How To Check Pc Specs is essential for understanding your computer’s capabilities and limitations, and HOW.EDU.VN provides expert guidance on navigating this crucial aspect of PC ownership. This knowledge allows you to optimize performance, troubleshoot issues, and make informed decisions about upgrades, ensuring your system meets your specific needs and expectations, including understanding the hardware configuration and system specifications.
1. Understanding the Importance of Checking PC Specs
Checking your PC specifications is more than just a technical exercise; it’s a fundamental step in ensuring your computer operates efficiently and effectively. By understanding your system’s components, you can proactively address potential issues, optimize performance, and make informed decisions about software compatibility and hardware upgrades. Let’s delve into the key reasons why checking PC specs is so crucial:
-
Ensuring Software Compatibility: Every software application, especially resource-intensive ones like video editing suites or modern games, has minimum and recommended hardware requirements. Verifying your PC specs ensures your system meets these requirements, preventing performance issues, crashes, or even the inability to run the software altogether.
-
Optimizing Performance: Identifying bottlenecks in your system, such as insufficient RAM or an outdated graphics card, allows you to target specific upgrades that will significantly improve performance. This targeted approach is more cost-effective than simply upgrading everything without understanding the root cause of performance limitations.
-
Troubleshooting Issues: When encountering system crashes, slowdowns, or graphical glitches, knowing your PC specs can help pinpoint the source of the problem. For example, if a game is running poorly, you can check if your graphics card meets the game’s requirements or if your drivers are up to date.
-
Making Informed Upgrade Decisions: Before investing in new hardware, it’s essential to understand your current system’s specifications. This allows you to make informed decisions about which components to upgrade, ensuring compatibility and maximizing the return on your investment.
-
Monitoring System Health: Regularly checking your PC specs can help you track changes in performance over time. This can be an early indicator of potential hardware issues, such as a failing hard drive or overheating components, allowing you to take preventative measures before a critical failure occurs.
In essence, checking PC specs is a proactive approach to PC ownership, empowering you to maintain a healthy, efficient, and optimized system that meets your specific needs and expectations. According to a study by Gartner, proactive IT maintenance can reduce downtime by as much as 30%. Understanding your system’s specifications is a key component of this proactive approach.
2. Methods for Checking PC Specs in Windows
Windows offers several built-in tools and methods for checking your PC specifications. Each method provides a different level of detail, allowing you to choose the one that best suits your needs and technical expertise. Here’s a breakdown of the most common and effective methods:
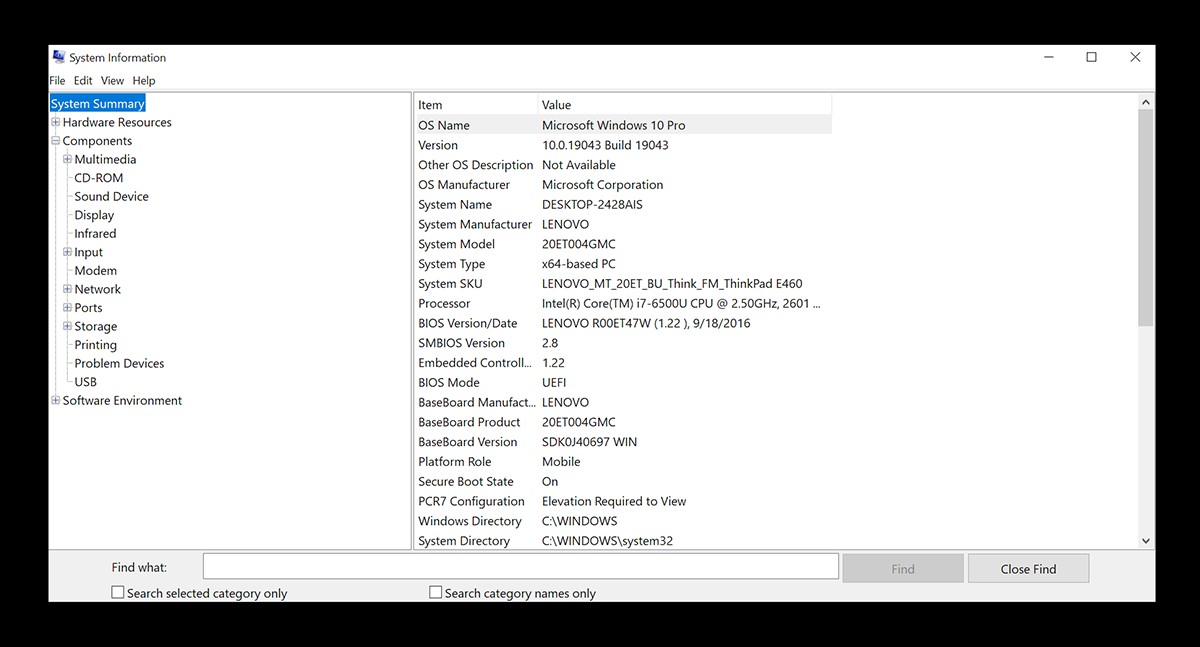
2.1. Using System Information
System Information provides a comprehensive overview of your PC’s hardware and software configuration. It’s a user-friendly tool that’s easily accessible and provides a wealth of information.
