Repairing a car alternator can be a confusing process, but understanding the costs involved is crucial, which is why HOW.EDU.VN offers expert guidance. The cost to repair a car alternator is influenced by several factors, including the car’s make and model, the type of alternator, and labor costs. Whether you’re dealing with voltage regulation issues, bearing wear, or diode failure, knowing the potential expenses can help you make an informed decision. For tailored advice and expert assistance, connect with our experienced PhDs at HOW.EDU.VN to ensure you get the best solutions for your automotive needs and understand the pricing structure, labor rates, and part sourcing.
1. Understanding the Role of the Alternator in Your Car
The alternator is a crucial component of your car’s electrical system. It converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, which powers the car’s electrical components and recharges the battery. Without a functioning alternator, your car will eventually run out of power, leading to a breakdown.
Cars today are packed with systems that demand a significant amount of electrical power. Beyond the obvious power-hungry features like the radio, power windows, door locks, sunroof, and heated seats, there are numerous modules and sensors working constantly. For instance, an anti-lock braking system (ABS) typically includes a wheel speed sensor at each wheel, an anti-lock brake control module, and an ABS pump, all of which require continuous power.
The alternator steps in to amplify the power drawn from the battery, acting as an electromagnet to supply enough electricity to keep all these electrical components running smoothly while the engine is on. It also generates surplus power to replenish the battery’s charge. Inside the alternator, a magnetic rotor and copper windings produce alternating current (AC), which is then converted into direct current (DC) by a set of diodes in the rectifier. This DC electricity is what your car’s devices need to operate. To prevent overcharging and damage, as well as issues from insufficient power, the voltage output is carefully regulated.
If the alternator isn’t producing between 13.5 and 14.5 volts, creating noises, or if the wrong type of current is finding its way through the alternator is failing, and it needs to be replaced.
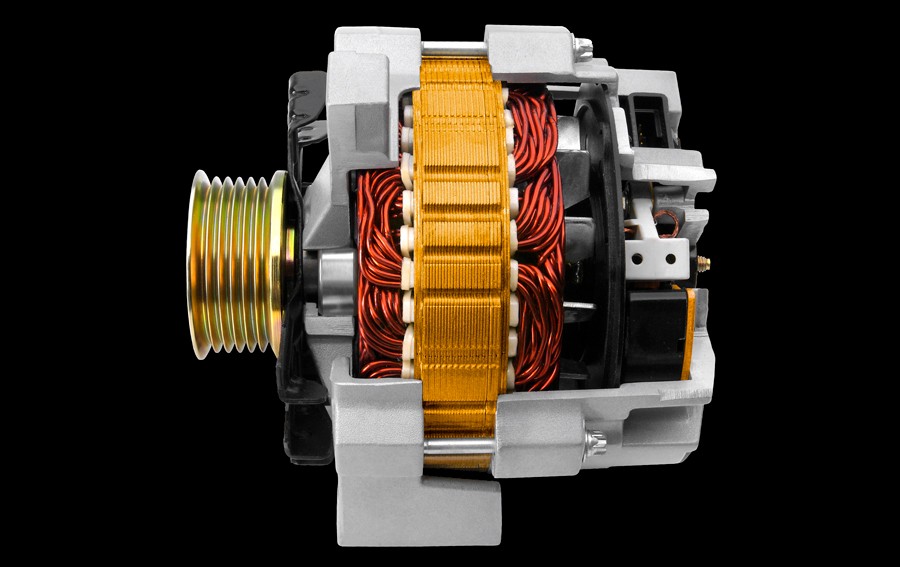 Car alternator cutaway showing internal components
Car alternator cutaway showing internal components
2. Common Signs That Your Alternator Needs Repair or Replacement
Recognizing the signs of a failing alternator early can prevent further damage and save you money in the long run. Keep an eye out for these common symptoms:
-
Illuminated Battery Light: The battery light on your dashboard often indicates a charging problem, signaling that the alternator might be undercharging or overcharging.
-
Dim or Flickering Lights: If your headlights or interior lights are dimmer than usual or flicker, it could be due to inconsistent voltage from the alternator.
-
Unusual Electrical Issues: Low voltage can cause a range of electrical problems, such as slow power windows, a radio that fades in and out, and reduced fan speed.
