Mountain Dew caffeine content is a topic of interest for many, especially those looking for an energy boost or monitoring their caffeine intake. At HOW.EDU.VN, we delve into the specifics of how much caffeine you’re really getting in your favorite Mountain Dew beverage, providing expert insights and comparisons to other caffeinated drinks. Understanding the caffeine levels in Mountain Dew can help you make informed choices about your consumption habits. Curious about caffeine side effects or the caffeine content in various beverages? Read on to discover more.
1. Understanding Caffeine Levels in Mountain Dew
Mountain Dew is known for its distinctive citrus flavor and energizing effects, largely attributed to its caffeine content. However, the exact caffeine amount can vary depending on the specific Mountain Dew product. To help you navigate this, let’s break down the caffeine levels in popular Mountain Dew varieties.
1.1. Caffeine Content in Various Mountain Dew Drinks
Different Mountain Dew flavors and formulations contain varying amounts of caffeine. Here’s a detailed look at some of the most popular options:
- Regular Mountain Dew: A 12-ounce can contains approximately 54 mg of caffeine. This is the standard benchmark for many comparisons.
- Diet Mountain Dew: This version has the same caffeine content as the regular one, around 54 mg per 12-ounce can.
- Mountain Dew Code Red: Known for its cherry flavor, it also contains about 54 mg of caffeine in a 12-ounce can.
- Mountain Dew Voltage: With a mix of raspberry citrus flavor, Voltage matches the others with 54 mg of caffeine per 12-ounce can.
- Mountain Dew Kickstart: This energy drink variant contains significantly more caffeine, approximately 92 mg per 16-ounce can.
- Mountain Dew Game Fuel: Marketed towards gamers, this variant can contain around 90-180 mg of caffeine per 16-ounce can, depending on the specific flavor and formulation.
- Mountain Dew Zero Sugar: Similar to Diet Mountain Dew, the zero-sugar version contains about 54 mg of caffeine per 12-ounce can.
It’s essential to check the label for the most accurate information, as caffeine content can sometimes change with new formulations or limited-edition flavors.
1.2. Factors Influencing Caffeine Levels
Several factors can influence the caffeine levels in Mountain Dew:
- Formulation Changes: Manufacturers may adjust the caffeine content in response to consumer preferences or regulatory requirements.
- Production Processes: The specific methods used to extract and add caffeine can result in slight variations in the final product.
- Ingredient Sourcing: Differences in the caffeine source (e.g., synthetic caffeine vs. caffeine from coffee beans) can affect the final caffeine level.
Staying informed about these factors can help you better understand and manage your caffeine intake from Mountain Dew.
2. Mountain Dew Caffeine Compared to Other Beverages
To put Mountain Dew’s caffeine content into perspective, it’s helpful to compare it to other popular caffeinated beverages like coffee, energy drinks, and other sodas. This comparison will give you a clearer understanding of where Mountain Dew stands in terms of caffeine levels.