- Accessing System Information:
- Press the Windows key, type “System Information,” and select the app from the search results.
- Alternatively, press Windows key + R, type “msinfo32,” and press Enter.
- Navigating the Interface:
- The System Summary section provides a general overview of your PC specs, including:
- OS Name: The version of Windows you’re running.
- System Manufacturer: The manufacturer of your computer (e.g., Dell, HP, ASUS).
- System Model: The specific model of your computer.
- Processor: The type and speed of your CPU.
- Installed Physical Memory (RAM): The amount of RAM installed in your system.
- BaseBoard Manufacturer/Product: Information about your motherboard.
- The System Summary section provides a general overview of your PC specs, including:
- Exploring Components:
- Expand the Components section in the left-hand panel to view details about specific hardware components, such as:
- Display: Information about your graphics card.
- Storage: Details about your hard drives and SSDs.
- Sound Device: Information about your audio hardware.
- Network: Details about your network adapters.
- Expand the Components section in the left-hand panel to view details about specific hardware components, such as:
Alt Text: PC specs displayed in System Information, highlighting the CPU, RAM, and operating system.
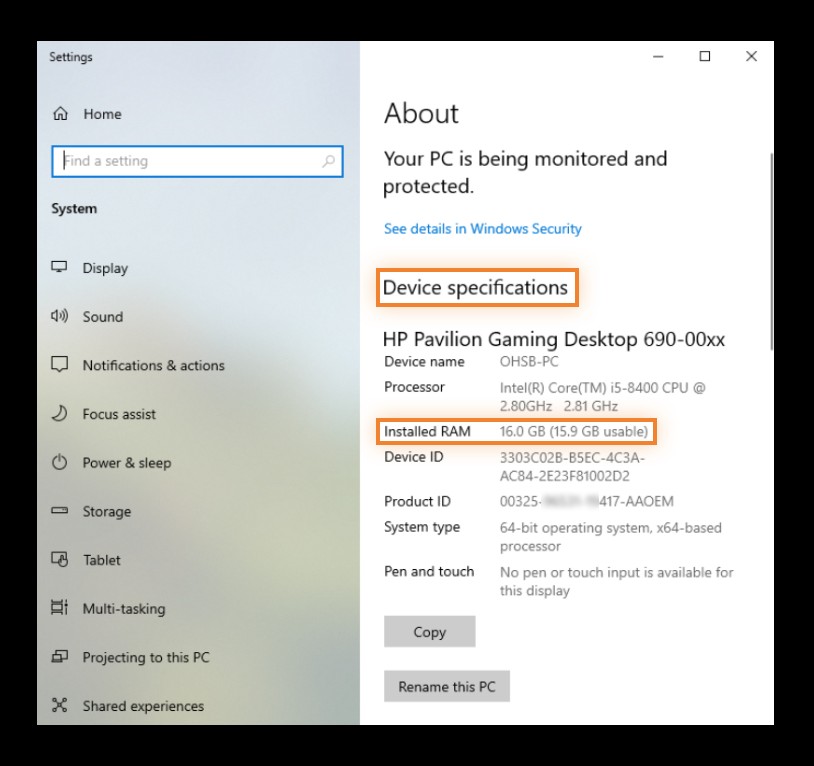
2.2. Using Windows Settings
The Windows Settings app offers a simplified view of your PC specs, focusing on the most essential information. It’s a great option for users who prefer a more streamlined approach.
- Accessing Windows Settings:
- Click the Windows icon in the lower-left corner of your screen and select the Settings icon (gear icon).
- Alternatively, press Windows key + I to open the Settings app directly.
- Navigating to the “About” Section:
- Click on System.
- Scroll down and click on About in the left-hand menu.