-
Burning Smells: A burning rubber smell could indicate a slipping belt on the alternator pulley, while a burning electrical smell might signal a fault inside the alternator.
-
Whirring or Whining Noise: Unusual noises under the hood, such as whirring or whining, can indicate worn or corroded alternator bearings, suggesting an impending failure.
-
Difficulty Starting the Car: A failing alternator can drain the battery, making it difficult to start your car, especially in cold weather.
-
Stalling: If your car stalls frequently, especially when using electrical components like air conditioning or headlights, it could be due to an underperforming alternator.
-
Dead Battery: A continuously failing alternator may not adequately recharge the battery, leading to a dead battery.
3. Factors Affecting the Cost of Alternator Repair
Several factors influence the cost of repairing or replacing a car alternator. Understanding these can help you anticipate the potential expenses involved.
- Vehicle Make and Model: The make and model of your car significantly affect the cost. High-end or luxury vehicles often have more expensive alternators and require specialized labor.
- Alternator Type: There are different types of alternators, including new, remanufactured, and aftermarket options. New alternators are typically the most expensive, while remanufactured or aftermarket options can be more affordable.
- Labor Costs: Labor costs vary depending on the mechanic’s hourly rate and the complexity of the job. Some cars have alternators that are easily accessible, while others require more extensive disassembly, increasing labor time.
- Part Availability: The availability of alternator parts can also affect the cost. If your car requires a rare or hard-to-find alternator, it may be more expensive to source.
- Warranty: The warranty on the alternator can impact the overall cost. A longer warranty may increase the initial cost but can save you money in the long run if the alternator fails prematurely.
- Location: Geographic location can also play a role. Urban areas with higher living costs tend to have higher labor rates than rural areas.
- Amperage: Smaller alternators that don’t need to generate as much electricity for the car tend to have less high-value material content like copper used in the windings. Thus manufacturing costs are lower. It isn’t always the case, though.
- Mounting Style: Since the alternator needs to fit perfectly, you can’t choose a low-cost alternator intended for a different car. It won’t work.
- Types of Electrical Connections: Alternators for older cars that are considered 1-wire alternators often are lower priced, while 3-wire alternators tend to be more expensive.
4. Average Cost of Alternator Repair vs. Replacement
The cost of alternator repair varies depending on the extent of the damage and the parts needed. Minor repairs, such as replacing brushes or diodes, may cost between $150 and $300. However, if the alternator has significant damage, replacement is often the more cost-effective option.
The average cost to replace an alternator ranges from $500 to $1000, including parts and labor. New alternators typically cost between $300 and $700, while labor costs range from $200 to $500, depending on the complexity of the job.
Here’s a breakdown of the typical costs:
- New Alternator: $300 – $700
- Remanufactured Alternator: $150 – $450
- Labor Costs: $200 – $500
- Total Replacement Cost: $500 – $1000
5. Can You Drive With a Faulty Alternator?
Driving with a faulty alternator is not recommended, as it can lead to further damage and potential safety hazards. When the alternator isn’t charging properly, the car relies solely on the battery for power. This can quickly drain the battery, causing the car to stall or break down.
However, a short drive is fine when the alternator isn’t charging enough. The battery’s reserve power can substitute electricity, such as if you’re driving a few blocks to the repair shop. However, if your alternator is overcharging, it could damage computer modules, the battery, and other electronics or wiring even during a short drive.
Additionally, a failing alternator can affect other electrical components, such as the headlights, power steering, and brakes, compromising your safety on the road. It’s best to have the alternator repaired or replaced as soon as possible to avoid these risks.
6. DIY vs. Professional Alternator Replacement
Replacing an alternator is a task that can be done DIY, but it requires mechanical knowledge, the right tools, and a good understanding of your car’s electrical system. If you’re comfortable working on cars and have the necessary skills, you can save money on labor costs by doing it yourself.
However, if you’re not experienced with car repairs, it’s best to leave the job to a professional mechanic. Incorrect installation can damage the alternator or other components, leading to additional expenses. Professional mechanics also offer warranties on their work, providing peace of mind.
Here are some factors to consider when deciding between DIY and professional alternator replacement:
- Skill Level: Assess your mechanical skills and experience with car repairs.