2.1. Mountain Dew vs. Coffee
Coffee is a well-known source of caffeine, and it’s often the go-to beverage for those needing a significant energy boost. Here’s how Mountain Dew compares:
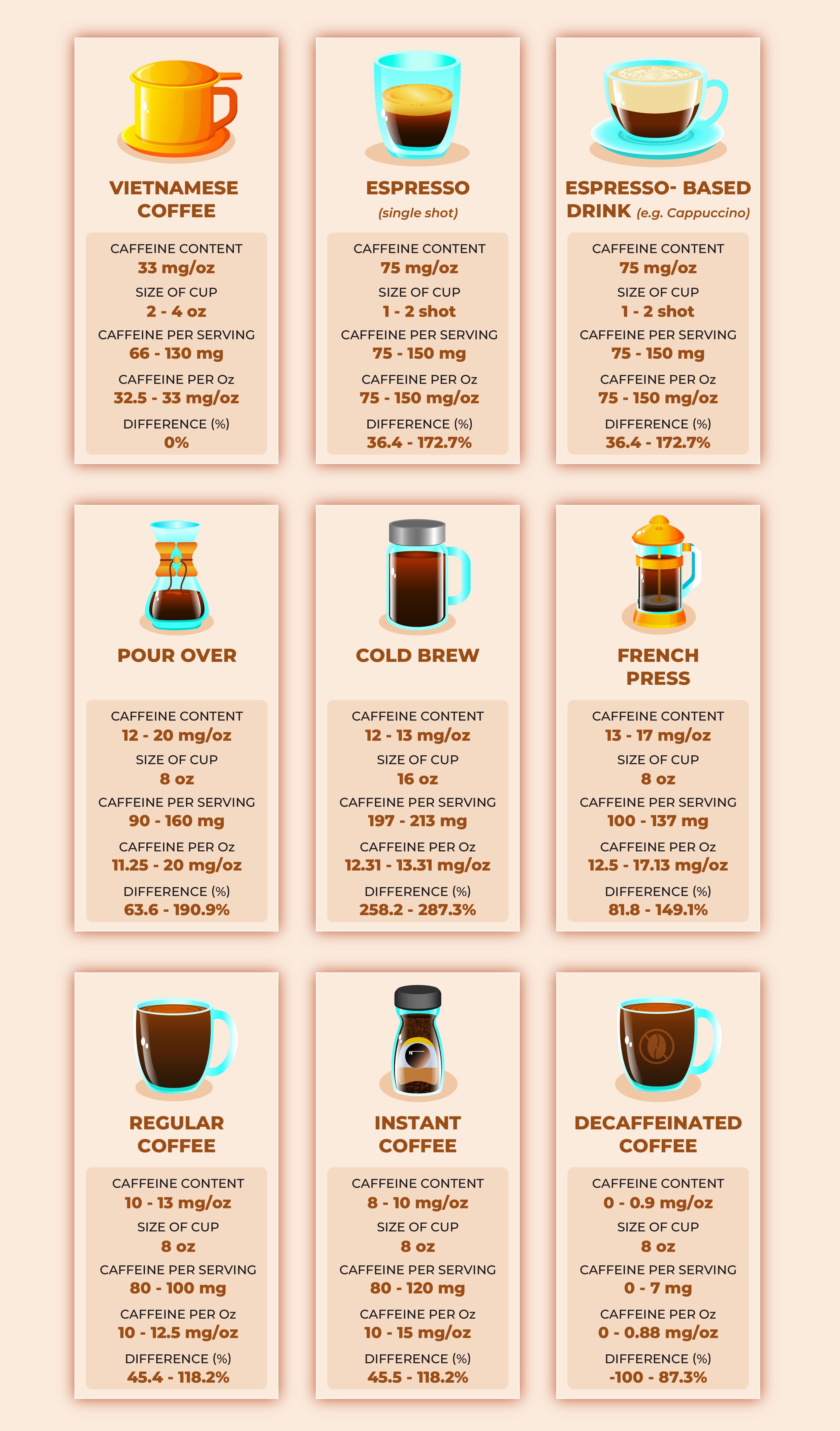
- Coffee: An average 8-ounce cup of coffee contains about 80-100 mg of caffeine. This means that coffee generally has a higher caffeine content than Mountain Dew per serving.
- Mountain Dew: A 12-ounce can of Mountain Dew contains approximately 54 mg of caffeine. To get the same caffeine dose as a cup of coffee, you would need to drink more than 1.5 cans of Mountain Dew.
The caffeine content in coffee can also vary widely depending on the type of coffee beans, brewing method, and serving size. For example, a shot of espresso can contain around 63 mg of caffeine, while a large brewed coffee can have upwards of 200 mg.
2.2. Mountain Dew vs. Energy Drinks
Energy drinks are specifically designed to provide a substantial energy boost, and they often contain much higher levels of caffeine compared to sodas like Mountain Dew.
- Typical Energy Drinks: Many energy drinks contain between 100-300 mg of caffeine per serving (usually around 16 ounces). Popular brands like Red Bull, Monster, and Rockstar often fall within this range.
- Mountain Dew: A 16-ounce can of Mountain Dew Kickstart, an energy drink variant, contains about 92 mg of caffeine, which is still lower than many other energy drinks on the market.