- Reviewing Device Specifications:
- The Device specifications section displays key information about your PC, including:
- Processor: The type and speed of your CPU.
- Installed RAM: The amount of RAM installed in your system.
- Device ID: A unique identifier for your device.
- Product ID: A unique identifier for your Windows installation.
- System type: Whether you have a 32-bit or 64-bit operating system.
- Pen and touch: Information about pen and touch support, if applicable.
- The Device specifications section displays key information about your PC, including:
- Reviewing Windows Specifications:
- The Windows specifications section displays details about your Windows installation, including:
- Edition: The edition of Windows you’re running (e.g., Windows 10 Home, Windows 10 Pro).
- Version: The specific version number of your Windows installation.
- Installed on: The date when Windows was installed on your system.
- OS build: The build number of your operating system.
- The Windows specifications section displays details about your Windows installation, including:
Alt Text: The “About” section in Windows Settings, showcasing the processor, RAM, and Windows version.
2.3. Using Task Manager
While primarily used for monitoring system performance, Task Manager also provides quick access to information about your CPU, memory, and disk usage.
- Opening Task Manager:
- Right-click on the Taskbar and select Task Manager.
- Alternatively, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager directly.
- Navigating to the “Performance” Tab:
- Click on the Performance tab.
- Viewing Hardware Information:
- Click on the specific hardware component you want to inspect (e.g., CPU, Memory, Disk, GPU).
- The right-hand pane will display detailed information about the selected component, including:
- CPU: Processor model, speed, number of cores, and utilization.
- Memory: Total RAM, utilization, speed, and type.
- Disk: Storage capacity, utilization, and type (SSD or HDD).
- GPU: Graphics card model, utilization, and memory.
2.4. Using DirectX Diagnostic Tool (DxDiag)
The DirectX Diagnostic Tool (DxDiag) is primarily used for troubleshooting DirectX-related issues, but it also provides valuable information about your graphics card and audio hardware.
- Opening DxDiag:
- Press Windows key + R, type “dxdiag,” and press Enter.
- Navigating the Interface:
- The System tab provides general information about your computer, including the operating system, processor, and memory.
- The Display tab provides detailed information about your graphics card, including the manufacturer, model, memory, and drivers.
- The Sound tab provides information about your audio hardware, including the sound card and drivers.
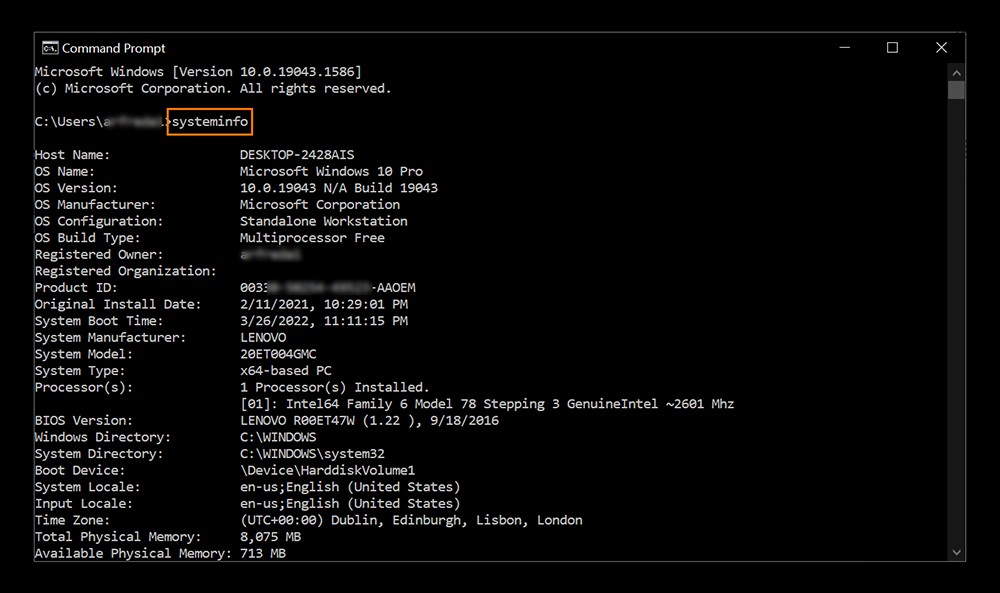
2.5. Using Command Prompt or PowerShell
For advanced users, Command Prompt and PowerShell offer powerful command-line interfaces for retrieving detailed PC specs.
