Are you looking to check how much memory you have on your computer or laptop? Checking your memory or RAM (random access memory) is the first step. At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of knowing your system’s memory capacity to optimize performance and troubleshoot issues. This guide will walk you through the process on Windows and macOS, ensuring you can easily find the information you need. Understanding your RAM and how to check its capacity can lead to better system management and informed decisions about upgrades, ultimately enhancing your computing experience.
1. Why Is It Important to Check How Much Memory You Have?
Understanding how much memory your computer possesses is crucial for several reasons. Knowing your system’s memory specifications can help you:
- Determine if your computer meets the minimum requirements for new software or games.
- Troubleshoot performance issues, such as slow loading times or frequent crashes.
- Decide if you need to upgrade your RAM to improve overall system performance.
- Monitor memory usage to identify which applications are consuming the most resources.
- Optimize your system for specific tasks, such as video editing or gaming.
By regularly checking your memory status, you can proactively manage your computer’s resources and ensure it runs smoothly.
2. Key Terminology
Before diving into the steps, let’s define some key terms:
- RAM (Random Access Memory): This is the short-term memory your computer uses to store data that it is actively using. The more RAM you have, the more data your computer can quickly access, which can improve performance.
- DDR (Double Data Rate): This refers to the type of RAM. DDR versions (DDR3, DDR4, DDR5) indicate the generation of the RAM technology, with newer versions offering faster speeds and greater efficiency.
- Memory Usage: This indicates how much of your RAM is currently in use by running applications and system processes. Monitoring memory usage can help you identify bottlenecks and optimize performance.
- Virtual Memory: When your computer runs out of RAM, it uses a portion of your hard drive as virtual memory. Accessing data from the hard drive is slower than accessing RAM, so excessive use of virtual memory can slow down your system.
Having a clear understanding of these terms will help you better interpret the information you find when checking your memory.
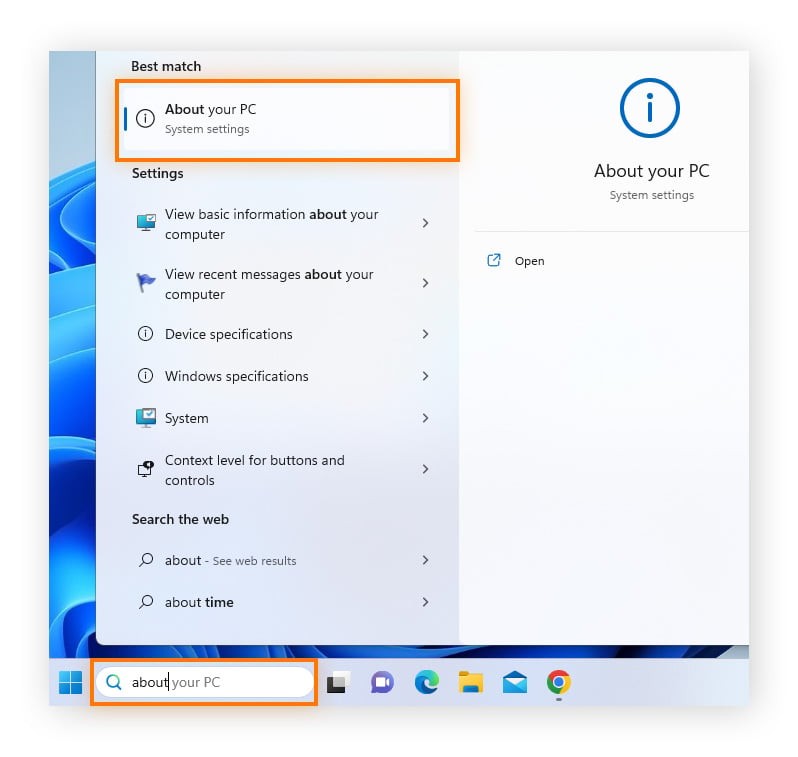
3. How to Check RAM on Windows 11
Checking RAM on Windows 11 is straightforward. Follow these steps:
- Open Settings: Click on the Windows icon in the taskbar and select the “Settings” icon (gear icon).
- Navigate to System: In the Settings window, click on “System.”
- Select About: Scroll down and click on “About.”
- View Installed RAM: Under the “Device specifications” section, you will find “Installed RAM.” This indicates the total amount of RAM installed on your system.
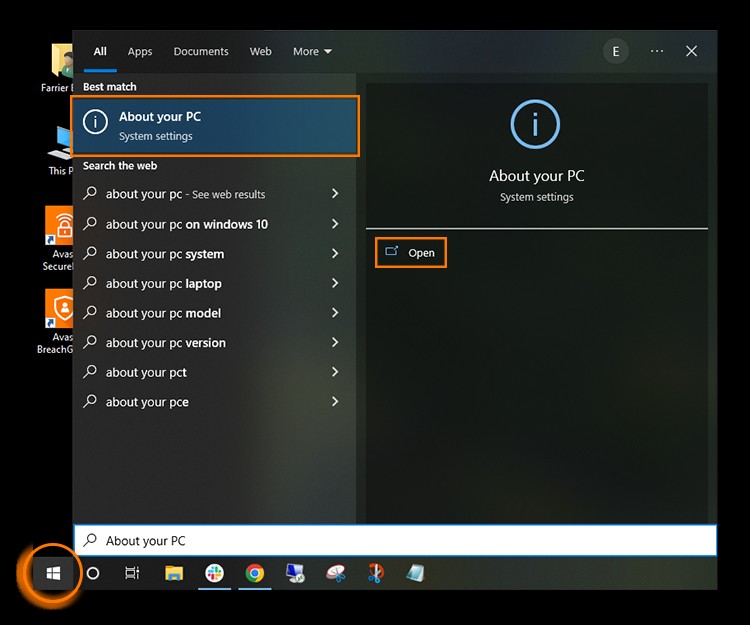
4. How to Check RAM on Windows 10
The process for checking RAM on Windows 10 is very similar to Windows 11:
- Open Settings: Click on the Windows icon and select the “Settings” icon.
