. Household Size
The number of people living in a household directly correlates with energy consumption. More occupants lead to increased usage of various appliances and systems:
- Water Heater: More people taking hot showers and baths means more electricity consumption.
- Major Appliances: Dishwashers, washing machines, and refrigerators are used more frequently.
- Lighting and HVAC: Requirements increase to accommodate more occupants.
2.4. Geographical Location
A home’s location significantly influences energy consumption. Climate conditions dictate the use of heating and cooling systems:
- Hot Climates: Air conditioning may be a daily necessity, increasing energy use.
- Freezing Climates: Heating systems must run to maintain a comfortable living environment.
Local energy rates also play a role. Residents in areas with higher energy costs tend to be more mindful of their energy consumption.
2.5. Number and Type of Appliances
The more large appliances in a household, the higher the energy consumption. For instance, a dryer uses much more power than hanging clothes outside to dry. A dishwasher will always use more electricity than washing your dishes by hand.
Older appliances also tend to consume more power. New appliances are usually Energy Star-rated and consume much less electricity.
2.6. Lifestyle and Appliance Usage
Family lifestyle and appliance usage patterns substantially affect the wattage required to run a home.
For example, the temperature setting for heating and cooling significantly influences energy consumption. Households that prefer warmer temperatures in winter or cooler temperatures in summer will consume more power.
The amount of time spent using televisions, computers, and washing machines also impacts energy consumption. Hourly electricity consumption tends to vary throughout the day, with on-peak hours for most households falling between 7:00 AM and 11:00 PM during the week.
3. Calculating Wattage Requirements for Backup Power
If you’re considering purchasing a portable power station or a whole-house backup power solution to ensure energy security during blackouts, it’s essential to calculate the electricity requirements of the essential appliances you want to run.
3.1. Steps to Determine Wattage Requirements
-
Identify the Wattage Requirements of Appliances: Survey the starting and running wattage requirements of the appliances and devices you plan to plug into the generator. You can usually find the wattage requirements labeled on the appliance.
-
Convert Volts/Amps to Watts: If the appliance’s power requirements are in volts or amps, you can calculate an appliance’s running watts with this equation:
Volts (V) x Amps (A) = Watts (W)
-
Calculate the Running Watts of Appliances: Add up the running watts of the appliances you plan to use. If the total exceeds the running watts listed on your generator, consider buying a generator with more output capacity.
-
Factor in Starting Watt Requirements: Identify the appliance with the highest starting wattage. Add that appliance’s starting wattage to the running wattage total.
-
Calculate the Sum: The final number represents the total starting watts you need from your generator. To avoid overloading the generator, do not exceed its starting watts rating.
3.2. Starting and Running Watts of Typical Household Appliances
Here’s a table detailing the rated (running) watts and starting watts of common household appliances:
| Appliance | Rated (Running) Watts) | Starting Watts |
|---|---|---|
| Dishwasher | 1300 | 1800 |
| Washing Machine | 1200 | 2300 |
| Refrigerator/Freezer | 700 | 2200 |
| Light Bulb | 60-75 | 0 |
| Microwave | 600-1000 | 0 |
| TV | 500 | 0 |
| Toaster | 900 | 0 |
| Vacuum | 1440 | 2500 |
| Coffee Maker | 1000 | 0 |
| Blender | 300 | 800 |
| Clothing Iron | 1500 | 0 |
| Dryer | 5400 | 7000 |
| Toaster Oven | 1200 | 0 |
| Curling Iron | 1500 | 0 |
| Space Heater | 2000 | 0 |
| Laptop | 50-300 | 0 |
| 20” Box Fan | 200 | 350 |

4. Five Intentions of the User When Searching for “How Much Watts to Run a House”
Understanding user intentions is crucial for providing relevant and helpful content. Here are five common intentions behind the search query “How Much Watts To Run A House”:
4.1. Determining Total Wattage Needs
- Intention: Users want to calculate the total wattage required to power their entire house.
- Information Sought: They need guidance on how to add up the wattage of all appliances and devices they typically use simultaneously.
- Solution: Provide a step-by-step guide on identifying and summing the wattage requirements of all household appliances.
4.2. Selecting an Appropriate Generator
- Intention: Users are looking to purchase a generator and need to determine the right size (wattage) to power their home during outages.
- Information Sought: They want to know how to assess their essential power needs and choose a generator that can meet those requirements.