- Opening Command Prompt or PowerShell:
- Type “cmd” or “powershell” in the Windows search bar and select the corresponding app.
- To run as administrator, right-click on the app and select “Run as administrator.”
- Using the “systeminfo” Command:
- Type “systeminfo” and press Enter.
- This command will display a comprehensive list of your PC’s hardware and software specifications.
- Using PowerShell Cmdlets:
- PowerShell offers more specific cmdlets for retrieving information about individual components. For example:
Get-ComputerInfo: Retrieves general system information.Get-WmiObject Win32_Processor: Retrieves information about the CPU.Get-WmiObject Win32_PhysicalMemory: Retrieves information about the RAM.Get-WmiObject Win32_VideoController: Retrieves information about the graphics card.
- PowerShell offers more specific cmdlets for retrieving information about individual components. For example:
Alt Text: Command Prompt displaying system information after running the “systeminfo” command.
Table 1: Comparison of Methods for Checking PC Specs in Windows
| Method | Ease of Use | Level of Detail | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| System Information | Easy | Comprehensive | General overview of PC specs |
| Windows Settings | Easy | Basic | Quick access to essential PC specs |
| Task Manager | Easy | Moderate | Monitoring real-time performance and viewing basic hardware information |
| DirectX Diagnostic Tool | Moderate | Detailed | Troubleshooting graphics and audio issues |
| Command Prompt/PowerShell | Advanced | Comprehensive | Advanced users who prefer command-line interfaces |
3. Understanding Key PC Components and Their Specifications
Checking your PC specifications is only the first step. To truly understand your system’s capabilities and limitations, it’s essential to know what each component does and how its specifications impact performance. Let’s break down the key PC components and their relevant specifications:
3.1. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU, often referred to as the “brain” of the computer, is responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. Its specifications directly impact the overall speed and responsiveness of your system.
- Manufacturer: Intel and AMD are the two main CPU manufacturers.
- Model: The specific model number indicates the CPU’s generation, features, and performance level. For example, Intel Core i7-12700K or AMD Ryzen 9 5900X.
- Cores: The number of cores determines the CPU’s ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. More cores generally translate to better multitasking performance.
- Clock Speed: Measured in GHz (gigahertz), the clock speed indicates how many instructions the CPU can execute per second. Higher clock speeds generally result in faster performance.
- Cache: Cache memory is a small, fast memory that stores frequently accessed data, allowing the CPU to retrieve it quickly. Larger cache sizes can improve performance.
Alt Text: CPU specs showing Intel Core i7 processor, highlighting the model and clock speed.
3.2. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
The GPU, also known as a graphics card or video card, is responsible for rendering images, videos, and other visual content. It’s a critical component for gamers, graphic designers, and anyone who works with visually intensive applications.
- Manufacturer: NVIDIA and AMD are the two main GPU manufacturers.
- Model: The specific model number indicates the GPU’s performance level and features. For example, NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 or AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT.
- Memory: The amount of video memory (VRAM) determines the GPU’s ability to store textures, models, and other graphical data. More VRAM is generally better for gaming at higher resolutions and detail settings.
- Clock Speed: Similar to the CPU, the GPU’s clock speed indicates how many calculations it can perform per second.
- CUDA Cores/Stream Processors: These are the parallel processing units within the GPU that perform the actual rendering calculations. More cores/processors generally translate to better performance.
3.3. Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM is a type of fast, temporary memory that the computer uses to store data and instructions that are actively being used. The amount of RAM directly impacts the system’s ability to multitask and handle large datasets.
- Capacity: Measured in GB (gigabytes), the capacity indicates the total amount of RAM installed in your system.
- Speed: Measured in MHz (megahertz), the speed indicates how quickly the RAM can transfer data.
- Type: The type of RAM (e.g., DDR4, DDR5) indicates the technology used and the performance level.
- Latency: Latency refers to the delay in accessing data stored in RAM. Lower latency generally results in faster performance.
3.4. Storage Devices (SSD/HDD)
Storage devices are used to store data permanently, including the operating system, applications, and personal files. There are two main types of storage devices: Solid State Drives (SSDs) and Hard Disk Drives (HDDs).
- Type: SSDs use flash memory to store data, while HDDs use spinning platters. SSDs are significantly faster than HDDs, resulting in faster boot times, application loading, and file transfer speeds.
- Capacity: Measured in GB or TB (terabytes), the capacity indicates the total amount of data that can be stored on the drive.
