Are you struggling with How To Fall Asleep Fast? HOW.EDU.VN offers expert guidance on quick sleep solutions, providing strategies grounded in research and practical techniques. Discover how to achieve restful sleep quickly, addressing insomnia and improving sleep quality with our easy-to-follow tips and expert advice.
1. Understanding the Science of Sleep: Why Can’t I Fall Asleep?
Understanding why you can’t fall asleep is the first step toward finding a solution. The process of falling asleep is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including your body’s natural circadian rhythm, environmental cues, and your overall physical and mental state.
1.1. Circadian Rhythm and Sleep-Wake Cycle
Your circadian rhythm is essentially your body’s internal clock, regulating various physiological processes over a roughly 24-hour cycle. This includes the sleep-wake cycle, hormone release, body temperature, and more.
- What it is: The circadian rhythm is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours.
- How it works: Light exposure, especially in the morning, helps to synchronize the circadian rhythm. Darkness triggers the release of melatonin, a hormone that promotes sleepiness.
- Disruptions: Modern lifestyles, including shift work, frequent travel across time zones (jet lag), and exposure to artificial light at night, can disrupt the circadian rhythm.
1.2. Factors Affecting Sleep Onset
Several factors can influence how quickly you fall asleep, including lifestyle habits, mental health, and environmental conditions.
- Stress and Anxiety: Elevated levels of stress hormones like cortisol can make it difficult to relax and fall asleep.
- Caffeine and Alcohol: These substances can interfere with the sleep cycle, either by stimulating alertness (caffeine) or disrupting sleep later in the night (alcohol).
- Screen Time: The blue light emitted from electronic devices can suppress melatonin production, delaying sleep onset.
- Room Environment: Factors such as room temperature, noise levels, and light exposure can all impact sleep quality.
1.3. Medical Conditions and Sleep Disorders
In some cases, difficulty falling asleep may be a symptom of an underlying medical condition or sleep disorder.
- Insomnia: Characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or both, despite having the opportunity to sleep.
- Sleep Apnea: A condition in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, leading to fragmented sleep.
- Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): A neurological disorder that causes an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations.
- Chronic Pain: Persistent pain can make it difficult to find a comfortable sleeping position and can disrupt sleep.
Understanding these factors can help you identify potential areas for improvement and tailor your approach to falling asleep faster. If you suspect an underlying medical condition or sleep disorder, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment options.
2. Immediate Techniques: How to Fall Asleep in 10, 60, or 120 Seconds?
While it’s unlikely to fall asleep instantly, certain techniques can help you relax and prepare your body for sleep, potentially shortening the time it takes to drift off.
2.1. The 4-7-8 Breathing Technique (10 Seconds)
This breathing exercise can help calm your nervous system and promote relaxation, potentially helping you fall asleep faster.
-
What it is: A breathing technique developed by Dr. Andrew Weil, based on ancient yoga practices.
-
How it works: It involves controlling your breath to slow your heart rate and quiet your mind.
-
How to do it:
- Exhale completely through your mouth, making a whooshing sound.
- Close your mouth and inhale quietly through your nose for a count of 4.
- Hold your breath for a count of 7.
- Exhale completely through your mouth, making a whooshing sound for a count of 8.
- Repeat steps 1-4 at least four times.
2.2. Progressive Muscle Relaxation (60 Seconds)
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) is a technique that involves tensing and releasing different muscle groups in the body to promote relaxation.
-
What it is: A relaxation technique that involves tensing and releasing different muscle groups.
-
How it works: By focusing on the physical sensations of tension and relaxation, PMR can help reduce overall body tension and promote calmness.
-
How to do it:
- Lie down in a comfortable position.
- Start with your toes and tense the muscles as tightly as possible for 5-10 seconds.
- Release the tension suddenly and focus on the feeling of relaxation for 20-30 seconds.
- Repeat the process with each muscle group, working your way up your body (calves, thighs, buttocks, abdomen, chest, arms, shoulders, neck, face).
2.3. Mental Exercises: Paradoxical Intention and Visualization (120 Seconds)
If physical techniques don’t work, engaging your mind with specific mental exercises can help distract you from racing thoughts and promote sleep.
- Paradoxical Intention: Instead of trying to fall asleep, intentionally try to stay awake. This can reduce performance anxiety and help you relax. Research from 2021 suggests that paradoxical intention (PI) may help reduce sleep performance anxiety and increase the perception of feeling well-rested after sleep.