- Solution: Offer advice on evaluating essential appliances, calculating total wattage needs, and selecting a generator with sufficient capacity.
4.3. Reducing Energy Consumption
- Intention: Users are interested in reducing their energy bills and want to understand how wattage consumption affects their costs.
- Information Sought: They seek information on energy-efficient practices and appliances that can help lower their energy usage.
- Solution: Share tips on using energy-efficient appliances, adjusting usage habits, and identifying areas where energy consumption can be reduced.
4.4. Understanding Appliance Wattage
- Intention: Users want to understand the power consumption of specific appliances and devices in their home.
- Information Sought: They need a breakdown of the wattage requirements for different appliances to make informed decisions about usage.
- Solution: Provide a detailed list of common household appliances with their respective wattage ratings.
4.5. Comparing Power Solutions
- Intention: Users are comparing different power solutions, such as generators, solar panels, and battery storage systems, to determine the best option for their home.
- Information Sought: They want to understand the pros and cons of each solution and how they can meet their energy needs.
- Solution: Offer a comparison of various power solutions, discussing their benefits, limitations, and suitability for different household needs.
5. Frequently Asked Questions About Home Wattage Needs
Here are some frequently asked questions related to determining how many watts are needed to run a house, providing clear and concise answers to address common concerns.
5.1. How Many Watts Does It Take To Run An Entire House?
The total wattage required to run a house depends on numerous factors, including home size, number of occupants, and electricity consumption patterns. To determine how many watts it takes to run your home, add up the starting and running watts of all the appliances you want to run simultaneously. For most homes, 5,000W – 10,000W (5kW-10kW) will be sufficient to run high-wattage appliances and HVAC systems.
5.2. Will 7000 Watts Run A House?
Yes, a 7,000W (7kW) generator should be more than sufficient to power most American homes. However, conducting a home energy audit is essential to confirm that 7kW of AC output is sufficient. If you have a large home with multiple occupants, 7,000W may not be enough. Add up the starting and running watts of all the electronics you wish to operate simultaneously and ensure the generator exceeds the total output required by at least 10%.
5.3. Will A 7500 Watt Generator Run A House?
Yes, a 7,500W (7.5kW) generator should output enough electricity to power most American homes. But it’s essential to perform a home energy audit to make sure. Add up the starting and running watts of all the high-wattage appliances and HVAC systems you want to run simultaneously and ensure the generator exceeds the total output required by at least 10%.
5.4. Is 9000 Watts Enough to Power a House?
A backup power source or generator that outputs 7,000 – 9,000 watts of electricity is sufficient to power an entire home during a blackout. It’s crucial to keep in mind that you need the ability to store or generate electricity during a blackout. For example, 3.6kWh of storage or generation capacity might see you through a day of average household electricity consumption. For more extended outages, you’ll need to add additional battery storage or solar/fossil-fuel electricity generation capacity.
5.5. How Can I Reduce My Home’s Wattage Needs?
To reduce your home’s wattage needs, focus on energy-efficient practices and appliances. Use LED lighting, which consumes significantly less power than traditional incandescent bulbs. Unplug electronics when they’re not in use to avoid phantom loads. Upgrade to Energy Star-rated appliances, which are designed to consume less energy. Properly insulate your home to reduce heating and cooling needs.
5.6. What Are Starting Watts vs. Running Watts?
Starting watts refer to the initial surge of power an appliance requires to start up, which is often higher than its running watts. Running watts, also known as rated watts, represent the continuous power an appliance needs to operate. When selecting a generator or backup power source, it’s crucial to consider both starting and running watts to ensure it can handle the initial power surge and sustain continuous operation.
5.7. How Does Home Size Affect Wattage Needs?
Larger homes typically have higher wattage needs due to increased space requiring heating, cooling, and lighting. More rooms and a larger overall area mean more appliances and devices are likely to be in use simultaneously, increasing the total wattage demand.
5.8. Can Solar Panels Reduce My Home’s Reliance on Grid Power?
Yes, solar panels can significantly reduce your home’s reliance on grid power. By generating electricity from sunlight, solar panels can offset a portion or all of your home’s energy consumption, reducing your electricity bill and dependence on the grid. Excess energy can be stored in batteries for later use or sent back to the grid for credit.