- Interface: The interface (e.g., SATA, NVMe) determines the speed at which data can be transferred between the storage device and the rest of the system. NVMe SSDs are significantly faster than SATA SSDs.
Table 2: Impact of PC Component Specifications on Performance
| Component | Specification | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | Cores | Determines the CPU’s ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. More cores generally translate to better multitasking performance. |
| CPU | Clock Speed | Indicates how many instructions the CPU can execute per second. Higher clock speeds generally result in faster performance. |
| GPU | Memory (VRAM) | Determines the GPU’s ability to store textures, models, and other graphical data. More VRAM is generally better for gaming at higher resolutions and detail settings. |
| GPU | CUDA/Stream Cores | These are the parallel processing units within the GPU that perform the actual rendering calculations. More cores/processors generally translate to better performance. |
| RAM | Capacity | Indicates the total amount of RAM installed in your system. More RAM allows the system to handle more data and applications simultaneously, reducing slowdowns and improving overall responsiveness. |
| RAM | Speed | Indicates how quickly the RAM can transfer data. Faster RAM speeds can improve performance, especially in memory-intensive applications. |
| Storage | Type (SSD vs HDD) | SSDs are significantly faster than HDDs, resulting in faster boot times, application loading, and file transfer speeds. |
| Storage | Interface (NVMe) | NVMe SSDs are significantly faster than SATA SSDs, providing even faster boot times, application loading, and file transfer speeds. |
4. Understanding User Intent and Optimizing Your PC Based on Usage
Once you know how to check PC specs and understand what they mean, the next step is to tailor your system to your specific needs and usage patterns. Different users have different requirements, and optimizing your PC accordingly can significantly improve performance and overall satisfaction. Let’s explore some common user intents and how to optimize your PC for each:
4.1. Gaming
Gamers require a PC that can deliver smooth frame rates, high resolutions, and stunning visual fidelity. Key components for gaming include:
- Powerful GPU: A high-end graphics card is essential for rendering complex game environments and effects. Look for models with ample VRAM (8GB or more) and high clock speeds.
- Fast CPU: While the GPU is the primary driver of gaming performance, a fast CPU is also important for handling game logic, AI, and physics calculations.
- Sufficient RAM: 16GB of RAM is generally recommended for modern games, allowing the system to load and process large game assets without slowdowns.
- Fast SSD: An SSD is crucial for reducing load times and ensuring a smooth gaming experience.
- High Refresh Rate Monitor: A monitor with a high refresh rate (144Hz or higher) can significantly improve the smoothness and responsiveness of gameplay.
To ensure optimal performance, keep your graphics drivers updated, optimize in-game settings, and consider overclocking your CPU and GPU (with caution).
4.2. Content Creation (Video Editing, Graphic Design)
Content creators require a PC that can handle large files, complex projects, and resource-intensive applications. Key components for content creation include:
- Powerful CPU: A multi-core CPU is essential for video editing, rendering, and other computationally intensive tasks.
- Ample RAM: 32GB or more of RAM is recommended for handling large video files and complex graphic design projects.
- Fast SSD: An SSD is crucial for storing and accessing large files quickly. Consider using a dedicated NVMe SSD for your operating system and applications, and a separate SSD for your project files.
- Professional-Grade GPU: While not as critical as for gaming, a professional-grade GPU can accelerate rendering and other tasks in content creation applications.
- Color-Accurate Monitor: A monitor with accurate color reproduction is essential for ensuring that your content looks its best.
To optimize performance, close unnecessary applications, use proxies for large video files, and optimize your project settings.
4.3. Office Productivity and General Use
For everyday tasks like browsing the web, writing documents, and sending emails, a high-end PC is not necessarily required. However, certain components can significantly improve the overall experience:
- Fast SSD: An SSD is the single most impactful upgrade for improving the responsiveness of a general-use PC.
- Sufficient RAM: 8GB of RAM is generally sufficient for most office productivity tasks, but 16GB can provide a smoother experience when multitasking.
- Comfortable Keyboard and Mouse: Investing in a comfortable keyboard and mouse can significantly improve your productivity and reduce strain.
- Ergonomic Monitor: An ergonomic monitor with adjustable height and tilt can help prevent neck and back pain.
To optimize performance, keep your operating system and applications updated, uninstall unnecessary software, and run a disk cleanup utility regularly.
4.4. Programming and Software Development
Programmers and software developers require a PC that can handle compiling code, running virtual machines, and managing large projects. Key components for programming include:
- Powerful CPU: A multi-core CPU is essential for compiling code quickly and running virtual machines smoothly.