If you’re looking for a significant energy boost, energy drinks might seem like the better option, but it’s crucial to consider the other ingredients they contain, such as high levels of sugar and artificial additives.
2.3. Mountain Dew vs. Other Sodas
Compared to other sodas, Mountain Dew generally has a higher caffeine content.
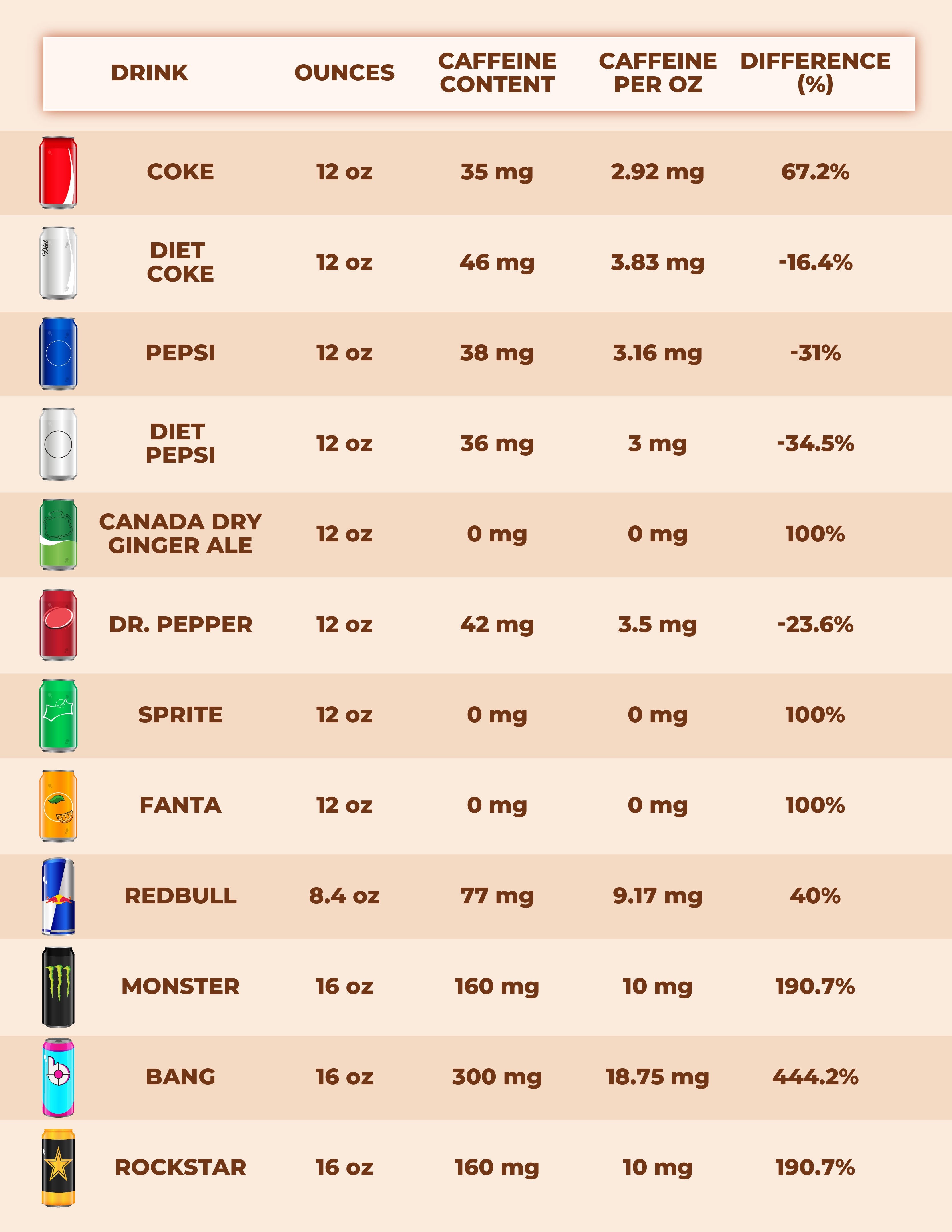
- Coca-Cola: A 12-ounce can of Coca-Cola contains approximately 34 mg of caffeine.