- Visualization: Imagine a calm and peaceful place, engaging all your senses. For example, visualize a beach with the sound of waves, the smell of salt air, and the warmth of the sun on your skin. In a 2002 study from the University of Oxford, researchers found that people who engaged in “imagery distraction” fell asleep faster than those who had general distraction or no instructions.
3. Optimizing Your Sleep Environment: Creating a Sleep Sanctuary
Creating a conducive sleep environment is crucial for falling asleep quickly and enjoying restful sleep.
3.1. Temperature, Darkness, and Noise
Optimizing these three factors can significantly impact your ability to fall asleep.
- Temperature: Keep your bedroom cool, ideally between 60-67°F (15-19°C). Research shows that a cooler room temperature is conducive to better sleep.
- Darkness: Make sure your room is as dark as possible. Use blackout curtains or an eye mask to block out light. Darkness signals the release of melatonin, a hormone that promotes sleep.
- Noise: Minimize noise in your bedroom. Use earplugs or a white noise machine to block out disruptive sounds. White noise can help mask distracting noises and create a more consistent sound environment.
3.2. Choosing the Right Bedding
Your mattress, pillows, and bedding can all affect your sleep quality.
- Mattress: Choose a mattress that provides adequate support and comfort. Consider your sleeping position and preferences when selecting a mattress.
- Pillows: Use pillows that support your neck and head in a comfortable position. Different pillow types are available for different sleeping positions.
- Bedding: Choose breathable and comfortable bedding materials. Natural fibers like cotton, linen, or bamboo can help regulate body temperature and prevent overheating.
3.3. Decluttering Your Bedroom
A cluttered bedroom can be visually stimulating and create a sense of unease, making it difficult to relax.
- Minimize Clutter: Keep your bedroom tidy and free from unnecessary items.
- Create a Relaxing Atmosphere: Use calming colors, soft lighting, and soothing decor to create a peaceful atmosphere.
- Remove Electronics: Avoid having electronic devices like TVs, computers, and smartphones in your bedroom.
4. Lifestyle Adjustments: Long-Term Habits for Better Sleep
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can have a significant impact on your ability to fall asleep quickly and consistently.
4.1. Consistent Sleep Schedule
Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends, helps regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Benefits: A consistent sleep schedule helps synchronize your circadian rhythm, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up at the same time each day.
- Tips: Establish a regular sleep schedule and stick to it as closely as possible. Avoid sleeping in on weekends, as this can disrupt your sleep cycle.
4.2. Diet and Exercise
Your diet and exercise habits can both impact your sleep quality.
- Diet: Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime. Eating a balanced diet and staying hydrated throughout the day can also improve sleep.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve sleep, but avoid intense workouts close to bedtime. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
4.3. Managing Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can significantly interfere with sleep.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to reduce stress and promote relaxation.
- Mindfulness: Engage in mindfulness practices to focus on the present moment and reduce racing thoughts.
- Journaling: Write down your thoughts and feelings before bed to clear your mind and reduce anxiety.
5. Pre-Sleep Routine: Preparing Your Mind and Body for Sleep
Establishing a relaxing pre-sleep routine can help signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
5.1. Creating a Relaxing Routine
Your pre-sleep routine should be calming and enjoyable, helping you to relax and transition from wakefulness to sleep.
- Warm Bath or Shower: Taking a warm bath or shower before bed can help relax your muscles and lower your body temperature, promoting sleepiness.
- Reading: Read a book or magazine (avoid screens) to help quiet your mind and reduce stress.
- Listening to Music: Listen to calming music or nature sounds to promote relaxation.
5.2. Avoiding Screens Before Bed
The blue light emitted from electronic devices can suppress melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep.
- Limit Screen Time: Avoid using electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, and computers for at least an hour before bed.
- Use Blue Light Filters: If you must use electronic devices before bed, use blue light filters to reduce the amount of blue light emitted.
5.3. Light Stretching or Yoga
Gentle stretching or yoga can help release tension in your muscles and promote relaxation.
- Benefits: Light stretching can help improve circulation, reduce muscle tension, and promote relaxation.
- Tips: Focus on gentle stretches that target major muscle groups. Avoid strenuous exercises close to bedtime.
6. Advanced Techniques and Tools: When Basic Methods Aren’t Enough
If basic techniques and lifestyle adjustments aren’t enough to help you fall asleep quickly, consider exploring some advanced techniques and tools.
