Snoring can disrupt your sleep and affect your partner’s rest, but understanding How To Not Snore involves addressing underlying causes and implementing effective strategies for peaceful nights with snoring remedies. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading experts who can provide personalized advice and solutions tailored to your specific needs, helping you discover sleep aids for snoring. From lifestyle adjustments to advanced medical interventions, we offer insights into achieving quieter, healthier sleep, and exploring the best ways to stop snoring.
1. What Causes Snoring and Why Should You Address It?
Snoring occurs when air flows past relaxed tissues in your throat, causing them to vibrate as you breathe. While occasional snoring might seem harmless, chronic snoring can indicate underlying health issues.
Snoring happens because the muscles in your throat and tongue relax during sleep. This relaxation causes the tissues to become floppy, narrowing your airway. As air passes through this constricted space, it causes the tissues to vibrate, resulting in the sound we know as snoring.
Here’s why addressing snoring is important:
- Underlying Health Conditions: Snoring can be a symptom of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a serious sleep disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts.
- Relationship Strain: Loud snoring can disrupt your partner’s sleep, leading to frustration and potential relationship issues.
- Daytime Fatigue: Disrupted sleep, even if you don’t fully wake up, can cause daytime sleepiness, affecting your performance and overall well-being.
- Increased Health Risks: OSA, linked to snoring, increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart problems, and stroke.
1.1 What are the main factors contributing to snoring?
Several factors can contribute to snoring, including:
- Anatomy: The structure of your mouth, nose, and throat can play a significant role. A narrow airway, enlarged tonsils or adenoids, or a deviated septum can all contribute to snoring.
- Weight: Excess weight, particularly around the neck, can narrow the airway.
- Alcohol and Medications: Alcohol and certain medications, like sedatives, relax the muscles in your throat, making snoring more likely.
- Sleep Position: Sleeping on your back can cause your tongue and soft palate to collapse against the back of your throat, narrowing the airway.
- Nasal Congestion: Colds, allergies, or sinus infections can cause nasal congestion, forcing you to breathe through your mouth, which increases the likelihood of snoring.
- Age: As you age, the muscles in your throat become weaker, increasing the risk of snoring.
- Genetics: Snoring can run in families, suggesting a genetic component.
1.2 Identifying the Type of Snoring
There are different types of snoring, each with its own causes and potential treatments:
- Simple Snoring: This is occasional snoring that doesn’t disrupt sleep or cause daytime symptoms.
- Habitual Snoring: This is regular snoring that occurs more than three nights a week but isn’t associated with OSA.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most serious type of snoring, characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep. OSA is associated with significant health risks and requires medical intervention.
Consulting with experts at HOW.EDU.VN can help you determine the type of snoring you have and the best course of action.
2. How Can Lifestyle Changes Help You Stop Snoring?
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce or eliminate snoring:
2.1 Weight Loss
Excess weight, especially around the neck, can narrow the airway and contribute to snoring. Losing weight can help open up the airway, reducing the vibrations that cause snoring.
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating.
2.2 Sleep Position
Sleeping on your back can cause your tongue and soft palate to collapse against the back of your throat, narrowing the airway. Sleeping on your side can help keep the airway open.
- Use a Body Pillow: Place a body pillow behind you to prevent rolling onto your back.
- Tennis Ball Trick: Sew a tennis ball into the back of your pajama top to make sleeping on your back uncomfortable.
- Adjustable Bed: Use an adjustable bed to elevate your head and upper body, which can help keep your airway open.
2.3 Avoid Alcohol and Sedatives
Alcohol and sedatives relax the muscles in your throat, making snoring more likely. Avoid these substances, especially close to bedtime.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Avoid drinking alcohol at least two hours before bedtime.
- Talk to Your Doctor: If you take sedatives, talk to your doctor about alternative medications or strategies.
2.4 Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can cause the secretions in your nose and soft palate to become stickier, increasing the likelihood of snoring.
- Drink Plenty of Water: Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day.
- Humidifier: Use a humidifier in your bedroom to keep the air moist.
2.5 Quit Smoking
Smoking irritates the tissues in your throat and nasal passages, leading to inflammation and increased mucus production, which can contribute to snoring.
- Nicotine Replacement Therapy: Consider using nicotine patches, gum, or lozenges to help manage cravings.
- Support Groups: Join a support group or talk to a therapist to help you stay motivated.
- Medications: Talk to your doctor about medications that can help you quit smoking.
2.6 Maintain Good Sleep Hygiene
Establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can improve sleep quality and reduce snoring.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Take a warm bath, read a book, or listen to calming music before bed.
- Comfortable Sleep Environment: Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool.
- Limit Screen Time: Avoid using electronic devices for at least an hour before bed.
 Sleeping position can affect snoring
Sleeping position can affect snoring
3. What are Some Home Remedies for Snoring?
Several home remedies can help alleviate snoring:
3.1 Nasal Strips and Dilators
Nasal strips are adhesive strips that you apply to the bridge of your nose to help open up your nasal passages. Nasal dilators are small devices that you insert into your nostrils to widen them. Both can improve airflow and reduce snoring.