- Pepsi: A 12-ounce can of Pepsi contains about 38 mg of caffeine.
- Dr. Pepper: A 12-ounce can of Dr. Pepper contains around 41 mg of caffeine.
- Mountain Dew: As mentioned earlier, a 12-ounce can of Mountain Dew contains about 54 mg of caffeine.
This means that Mountain Dew provides a more significant caffeine kick compared to these other popular soda choices. If you’re sensitive to caffeine or trying to limit your intake, this difference can be important.
Caffeine Content of Common Sodas & Energy Drinks:
| Beverage | Caffeine Content (per 12 oz) |
|---|---|
| Mountain Dew | 54 mg |
| Coca-Cola | 34 mg |
| Pepsi | 38 mg |
| Dr. Pepper | 41 mg |
| Red Bull (8.4 oz can) | 80 mg |
| Monster Energy | 160 mg (per 16 oz) |

3. The Effects of Caffeine: Benefits and Risks
Caffeine is a stimulant that affects the central nervous system, and it can have both positive and negative effects on the body. Understanding these effects can help you consume Mountain Dew and other caffeinated beverages responsibly.
3.1. Potential Benefits of Caffeine
When consumed in moderation, caffeine can offer several benefits:
- Increased Alertness and Focus: Caffeine is known for its ability to enhance alertness and concentration. It blocks adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and sleepiness.
- Improved Cognitive Function: Studies have shown that caffeine can improve memory, reaction time, and overall cognitive performance.
- Enhanced Physical Performance: Caffeine can boost athletic performance by increasing adrenaline levels and reducing perceived exertion.
- Mood Elevation: Caffeine can stimulate the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and motivation, leading to an improved mood.
However, it’s crucial to note that these benefits are typically observed with moderate caffeine consumption. Excessive intake can lead to adverse effects.
3.2. Potential Risks and Side Effects of Excessive Caffeine
Consuming too much caffeine can lead to a range of unpleasant and potentially harmful side effects:
- Anxiety and Nervousness: High doses of caffeine can cause anxiety, jitters, and nervousness.
- Insomnia: Caffeine can interfere with sleep patterns, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep.
- Increased Heart Rate and Blood Pressure: Caffeine can temporarily increase heart rate and blood pressure, which can be problematic for individuals with heart conditions.
- Digestive Issues: Some people may experience stomach upset, nausea, or diarrhea from excessive caffeine intake.
- Headaches: While caffeine can sometimes relieve headaches, it can also cause them, especially during withdrawal.
- Dependence and Withdrawal: Regular caffeine consumption can lead to physical dependence, and withdrawal symptoms like headaches, fatigue, and irritability can occur when caffeine intake is reduced or stopped.
Most healthy adults can safely consume up to 400 milligrams of caffeine daily. Keep in mind that this varies from person to person, as age, gender, and underlying medical conditions can impact caffeine tolerance.
Consuming excessive amounts of caffeine puts you at risk of developing a number of unpleasant side effects, including:
- Insomnia
- Anxiety
- Increased heart rate
- Upset stomach
- Headache
- Chest pain
- Heart palpitations
In extreme cases, overconsumption of caffeine can lead to more life-threatening medical issues.
Although uncommon, the severity of the symptoms often requires immediate medical attention. They include confusion, hallucinations, difficulty breathing, and uncontrollable movements [1].
3.3. Factors Affecting Caffeine Sensitivity
Individual sensitivity to caffeine can vary widely based on several factors:
- Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to be more sensitive to the effects of caffeine.
- Body Weight: Individuals with lower body weights may experience stronger effects from the same amount of caffeine compared to those with higher body weights.
- Age: Older adults may be more sensitive to caffeine due to changes in metabolism and overall health.
- Medications: Certain medications can interact with caffeine, either enhancing or reducing its effects.
- Tolerance: Regular caffeine consumption can lead to tolerance, meaning that more caffeine is needed to achieve the same effects.
Understanding your own sensitivity to caffeine is essential for managing your intake and avoiding negative side effects.