- Navigate to System: In the Settings window, click on “System.”
- Select About: In the left sidebar, click on “About.”
- View Installed RAM: Under the “Device specifications” section, find “Installed RAM.” This shows the total RAM capacity of your system.
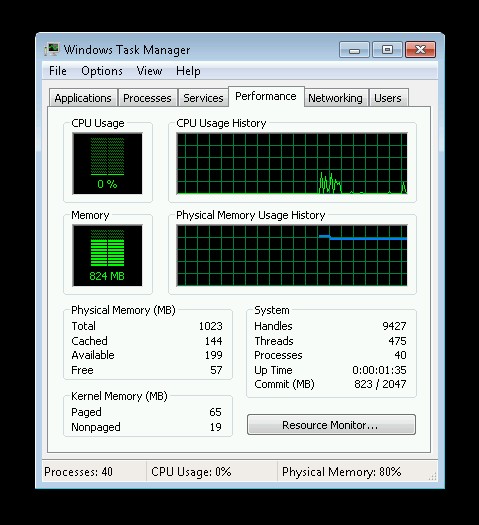
5. How to Check RAM on Windows 7
If you are still using Windows 7, you can check your RAM using the Task Manager:
- Open Task Manager: Press
Ctrl + Shift + Escto open the Task Manager. Alternatively, right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager.” - Select Performance Tab: In the Task Manager, click on the “Performance” tab.
- View Memory Information: Under the “Physical Memory” section, you will see the total RAM capacity listed.
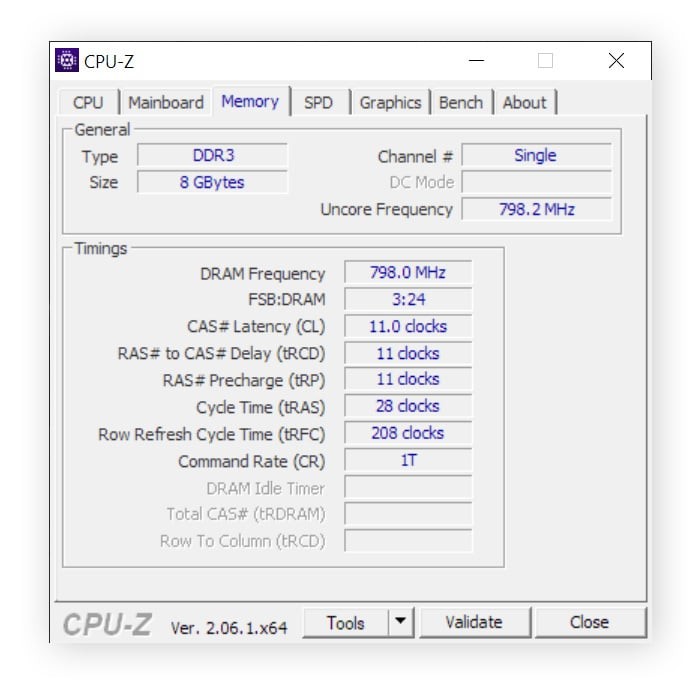
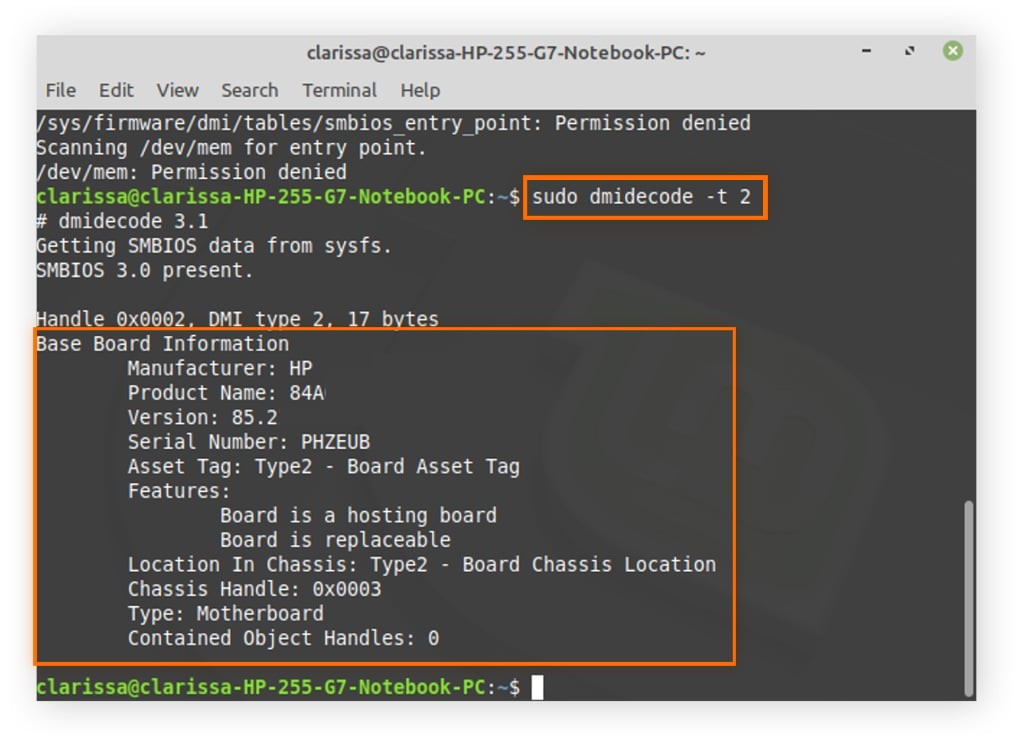
6. How to Check RAM Type on PC
Knowing the type of RAM your computer uses is essential when considering upgrades. Here’s how to check the RAM type:
- Download CPU-Z: Download and install the free CPU-Z utility from CPUID.
