How Much Do Pilots Make Per Flight? The earnings of airline pilots vary significantly, but understanding the compensation structure is key. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights to help you navigate the complexities of pilot salaries and career paths. This article explores the factors influencing a pilot’s per-flight earnings, offering a detailed look at the aviation compensation landscape. Learn about flight compensation, pilot pay rates, and aviation career earnings.
Attracted by the potential income in aviation and curious about the earning potential of a pilot? Contact the specialists at HOW.EDU.VN now for individualized advice.
1. Factors Influencing Pilot Pay Per Flight
Pilot compensation isn’t a fixed number; it depends on a variety of factors.
1.1 Airline Type: Major vs. Regional
Pilots at major airlines generally earn more per flight than those at regional airlines. Major airlines operate larger aircraft on longer routes, which translates to higher pay rates. Regional airlines, while providing valuable experience, typically have lower operating costs and, consequently, lower salaries.
- Major Airlines: Higher pay, longer routes, larger aircraft
- Regional Airlines: Lower pay, shorter routes, smaller aircraft
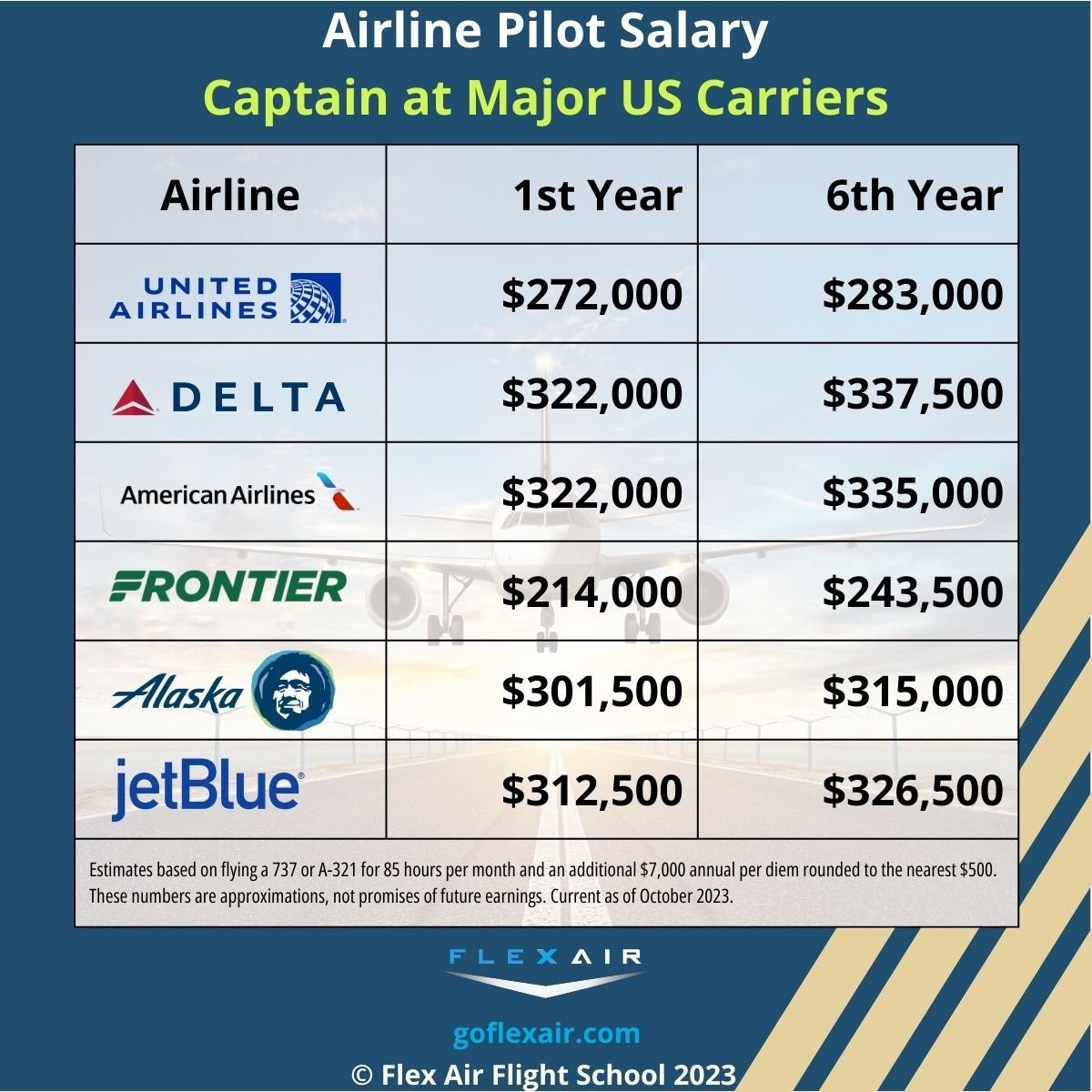
For example, a captain at a major airline like United or Delta might earn significantly more per flight than a captain at a regional carrier like SkyWest or Envoy.