4. Tips for Managing Your Caffeine Intake
Managing your caffeine intake is crucial for maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential risks. Here are some practical tips to help you stay within a healthy range.
4.1. Know Your Limits
The first step in managing caffeine intake is to know your personal limits. Most healthy adults can safely consume up to 400 mg of caffeine per day, but individual tolerance can vary. Start by monitoring how caffeine affects you and adjust your intake accordingly.
4.2. Read Labels Carefully
Always read the labels of beverages and foods to understand their caffeine content. This is especially important for energy drinks and specialty coffee drinks, where caffeine levels can vary widely. Pay attention to serving sizes as well, as a single container may contain multiple servings.
4.3. Time Your Caffeine Consumption
To avoid sleep disturbances, avoid consuming caffeine late in the day. It’s best to have your last caffeinated beverage at least six hours before bedtime. Consider switching to decaffeinated options in the afternoon and evening.
4.4. Stay Hydrated
Caffeine can have a diuretic effect, meaning it can increase urine production and potentially lead to dehydration. Be sure to drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated, especially if you consume caffeinated beverages regularly.
4.5. Be Mindful of Hidden Caffeine Sources
Caffeine can be found in unexpected places, such as chocolate, certain medications, and some herbal supplements. Be aware of these hidden sources and factor them into your overall caffeine intake.
4.6. Gradually Reduce Intake
If you’re looking to reduce your caffeine intake, do so gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms like headaches, fatigue, and irritability. Slowly decrease your consumption over a period of days or weeks to allow your body to adjust.
4.7. Choose Healthier Alternatives
Consider replacing some of your caffeinated beverages with healthier alternatives, such as herbal tea, fruit-infused water, or decaffeinated coffee. These options can provide hydration and flavor without the caffeine.
5. Mountain Dew and Specific Health Considerations
Certain groups, such as pregnant women and individuals with specific health conditions, need to be especially careful about their caffeine intake. Here’s what you need to know.
5.1. Caffeine and Pregnancy
Pregnant women are advised to limit their caffeine intake to no more than 200 mg per day. Excessive caffeine consumption during pregnancy has been linked to an increased risk of miscarriage, premature birth, and low birth weight.
Drinking more than 200 mg a day puts expectant mothers at risk of:
- Miscarriage
- Birth defects
- Premature labor
- Reduced fertility [3]
However, caffeine isn’t the only reason women should avoid Mountain Dew during pregnancy. Mountain Dew also contains a lot of sugar and artificial additives, many of which have been linked to health complications. So, while the occasional Mountain Dew is fine, pregnant women should avoid making it a daily habit [4].
5.2. Caffeine and Heart Health
Individuals with heart conditions, such as arrhythmias or high blood pressure, should be cautious about their caffeine intake. Caffeine can increase heart rate and blood pressure, which can exacerbate these conditions. It’s best to consult with a healthcare provider to determine a safe level of caffeine consumption.
5.3. Caffeine and Anxiety Disorders
Caffeine can worsen anxiety symptoms in people with anxiety disorders. If you experience anxiety, panic attacks, or other anxiety-related symptoms, it’s advisable to limit or avoid caffeine altogether.
5.4. Caffeine and Sleep Disorders
Caffeine can interfere with sleep, so individuals with sleep disorders like insomnia should avoid caffeine, especially in the afternoon and evening.
5.5. Caffeine and Children
Children and adolescents are more sensitive to the effects of caffeine than adults. Excessive caffeine intake in children has been linked to anxiety, sleep problems, and behavioral issues. It’s generally recommended that children and adolescents limit or avoid caffeine consumption.
6. Exploring Caffeine-Free Alternatives
If you enjoy the taste of Mountain Dew but want to avoid caffeine, exploring caffeine-free alternatives can be a great option.
6.1. Caffeine-Free Mountain Dew Options
While most Mountain Dew formulas contain caffeine, Caffeine-Free Diet Mountain Dew contains none. That makes it an excellent option for anyone looking to limit caffeine consumption. But it’s important to note that Caffeine-Free Diet Mountain Dew is not widely available and can only be found in certain regions.