- Launch CPU-Z: Open the CPU-Z application.
- Navigate to the Memory Tab: Click on the “Memory” tab at the top of the window.
- View Memory Type: Under the “General” section, you will find the “Type” field, which indicates the RAM type (e.g., DDR3, DDR4).
7. How to Check RAM Usage on Windows
Monitoring RAM usage can help you identify which applications are consuming the most memory:
- Open Task Manager: Right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager.”
- Select Performance Tab: In the Task Manager, click on the “Performance” tab.
- Click Memory: In the left sidebar, click on “Memory.”
- View Usage Details: You will see a graph of your RAM usage over time, as well as detailed information about the amount of RAM being used by different processes.
- Check Processes: To see which specific tasks are using the most RAM, click the “Processes” tab. This will show you a list of running processes and their memory usage.
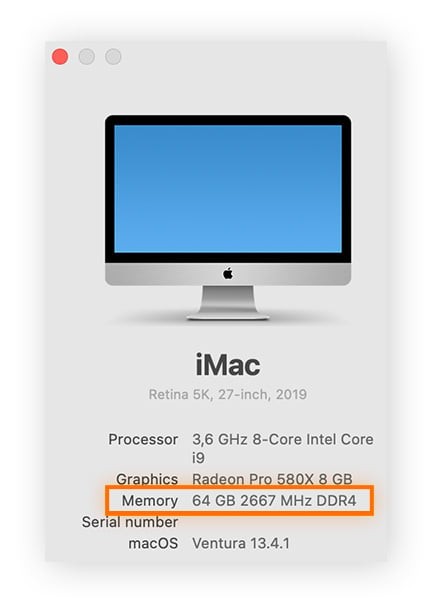
8. How to Check RAM on macOS
Checking RAM on a Mac is simple and can be done through the “About This Mac” option:
- Open Apple Menu: Click on the Apple icon in the top-left corner of the screen.
- Select About This Mac: In the dropdown menu, select “About This Mac.”
- View Memory Details: In the “Overview” tab, you will find the “Memory” section, which displays the total amount of RAM installed on your Mac.
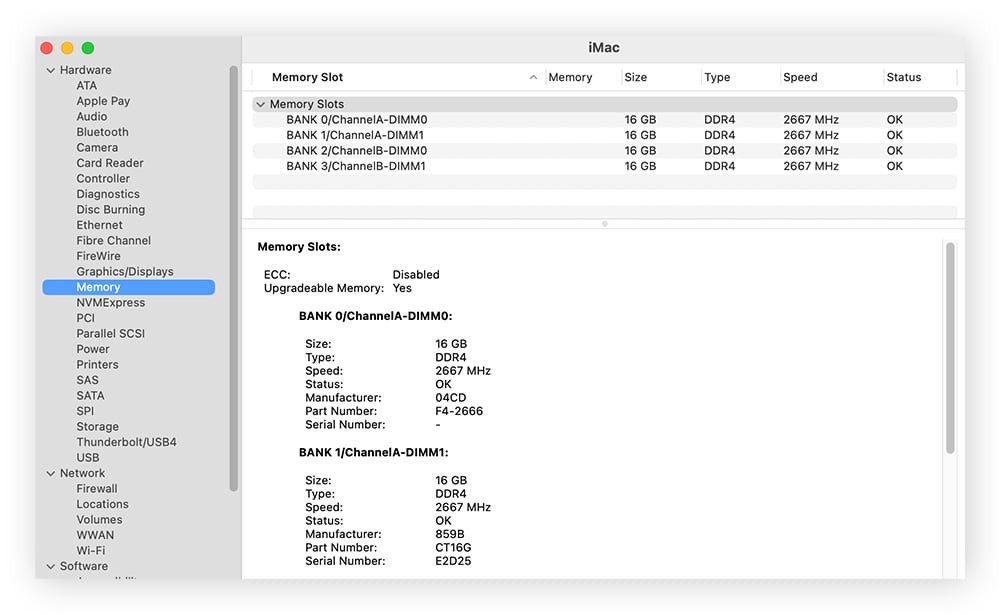
9. How to Check RAM Type on macOS
To check the type of RAM installed on your Mac:
- Open Spotlight Search: Press
Cmd + Spaceto open Spotlight Search. - Type System Information: Type “System Information” and press Enter.
- Select Memory: In the left sidebar, click on “Memory.”
- View Memory Type: In the right pane, you will see detailed information about your RAM, including the type, speed, and size of each module.