- How They Work: By opening up the nasal passages, nasal strips and dilators reduce resistance to airflow, making it easier to breathe through your nose.
- Effectiveness: These remedies are most effective for people who snore due to nasal congestion or narrow nasal passages.
3.2 Throat Exercises
Strengthening the muscles in your throat can help prevent them from collapsing during sleep, reducing snoring.
- Tongue Slide: Press your tongue against the roof of your mouth and slide it backward. Repeat 20 times.
- Tongue Push: Push your tongue against your teeth. Repeat 20 times.
- Jaw Exercise: Open your mouth and move your jaw to the right, hold for 30 seconds, then move it to the left and hold for 30 seconds. Repeat several times.
- Singing: Singing can strengthen the muscles in your throat and soft palate.
3.3 Elevate Your Head
Raising the head of your bed by about 4 inches can help keep your airway open.
- Adjustable Bed: Use an adjustable bed to elevate your head and upper body.
- Wedges: Place wedges under the head of your mattress to raise it.
3.4 Humidifier
Dry air can irritate the nasal passages and throat, leading to inflammation and increased mucus production, which can contribute to snoring.
- How They Work: Humidifiers add moisture to the air, which can help soothe irritated tissues and reduce congestion.
- Types: There are several types of humidifiers, including cool mist, warm mist, and ultrasonic humidifiers.
3.5 Herbal Remedies
Some people find relief from snoring using herbal remedies like eucalyptus oil, peppermint oil, or honey.
- Eucalyptus Oil: Add a few drops of eucalyptus oil to a humidifier or inhale the steam from a bowl of hot water with eucalyptus oil.
- Peppermint Oil: Use a peppermint oil nasal spray or add a few drops to a humidifier.
- Honey: Mix a tablespoon of honey into a glass of warm water and drink it before bed to soothe the throat.
4. When Should You See a Doctor for Snoring?
While lifestyle changes and home remedies can be effective for many people, it’s important to see a doctor if:
- Loud Snoring: Your snoring is so loud that it disrupts your or your partner’s sleep.
- Daytime Sleepiness: You feel excessively tired during the day, even after getting enough sleep.
- Observed Apnea: Your partner has noticed that you stop breathing during sleep.
- Gasping or Choking: You wake up gasping or choking.
- High Blood Pressure: You have high blood pressure.
- Heart Problems: You have a history of heart problems.
- Headaches: You experience frequent morning headaches.
- Difficulty Concentrating: You have trouble concentrating during the day.
These symptoms may indicate obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a serious condition that requires medical treatment.
5. Medical Treatments for Snoring
If lifestyle changes and home remedies aren’t enough, there are several medical treatments available for snoring:
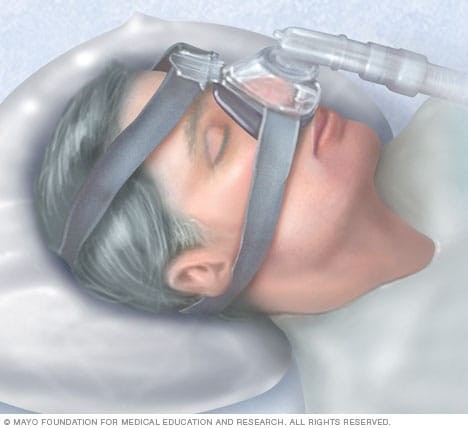
5.1 Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
CPAP is a common treatment for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). It involves wearing a mask over your nose or mouth while you sleep. The mask is connected to a machine that delivers a constant stream of air pressure, keeping your airway open.
- How It Works: CPAP prevents the airway from collapsing during sleep by providing continuous air pressure.
- Effectiveness: CPAP is highly effective for treating OSA and reducing snoring.
- Challenges: Some people find CPAP uncomfortable or have trouble adjusting to the mask and machine.
5.2 Oral Appliances
Oral appliances are custom-fitted mouthpieces that help keep your airway open by bringing your jaw forward or holding your tongue in place.
- Mandibular Advancement Devices (MADs): These devices fit over your upper and lower teeth and push your lower jaw forward.
- Tongue-Retaining Devices (TRDs): These devices hold your tongue in place to prevent it from blocking your airway.
- Effectiveness: Oral appliances can be effective for treating mild to moderate snoring and OSA.
- Side Effects: Possible side effects include jaw pain, dry mouth, and excessive salivation.
5.3 Surgical Options
Several surgical procedures can be used to treat snoring by opening up the airway.
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): This procedure involves removing excess tissue from the throat, including the uvula, soft palate, and tonsils.
- Maxillomandibular Advancement (MMA): This surgery involves moving the upper and lower jaws forward to increase the size of the airway.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): This procedure uses radiofrequency energy to shrink tissues in the soft palate, tongue, or nose.
- Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation: This newer technique involves implanting a device that stimulates the nerve controlling tongue movement, preventing the tongue from blocking the airway.