1.2 Experience and Seniority
Experience is a major determinant of pilot pay. As pilots accumulate flight hours and years of service, their pay rates increase. Seniority within an airline also plays a crucial role, as more senior pilots have access to better schedules and higher-paying routes.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for airline pilots, copilots, and flight engineers was $211,790 in May 2022, but experienced captains can earn significantly more. A pilot with 20 years of experience might earn over $400,000 per year.
1.3 Aircraft Type and Route Length
The type of aircraft a pilot flies and the length of the route also impact their pay per flight. Flying larger, wide-body aircraft on long-haul international routes typically commands higher pay rates than flying smaller, regional jets on short domestic routes.
For instance, a captain flying a Boeing 777 on a long-haul flight from New York to London will earn more per flight hour than a first officer flying a regional jet on a short hop between smaller cities.
1.4 Pay Structure: Hourly vs. Per Flight
Pilots are typically paid by the hour, not per flight. However, hourly pay rates mean that the per flight compensation ranges from over $3000 per flight for senior captains on long flights with large aircraft to as little as $20 for the lowest paid pilots on the shortest flights. Most airlines operate on a concept called Minimum Monthly Guarantee. This ensures pilots will be compensated regardless, and they will receive a salary each month. In most cases, the number of guaranteed hours varies but is approximately 72-76 hours each month. This is just a minimum pilots earn more if they fly more than the guaranteed hours or receive other incentives.
1.5 Additional Compensation: Bonuses and Overtime
Pilots may also receive additional compensation in the form of signing bonuses, overtime pay, and profit-sharing. Some airlines offer signing bonuses to attract and retain pilots, especially in times of pilot shortages. Overtime pay is typically awarded for flying hours exceeding the guaranteed minimum, while profit-sharing allows pilots to benefit from the airline’s financial success.
1.6 Union Contracts
Pilot unions, such as the Air Line Pilots Association (ALPA), play a significant role in negotiating pay and benefits for their members. Union contracts often include provisions for pay increases, bonuses, and improved working conditions. Airlines with strong pilot unions tend to offer better compensation packages.
2. Average Pilot Pay Per Flight: A Detailed Breakdown
To provide a clearer picture of how much pilots make per flight, let’s break down the average earnings based on different factors.
2.1 Regional Airline Pilots
Regional airline pilots typically earn less per flight than their counterparts at major airlines. First officers at regional airlines may earn around $36 to $56 per hour, while captains can earn between $56 and $120 per hour.
Example:
- First Officer: $40 per hour x 3-hour flight = $120 per flight
- Captain: $80 per hour x 3-hour flight = $240 per flight
2.2 Major Airline Pilots
Major airline pilots earn significantly more per flight due to higher hourly rates and longer flight durations. First officers at major airlines may earn between $56 and $120 per hour, while captains can earn from $120 to over $700 per hour. This increases with major airlines where flying a Boeing 777 pays in the neighborhood of $320.
Example:
- First Officer: $80 per hour x 6-hour flight = $480 per flight
- Captain: $200 per hour x 6-hour flight = $1200 per flight
2.3 International Airline Pilots
International airline pilots often earn higher per-flight compensation due to the longer flight durations and the complexity of international operations. Salaries can vary widely depending on the airline and the region. For instance, pilots at Qatar Airways average $173,000-$187,000 annually.