10. How to Check RAM Usage on macOS
Monitoring RAM usage on a Mac is essential for maintaining optimal performance:
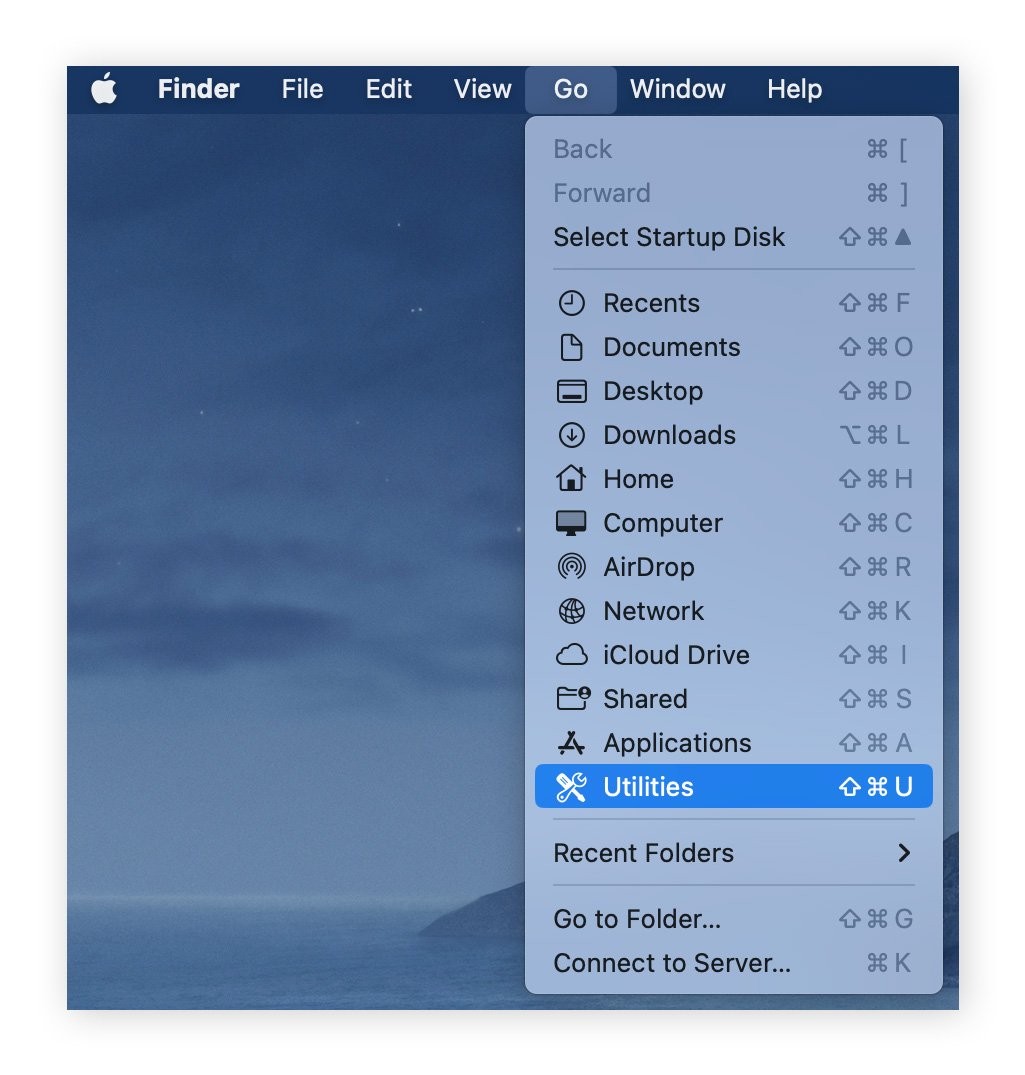
- Open Activity Monitor: Open Finder, click on “Go” in the menu bar, and select “Utilities.”
- Select Activity Monitor: Double-click on “Activity Monitor.”
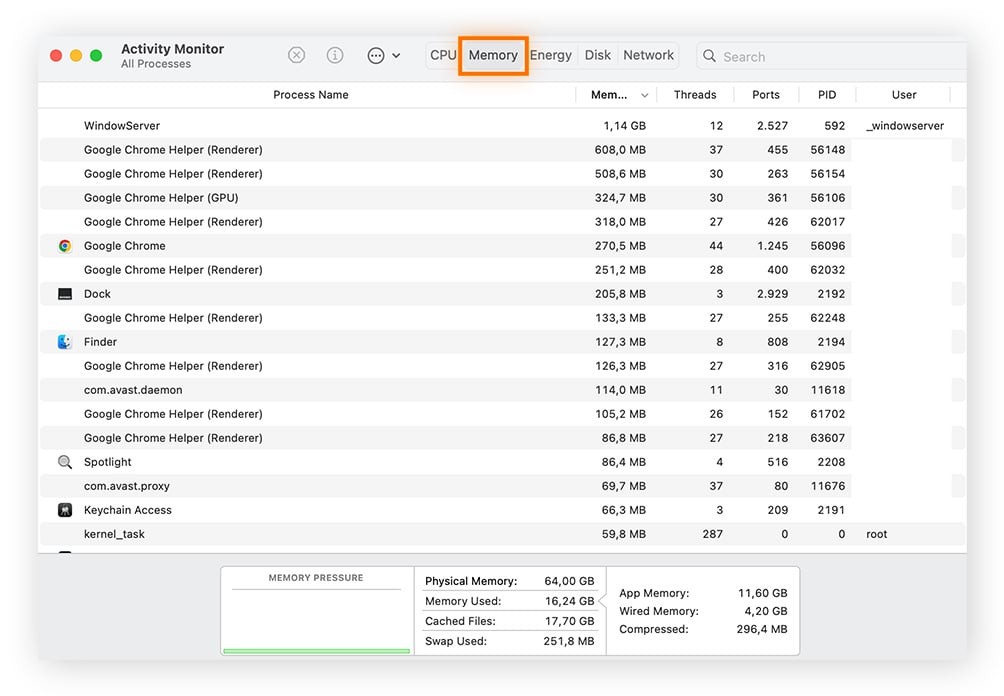
- Click Memory Tab: In the Activity Monitor window, click on the “Memory” tab.