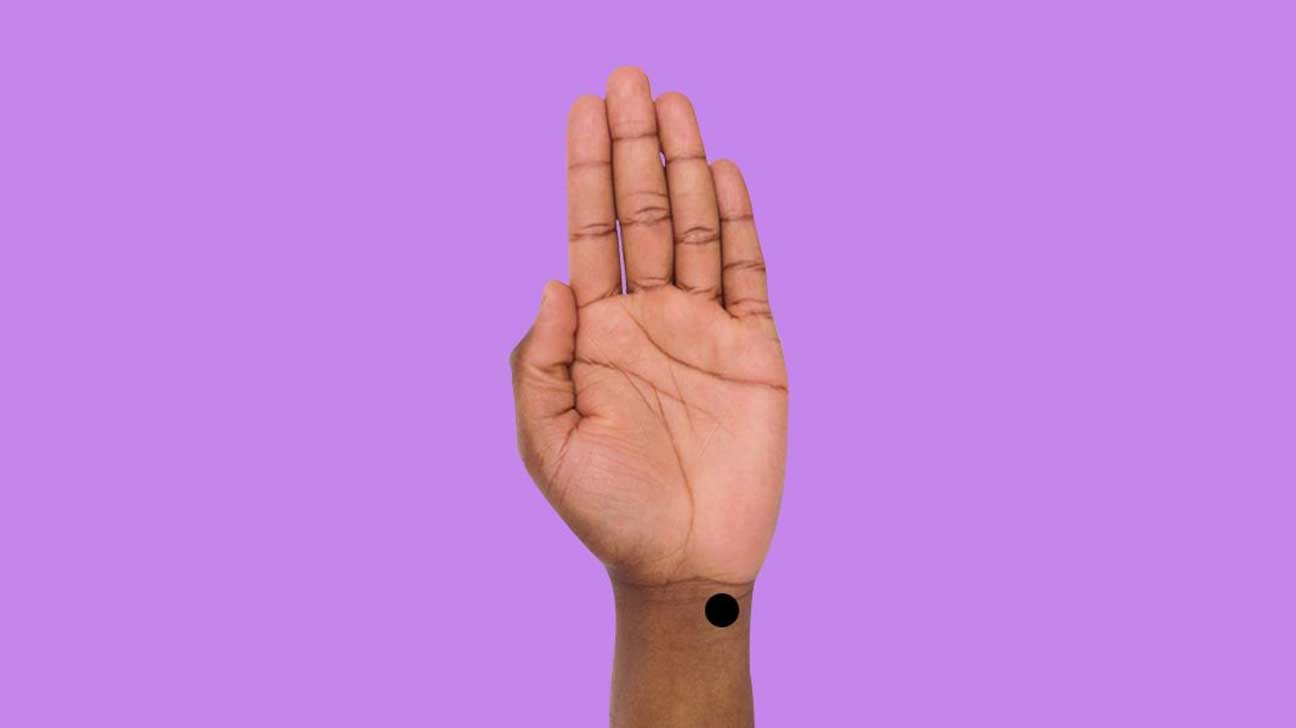
6.1. Acupressure for Sleep
Acupressure involves applying pressure to specific points on the body to promote relaxation and improve sleep.
-
What it is: A traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves applying pressure to specific points on the body. A 2019 meta-analysis suggests that acupressure may slightly decrease the time you fall asleep. It may also increase your sleep efficiency and duration. However, there’s limited research to determine whether acupressure is beneficial.
-
How it works: Acupressure is believed to stimulate the release of endorphins, which can help reduce pain and promote relaxation.
-
Specific Pressure Points:
- Spirit Gate: Located on the wrist, on the pinky side, in the small hollow space under your palm. Gently apply pressure in a circular or up-and-down movement for 2 to 3 minutes.
- Inner Frontier Gate: Located on the palm-facing side of the wrist, three finger-widths down from the wrist crease, between the two tendons. With your thumb, apply a steady downward pressure between the two tendons.
- Wind Pool: Located at the base of the skull, where the neck and head connect. Interlock your fingers and position your thumbs at the base of your skull, applying deep and firm pressure.
6.2. White Noise Machines and Apps
White noise can help mask distracting sounds and create a more consistent sound environment, promoting sleep.
- What it is: A sound that contains all frequencies at equal intensity.
- How it works: White noise can help mask distracting sounds, creating a more consistent and calming sound environment.