- Tools: Ensure you have the necessary tools, such as wrenches, sockets, and a multimeter.
- Time: Consider the amount of time required to complete the job, as it can take several hours for a novice.
- Warranty: Professional mechanics offer warranties on their work, providing protection against defects or failures.
7. Choosing the Right Alternator: New, Remanufactured, or Aftermarket?
When replacing your alternator, you have several options to choose from: new, remanufactured, or aftermarket. Each option has its own pros and cons in terms of cost, quality, and warranty.
- New Alternators: New alternators are the most expensive option but offer the best quality and reliability. They come with a manufacturer’s warranty, providing protection against defects or failures.
- Remanufactured Alternators: Remanufactured alternators are rebuilt using original parts and undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet factory specifications. They are more affordable than new alternators and often come with a warranty.
- Aftermarket Alternators: Aftermarket alternators are manufactured by third-party companies and are typically the most affordable option. However, their quality and reliability can vary, and they may not come with a warranty.
Consider your budget, the age of your car, and your long-term plans when choosing the right alternator. If you plan to keep your car for many years, a new or remanufactured alternator may be the best investment. If you’re on a tight budget and don’t plan to keep the car for long, an aftermarket alternator may suffice.
8. Step-by-Step Guide to Alternator Replacement (DIY)
If you decide to replace the alternator yourself, follow these steps:
- Gather Your Tools: You’ll need a wrench set, socket set, screwdrivers, a multimeter, safety glasses, and gloves.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shocks.
- Locate the Alternator: The alternator is typically located at the front of the engine and is driven by a belt.
- Remove the Belt: Use a wrench to loosen the tensioner pulley and remove the belt from the alternator pulley.
- Disconnect Electrical Connections: Disconnect the electrical connectors from the alternator, noting their positions.
- Remove the Alternator: Remove the bolts securing the alternator to the engine and carefully remove the alternator.
- Install the New Alternator: Install the new alternator in the reverse order, ensuring all bolts and connections are secure.
- Reinstall the Belt: Reinstall the belt, making sure it’s properly aligned on the alternator pulley.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Start the Car: Start the car and check that the alternator is charging properly using a multimeter.
9. How to Find a Reputable Mechanic for Alternator Repair
If you prefer to have a professional mechanic handle the alternator repair, it’s important to find a reputable and trustworthy shop. Here are some tips for finding the right mechanic:
- Ask for Recommendations: Ask friends, family, or colleagues for recommendations of mechanics they trust.
- Read Online Reviews: Check online review sites like Yelp or Google Reviews to see what other customers have to say about local mechanics.
- Check for Certifications: Look for mechanics who are certified by organizations like the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
- Get Multiple Quotes: Get quotes from several mechanics before making a decision to ensure you’re getting a fair price.
- Ask About Warranty: Ask about the warranty offered on the alternator and the labor.
- Visit the Shop: Visit the shop to see if it’s clean, organized, and well-equipped.
- Inquire About Experience: Ask about the mechanic’s experience with alternator repairs, especially on your car’s make and model.
10. Tips for Maintaining Your Car Alternator
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your car alternator and prevent costly repairs. Here are some tips for keeping your alternator in good condition:
- Regular Inspections: Have your mechanic inspect the alternator during routine maintenance to check for signs of wear or damage.
- Keep the Engine Clean: A clean engine compartment can prevent dirt and debris from damaging the alternator.
- Avoid Overloading the Electrical System: Avoid using too many electrical components at once, as this can strain the alternator.
- Check the Battery: Ensure the battery is in good condition, as a weak battery can overwork the alternator.
- Replace Worn Belts: Replace worn or cracked belts promptly to prevent slipping and ensure the alternator is properly driven.
- Address Electrical Issues Promptly: Address any electrical issues promptly to prevent them from affecting the alternator.
- Proper Battery Maintenance: Make sure your battery terminals are clean and free of corrosion.
- Avoid Deep Battery Drains: Try not to let your battery drain completely, as this can put extra stress on the alternator when recharging.
By following these maintenance tips, you can extend the life of your alternator and avoid costly repairs.
11. Understanding Alternator Warranties
When you replace your alternator, it’s essential to understand the warranty that comes with it. Warranties provide protection against defects or failures and can save you money in the long run. Here are some key aspects of alternator warranties:
- Warranty Period: The warranty period can range from a few months to several years. Longer warranty periods offer more extended protection.