- View Usage Details: You will see a list of all running processes and their memory usage, as well as a graph of overall memory pressure.
11. Understanding RAM Specifications
When checking your RAM, you might encounter several specifications. Here’s what they mean:
- Capacity: The total amount of RAM installed (e.g., 8 GB, 16 GB).
- Type: The generation of RAM technology (e.g., DDR3, DDR4, DDR5).
- Speed: The rate at which data can be transferred (e.g., 2400 MHz, 3200 MHz). Higher speeds generally result in better performance.
- Form Factor: The physical design of the RAM module (e.g., DIMM for desktops, SO-DIMM for laptops).
- Latency: The delay in accessing data, measured in CAS latency (CL) cycles. Lower latency generally results in better performance.
Understanding these specifications can help you make informed decisions when upgrading or troubleshooting your RAM.
12. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues with your RAM, consider these troubleshooting steps:
- Check RAM Compatibility: Ensure that the RAM you are using is compatible with your motherboard. Refer to your motherboard’s documentation for supported RAM types and speeds.
- Run Memory Diagnostics: Use the built-in memory diagnostic tools in Windows or macOS to check for errors. These tools can help identify faulty RAM modules.
- Reseat RAM Modules: Remove and reinsert your RAM modules to ensure they are properly seated in their slots.
- Update BIOS/UEFI: Ensure that your BIOS/UEFI is up to date, as updates can improve RAM compatibility and performance.
- Monitor Temperature: Overheating can cause RAM instability. Ensure that your system has adequate cooling to prevent overheating.
13. When to Consider a RAM Upgrade
Deciding when to upgrade your RAM is crucial for maintaining optimal system performance. Here are some signs that it might be time for a RAM upgrade:
- Slow Performance: Your computer takes a long time to open applications or switch between tasks.
- Frequent Crashes: You experience frequent system crashes or blue screen errors.
- Full Memory Usage: Your RAM usage is consistently high, even when running basic applications.
- Inability to Run New Software: You are unable to run new software or games due to insufficient memory.
- Increased Virtual Memory Usage: Your system is heavily relying on virtual memory, which slows down performance.
14. How Much RAM Do You Need?
The amount of RAM you need depends on your usage patterns. Here are some general guidelines:
- 4 GB: Suitable for basic tasks like web browsing, email, and word processing.
- 8 GB: Recommended for general use, including multitasking and running moderately demanding applications.
- 16 GB: Ideal for gaming, video editing, and running multiple resource-intensive applications simultaneously.
- 32 GB or More: Necessary for professional use, such as 3D modeling, video production, and running virtual machines.
| RAM | 8 – 16 GB | 16 – 32 GB | 32 – 64 GB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Use Type | Entertainment / Light Work Apps | Gaming / Multitasking / Heavier Apps | Professional / Intensive Apps |
| Activities | Playing games released before 2016 | Playing/streaming the latest games with high performance settings | Video editing |
| Data entry | Multitasking between many programs | 3D modeling, design engineering | |
| Checking email | Having lots of tabs open in a web browser | Software engineering, programming, database development | |
| Standard business software | Photoshop | Graphic design | |
| Entertainment (movies, music) | Microsoft Office — multitasking and using graphics or large files | Medical imaging | |
| Microsoft Office: Word, Excel, Powerpoint | Amateur music production in digital audio workstations (DAW) | Professional music performance/production |

15. Benefits of Upgrading RAM
Upgrading your RAM can provide several benefits:
- Improved Performance: Faster application loading times and smoother multitasking.
- Enhanced Gaming Experience: Higher frame rates and reduced stuttering in games.
- Increased Productivity: Ability to handle more tasks simultaneously without slowdowns.
- Better Software Compatibility: Ability to run the latest software and games without performance issues.
- Extended System Lifespan: Improved overall system responsiveness and longevity.
16. Optimizing RAM Usage
Even with sufficient RAM, optimizing its usage can improve performance:
- Close Unnecessary Applications: Close any applications that you are not currently using to free up memory.
- Disable Startup Programs: Prevent unnecessary programs from launching at startup to reduce memory usage.
- Use Lightweight Software: Opt for lightweight applications that consume fewer resources.
- Update Drivers: Ensure that your drivers are up to date, as outdated drivers can cause memory leaks and performance issues.
- Run Disk Cleanup: Regularly run disk cleanup to remove temporary files and free up disk space, which can improve virtual memory performance.