- Options: White noise machines, apps, and online sound generators are available.
6.3. Sleep Tracking Apps and Devices
These tools can help you monitor your sleep patterns and identify potential issues.
- What they are: Apps and devices that track your sleep patterns, including sleep duration, sleep stages, and sleep quality.
- How they work: These tools use sensors to monitor your movements, heart rate, and breathing patterns during sleep.
- Benefits: Sleep tracking can help you identify potential sleep problems, such as insomnia or sleep apnea, and track the effectiveness of different sleep strategies.
7. Addressing Underlying Issues: When to Seek Professional Help
If you consistently struggle to fall asleep, it may be a sign of an underlying medical condition or sleep disorder.
7.1. Identifying Potential Sleep Disorders
Common sleep disorders include insomnia, sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, and narcolepsy.
- Insomnia: Characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or both.
- Sleep Apnea: A condition in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep.
- Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): A neurological disorder that causes an irresistible urge to move the legs.
- Narcolepsy: A neurological disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate the sleep-wake cycle.
7.2. Consulting a Sleep Specialist
A sleep specialist can help diagnose and treat sleep disorders, providing personalized recommendations for improving sleep.
- Benefits: A sleep specialist can conduct a thorough evaluation of your sleep patterns and identify any underlying issues.
- What to Expect: You may be asked to keep a sleep diary, undergo a sleep study (polysomnography), or complete questionnaires about your sleep habits.
7.3. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
CBT-I is a structured program that helps people with insomnia identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors that interfere with sleep.
- What it is: A type of therapy that focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to insomnia.
- How it works: CBT-I typically involves sleep hygiene education, stimulus control, sleep restriction, and cognitive restructuring.
- Benefits: CBT-I is considered the first-line treatment for chronic insomnia and has been shown to be more effective than sleep medications in the long term.
8. The Role of Supplements and Medications: Proceed with Caution
While some supplements and medications can help promote sleep, it’s important to use them cautiously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
8.1. Melatonin
Melatonin is a hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and is often used as a sleep aid.
- What it is: A hormone produced by the pineal gland that regulates the sleep-wake cycle.
- How it works: Melatonin supplements can help regulate the circadian rhythm and promote sleepiness.
- Dosage: The recommended dosage of melatonin is typically between 0.5 and 5 mg, taken 30-60 minutes before bed.
8.2. Magnesium
Magnesium is a mineral that plays a role in many bodily functions, including sleep.
- What it is: A mineral that is essential for many bodily functions, including nerve and muscle function.
- How it works: Magnesium can help relax muscles and calm the nervous system, promoting sleep.
- Dosage: The recommended dosage of magnesium for sleep is typically between 200 and 400 mg, taken before bed.
8.3. Prescription Sleep Medications
Prescription sleep medications can be effective for treating insomnia, but they also carry risks and side effects.
- Types: Common prescription sleep medications include benzodiazepines, non-benzodiazepines, and melatonin receptor agonists.
- Risks: Prescription sleep medications can cause side effects such as daytime drowsiness, dizziness, and dependence.
- Important Considerations: Use prescription sleep medications only under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
9. Debunking Sleep Myths: Separating Fact from Fiction
It’s important to separate fact from fiction when it comes to sleep.
9.1. Common Misconceptions about Sleep
- Myth: You can “catch up” on sleep on weekends.
- Fact: While sleeping in on weekends can help you feel more rested, it can also disrupt your sleep cycle, making it harder to fall asleep during the week.
- Myth: Alcohol helps you sleep better.
- Fact: Alcohol may help you fall asleep faster, but it disrupts your sleep later in the night, leading to fragmented sleep.
- Myth: Everyone needs 8 hours of sleep.
- Fact: The amount of sleep needed varies from person to person. Most adults need between 7 and 9 hours of sleep per night.
9.2. Relying on Experts for Accurate Information
Consulting with sleep specialists and relying on evidence-based information can help you make informed decisions about your sleep.
- HOW.EDU.VN: Provides access to experts in various fields, including sleep science, offering personalized advice and support.
- Sleep Research: Stay informed about the latest research on sleep and sleep disorders to make informed decisions about your sleep health.
10. Real-Life Examples: Success Stories and Case Studies
Learning from the experiences of others can provide valuable insights and motivation.