- Ample RAM: 16GB or more of RAM is recommended for handling large projects and running multiple virtual machines.
- Fast SSD: An SSD is crucial for storing and accessing code files quickly.
- Comfortable Keyboard: A comfortable and responsive keyboard is essential for long coding sessions.
- Multiple Monitors: Using multiple monitors can significantly improve productivity by allowing you to view more code and documentation simultaneously.
To optimize performance, use a lightweight IDE, optimize your build process, and consider using a code profiler to identify performance bottlenecks.
Table 3: PC Optimization Based on User Intent
| User Intent | Key Components | Optimization Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Gaming | Powerful GPU, Fast CPU, Sufficient RAM, Fast SSD | Keep graphics drivers updated, optimize in-game settings, consider overclocking (with caution) |
| Content Creation | Powerful CPU, Ample RAM, Fast SSD, Pro GPU | Close unnecessary applications, use proxies for large video files, optimize project settings |
| Office Productivity | Fast SSD, Sufficient RAM, Comfortable Peripherals | Keep OS and applications updated, uninstall unnecessary software, run disk cleanup utility regularly |
| Programming/Development | Powerful CPU, Ample RAM, Fast SSD, Comfortable Keyboard | Use a lightweight IDE, optimize build process, consider using a code profiler to identify performance bottlenecks |
5. Troubleshooting Common PC Performance Issues Based on Specs
Knowing how to check PC specs and understanding their impact on performance is invaluable when troubleshooting common PC issues. By analyzing your system’s specifications, you can pinpoint potential bottlenecks and implement targeted solutions. Let’s explore some common performance issues and how to troubleshoot them based on your PC specs:
5.1. Slow Boot Times
- Possible Cause: Slow HDD, insufficient RAM, too many startup programs.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Storage Device: If you’re still using an HDD, upgrading to an SSD will dramatically improve boot times.
- Check RAM: If you have less than 8GB of RAM, upgrading to 8GB or 16GB can help.
- Disable Startup Programs: Use Task Manager to disable unnecessary startup programs that are slowing down the boot process.
5.2. Slow Application Loading
- Possible Cause: Slow HDD, insufficient RAM, outdated CPU.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Storage Device: As with slow boot times, upgrading to an SSD is the most effective solution.
- Check RAM: Ensure you have enough RAM to run the application smoothly.
- Check CPU: If your CPU is outdated, upgrading to a newer model with more cores and a higher clock speed can help.
5.3. Game Lag and Low Frame Rates
- Possible Cause: Insufficient GPU, outdated graphics drivers, insufficient RAM, outdated CPU.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check GPU: Ensure your graphics card meets the game’s minimum or recommended requirements. If not, upgrading to a more powerful GPU is necessary.
- Update Graphics Drivers: Outdated drivers can cause performance issues. Download and install the latest drivers from the NVIDIA or AMD website.
- Check RAM: Ensure you have enough RAM to run the game smoothly.
- Check CPU: While the GPU is the primary factor, an outdated CPU can also bottleneck gaming performance.
5.4. System Crashes and Blue Screens
- Possible Cause: Overheating, faulty RAM, driver conflicts, operating system errors.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Temperatures: Monitor your CPU and GPU temperatures to ensure they are not overheating. Clean your PC’s fans and heatsinks to improve cooling.
- Test RAM: Use a memory testing tool like Memtest86 to check for faulty RAM modules.
- Update Drivers: Ensure all your drivers are up to date, especially graphics drivers and chipset drivers.
- Check Event Viewer: The Windows Event Viewer can provide clues about the cause of system crashes.
5.5. Slow File Transfers
- Possible Cause: Slow HDD, outdated USB ports, network issues.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Storage Device: If you’re transferring files to or from an HDD, upgrading to an SSD will significantly improve transfer speeds.
- Check USB Ports: Ensure you’re using USB 3.0 or USB 3.1 ports for faster transfer speeds.
- Check Network: If you’re transferring files over a network, ensure your network connection is stable and fast.