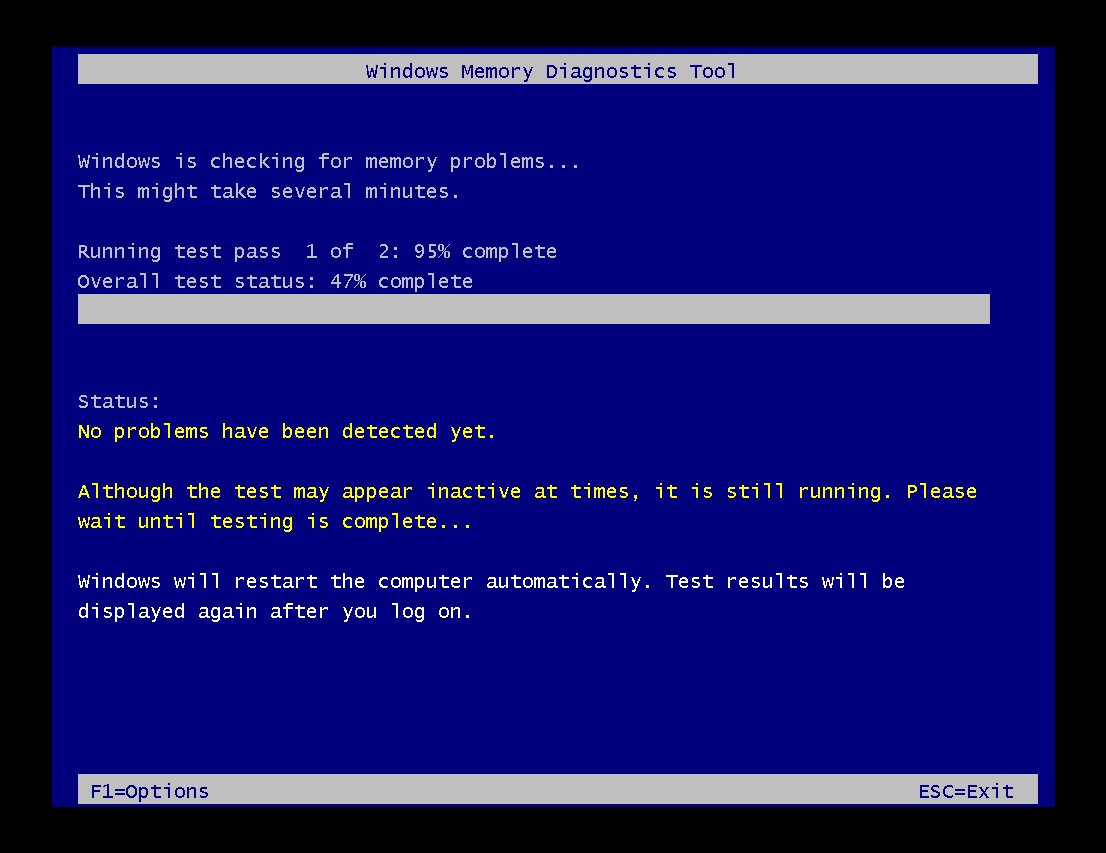
17. Checking Memory for Errors
It’s essential to check your memory for errors to ensure system stability. Here’s how to do it:
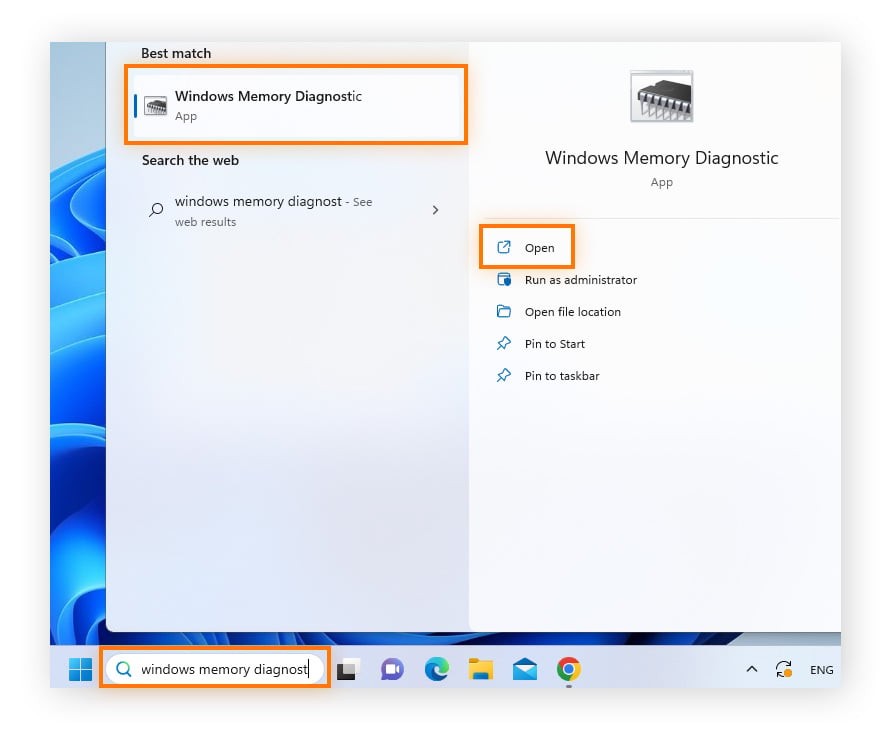
- Open Windows Memory Diagnostic: Type “Windows Memory Diagnostic” in the Windows search box and open the application.