10.1. Individuals Who Improved Their Sleep with Lifestyle Changes
- Case Study 1: A 45-year-old professional who struggled with insomnia for years was able to improve her sleep by establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing pre-sleep routine, and practicing relaxation techniques.
- Case Study 2: A 30-year-old shift worker who had difficulty falling asleep was able to improve his sleep by using blackout curtains, a white noise machine, and practicing the 4-7-8 breathing technique.
10.2. The Impact of Professional Guidance on Sleep Quality
Seeking professional guidance from sleep specialists and therapists can have a significant impact on sleep quality.
- Expert Advice: Experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide personalized recommendations for improving sleep based on your individual needs and circumstances.
11. Tailoring Your Approach: Finding What Works for You
The most effective approach to falling asleep quickly is to tailor your strategies to your individual needs and preferences.
11.1. Experimenting with Different Techniques
Try different techniques and strategies to see what works best for you.
- Keep a Sleep Diary: Track your sleep patterns and experiment with different techniques to see what improves your sleep.
- Be Patient: It may take time to find the right combination of strategies that works for you.
11.2. Customizing Your Sleep Environment
Adjust your sleep environment to create a comfortable and relaxing space that promotes sleep.
- Personalize Your Routine: Create a pre-sleep routine that you enjoy and that helps you relax.
12. The Future of Sleep Science: Emerging Trends and Technologies
The field of sleep science is constantly evolving, with new trends and technologies emerging all the time.
12.1. Advancements in Sleep Tracking Technology
- Wearable Devices: New wearable devices are able to track sleep stages with greater accuracy.
- Smart Beds: Smart beds are able to adjust firmness, temperature, and other factors to optimize sleep.
12.2. Innovative Therapies for Sleep Disorders
- Digital CBT-I: Digital CBT-I programs are making this effective therapy more accessible to people with insomnia.
- New Medications: New medications for sleep disorders are being developed that have fewer side effects.
By staying informed about the latest advancements in sleep science, you can take advantage of new technologies and therapies to improve your sleep.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Falling Asleep Fast
Here are some frequently asked questions about falling asleep fast.
- What is the fastest way to fall asleep? The fastest way to fall asleep involves using techniques like the 4-7-8 breathing method or progressive muscle relaxation to quickly calm your mind and body.
- How can I fall asleep in 5 minutes? While falling asleep in 5 minutes may be challenging, techniques like deep breathing exercises, visualizing a calm place, or using white noise can help expedite the process.
- Why can’t I fall asleep even when I’m tired? The inability to fall asleep when tired can be due to various factors, including stress, anxiety, an irregular sleep schedule, exposure to blue light, or underlying medical conditions.
- What are some natural remedies to help me fall asleep? Natural remedies include melatonin supplements, magnesium, chamomile tea, and valerian root, all known for their sleep-promoting properties.
- How does diet affect my ability to fall asleep? Diet significantly impacts sleep. Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol before bed. Eating a balanced diet with complex carbohydrates and lean proteins can promote better sleep.
- What is the ideal room temperature for sleeping? The ideal room temperature for sleeping is between 60-67°F (15-19°C), as a cooler environment helps regulate your body temperature and promotes sleepiness.
- How does exercise affect my sleep? Regular exercise can improve sleep quality. However, avoid intense workouts close to bedtime, as they can be stimulating and make it harder to fall asleep.
- When should I seek professional help for my sleep problems? You should seek professional help if you consistently struggle to fall asleep, stay asleep, or experience symptoms of a sleep disorder, such as sleep apnea or restless legs syndrome.
- What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)? CBT-I is a structured program that helps people with insomnia identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors that interfere with sleep.
- How do sleep tracking apps and devices work? Sleep tracking apps and devices use sensors to monitor your movements, heart rate, and breathing patterns during sleep, providing data on sleep duration, sleep stages, and sleep quality.
14. Call to Action: Transform Your Sleep with Expert Guidance
Are you tired of counting sheep and struggling to fall asleep? At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the frustration and impact of poor sleep on your daily life. Our team of over 100 world-renowned Ph.D. experts is dedicated to providing you with personalized guidance and solutions to help you achieve restful, rejuvenating sleep.
Don’t let sleepless nights hold you back any longer. Contact our experts at HOW.EDU.VN today for a consultation and take the first step towards transforming your sleep and your life.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: how.edu.vn
Let us help you unlock the secret to falling asleep fast and enjoying the countless benefits of consistent, quality sleep. Your journey to better sleep starts now!