Table 4: Troubleshooting PC Issues Based on Specs
| Issue | Possible Cause(s) | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Boot Times | Slow HDD, Insufficient RAM, Startup Programs | Upgrade to SSD, increase RAM, disable unnecessary startup programs |
| Slow Application Loading | Slow HDD, Insufficient RAM, Outdated CPU | Upgrade to SSD, increase RAM, upgrade CPU |
| Game Lag/Low FPS | Insufficient GPU, Outdated Drivers, Insufficient RAM, Outdated CPU | Upgrade GPU, update graphics drivers, increase RAM, upgrade CPU |
| System Crashes/Blue Screen | Overheating, Faulty RAM, Driver Conflicts, OS Errors | Check temperatures, test RAM, update drivers, check Event Viewer |
| Slow File Transfers | Slow HDD, Outdated USB, Network Issues | Upgrade to SSD, use USB 3.0/3.1 ports, check network connection |
By systematically checking your PC specs and following these troubleshooting steps, you can effectively diagnose and resolve common performance issues, ensuring a smooth and efficient computing experience.
6. Maximizing PC Performance Through Upgrades
If checking your PC specifications reveals that your system is falling behind your needs, upgrading specific components can significantly boost performance without requiring a complete system overhaul. However, it’s crucial to choose the right upgrades based on your budget, usage patterns, and existing hardware. Let’s explore some common PC upgrades and their potential impact:
6.1. Upgrading to an SSD
- Impact: The single most impactful upgrade for improving overall system responsiveness. SSDs offer significantly faster boot times, application loading, and file transfer speeds compared to HDDs.
- Considerations: Choose an SSD with sufficient capacity for your operating system, applications, and frequently used files. NVMe SSDs offer even faster performance than SATA SSDs but may require a compatible motherboard.
- Cost: Varies depending on capacity and type (SATA vs NVMe).
6.2. Adding More RAM
- Impact: Improves multitasking performance and allows the system to handle larger datasets without slowdowns.
- Considerations: Check your motherboard’s maximum RAM capacity and supported RAM type (DDR4, DDR5). Ensure the new RAM modules are compatible with your existing RAM in terms of speed and latency.
- Cost: Relatively affordable, but prices vary depending on capacity and speed.
6.3. Upgrading Your Graphics Card
- Impact: Significantly improves gaming performance and accelerates graphics-intensive tasks like video editing and 3D rendering.
- Considerations: Choose a graphics card that meets the requirements of the games or applications you use. Ensure your power supply has sufficient wattage to support the new graphics card.
- Cost: Can be expensive, especially for high-end models.
6.4. Upgrading Your CPU
- Impact: Improves overall system performance, especially for CPU-intensive tasks like video editing, encoding, and compiling code.
- Considerations: Check your motherboard’s CPU compatibility list before upgrading. Upgrading to a newer CPU may require a new motherboard and RAM.
- Cost: Can be expensive, especially for high-end models.
6.5. Upgrading Your Power Supply
- Impact: Provides sufficient power for your components, especially after upgrading to a more power-hungry graphics card or CPU.
- Considerations: Choose a power supply with enough wattage to handle all your components, with some headroom for future upgrades. Look for a power supply with a good efficiency rating (80+ Bronze, Silver, Gold, etc.).
- Cost: Relatively affordable, but important for system stability.
Table 5: PC Upgrade Options and Their Impact
| Upgrade | Impact | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| SSD | Drastically improves boot times, application loading, and file transfer speeds. | Choose sufficient capacity, consider NVMe for faster performance, ensure motherboard compatibility. |
| RAM | Improves multitasking, allows handling of larger datasets. | Check motherboard’s maximum capacity and supported type, ensure compatibility with existing RAM. |
| Graphics Card | Significantly improves gaming performance and accelerates graphics-intensive tasks. | Choose a card that meets your application needs, ensure sufficient power supply wattage, check case compatibility. |
| CPU | Improves overall system performance, especially for CPU-intensive tasks. | Check motherboard compatibility, may require new motherboard and RAM, consider TDP and cooling requirements. |
| Power Supply | Provides sufficient power for components, especially after upgrades. | Choose sufficient wattage with headroom, look for good efficiency rating, ensure connectors match component requirements. |
Before making any upgrades, research compatibility, read reviews, and compare prices to ensure you’re getting the best value for your money.
7. Why Consult with a Doctor of Expertise at HOW.EDU.VN?
While the information provided in this guide can help you understand your PC specifications and troubleshoot common issues, there are times when seeking expert advice is the best course of action. Here’s why consulting with a Doctor of Expertise at HOW.EDU.VN can be invaluable:
- In-Depth Analysis: A Doctor of Expertise can provide a more thorough analysis of your PC specifications and identify subtle bottlenecks that may be difficult for a non-expert to detect.
- Personalized Recommendations: Based on your specific needs and usage patterns, a Doctor of Expertise can recommend the most effective upgrades and optimizations for your system.