- Coverage: Understand what the warranty covers, such as parts, labor, or both.
- Exclusions: Be aware of any exclusions to the warranty, such as damage caused by improper installation or misuse.
- Claim Process: Know the process for filing a warranty claim in case of a defect or failure.
- Warranty Provider: Determine who is providing the warranty, such as the manufacturer, retailer, or mechanic.
- Transferability: Check if the warranty is transferable if you sell the car.
- Read the Fine Print: Carefully read the warranty terms and conditions to understand your rights and responsibilities.
12. Cost-Saving Tips for Alternator Repair
If you’re looking to save money on alternator repair, here are some cost-saving tips:
- Get Multiple Quotes: Compare quotes from several mechanics to find the best price.
- Consider a Remanufactured Alternator: Remanufactured alternators are more affordable than new ones and often come with a warranty.
- DIY Replacement: If you have the skills and tools, consider replacing the alternator yourself to save on labor costs.
- Buy Parts Online: Buying alternator parts online can often be cheaper than buying them from a local auto parts store.
- Regular Maintenance: Proper maintenance can extend the life of the alternator and prevent costly repairs.
- Ask About Discounts: Ask the mechanic about any discounts or promotions they may offer.
- Use a Coupon: Look for coupons or discounts from auto parts stores or repair shops.
- Negotiate: Don’t be afraid to negotiate the price with the mechanic.
13. The Lifespan of an Alternator: What to Expect
The lifespan of an alternator can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the alternator, driving conditions, and maintenance practices. Generally, an alternator can last between 7 and 10 years, or 100,000 to 150,000 miles.
Factors that can shorten the lifespan of an alternator include:
- Extreme Temperatures: Hot or cold temperatures can stress the alternator and reduce its lifespan.
- Frequent Short Trips: Frequent short trips can prevent the alternator from fully charging the battery, leading to premature wear.
- Overloading the Electrical System: Using too many electrical components at once can strain the alternator and shorten its lifespan.
- Poor Maintenance: Neglecting regular maintenance, such as replacing worn belts, can damage the alternator.
- Low-Quality Parts: Using low-quality replacement parts can result in premature failure.
Regular inspections and proper maintenance can help extend the life of your alternator.
14. Identifying and Preventing Alternator Failure
Preventing alternator failure starts with understanding the factors that contribute to its wear and tear. Regular inspections can help identify potential problems early, allowing for timely repairs and preventing more significant damage.
- Visual Inspections: Regularly check the alternator for physical damage, such as cracks or corrosion. Also, inspect the wiring and connections for any signs of wear or looseness.
- Belt Maintenance: Ensure the drive belt that powers the alternator is in good condition. A loose or worn belt can cause the alternator to work harder and reduce its efficiency.
- Voltage Checks: Use a multimeter to check the voltage output of the alternator. A healthy alternator should produce between 13.5 and 14.5 volts when the engine is running.
- Load Testing: Have a professional perform a load test on the alternator to assess its ability to handle the electrical demands of the vehicle.
By addressing these issues proactively, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your alternator and avoid unexpected breakdowns.
15. Case Studies: Real-World Alternator Repair Costs
To provide a clearer picture of the costs involved in alternator repair, let’s look at a few real-world case studies:
-
Case Study 1: 2015 Honda Civic
- Problem: Illuminated battery light and difficulty starting the car.
- Diagnosis: Failed alternator.
- Solution: Replaced with a remanufactured alternator.
- Cost:
- Remanufactured Alternator: $250
- Labor: $200
- Total: $450
-
Case Study 2: 2012 Ford F-150
- Problem: Dim headlights and stalling.
- Diagnosis: Faulty alternator.
- Solution: Replaced with a new alternator.
- Cost:
- New Alternator: $400
- Labor: $300
- Total: $700
-
Case Study 3: 2018 BMW 3 Series
- Problem: Burning smell and unusual electrical issues.
- Diagnosis: Failing alternator.
- Solution: Replaced with a new OEM alternator.
- Cost:
- New OEM Alternator: $600
- Labor: $400
- Total: $1000
These case studies illustrate how the cost of alternator repair can vary depending on the make and model of the car, the type of alternator, and labor rates.