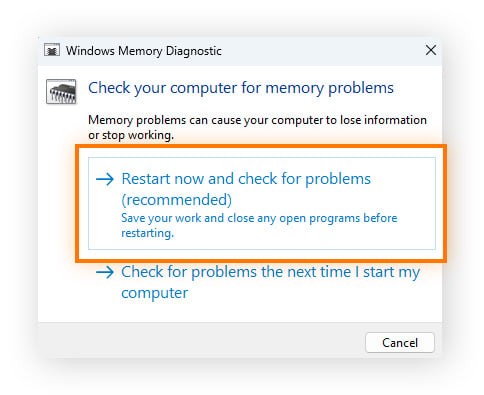
- Restart and Check: Select “Restart now and check for problems.”
- Wait for the Test: Your computer will restart and run a memory diagnostic test. If any errors are found, you should consider replacing your RAM.
18. Freeing Up More RAM
If your computer often runs out of memory, consider these steps:
- Close Unused Apps: Close any applications that you are not currently using.
- Uninstall Unnecessary Programs: Remove programs that you no longer need.
- Disable Startup Programs: Prevent unnecessary programs from launching at startup.
- Use a Memory Cleaner: Consider using a memory cleaner utility to free up RAM.
- Upgrade RAM: If you consistently run out of memory, upgrading to a higher capacity is the best solution.
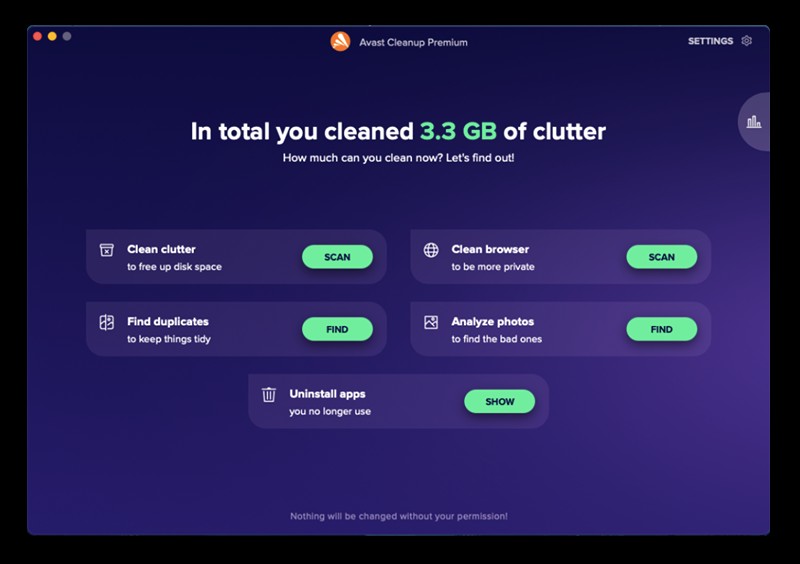
19. Using Avast Cleanup to Optimize RAM
Avast Cleanup is a tool that can help you optimize your RAM usage and improve overall system performance. It includes features such as:
- Sleep Mode: Hibernates resource-intensive applications when they are not in use.
- Junk File Removal: Cleans up temporary files and other unnecessary data.
- Startup Manager: Disables unnecessary startup programs.
By using Avast Cleanup, you can easily free up RAM and improve your computer’s performance.
20. Expert Insights from HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of experts understands the challenges users face when dealing with computer performance issues. We recommend regularly monitoring your RAM usage and considering an upgrade if you consistently experience slowdowns. Additionally, optimizing your system through regular maintenance and the use of tools like Avast Cleanup can significantly improve performance.
According to a study by the University of California, upgrading RAM can lead to a performance increase of up to 40% in memory-intensive applications. This highlights the importance of having sufficient RAM for your specific needs.
21. Additional Tips and Tricks
Here are some additional tips and tricks to help you manage your RAM:
- Monitor Resource Usage: Use Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (macOS) to regularly monitor resource usage and identify any processes that are consuming excessive memory.
- Use ReadyBoost (Windows): If you have an older computer with limited RAM, consider using ReadyBoost to utilize a USB drive as additional memory.
- Defragment Your Hard Drive: Regularly defragment your hard drive to improve virtual memory performance.
- Adjust Visual Effects: Reduce visual effects in Windows or macOS to free up memory.
- Keep Your System Updated: Ensure that your operating system and applications are up to date, as updates often include performance improvements and bug fixes.
22. The Role of SSDs in Memory Management
While RAM is crucial for short-term data access, Solid State Drives (SSDs) play a significant role in overall memory management. SSDs offer much faster read and write speeds compared to traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), which can improve virtual memory performance.
When your computer runs out of RAM, it uses virtual memory, which is a portion of your hard drive. If you have an SSD, accessing virtual memory will be much faster than if you have an HDD, resulting in improved overall system performance.
Consider upgrading to an SSD if you are still using an HDD, as it can significantly improve your computer’s responsiveness, especially when dealing with memory-intensive tasks.
23. Understanding Memory Leaks
A memory leak occurs when an application fails to release memory that it has allocated, leading to a gradual decrease in available RAM. Over time, memory leaks can cause your computer to slow down or even crash.
To identify memory leaks, monitor your RAM usage using Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (macOS). If you notice that an application’s memory usage is constantly increasing, even when it is not actively being used, it may be experiencing a memory leak.
To address memory leaks, try the following:
- Update the Application: Check for updates to the application, as updates often include fixes for memory leaks.