- Troubleshooting Complex Issues: If you’re experiencing persistent PC problems that you can’t resolve on your own, a Doctor of Expertise can provide advanced troubleshooting and diagnostic services.
- Compatibility Assurance: A Doctor of Expertise can ensure that any upgrades you’re considering are compatible with your existing hardware and will work together seamlessly.
- Time and Cost Savings: By getting expert advice upfront, you can avoid costly mistakes and ensure that you’re making the most of your upgrade budget.
At HOW.EDU.VN, we have a team of experienced Doctors of Expertise who can provide personalized guidance and support for all your PC-related needs. Our experts can help you:
- Choose the right components for your specific needs.
- Optimize your system for maximum performance.
- Troubleshoot complex PC issues.
- Ensure compatibility between hardware and software.
Don’t waste time and money on guesswork. Contact a Doctor of Expertise at HOW.EDU.VN today and get the expert advice you need to maximize your PC’s performance and longevity.
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let our team of over 100 renowned Doctors guide you to the perfect PC setup for your unique requirements.
8. Staying Updated on PC Technology
The world of PC technology is constantly evolving, with new components, standards, and software being released regularly. Staying updated on these advancements is essential for making informed decisions about your PC and maximizing its performance over time. Here are some tips for staying up-to-date:
- Read Tech News and Reviews: Follow reputable tech websites, blogs, and publications to stay informed about the latest PC hardware and software releases.
- Watch Tech YouTube Channels: Many tech enthusiasts and experts create YouTube videos reviewing new products, providing tutorials, and discussing industry trends.
- Participate in Online Forums and Communities: Engage with other PC users in online forums and communities to share knowledge, ask questions, and learn from others’ experiences.
- Attend Tech Conferences and Events: Attending tech conferences and events can provide valuable insights into the latest PC technologies and allow you to network with industry professionals.
By staying informed about PC technology, you can make smarter decisions about upgrades, optimizations, and troubleshooting, ensuring that your system remains up-to-date and performs at its best for years to come.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Checking PC Specs
Here are some frequently asked questions about checking PC specifications:
- Why is it important to check my PC specs?
- Checking your PC specs is important for ensuring software compatibility, optimizing performance, troubleshooting issues, and making informed upgrade decisions.
- How do I check my PC specs in Windows?
- You can check your PC specs using System Information, Windows Settings, Task Manager, DirectX Diagnostic Tool (DxDiag), Command Prompt, or PowerShell.
- What are the key PC components I should be aware of?
- The key PC components include the CPU, GPU, RAM, and storage devices (SSD/HDD).
- How do I know if my PC meets the requirements for a specific game or application?
- Compare your PC specs to the minimum and recommended requirements listed on the game or application’s website.
- What should I do if my PC doesn’t meet the requirements for a game or application?
- Consider upgrading the relevant components, such as the GPU, RAM, or CPU.
- How often should I check my PC specs?
- You should check your PC specs whenever you’re experiencing performance issues, considering upgrading your hardware, or installing new software.
- Can I check my PC specs on a Mac?
- Yes, you can check your PC specs on a Mac by going to the Apple menu and selecting “About This Mac.”
- What is the difference between RAM and VRAM?
- RAM (Random Access Memory) is used by the CPU for general-purpose tasks, while VRAM (Video RAM) is used by the GPU for rendering images and videos.
- What is the difference between an SSD and an HDD?
- SSDs (Solid State Drives) use flash memory to store data, while HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) use spinning platters. SSDs are significantly faster than HDDs.
- Where can I get expert advice on PC upgrades and optimization?
- You can consult with a Doctor of Expertise at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized guidance and support.
10. Conclusion: Empowering You with Knowledge of Your PC
Understanding how to check PC specs is a fundamental skill for any computer user. It empowers you to make informed decisions, troubleshoot problems, and optimize your system for peak performance. By utilizing the methods and information provided in this guide, you can take control of your PC and ensure that it meets your specific needs and expectations.
However, remember that the world of PC technology is vast and complex. If you ever encounter challenges that you can’t resolve on your own, don’t hesitate to seek expert advice from a Doctor of Expertise at HOW.EDU.VN. Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to helping you get the most out of your PC and ensuring a smooth and efficient computing experience.
Ready to optimize your PC and unlock its full potential?
- Visit how.edu.vn today to learn more about our services and connect with a Doctor of Expertise.
- **Contact us at +1 (310) 555-12