16. Tax Implications of Car Repairs
While the primary focus is on understanding and managing the costs of alternator repair, it’s also essential to consider any potential tax implications associated with car maintenance.
- Business Use: If you use your vehicle for business purposes, you may be able to deduct car repairs as a business expense. The IRS allows you to deduct the actual expenses of operating your vehicle or take the standard mileage rate.
- Medical Use: If you have a medical condition that requires modifications to your vehicle, such as installing hand controls or a wheelchair lift, you may be able to deduct these expenses.
- Itemized Deductions: You can only deduct car expenses if you itemize deductions on your tax return. This means you must forgo the standard deduction and instead list each deduction separately.
- Consult a Professional: Tax laws can be complex, so it’s always a good idea to consult with a tax professional or accountant to determine how car repairs may affect your tax liability.
Keep detailed records of all car repair expenses, including receipts and invoices, to support any tax deductions you may claim.
17. How Often Does an Alternator Need to Be Replaced?
Unlike some car parts that need regular replacement, alternators don’t have a fixed replacement schedule. Their lifespan can vary widely based on factors like vehicle usage, maintenance, and environmental conditions.
That may be between 100,000 and 150,000 miles. If you’re questioning whether your alternator is functioning properly or you’d like to arrange to test it, an AutoZoner is an excellent resource to tap into with our free Alternator test service.
Generally speaking, an alternator should last in the range of 7 and 10 years. Also, if at any time the job appears to be too big, look at our list of local Preferred Shops in your area that can help you tackle the job.
18. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Alternator Repair
-
Q: How do I know if my alternator is bad?
- A: Common signs of a bad alternator include an illuminated battery light, dim or flickering lights, unusual electrical issues, burning smells, and difficulty starting the car.
-
Q: Can a bad alternator drain my battery?
- A: Yes, a bad alternator can drain your battery, as it may not be charging the battery properly.
-
Q: Is it safe to drive with a faulty alternator?
- A: No, it’s not safe to drive with a faulty alternator, as it can lead to further damage and potential safety hazards.
-
Q: How much does it cost to replace an alternator?
- A: The average cost to replace an alternator ranges from $500 to $1000, including parts and labor.
-
Q: Can I replace the alternator myself?
- A: Yes, you can replace the alternator yourself if you have the skills and tools, but it’s best to leave it to a professional if you’re not experienced.
-
Q: What’s the difference between a new and remanufactured alternator?
- A: New alternators are brand new, while remanufactured alternators are rebuilt using original parts and undergo rigorous testing.
-
Q: How long does an alternator last?
- A: An alternator typically lasts between 7 and 10 years, or 100,000 to 150,000 miles.
-
Q: What are some tips for maintaining my car alternator?
- A: Tips for maintaining your alternator include regular inspections, keeping the engine clean, and avoiding overloading the electrical system.
-
Q: How can I find a reputable mechanic for alternator repair?
- A: You can find a reputable mechanic by asking for recommendations, reading online reviews, and checking for certifications.
-
Q: Is alternator repair tax-deductible?
- A: If you use your vehicle for business purposes, you may be able to deduct car repairs as a business expense.
19. Navigating Alternator Repair: Expert Advice from HOW.EDU.VN
Navigating alternator repair can be complex, but with the right knowledge and resources, you can make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes. By understanding the factors that influence repair costs, recognizing the signs of a failing alternator, and following maintenance tips, you can extend the life of your alternator and keep your car running smoothly.
For personalized advice and expert guidance, turn to HOW.EDU.VN. Our team of experienced PhDs is dedicated to providing tailored solutions to your automotive needs. Whether you’re dealing with a faulty alternator, a dead battery, or any other car problem, we can help you find the best solution for your unique situation.
Contact us today at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or reach us via WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212. Visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN to learn more about our services and connect with our team of experts. Let HOW.EDU.VN be your trusted resource for all your car repair needs.
Are you struggling to diagnose your car’s electrical issues or unsure about the best course of action for alternator repair? Don’t let uncertainty lead to costly mistakes. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of over 100 world-renowned PhDs is ready to provide you with expert guidance and personalized solutions. Contact us today and experience the peace of mind that comes with having the best minds in the industry on your side.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: how.edu.vn