2.4 Cargo Pilots
Cargo pilots, such as those working for FedEx or UPS, also command competitive per-flight pay rates. These pilots typically fly larger aircraft and transport goods rather than passengers, often on overnight or long-haul flights. Cargo pilots at FedEx can earn an average salary of $270,160.
2.5 Corporate Pilots
Corporate pilots fly business jets for companies or executives, often on-demand schedules. Their per-flight earnings can be quite lucrative, with an estimated average salary of around $124,868 per year. However, corporate pilots may have less stability and benefits compared to airline pilots.
3. Career Progression and Earning Potential
Becoming a commercial airline pilot involves several steps and stages, each with its own earning potential.
3.1 Student Pilot
This is the initial stage of flight training, where the student learns the basics of flying and earns a Student Pilot Certificate. Student pilots do not earn a salary at this stage but must pay for their flight training and other expenses.
3.2 Private Pilot
In this stage, the student earns a Private Pilot License (PPL), allowing them to fly for pleasure or personal business. Private pilots cannot be paid for their flying services.
3.3 Commercial Pilot
Earning a Commercial Pilot License (CPL) allows pilots to be paid for their flying services. The salary of a commercial pilot can range from $20,000 to $100,000 per year, depending on the job and location.
3.4 Airline Pilot
The final stage involves earning an Airline Transport Pilot License (ATPL), enabling pilots to work for regional or major airlines. The salary of an airline pilot can range from $36,000 to $700,000+ per year, depending on the airline, aircraft, and seniority.
4. Additional Benefits and Perks
In addition to per-flight earnings, airline pilots receive various benefits and perks, including:
4.1 Health Insurance
Airlines provide comprehensive health insurance benefits, including health, dental, and vision coverage.
4.2 Retirement Plans
Generous retirement plans, such as 401(k) plans with company match and traditional pension plans, are offered.
4.3 Paid Vacation
Pilots receive paid vacation time, which increases based on years of service.
4.4 Travel Benefits
Free or discounted travel for themselves and family members is a significant perk.
4.5 Other Benefits
Hotel accommodations and meal allowances are often provided during layovers.
5. Factors Influencing Overall Pilot Compensation
Several factors can influence a pilot’s overall compensation, including:
5.1 Education and Training
While a college degree is not strictly required, it can enhance hiring opportunities. Airlines often prefer candidates with a bachelor’s degree in aviation, aeronautical science, or a related field. Accelerated flight training programs, like the Flex Air Pilot Pathway program, can expedite the process of becoming a pilot.
5.2 Networking
Building connections throughout their career can lead to higher-paying roles. Networking can help pilots find opportunities in different sectors of aviation and gain insights into industry trends.
5.3 Additional Certifications
Gaining additional certifications and ratings can make pilots more qualified and competitive for higher-paying roles.
6. Current Trends and News
Several current trends are impacting airline pilot salaries in 2023:
6.1 Pilot Shortage
The ongoing pilot shortage has led to increased demand and higher salaries for pilots. Airlines are competing to attract and retain pilots through higher pay, bonuses, and benefits.
6.2 Technological Advancements
New technologies and innovations, such as electric aircraft and autonomous flight, may impact the future of pilot salaries and job roles.
6.3 Workforce Diversity
Efforts to diversify the pilot workforce are underway, with more women, minorities, and veterans becoming pilots.
6.4 Economic Factors
The overall economy and the performance of the airline industry can impact pilot salaries and job security.
7. Tips for Maximizing Pilot Earnings
To maximize their earnings, pilots can:
- Gain more experience and certifications.
- Seek opportunities in different sectors of aviation.
- Apply for airlines that offer higher pay and better benefits.
- Work more hours or pick up extra trips.
- Keep track of expenses and deductions related to the pilot job.
8. Pilot Pay FAQ
8.1 Do You Need a Degree to Become a Pilot?
A college degree is not required by many commercial airlines. However, having a degree can enhance hiring opportunities with some.
8.2 How Do Experienced Pilots’ Salaries Compare to New Entrants?
Experienced pilots earn significantly more than new entrants. For instance, airline pilot’s salary at major airlines in 2022 ranged from $56,000 to $700,000+.
8.3 Does Having a College Degree Affect Pilot Salary?
A college degree is not strictly required to become a pilot, but it can offer several advantages. For example, airlines and other employers often prefer candidates with a bachelor’s degree.