- Restart the Application: Restarting the application can release the memory that has been leaked.
- Reinstall the Application: Reinstalling the application can resolve issues caused by corrupted files.
- Contact the Developer: If the memory leak persists, contact the developer of the application for assistance.
24. The Impact of Background Processes on RAM
Background processes are applications and services that run in the background, even when you are not actively using them. These processes can consume RAM and slow down your computer.
To manage background processes:
- Open Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (macOS):
- Identify Resource-Intensive Processes: Look for processes that are consuming a significant amount of RAM.
- Disable Unnecessary Processes: Disable any processes that are not essential for your system to function properly. Be cautious when disabling processes, as disabling critical system processes can cause instability.
25. How to Choose the Right RAM for Your Needs
Choosing the right RAM for your needs can significantly impact your computer’s performance. Consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the RAM is compatible with your motherboard. Check your motherboard’s documentation for supported RAM types, speeds, and capacities.
- Capacity: Choose a capacity that meets your needs. Refer to the guidelines in Section 14 to determine the appropriate amount of RAM for your usage patterns.
- Speed: Opt for RAM with a speed that is supported by your motherboard. Higher speeds can improve performance, but only if your motherboard can take advantage of them.
- Latency: Look for RAM with low latency (CAS latency), as lower latency generally results in better performance.
- Brand: Choose RAM from a reputable brand to ensure quality and reliability.
26. Advanced RAM Management Techniques
For advanced users, here are some additional RAM management techniques:
- XMP (Extreme Memory Profile): Enable XMP in your BIOS/UEFI to automatically configure your RAM to its rated speed and timings.
- Dual-Channel and Quad-Channel Configurations: Install RAM in dual-channel or quad-channel configurations to increase memory bandwidth. Refer to your motherboard’s documentation for instructions on how to properly install RAM in these configurations.
- Overclocking: Overclocking RAM can improve performance, but it can also increase the risk of instability. Proceed with caution and monitor your system’s temperature to prevent overheating.
27. The Future of RAM Technology
RAM technology is constantly evolving, with new standards and innovations emerging regularly. Some of the key trends in RAM technology include:
- DDR5: DDR5 is the latest generation of RAM technology, offering faster speeds, greater efficiency, and higher capacities compared to DDR4.
- Non-Volatile Memory: Non-volatile memory technologies, such as Intel Optane, offer persistent storage that is much faster than traditional SSDs.
- 3D Stacking: 3D stacking allows for higher densities of RAM modules, enabling larger capacities in smaller form factors.
28. Conclusion: Mastering Memory Management for Optimal Performance
Knowing How To Check How Much Memory You Have and understanding how to manage it effectively is crucial for maintaining optimal computer performance. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can easily monitor your RAM usage, troubleshoot issues, and make informed decisions about upgrades.
Remember to regularly monitor your RAM usage, optimize your system through regular maintenance, and consider an upgrade if you consistently experience slowdowns. With the right knowledge and tools, you can ensure that your computer always performs at its best.
If you’re facing persistent issues or need personalized advice, don’t hesitate to reach out to the experts at HOW.EDU.VN. We offer comprehensive consultation services to help you optimize your system and achieve peak performance.
29. Call to Action: Get Expert Assistance from HOW.EDU.VN
Are you struggling with slow computer performance or unsure if you need a RAM upgrade? The team of experienced PhDs at HOW.EDU.VN is here to help. We offer personalized consultations to assess your system’s needs and provide expert recommendations for optimizing performance.
Don’t waste time and money on unnecessary upgrades. Let our experts guide you to the best solutions for your specific needs. Contact us today for a consultation and experience the difference that expert advice can make.
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Reach out to us and let the leading PhDs worldwide address your queries and provide tailored solutions.
30. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How do I check how much RAM I have on my computer?
You can check your RAM in Windows by going to Settings > System > About and looking under “Device specifications.” On macOS, click the Apple menu > About This Mac and look under “Memory.”
Q2: Why is it important to know how much RAM I have?
Knowing your RAM capacity helps you determine if your computer meets the requirements for new software, troubleshoot performance issues, and decide if you need an upgrade.
Q3: How do I check the type of RAM my computer has?
On Windows, download and run CPU-Z. On macOS, go to System Information (accessed via Spotlight) and select “Memory.”
Q4: How much RAM do I need for gaming?
For modern gaming, 16 GB of RAM is generally recommended for smooth performance and higher frame rates.
Q5: Can too much RAM slow down my computer?
No, too much RAM will not slow down your computer. However, having more RAM than you need is a waste of money.
Q6: How can I free up RAM on my computer?
Close unused applications, disable startup programs, uninstall unnecessary programs, and use a memory cleaner utility.
Q7: What is virtual memory, and how does it affect performance?
Virtual memory is a portion of your hard drive used as additional memory when RAM is full. Accessing virtual memory is slower than accessing RAM, so excessive use can slow down your system.
Q8: Should I upgrade to an SSD to improve memory performance?
Yes, upgrading to an SSD can significantly improve virtual memory performance due to its faster read and write speeds.
Q9: What is a memory leak, and how can I fix it?
A memory leak occurs when an application fails to release memory, leading to decreased performance. Update, restart, or reinstall the application to fix it.
Q10: How can HOW.EDU.VN help me with RAM-related issues?
how.edu.vn offers personalized consultations with experienced PhDs to assess your system’s needs and provide expert recommendations for optimizing performance.