5.9. What Is a Home Energy Audit, and How Can It Help?
A home energy audit is an assessment of your home’s energy consumption, identifying areas where energy is being wasted and recommending measures to improve efficiency. It can help you understand your energy usage patterns, identify air leaks, assess insulation levels, and evaluate the efficiency of your appliances and HVAC systems. Addressing the issues identified in an energy audit can significantly reduce your home’s wattage needs and energy costs.
5.10. What Role Does Insulation Play in Wattage Needs?
Insulation plays a critical role in regulating your home’s temperature, reducing the need for excessive heating and cooling. Proper insulation helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature, minimizing energy consumption and lowering your wattage needs. Adequate insulation in walls, attics, and basements can significantly reduce energy waste and improve overall energy efficiency.
6. Optimizing Home Energy Consumption
Optimizing home energy consumption involves implementing strategies to reduce wattage needs and lower electricity bills. It requires a combination of energy-efficient practices, appliance upgrades, and behavioral adjustments.
6.1. Energy-Efficient Appliances
Upgrading to Energy Star-rated appliances is one of the most effective ways to reduce energy consumption. Energy Star appliances are designed to consume less energy while maintaining performance, leading to significant savings over time.
6.2. LED Lighting
Switching to LED lighting can dramatically reduce lighting-related energy consumption. LED bulbs use up to 75% less energy and last much longer than traditional incandescent bulbs, providing both energy and cost savings.
6.3. Smart Home Devices
Smart home devices, such as smart thermostats and smart plugs, can help optimize energy usage. Smart thermostats allow you to control your home’s temperature remotely and set schedules to reduce energy consumption when you’re away. Smart plugs can turn off devices that consume standby power, eliminating phantom loads.
6.4. Proper Insulation
Ensuring your home is properly insulated is crucial for maintaining consistent indoor temperatures and reducing the need for excessive heating and cooling. Proper insulation in walls, attics, and basements can significantly reduce energy waste.
6.5. Behavioral Adjustments
Making simple behavioral adjustments can also contribute to energy savings. These include turning off lights when leaving a room, unplugging electronics when not in use, and using energy-intensive appliances during off-peak hours.
7. Expert Insights and Recommendations
To effectively manage and reduce your home’s wattage needs, consider consulting with energy experts or professional consultants. These specialists can provide personalized recommendations tailored to your specific circumstances.
7.1. Professional Energy Audits
Hiring a professional to conduct a comprehensive home energy audit can provide valuable insights into your energy consumption patterns. These audits typically involve a thorough assessment of your home’s insulation, HVAC systems, and appliances, identifying areas where energy is being wasted.
7.2. Customized Energy Plans
Energy experts can help you develop customized energy plans tailored to your home’s specific needs and energy goals. These plans may include recommendations for appliance upgrades, insulation improvements, and behavioral adjustments, providing a roadmap for reducing your home’s wattage needs and lowering your electricity bills.
7.3. Government and Utility Programs
Many government and utility companies offer programs and incentives to encourage energy efficiency. These programs may include rebates for purchasing Energy Star appliances, tax credits for installing solar panels, and assistance with home energy audits. Taking advantage of these programs can help offset the costs of energy-efficient upgrades and lower your overall energy expenses.
7.4. Consulting with Electrical Engineers
For complex energy-related issues, such as designing a backup power system or optimizing electrical load distribution, consulting with an electrical engineer can be beneficial. Electrical engineers have the expertise to assess your home’s electrical infrastructure and provide solutions that meet your specific needs.
Calculating the total wattage required to run your home can be time-consuming, but if you’re looking to purchase a generator for home backup and energy security, it’s time well spent.
Consider the alternative…
You end up spending a significant amount of money on a generator that fails to meet your family’s needs.
That’s the kind of expensive mistake that nobody wants to make.
Seeking Expert Guidance at HOW.EDU.VN
Navigating the complexities of home energy consumption and determining the right wattage for your needs can be challenging, but HOW.EDU.VN is here to help. Our team of experienced PhDs and specialists offers personalized consultations to address your specific concerns and provide tailored solutions.
Are you struggling to understand your home’s energy consumption? Do you want to optimize your energy usage and lower your electricity bills? Our experts can conduct a thorough assessment of your energy needs and recommend the best strategies for achieving your goals.
Connect with our Experts Today
Contact HOW.EDU.VN for expert guidance on determining the right wattage for your home. Our team of PhDs is ready to provide personalized solutions that meet your unique needs.
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let how.edu.vn help you take control of your energy consumption and create a more sustainable and cost-effective home.