8.4 What’s the Average Salary for Airline Pilots in Major Airlines vs. Regional?
The average salary for airline pilots in major airlines is significantly higher than that of regional airlines. For instance, Southwest Airlines pilots earn an average annual salary of $222,000. On the other hand, the average annual pay for a Regional Airline Pilot in the United States is $86,579.
8.5 How Much Do International Airline Pilots Make?
International airline pilots also earn well. For instance, Qatar pilots average $173,000-$187,000 annually. However, international airline pilots may also face some challenges, such as different regulations, cultural differences, and visa requirements.
8.6 How Much Do Cargo Pilots Make?
Cargo pilots, such as those working for FedEx, can earn an average salary of $270,160. Cargo pilots typically fly larger aircraft and transport goods rather than passengers.
8.7 How Much Do Charter Pilots Make?
A Charter Pilot makes an average of $102,243 a year. Charter pilots fly private aircraft for individuals or groups who hire them for specific trips.
8.8 How Much Do Corporate Pilots Make?
A Corporate Pilot’s salary is estimated to be around $124,868 per year. Corporate pilots fly business jets for companies or executives who own or lease them.
8.9 How Much Do Flight Instructors Make?
A certified flight instructor can expect to earn between $25 and $50 per hour depending on region.
8.10 Is There a Guaranteed Minimum Pay for Airline Pilots?
Yes, airline pilots have a guaranteed minimum pay based on the Minimum Monthly Guarantee concept. However, the exact amount of the minimum pay may vary depending on the airline, the pilot’s seniority, and the type of aircraft.
8.11 Do Airlines Offer Signing Bonuses?
Yes, some airlines offer signing bonuses to attract and retain pilots. For example, regional airlines are offering huge signing bonuses to pilots due to a shortage of pilots qualified to fly for the airlines. Signing bonuses can range from $10,000 to $50,000 or more.
8.12 Can Pilots Earn More by Working on Their Days Off?
Yes, pilots can earn more by working on their days off, depending on the airline and the pilot’s contract.
8.13 What Benefits Do Pilots Receive?
In addition to annual earnings, pilots receive paid vacation time, participate in employer health, life and disability insurance and retirement plans.
8.14 Does Transitioning from a Military Pilot to a Commercial Pilot Affect Salary?
Yes, transitioning from a military pilot to a commercial pilot can affect salary. Military pilots may have an advantage in getting hired by airlines, as they have valuable experience, skills, and credentials.
8.15 How Can Pilots Negotiate Better Salaries?
Pilots can negotiate better salaries by following some tips and strategies, such as:
- Doing research and gathering information about the average salary, benefits, and incentives of the airline and the position they are applying for.
- Highlighting their skills, qualifications, and achievements that make them stand out from other candidates.
- Asking for a salary range rather than a specific number, and being prepared to justify their expectations.
- Being flexible and willing to compromise on other aspects of the job, such as the schedule, the location, or the aircraft type.
- Being respectful and professional throughout the negotiation process, and expressing their enthusiasm and interest in working for the airline.
9. The HOW.EDU.VN Advantage
Navigating the complexities of a pilot’s career and compensation can be challenging. HOW.EDU.VN connects you with leading experts who provide personalized guidance and support.
9.1 Expert Consultations
Connect with over 100 renowned PhDs and specialists worldwide for in-depth consultations.
9.2 Personalized Solutions
Receive tailored advice and solutions to address your specific career and financial goals.
9.3 Time and Cost Savings
Save time and money by accessing high-quality expertise efficiently.
9.4 Confidentiality and Reliability
Ensure the privacy and security of your information with trusted experts.
9.5 Practical Advice
Get actionable advice and solutions that you can implement immediately.
10. Take the Next Step with HOW.EDU.VN
Are you facing challenges in understanding the aviation industry’s compensation structure or seeking personalized advice on maximizing your earnings as a pilot? At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the difficulties in finding qualified experts and the desire for reliable and practical guidance.
Don’t navigate these challenges alone. Contact us today to connect with our team of experienced PhDs and aviation specialists who can provide you with the insights and solutions you need.
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let how.edu.vn be your partner in achieving your aviation career and financial goals. Our experts are ready to help you take flight towards a successful and rewarding career.