6.2. Other Caffeine-Free Beverages
There are numerous other caffeine-free beverages to choose from, including:
- Herbal Teas: Many herbal teas, such as chamomile, peppermint, and rooibos, are naturally caffeine-free and offer various health benefits.
- Fruit-Infused Water: Infusing water with fruits like berries, citrus, or cucumber can create a refreshing and flavorful drink without caffeine.
- Sparkling Water: Sparkling water is a great alternative to soda, providing fizz and hydration without caffeine or added sugars.
- Decaffeinated Coffee and Tea: Decaffeinated versions of coffee and tea offer the flavor and aroma of these beverages with minimal caffeine content.
7. Potential Interactions of Mountain Dew with Other Substances
Understanding how Mountain Dew interacts with other substances, such as alcohol and medications, is crucial for avoiding potential health risks.
7.1. Mixing Mountain Dew with Alcohol
Although Mountain Dew was initially created to be mixed with moonshine, it’s important to be aware of the potential consequences.
Both sugar and caffeine can interact with alcohol and mask its intoxicating effects. As a result, you’re more likely to overindulge or develop alcohol poisoning. Mixing alcohol and Mountain Dew can also contribute to alcohol’s dehydrating effects and cause a more severe hangover.
7.2. Mountain Dew and Medications
Caffeine can interact with certain medications, either enhancing or reducing their effects. For example, caffeine can increase the effects of stimulants and decrease the effectiveness of sedatives. If you’re taking any medications, it’s essential to talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist about potential interactions with caffeine.
7.3. Mountain Dew and Supplements
Some dietary supplements contain caffeine or other stimulants that can interact with the caffeine in Mountain Dew. Combining these substances can lead to excessive stimulation and adverse effects. Be sure to read the labels of supplements carefully and consult with a healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
8. Caffeine Addiction and Withdrawal
Regular consumption of caffeine can lead to physical dependence, and withdrawal symptoms can occur when caffeine intake is reduced or stopped.
8.1. Signs of Caffeine Addiction
Unfortunately, any drink that’s high in caffeine can potentially lead to caffeine addiction. Because it’s a stimulant, caffeine activates the reward centers in your brain. As a result, regular consumption can lead to physical dependence.
Symptoms of caffeine addiction include:
- An inability to reduce or control caffeine consumption
- Withdrawal symptoms like headaches, depression, and anxiety
- Severe cravings
8.2. Managing Caffeine Withdrawal
If you’re experiencing caffeine withdrawal symptoms, there are several strategies you can use to manage them:
- Gradual Reduction: Slowly decrease your caffeine intake over a period of days or weeks to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and help flush caffeine out of your system.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate headaches and muscle aches.
- Rest: Get plenty of rest to help your body recover from withdrawal.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet to support your overall health and energy levels.
9. Debunking Common Myths About Mountain Dew and Caffeine
There are many misconceptions about Mountain Dew and its caffeine content. Let’s set the record straight.
9.1. Myth: Mountain Dew Has More Caffeine Than Coffee
Fact: While Mountain Dew has a significant amount of caffeine compared to other sodas, it typically contains less caffeine than coffee per serving. An average 8-ounce cup of coffee contains more caffeine than a 12-ounce can of Mountain Dew.
9.2. Myth: All Mountain Dew Flavors Have the Same Amount of Caffeine
Fact: The caffeine content can vary depending on the specific Mountain Dew flavor and formulation. Some variants, like Mountain Dew Kickstart, contain more caffeine than the regular version.
9.3. Myth: Caffeine-Free Mountain Dew Is Completely Free of Caffeine
Fact: While Caffeine-Free Diet Mountain Dew is labeled as caffeine-free, it may still contain trace amounts of caffeine. However, the amount is minimal and unlikely to cause significant effects.
9.4. Myth: Mountain Dew Is a Healthy Source of Energy
Fact: Mountain Dew is not a healthy source of energy. It is high in sugar and artificial additives, which can have negative health effects.
10. Frequently Asked Questions About Caffeine in Mountain Dew
To address any remaining questions, here are some frequently asked questions about the caffeine content in Mountain Dew.