5.4 Medications
While there are no medications specifically for snoring, certain medications can help treat underlying conditions that contribute to snoring, such as nasal congestion or allergies.
- Nasal Decongestants: These medications can help clear nasal congestion, allowing you to breathe more easily through your nose.
- Antihistamines: These medications can help reduce allergy symptoms that contribute to nasal congestion.
- Nasal Steroid Sprays: These sprays can help reduce inflammation in the nasal passages, improving airflow.
6. Diagnosing Snoring: What to Expect
To properly diagnose your snoring, your doctor will likely conduct a physical exam and ask about your symptoms, medical history, and sleep habits.
6.1 Physical Examination
Your doctor will examine your mouth, nose, and throat to look for any abnormalities that may be contributing to your snoring.
- Mouth and Throat: They will check the size of your tonsils, the position of your soft palate, and the size of your tongue.
- Nose: They will check for nasal congestion, deviated septum, or other structural issues.
6.2 Sleep Study
If your doctor suspects you have obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), they may recommend a sleep study, also known as polysomnography. This test monitors your breathing, heart rate, brain waves, and other vital signs while you sleep.
- In-Lab Sleep Study: This involves spending the night at a sleep center, where you’ll be monitored by trained technicians.
- Home Sleep Study: This involves using a portable monitoring device at home.
6.3 Imaging Tests
In some cases, your doctor may order imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, to get a better look at the structure of your airway.
- X-Rays: These can help identify structural abnormalities in the nose and throat.
- CT Scans: These provide more detailed images of the airway.
- MRIs: These can help identify soft tissue abnormalities in the airway.
7. How Can Experts at HOW.EDU.VN Help?
At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading experts in sleep medicine who can provide personalized advice and solutions for your snoring.
7.1 Personalized Consultations
Our experts can conduct thorough assessments of your snoring, taking into account your medical history, lifestyle, and specific symptoms. They can then develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.
7.2 Access to the Latest Research
Our experts stay up-to-date on the latest research and advancements in sleep medicine, ensuring that you receive the most effective and evidence-based treatments.
7.3 Comprehensive Support
We provide ongoing support and guidance to help you manage your snoring and improve your sleep quality. Our experts can answer your questions, address your concerns, and help you stay motivated.
7.4 Convenient Access
Through HOW.EDU.VN, you can access expert advice from the comfort of your own home, saving you time and travel costs.
8. FAQ: Addressing Common Concerns About Snoring
8.1 Is snoring always a sign of a serious health problem?
Not always. Simple snoring is common and doesn’t usually indicate a serious health problem. However, if your snoring is loud, frequent, or accompanied by daytime sleepiness, it could be a sign of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which requires medical attention.
8.2 Can children snore?
Yes, children can snore. Snoring in children can be caused by enlarged tonsils or adenoids, allergies, or other factors. If your child snores regularly, it’s important to talk to their doctor to rule out any underlying health problems.
8.3 How can I tell if my snoring is affecting my health?
If you experience daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, difficulty concentrating, or high blood pressure, your snoring may be affecting your health. It’s important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
8.4 Are there any over-the-counter devices that can help with snoring?
Yes, there are several over-the-counter devices that can help with snoring, such as nasal strips, nasal dilators, and anti-snoring mouthpieces. However, it’s important to talk to your doctor before using any of these devices to make sure they are appropriate for you.
8.5 Can allergies cause snoring?
Yes, allergies can cause nasal congestion and inflammation, which can contribute to snoring. Managing your allergies with medications or other treatments can help reduce snoring.
8.6 Is surgery a common treatment for snoring?
Surgery is not usually the first-line treatment for snoring. It’s typically reserved for cases where other treatments have failed or when there are structural abnormalities in the airway.
8.7 Can snoring affect my relationship?
Yes, loud snoring can disrupt your partner’s sleep, leading to frustration and relationship problems. Addressing your snoring can improve your relationship and overall quality of life.
8.8 What is the best sleep position to avoid snoring?
Sleeping on your side is generally the best sleep position to avoid snoring, as it helps keep your airway open.
8.9 How can I convince my partner to see a doctor about their snoring?
Express your concerns in a supportive and non-judgmental way. Explain how their snoring is affecting your sleep and overall well-being. Offer to go with them to the doctor’s appointment for support.
8.10 Can weight loss really help with snoring?
Yes, weight loss can significantly reduce or eliminate snoring, especially if you are overweight or obese. Excess weight around the neck can narrow the airway, contributing to snoring.
9. Call to Action
Are you tired of sleepless nights due to snoring? Do you want to find effective solutions and personalized advice from leading experts? HOW.EDU.VN connects you with over 100 renowned PhDs ready to address your concerns and provide tailored treatment plans. Don’t let snoring disrupt your life any longer. Contact us today for a consultation and start your journey towards quieter, healthier sleep.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Take the first step towards a better night’s sleep and a healthier you with how.edu.vn. Let our experts guide you on the path to stop snoring naturally and discover the best snoring solutions available.