10.1. How Much Mountain Dew Is Too Much?
Due to its high sugar content, consuming too much Mountain Dew can also lead to the following health issues:
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Dental problems
- Heart disease
- Fatty liver disease [2]
But Mountain Dew’s caffeine content isn’t the only problem. At 46 grams per 12 oz can, Mountain Dew is exceptionally high in sugar.
According to the American Heart Association, women should consume no more than 25 grams of added sugar daily, and men should try to stay under 36 grams [2]. With these guidelines in mind, it’s best to keep Mountain Dew consumption to a minimum.
10.2. Is Mountain Dew Safe for Pregnant Women?
According to experts, pregnant women should limit their daily caffeine intake to under 200 mg.
10.3. What Happens When You Mix Mountain Dew with Alcohol?
Both sugar and caffeine can interact with alcohol and mask its intoxicating effects. As a result, you’re more likely to overindulge or develop alcohol poisoning. Mixing alcohol and Mountain Dew can also contribute to alcohol’s dehydrating effects and cause a more severe hangover.
10.4. Can Mountain Dew Cause a Caffeine Addiction?
Unfortunately, any drink that’s high in caffeine can potentially lead to caffeine addiction. Because it’s a stimulant, caffeine activates the reward centers in your brain. As a result, regular consumption can lead to physical dependence.
10.5. Are There Any Caffeine-Free Mountain Dew Flavors?
While most Mountain Dew formulas have caffeine, Caffeine-Free Diet Mountain Dew contains none. That makes it an excellent option for anyone looking to limit caffeine consumption. But it’s important to note that Caffeine-Free Diet Mountain Dew is not widely available and can only be found in certain regions.
10.6. How Does Mountain Dew’s Caffeine Content Compare to Other Energy Drinks?
Mountain Dew generally has a lower caffeine content than most energy drinks. A typical energy drink can contain between 100-300 mg of caffeine per serving, while a 12-ounce can of Mountain Dew contains about 54 mg.
10.7. Can Caffeine in Mountain Dew Affect Sleep?
Yes, caffeine can interfere with sleep patterns, especially if consumed close to bedtime. It’s best to avoid Mountain Dew and other caffeinated beverages at least six hours before going to sleep.
10.8. What Are the Long-Term Effects of Regular Mountain Dew Consumption?
Regular consumption of Mountain Dew, due to its high sugar and caffeine content, can lead to various health issues, including weight gain, dental problems, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and heart problems.
10.9. Is It Safe to Drink Mountain Dew Every Day?
Drinking Mountain Dew every day is not recommended due to its high sugar and caffeine content. Occasional consumption is fine, but it’s best to limit your intake and choose healthier alternatives.
10.10. How Can I Reduce My Caffeine Intake from Mountain Dew?
To reduce your caffeine intake from Mountain Dew, try switching to caffeine-free options, limiting your serving sizes, and gradually decreasing your consumption over time.
References
- Ágoston C, Bernáth L, Rogers PJ, Demetrovics Z. Stress, caffeine, and psychosis-like experiences-A double-blind, placebo-controlled experiment. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2022 May;37(3):e2828. doi: 10.1002/hup.2828. Epub 2021 Nov 18. PMID: 34792804.
- Lakin H, Sheehan P, Soti V. Maternal Caffeine Consumption and Its Impact on the Fetus: A Review. Cureus. 2023 Nov 4;15(11):e48266.
- Substances of Concern during Pregnancy. Accessed June 7, 2024.
Navigating the world of caffeine can be challenging, but understanding the specifics of beverages like Mountain Dew is a great start. At HOW.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing expert insights to help you make informed decisions about your health and lifestyle.
Are you facing challenges in managing your caffeine intake or understanding the effects of certain beverages on your health? Do you need personalized advice from experienced professionals?
At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with over 100 renowned Ph.D. experts across various fields. Our experts offer tailored guidance and solutions to address your unique concerns. Benefit from the knowledge and experience of top-tier professionals who are committed to helping you achieve your goals.
Don’t navigate these challenges alone. Contact us today for a consultation and take the first step towards a healthier, more informed lifestyle.
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let how.edu.vn be your trusted partner in health and wellness.
